Spring AOP中动态代理如何区分JDK还是CGLib
Spring AOP的实现是通过动态代理,并且有两种实现方式,分别是JDK动态代理和CGLib动态代理。Spring默认使用JDK动态代理,只有在类没有实现接口或配置@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)时,才会使用CGLib。
在Spring Boot应用程序中,你需要配置CGLIB代理以确保它在事务管理方面生效。这可以通过在配置类中添加@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解来完成,如下所示:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement; @Configuration @EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true) @EnableTransactionManagement public class AppConfig { @Bean public CustomTransactionManager transactionManager() { return new CustomTransactionManager(); } }
JDK的动态代理存在限制,那就是被代理的类必须是一个实现了接口的类,代理类需要实现相同的接口,代理接口中声明的方法。若需要代理的类没有实现接口,此时JDK的动态代理将没有办法使用,于是Spring会使用CGLib的动态代理来生成代理对象。
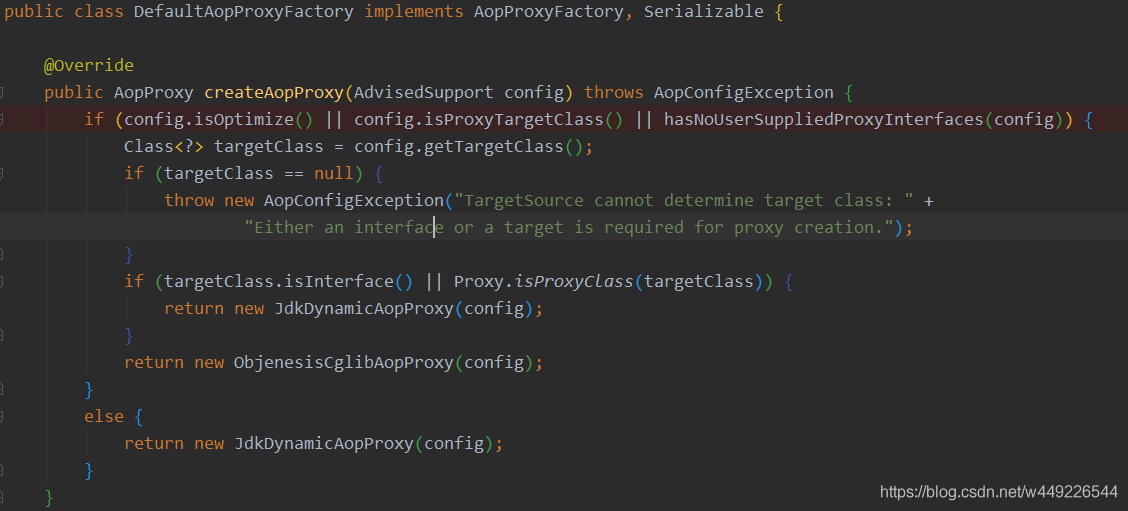
在 DefaultAopProxyFactory里的创建代理对象的方法里会判断,如果目标对象没有实现接口、或者实现的接口都是空接口,或者配置的cglib方式,则返回cglib代理对象,否则使用动态代理。
本文来自博客园,作者:领着小丫闯江湖,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/lzxycjh/p/17869717.html



