spi驱动框架学习记录
目录
1. spi驱动框架简要描述
2. 通过编写itop4412开发板rfid接口的spi驱动来熟悉spi驱动的编写
1. spi驱动框架简要描述
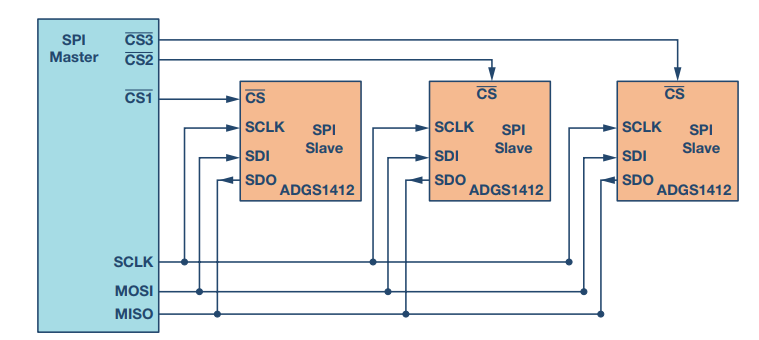
如上图所示,spi硬件架构中,一个spi控制器可以同时接多个spi外设,通信时通过片选脚来选择和某个spi外设通信。
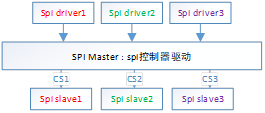

如上图,在linux内核中,将spi驱动分为spi主机控制器驱动和具体的spi设备驱动两个部分;spi主机控制器设备和spi主机控制器驱动挂载在平台总线上,在spi控制器驱动加载成功后,会创建一个SPI总线,spi主控制上连接的spi设备以及对应的spi设备驱动挂载在这个SPI总线上。
spi控制器驱动部分大致实现如下功能
1. 通过spi总线,将具体的spi设备和spi设备驱动匹配起来
2. 提供数据收发函数给spi设备驱动,将spi设备驱动下发的数据转成总线波形发送出去,将总线上接收的数据上发给spi设备驱动
spi控制器驱动一般由厂家编写,比如itop4412开发板,spi控制器驱动对应drivers/spi/spi-s3c64xx.c这个文件;
spi控制器驱动中使用虚拟平台驱动结构体platform_driver注册的代码段如下
1 drivers/spi/spi-s3c64xx.c 2 3 static struct platform_driver s3c64xx_spi_driver = { 4 .driver = { 5 .name = "s3c64xx-spi", 6 .pm = &s3c64xx_spi_pm, 7 .of_match_table = of_match_ptr(s3c64xx_spi_dt_match), 8 }, 9 .probe = s3c64xx_spi_probe, 10 .remove = s3c64xx_spi_remove, 11 .id_table = s3c64xx_spi_driver_ids, 12 }; 13 14 module_platform_driver(s3c64xx_spi_driver);
在编写spi设备驱动时,我们只需要在对应spi控制器中添加spi设备描述,然后编写spi设备驱动即可;
有两种方法添加spi设备描述,第一,在arm/mach-xxx对应的板级描述文件的spi_board_info结构体中添加;第二,在设备树中的spi控制器节点中添加。
2. 通过编写itop4412开发板rfid接口的spi驱动来熟悉spi驱动的编写
2.1 rfid接口对应的引脚图
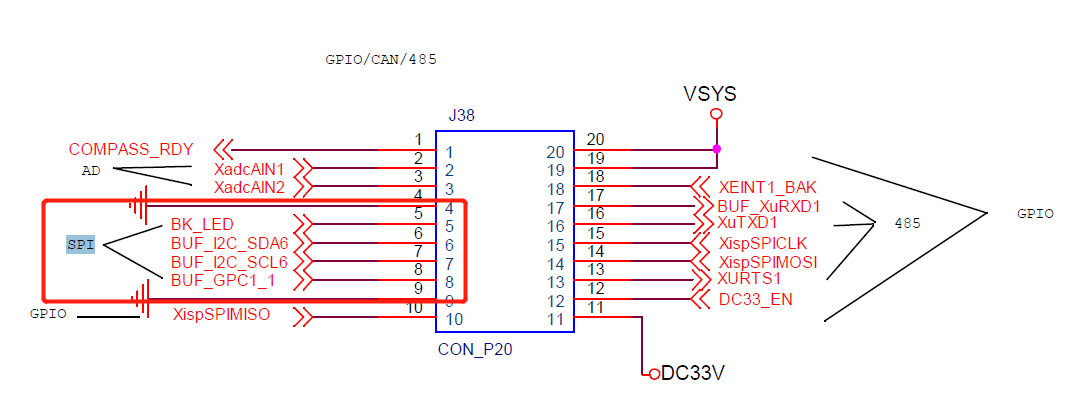

如上图所示,rfid的spi接在SPI_2控制器上,片选引脚是GPC1_2
2.2 在设备树文件的spi_2控制器节点中添加rfid的spi设备
spi_2控制器节点如下图所示
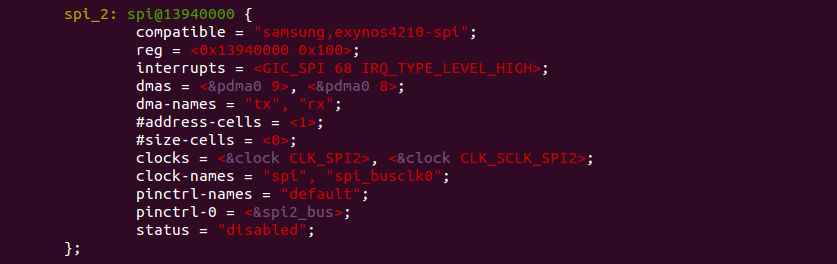
在dts文件中,引用spi_2节点,添加rfid的spi设备
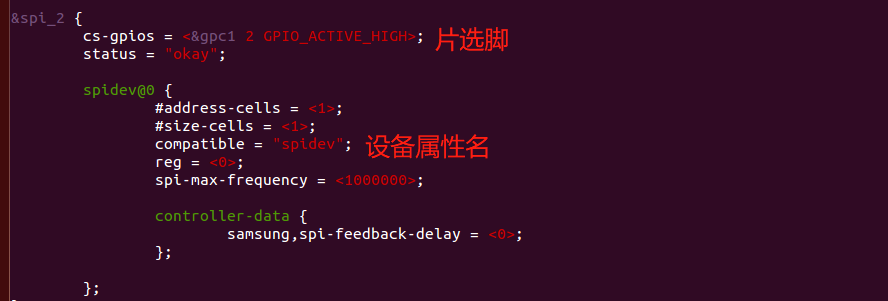
在设备树spi控制器的节点中添加spi设备后,内核解析设备树时,就会在这个控制器对应的spi总线上注册一个spi设备spi_device,设备对应的属性名是”spidev”。
2.3 编写spi设备驱动
spi设备驱动主体由两部分组成:
1. 创建注册struct spi_driver结构体,指定结构体的compatible属性为”spidev”,这样就可以和spi设备匹配
1 static const struct of_device_id spidev_dt_ids[] = { 2 { .compatible = "spidev" }, 3 {}, 4 }; 5 MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, spidev_dt_ids); 6 7 static struct spi_driver spidev_spi_driver = { 8 .driver = { 9 .name = "spidev", 10 .of_match_table = of_match_ptr(spidev_dt_ids), 11 }, 12 .probe = spidev_probe, 13 .remove = spidev_remove, 14 15 }; 16 17 spi_register_driver(&spidev_spi_driver);
2. 在应用程序接口函数中使用spi控制器驱动程序提供的接口函数收发数据,函数主体如下
1 /* 数据传输结构体 */ 2 struct spi_transfer t = { 3 .tx_buf = tx_buf, 4 .len = count, 5 }; 6 7 struct spi_message m; 8 spi_message_init(&m); 9 spi_message_add_tail(&t, &m); 10 DECLARE_COMPLETION_ONSTACK(done); 11 m.complete = complete; 12 m.context = &done; 13 14 printk("spi_async send begin!\n"); 15 /* 异步收发函数 */ 16 status = spi_async(my_spi,&m); 17 if(status == 0){ 18 wait_for_completion(&done); 19 status = m.status; 20 if (status == 0) 21 status = m.actual_length; 22 }
设备驱动示例如下,驱动中注册了一个spi_driver,然后创建了一个杂项设备和应用程序交互
1 #include <linux/init.h> 2 #include <linux/module.h> 3 #include <linux/ioctl.h> 4 #include <linux/fs.h> 5 #include <linux/device.h> 6 #include <linux/err.h> 7 #include <linux/list.h> 8 #include <linux/errno.h> 9 #include <linux/mutex.h> 10 #include <linux/slab.h> 11 #include <linux/compat.h> 12 #include <linux/of.h> 13 #include <linux/of_device.h> 14 #include <linux/acpi.h> 15 #include <linux/miscdevice.h> 16 17 #include <linux/spi/spi.h> 18 #include <linux/spi/spidev.h> 19 20 #include <linux/uaccess.h> 21 22 /* 创建spi结构体,填入设备树属性 */ 23 /* 创建杂项设备,用于读写及ioctl控制 */ 24 25 static struct spi_device *my_spi; 26 static spinlock_t spi_lock; 27 static struct mutex buf_lock; 28 29 static long 30 rc522_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg) 31 { 32 int retval = 0; 33 struct spidev_data *spidev; 34 struct spi_device *spi; 35 u32 tmp; 36 unsigned n_ioc; 37 struct spi_ioc_transfer ioc; 38 39 int i; 40 int status; 41 struct spi_message m; 42 char *usertx_buf, *userrx_buf, txbuf[255]; 43 44 copy_from_user(&ioc, (struct spi_ioc_transfer __user *)arg, sizeof(struct spi_ioc_transfer)); 45 usertx_buf = (unsigned long)ioc.tx_buf; 46 copy_from_user(txbuf, usertx_buf, ioc.len); 47 48 printk("ioc.len = %d\n", ioc.len); 49 #if 1 50 struct spi_transfer t = { 51 .tx_buf = txbuf, 52 .rx_buf = txbuf, 53 .len = ioc.len, 54 }; 55 56 spi_message_init(&m); 57 spi_message_add_tail(&t, &m); 58 DECLARE_COMPLETION_ONSTACK(done); 59 m.complete = complete; 60 m.context = &done; 61 62 printk("spi_async spidev_ioctl begin!\n"); 63 status = spi_async(my_spi,&m); 64 if(status == 0){ 65 wait_for_completion(&done); 66 status = m.status; 67 if (status == 0) 68 status = m.actual_length; 69 } 70 71 userrx_buf = (unsigned long)ioc.rx_buf; 72 copy_to_user(userrx_buf, txbuf, ioc.len); 73 74 printk("\n"); 75 #endif 76 return status; 77 } 78 79 static ssize_t rc522_write(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos) 80 { 81 int status; 82 unsigned char tx_buf[512]; 83 84 if (count > 512) { 85 printk("count > 512, rc522_write write failed, return.\n"); 86 return -EMSGSIZE; 87 } 88 89 status = copy_from_user(tx_buf,buf,count); 90 91 struct spi_transfer t = { 92 .tx_buf = tx_buf, 93 .len = count, 94 }; 95 struct spi_message m; 96 spi_message_init(&m); 97 spi_message_add_tail(&t, &m); 98 DECLARE_COMPLETION_ONSTACK(done); 99 m.complete = complete; 100 m.context = &done; 101 102 printk("spi_async send begin!\n"); 103 status = spi_async(my_spi,&m); 104 if(status == 0){ 105 wait_for_completion(&done); 106 status = m.status; 107 if (status == 0) 108 status = m.actual_length; 109 } 110 return status; 111 } 112 113 static ssize_t rc522_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos) 114 { 115 int status; 116 unsigned char rx_buf[255]; 117 118 struct spi_transfer t = { 119 .rx_buf = rx_buf, 120 .len = count, 121 }; 122 struct spi_message m; 123 spi_message_init(&m); 124 spi_message_add_tail(&t, &m); 125 DECLARE_COMPLETION_ONSTACK(done); 126 m.complete = complete; 127 m.context = &done; 128 129 printk("spi_async read begin!\n"); 130 status = spi_async(my_spi,&m); 131 if(status == 0){ 132 wait_for_completion(&done); 133 status = m.status; 134 if (status == 0) 135 status = m.actual_length; 136 } 137 138 status = copy_to_user(buf,&rx_buf,status); 139 140 return status; 141 } 142 143 int rc522_open(struct inode *inode,struct file *filp) 144 { 145 printk("rc522_open.\n"); 146 return 0; 147 } 148 149 static struct file_operations rc522_ops = { 150 .owner = THIS_MODULE, 151 .open = rc522_open, 152 .read = rc522_read, 153 .write = rc522_write, 154 .unlocked_ioctl = rc522_ioctl, 155 }; 156 157 static struct miscdevice rc522_dev = { 158 .minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR, 159 .fops = &rc522_ops, 160 .name = "rc522", 161 }; 162 163 #ifdef CONFIG_OF 164 static const struct of_device_id spidev_dt_ids[] = { 165 { .compatible = "spidev" }, 166 {}, 167 }; 168 MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, spidev_dt_ids); 169 #endif 170 171 static int spidev_probe(struct spi_device *spi) 172 { 173 int status; 174 175 /* 检查是否是设备树节点 */ 176 if (spi->dev.of_node && !of_match_device(spidev_dt_ids, &spi->dev)) { 177 dev_err(&spi->dev, "buggy DT: spidev listed directly in DT\n"); 178 WARN_ON(spi->dev.of_node && 179 !of_match_device(spidev_dt_ids, &spi->dev)); 180 } 181 182 my_spi = spi; 183 spin_lock_init(&spi_lock); 184 mutex_init(&buf_lock); 185 186 return status; 187 } 188 189 static int spidev_remove(struct spi_device *spi) 190 { 191 printk("spidev_remove\n"); 192 return 0; 193 } 194 195 static struct spi_driver spidev_spi_driver = { 196 .driver = { 197 .name = "spidev", 198 .of_match_table = of_match_ptr(spidev_dt_ids), 199 }, 200 .probe = spidev_probe, 201 .remove = spidev_remove, 202 203 }; 204 205 static int __init spidrv_dts_init(void) 206 { 207 int status; 208 209 misc_register(&rc522_dev); 210 211 status = spi_register_driver(&spidev_spi_driver); 212 if (status < 0) { 213 misc_deregister(&rc522_dev); 214 } 215 return status; 216 } 217 218 static void __exit spidrv_dts_exit(void) 219 { 220 spi_unregister_driver(&spidev_spi_driver); 221 misc_deregister(&rc522_dev); 222 } 223 224 module_init(spidrv_dts_init); 225 module_exit(spidrv_dts_exit); 226 227 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
测试应用程序如下,在测试时,将spi接口的MOSI和MISO引脚对接,这样spi就可以收到自己发送的数据,这两个引脚是rfid接口的外侧第3脚和内测di4脚
1 #include <stdint.h> 2 #include <unistd.h> 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 #include <stdlib.h> 5 #include <getopt.h> 6 #include <fcntl.h> 7 #include <sys/ioctl.h> 8 #include <linux/types.h> 9 #include <linux/spi/spidev.h> 10 #include <pthread.h> 11 #include <errno.h> 12 #include <time.h> 13 #include <string.h> 14 15 #define filename "/dev/rc522" 16 17 #define ARRAY_SIZE(a) (sizeof(a) / sizeof((a)[0])) 18 19 /* 读写需要互斥 */ 20 static pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; 21 /* 1. 打开设备 */ 22 static int fd; 23 /* 2. 创建三个线程 */ 24 /* 3. 一个线程每隔2s向设备写数据 */ 25 static void createThread_write(void); 26 static void *thread_func_write(void *arg); 27 /* 4. 另一个线程不停地读数据 */ 28 static void createThread_read(void); 29 static void *thread_func_read(void *arg); 30 /* 5. 第三个线程用ioctl测试数据读写 */ 31 static void createThread_ioctl(void); 32 static void *thread_func_ioctl(void *arg); 33 34 /* repetition repetition repetition */ 35 /* 按照正常的文件读写,不停地写数据 */ 36 /* 以阻塞的方式读数据 */ 37 /* XXX 多线程操作,将同步阻塞信号通知都走一遍 */ 38 /* 驱动,实现阻塞读 */ 39 /* 线程1 */ 40 static void *thread_func_write(void *arg) 41 { 42 int nByte; 43 char data[6] = {0x12, 0x22, 0x34, 0x66, 0x32, 0x11}; 44 45 while (1) { 46 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 47 printf("write.\n"); 48 if ((nByte = write(fd, data, sizeof(data))) == -1) { 49 printf("write failed, thread_func_write return.\n"); 50 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 51 return; 52 } 53 else { 54 printf("write %d bytes.\n", nByte); 55 } 56 57 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 58 59 /* 每2秒发一个数据包 */ 60 sleep(2); 61 } 62 } 63 64 static void createThread_write(void) 65 { 66 pthread_attr_t attr; 67 pthread_t pthread_id; 68 69 /* set pthread detach */ 70 pthread_attr_init(&attr); 71 pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED); 72 pthread_create(&pthread_id, &attr, thread_func_write, NULL); 73 pthread_attr_destroy(&attr); 74 } 75 76 /* 线程2 */ 77 static void *thread_func_read(void *arg) 78 { 79 int nByte; 80 char buffer[255]; 81 82 while (1) { 83 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 84 memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer)); 85 if ((nByte = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer))) == -1) { 86 printf("read failed , thread_func_read return.\n"); 87 return; 88 } 89 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 90 91 printf("read %d bytes, buffer is : %s\n", nByte, buffer); 92 93 usleep(50); 94 sleep(2); 95 } /* end of while (1) */ 96 } 97 98 static void createThread_read(void) 99 { 100 pthread_attr_t attr; 101 pthread_t pthread_id; 102 103 /* set pthread detach */ 104 pthread_attr_init(&attr); 105 pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED); 106 pthread_create(&pthread_id, &attr, thread_func_read, NULL); 107 pthread_attr_destroy(&attr); 108 } 109 110 /* 线程3 */ 111 static void *thread_func_ioctl(void *arg) 112 { 113 int ret, i; 114 115 uint8_t tx[] = { 116 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 117 0x40, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x95, 118 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 119 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 120 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 121 0xDE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xBA, 0xAD, 122 0xF0, 0x0D, 123 }; 124 uint8_t rx[ARRAY_SIZE(tx)] = {0, }; 125 struct spi_ioc_transfer tr = { 126 .tx_buf = (unsigned long)tx, 127 .rx_buf = (unsigned long)rx, 128 .len = ARRAY_SIZE(tx), 129 .delay_usecs = 0, 130 .speed_hz = 500000, 131 .bits_per_word = 8, 132 }; 133 while (1) { 134 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 135 if ((ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_MESSAGE(1), &tr)) == -1) { 136 printf("ioctl failed, thread_func_ioctl return.\n"); 137 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 138 return; 139 } 140 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 141 142 for (i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE(tx); i++) { 143 if (i % 6 == 0) { 144 printf("\n"); 145 } 146 printf("%.2X,", rx[i]); 147 } 148 printf("\n"); 149 printf("ioctl.\n"); 150 sleep(2); 151 } 152 } 153 154 static void createThread_ioctl(void) 155 { 156 pthread_attr_t attr; 157 pthread_t pthread_id; 158 159 /* set pthread detach */ 160 pthread_attr_init(&attr); 161 pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED); 162 pthread_create(&pthread_id, &attr, thread_func_ioctl, NULL); 163 pthread_attr_destroy(&attr); 164 } 165 166 int main(int argc, char ** argv) 167 { 168 /* 打开文件 */ 169 if ((fd = open(filename, O_RDWR)) == -1) { 170 printf("open file %s failed.\n", filename); 171 return -1; 172 } 173 else { 174 printf("open file %s successful.\n", filename); 175 } 176 177 /* 创建第一个线程,每2s向设备写入数据 */ 178 createThread_write(); 179 180 /* 创建第二个线程,不停地读数据 */ 181 /* 阻塞需要驱动程序中实现 */ 182 createThread_read(); 183 184 /* 创建第三个线程 */ 185 createThread_ioctl(); 186 187 while (1) { 188 sleep(1000); 189 } 190 191 return 0; 192 }
参考博客
https://www.cnblogs.com/-4412/articles/5202793.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号