1. 调用全局变量: (::global)
2.
静态函数和静态变量
class Test
{
private:
static int val;
int a;
public:
static int func();
void sfunc(Test& r);
};
int Test::val = 200;
int Test::func()
{
return val++; //先return val,再val++
}
void Test::sfunc(Test& r)
{
r.a = 123;
cout << "Result3 = " << r.a << endl;
}
int main()
{
cout << "Result = " << Test::func() << endl; //此时应该是先执行return val,可以把func()内容替换进来
Test a;
cout << "Result2 = " << a.func() << endl;
a.sfunc(a);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
/*output
Result = 200
Result2 = 201
Result3 = 123
*/3. 构造函数
构造函数
class Con
{
char ID;
public:
char getID() const { return ID; }
Con() :ID('A') { cout << 1; }
Con(char id) :ID(id) { cout << 2; }
Con(Con& c) :ID(c.getID()) { cout << 3; }
};
// 非成员函数不能使用const等类型限定符
//void show(Con c) const { cout << c.getID(); }
void show(Con c) { cout << c.getID(); }
int main()
{
Con c1; //调用不含参数的构造函数 1 次
show(c1); //先调用拷贝构造函数 1 次,再调用show函数
Con c2('B');
show(c2);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
/*output
13A23B
*/4.
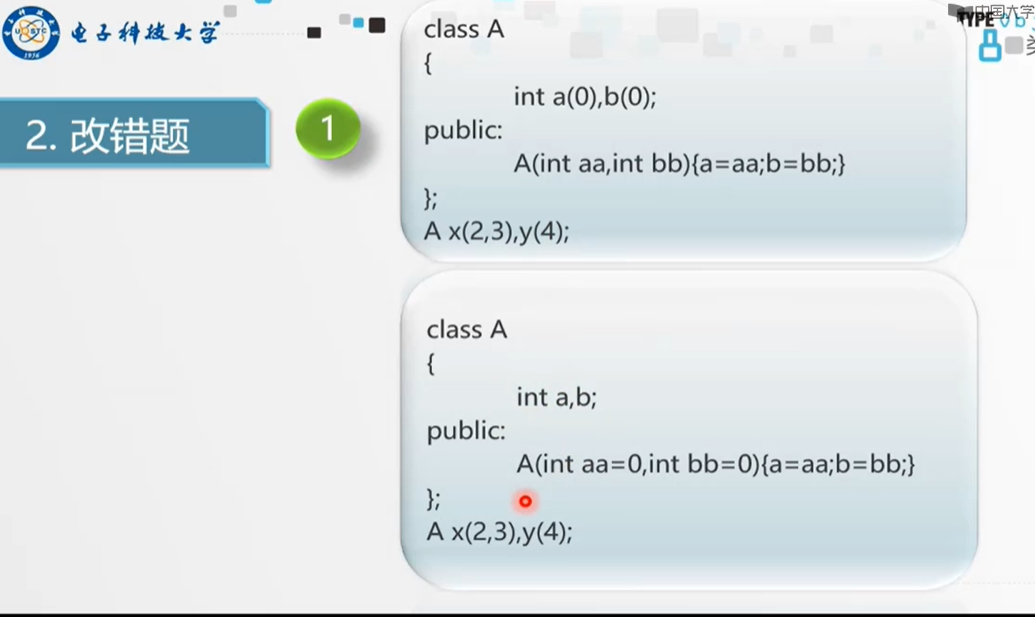

5. 实战
CTriangle.h
#ifndef _CTRIANGLE_H
#define _CTRIANGLE_H
class CTriangle
{
float a, b, c;
public:
CTriangle(float, float, float);
CTriangle(CTriangle&);
~CTriangle();
float getArea();
float getPrimeter();
void display();
};
#endif
CTriangle.cpp
#include "CTriangle.h"
#include <iostream>
CTriangle::CTriangle(float aa = 3, float bb = 5, float cc = 8) :a(aa), b(bb), c(cc) {}
CTriangle::CTriangle(CTriangle& ct)
{
this->a = ct.a;
this->a = ct.b;
this->c = ct.c;
}
CTriangle::~CTriangle()
{
}
float CTriangle::getPrimeter()
{
if (this->a <= 0 || this->b <= 0 || this->c <= 0)
{
std::cout << "no this triangle!\n";
return 0;
}
if ((this->a + this->b < this->c) || (this->a + this->c < this->a) || (this->b + this->c < this->a))
{
std::cout << "no this triangle!\n";
return 0;
}
std::cout << "三角形的周长:";
return this->a + this->b + this->c;
}
float CTriangle::getArea()
{
if (this->a <= 0 || this->b <= 0 || this->c <= 0)
{
std::cout << "no this triangle!\n";
return 0;
}
if ((this->a + this->b < this->c) || (this->a + this->c < this->a) || (this->b + this->c < this->a))
{
std::cout << "no this triangle!\n";
return 0;
}
std::cout << "三角形的面积:";
float s = (this->a + this->b + this->c) / 2;
return sqrt(s * (s - this->a) * (s - this->b) * (s - this->c));
}
void CTriangle::display()
{
std::cout << "三角形三边为:" << "x = " << this->a
<< ", y = " << this->b << ", z = " << this->c << std::endl;
}main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "CTriangle.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float x, y, z;
cin >> x >> y >> z;
CTriangle ct(x, y, z);
ct.display();
cout << ct.getPrimeter() << endl;
cout << ct.getArea() << endl;
cout << endl;
return 0;
}



