算术运算
octave:1> 5+6 ans = 11 octave:2> 3-2 ans = 1 octave:3> 5*8 ans = 40 octave:4> 1/2 ans = 0.50000 octave:5> 2 ans = 2 octave:6> 2^6 ans = 64
逻辑运算
octave:7> 1==2 ans = 0 octave:8> 1~=2 ans = 1 octave:9> 8>1 && 0 ans = 0 octave:10> 9>1 || 1 ans = 1 octave:11> xor(1,0) ans = 1 octave:12>
定制octave命令行提示
octave:12> PS1('>>>') >>> >>>
变量赋值
>>>a=3 a = 3 >>>a=3; >>>
对变量赋值时,使用分号,即形如 a=3; ,可以抑制打印输出
利用disp命令和sprintf命令一起可以完成格式化输出
>>>disp(a) 3 >>>disp(sprintf('2 decimals: %.2f', a)) 2 decimals: 3.00 >>>
向量矩阵
>>>v=[1 2;3 4; 5 6] v = 1 2 3 4 5 6 >>>
矩阵快速生成方式
>>>v=1:6 v = 1 2 3 4 5 6 >>>v=ones(2,3) v = 1 1 1 1 1 1 >>>v=rand(3,3) v = 0.492887 0.253071 0.516081 0.022844 0.585264 0.200849 0.696016 0.864906 0.757668 >>>randn(1,3) ans = 0.49692 0.19770 -1.92125 >>>eye(3) ans = Diagonal Matrix 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1
获取矩阵的长度
>>>a=[1 2; 3 4; 5 6] a = 1 2 3 4 5 6 >>>size(a) ans = 3 2 >>> >>> >>>size(a, 1) ans = 3 >>>length(a) ans = 3 >>> >>>
变量查看
>>>whos Variables in the current scope: Attr Name Size Bytes Class ==== ==== ==== ===== ===== a 3x2 48 double ans 1x3 3 char featuresX 7x2 112 double priceY 7x1 56 double Total is 30 elements using 219 bytes >>>who Variables in the current scope: a ans featuresX priceY
数据加载及保存
>>>load featuresX.dat >>>load priceY.dat >>>save hello.mat ans >>>save hello.txt ans -ascii
删除变量
>>>clear >>>clear ans
矩阵访问方式
>>>a=[1 2; 3 4; 5 6] a = 1 2 3 4 5 6 >>>a(3, 2) ans = 6 >>>a(2, :) ans = 3 4 >>>a(:, 2) ans = 2 4 6 >>>a([1 2], :) ans = 1 2 3 4 >>>a(:, 2)=[10; 11; 12] a = 1 10 3 11 5 12 >>>a=[a, [100; 101; 102]] a = 1 10 100 3 11 101 5 12 102 >>>a(:) ans = 1 3 5 10 11 12 100 101 102 >>>a=[1 2; 3 4; 5 6] a = 1 2 3 4 5 6 >>>b=[11 12; 13 14; 15 16] b = 11 12 13 14 15 16 >>>c=[a b] c = 1 2 11 12 3 4 13 14 5 6 15 16 >>>c=[a; b] c = 1 2 3 4 5 6 11 12 13 14 15 16 >>>
矩阵运算
>>>a=[1 2; 3 4; 5 6] a = 1 2 3 4 5 6 >>>b=[11 12; 13 14; 15 16] b = 11 12 13 14 15 16 >>>c=[1 1; 2 2] c = 1 1 2 2 >>>a * c ans = 5 5 11 11 17 17 >>>a .* b ans = 11 24 39 56 75 96 >>>a .^ 2 ans = 1 4 9 16 25 36 >>>1 ./ a ans = 1.00000 0.50000 0.33333 0.25000 0.20000 0.16667 >>>1 ./ c ans = 1.00000 1.00000 0.50000 0.50000 >>>V = [1; 2; 3] V = 1 2 3 >>>log(V) ans = 0.00000 0.69315 1.09861 >>>exp(V) ans = 2.7183 7.3891 20.0855 >>>abs(V) ans = 1 2 3 >>>V + ones(length(V), 1) ans = 2 3 4 >>>V + 1 ans = 2 3 4 >>>1 .+ V ans = 2 3 4 >>>a a = 1 2 3 4 5 6 >>>a' ans = 1 3 5 2 4 6 >>>a = [1 15 2 .5] a = 1.00000 15.00000 2.00000 0.50000 >>>val=max(a) val = 15 >>>[val, ind] = max(a) val = 15 ind = 2 >>>a<3 ans = 1 0 1 1 >>>find(a<3) ans = 1 3 4 >>>A=magic(3) A = 8 1 6 3 5 7 4 9 2 >>>find(A>=7) ans = 1 6 8 >>>[r, c]=find(A>=7) r = 1 3 2 c = 1 2 3 >>>a a = 1.00000 15.00000 2.00000 0.50000 >>>sum(a) ans = 18.500 >>>prod(a) ans = 15 >>>floor(a) ans = 1 15 2 0 >>>ceil(a) ans = 1 15 2 1 >>>max(rand(3), rand(3)) ans = 0.24528 0.30296 0.74424 0.97481 0.40352 0.33233 0.94606 0.96147 0.38318 >>>A A = 8 1 6 3 5 7 4 9 2 >>>max(A) ans = 8 9 7 >>>max(A,[],2) ans = 8 7 9 >>>max(A,[],1) ans = 8 9 7 >>>max(A,1) ans = 8 1 6 3 5 7 4 9 2 >>>max(max(A)) ans = 9 >>>max(A(:)) ans = 9 >>>A=magic(5) A = 17 24 1 8 15 23 5 7 14 16 4 6 13 20 22 10 12 19 21 3 11 18 25 2 9 >>>sum(A, 1) ans = 65 65 65 65 65 >>>sum(A, 2) ans = 65 65 65 65 65 >>>sum(sum(A .* eye(5))) ans = 65 >>>eye(5) ans = Diagonal Matrix 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 >>>flipud(eye(5)) ans = Permutation Matrix 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 >>>flipud(eye(5)) ans = Permutation Matrix 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 >>>A=magic(3) A = 8 1 6 3 5 7 4 9 2 >>>pinv(A) ans = 0.147222 -0.144444 0.063889 -0.061111 0.022222 0.105556 -0.019444 0.188889 -0.102778 >>>A*pinv(A) ans = 1.00000 -0.00000 0.00000 0.00000 1.00000 -0.00000 -0.00000 0.00000 1.00000 >>>
绘图
>> t=[0:0.01:0.98]; >> y1 = sin(2*pi*4*t); >> plot(t,y1);
输入close命令可以关闭图像
hold on 命令可在原图像中再添加新曲线
octave:6> plot(t,y1); octave:7> hold on; octave:8> y2=cos(2*pi*4*t); octave:9> plot(t, y2, 'r') octave:10> xlabel('time') octave:11> ylabel('value') octave:12> legend('sin', 'cos') octave:13> title('my plot') octave:14> cd D:;print -dpng 'myplot.png'
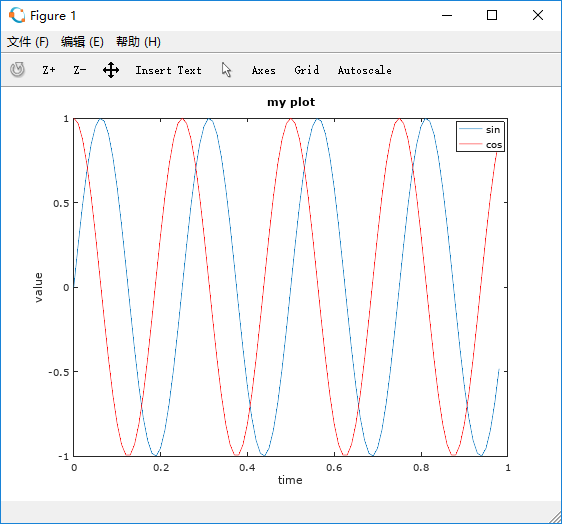
同时绘几张图片
>> figure(1); plot(t, y1); >> figure(2); plot(t, y2);
subplot可以将图片分割,同时在不同的图片上作画
octave:20> subplot(1,2,1); octave:21> plot(t,y1); octave:22> subplot(1,2,2); octave:23> plot(t,y2);
octave:24> axis([0.5 1 -1 1])
利用clf可以清除图像
可视化矩阵imagesc
octave:26> a=magic(15); octave:27> imagesc(a);
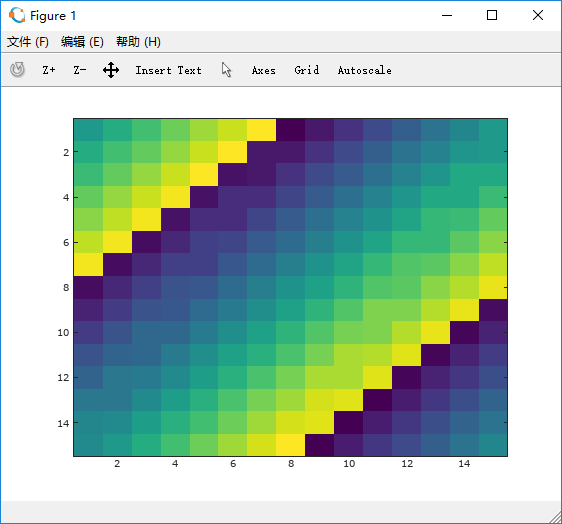
octave:28> imagesc(a), colorbar, colormap gray;
在octave中,使用 逗号, 和 分号; 作为命令连接最终效果都是一样的,但是使用分号可以不打印输出
控制流
octave中控制语句有for while if,均以end作为结束标志
>> v=zeros(10,1); >> for i=1:10, v(i) = 2^i; end; >> v v = 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 512 1024 >> for i=indices, disp(i); end; 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 >> i = 1; >> while i <= 5, v(i) = 100; i = i+1; end; >> v v = 100 100 100 100 100 64 128 256 512 1024 >> i=1; >> while true, v(i) = 999; i = i+1; if i == 6, break; end; end; >> v v = 999 999 999 999 999 64 128 256 512 1024 >> v(1) ans = 999 >> v(1) = 2; >> if v(1)==1, disp('The value is one'); elseif v(1) == 2, disp('The value is two'); else disp('The value is not one or two'); end;
上述各种控制流中,使用逗号作为换行标志,但使用时直接换行也是可以的
函数
octave中函数可以定义在一个文件中,文件名应以.m结束。使用该函数时,就将该函数的路径加入octave的环境中(addpath('path'))
octave中的函数可以同时返回多个参数
function y = squareThisNumber(x) y = x^2; function [y1, y2] = squareAndCubeThisNumber(x) y1 = x^2; y2 = x^3;
一个线性拟合例子
>> x = [1 1; 1 2; 1 3]; >> y = [1; 2; 3]; >> theta = [0;1];
>> j = costFunctionJ(X,y,theta)
函数为
function J = costFunctionJ(X,y,theta) m = size(X,1); predictions = X*theta; sqrErrors = (predictions-y).^2; J = 1/(2*m) * sum(sqrErrors);



