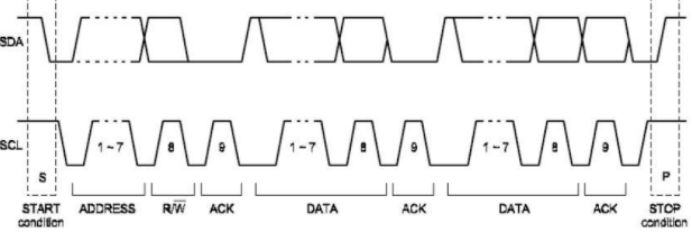
启动信号:scl为高,sda从高往低跳变
结束信号:scl为高,sda从低往高跳变
数据信号:scl为高,sda电平保持稳定,这个即为一位数据;scl为低,sda才能改变电平
空闲信号:scl,sda都为高,即释放总线
驱动框架:
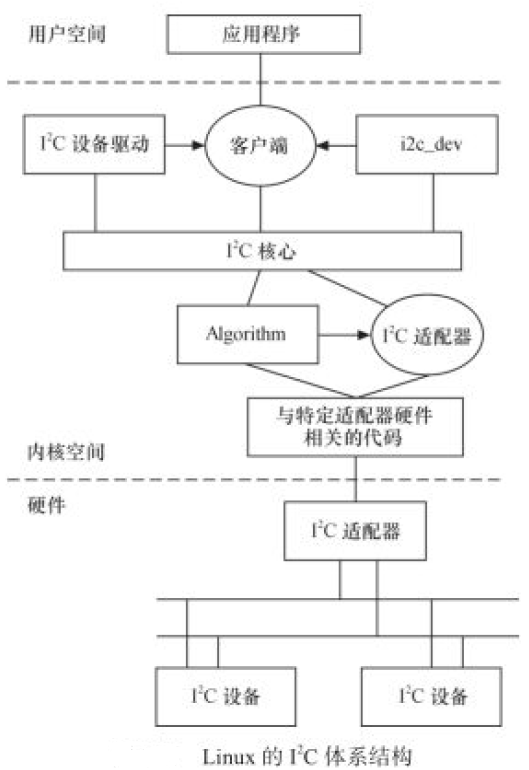
总线驱动:
I2C总线驱动就是 SOC的I2C 控制器驱动,也叫做I2C适配器驱动;Linux 内核将 SOC 的 I2C 适配器(控制器) 抽象成 i2c_adapter,i2c_adapter 结构体定义在 include/linux/i2c.h 文件中
/* * i2c_adpater is the structure used to identify a physical i2c bus along * with the access algorithms necessary to access it. */ struct i2c_adpater { //i2c 适配器 ...... const struct i2c_algorithm *algo; //访问总线的通信方法 struct device dev; /* the adpater device */ char name[48]; /* 适配器名称 */ ...... struct list_head userspace_clients; /* client链表头 */ };
i2c_algorithm 类型的指针变量 algo,对于一个 I2C 适配器,肯定要对外提供读写 API 函数,设备驱动程序可以使用这些 API 函数来完成读写操作。i2c_algorithm 就是 I2C 适配器与 IIC 设备进行通信的方法,究其根本也就是对寄存器的操作
struct i2c_algorithm { i2c通信方法 /* If an adpater algorithm can't do I2C-level access, set master_xfer to NULL. If an adpater algorithm can do SMBus access, set smbus_xfer. If set to NULL, the SMBus protocol is simulated using common I2C messages */ /* master_xfer should return the number of messages successfully processed, or a negative value on error */ int (*master_xfer)(struct i2c_adpater *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num); /* I2C 传输函数指针 */ int (*smbus_xfer) (struct i2c_adpater *adap, u16 addr, unsigned short flags, char read_write, u8 command, int size, union i2c_smbus_data *data); /* smbus传输函数指针 */ /* To determine what the adpater supports */ u32 (*functionality) (struct i2c_adpater *); /* 返回适配器支持的功能 */ };
综上所述,I2C 总线驱动,或者说 I2C 适配器驱动的主要工作就是初始化 i2c_adapter 结构 体变量,然后设置 i2c_algorithm 中的 master_xfer 函数。完成以后通过 i2c_add_numbered_adapter 或 i2c_add_adapter 这两个函数向系统注册设置好的 i2c_adapter,如果要删除 I2C 适配器的话使用 i2c_del_adapter 函数即可
设备驱动:
据总线、设备和驱动模型,还剩下设备和驱动,i2c_client 就是描述设备信息的,i2c_driver 描述驱动内容;一个设备对应一个 i2c_client,每检测到一个 I2C 设备就会给这个 I2C 设备分配一个 i2c_client
struct i2c_client { //i2c 设备 unsigned short flags; /* div., see below */ unsigned short addr; /* chip address - NOTE: 7bit */ /* addresses are stored in the */ /* _LOWER_ 7 bits */ char name[I2C_NAME_SIZE]; // 设备名称 struct i2c_adpater *adpater;// 所属的适配器 struct i2c_driver *driver; // 所对应的设备驱动 struct device dev; // 设备结构体 int irq; /* irq issued by device */ struct list_head detected; //设备链表 };
i2c_driver 类似 platform_driver,是我们编写 I2C 设备驱动重点要处理的内容,i2c_driver 结构体定义在 include/linux/i2c.h 文件中;
struct i2c_driver { //i2c 设备驱动 int (*attach_adpater)(struct i2c_adpater *) __deprecated; //依附 i2c_adpater 函数指针 int (*detach_adpater)(struct i2c_adpater *) __deprecated; //脱离 i2c_adpater 函数指针 ...... int (*probe)(struct i2c_client *, const struct i2c_device_id *); //检测函数 int (*remove)(struct i2c_client *); ...... struct device_driver driver; //表示驱动 const struct i2c_device_id *id_table; //该驱动所支持的设备ID表 /* Device detection callback for automatic device creation */ int (*detect)(struct i2c_client *, struct i2c_board_info *); const unsigned short *address_list; struct list_head clients; };
当 I2C 设备和驱动匹配成功以后 probe 函数就会执行,和 platform 驱动一样;device_driver 驱动结构体,如果使用设备树的话,需要设置 device_driver 的of_match_table 成员变量,也就是驱动的兼容(compatible)属性,id_table 是传统的、未使用设备树的设备匹配 ID 表;驱动编写的重点工作就是构建 i2c_driver,构建完成以后需要向Linux 内核注册这个 i2c_driver。i2c_driver 注册函数i2c_register_driver(),这个函数也可用i2c_add_driver(struct i2c_driver *driver)替代,注销设备驱动则用i2c_del_driver(struct i2c_driver *driver)。
适配器驱动分析:
适配器驱动是个标准的 platform 驱动,由此 可以看出,虽然 I2C 总线为别的设备提供了一种总线驱动框架,但是 I2C 适配器却是 platform 驱动
static struct platform_device_id imx_i2c_devtype[] = { { .name = "imx1-i2c", .driver_data = (kernel_ulong_t)&imx1_i2c_hwdata, }, { .name = "imx21-i2c", .driver_data = (kernel_ulong_t)&imx21_i2c_hwdata, }, { /* sentinel */ } }; MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(platform, imx_i2c_devtype); static const struct of_device_id i2c_imx_dt_ids[] = { { .compatible = "fsl,imx1-i2c", .data = &imx1_i2c_hwdata, }, { .compatible = "fsl,imx21-i2c", .data = &imx21_i2c_hwdata, }, { .compatible = "fsl,vf610-i2c", .data = &vf610_i2c_hwdata, }, { /* sentinel */ } }; MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, i2c_imx_dt_ids); ...... static struct platform_driver i2c_imx_driver = { .probe = i2c_imx_probe, .remove = i2c_imx_remove, .driver = { .name = DRIVER_NAME, .owner = THIS_MODULE, .of_match_table = i2c_imx_dt_ids, .pm = IMX_I2C_PM, }, .id_table = imx_i2c_devtype, }; static int __init i2c_adap_imx_init(void) { return platform_driver_register(&i2c_imx_driver); } subsys_initcall(i2c_adap_imx_init); static void __exit i2c_adap_imx_exit(void) { platform_driver_unregister(&i2c_imx_driver); } module_exit(i2c_adap_imx_exit);
当设备和驱动匹配成功以后 i2c_imx_probe 函数就会执行,i2c_imx_probe 函数就会完成 I2C 适配器初始化工作:比如调用 platform_get_irq 函数获取中断号,调用 platform_get_resource 函数从设备树中获取 I2C1 控制器寄存器物理基地址,NXP 使用 imx_i2c_struct 结构体来表示 I.MX 系列 SOC 的 I2C 控制器,这里使用devm_kzalloc 函数来申请内存,imx_i2c_struct 结构体有个叫做 adapter 的成员变量,adapter 就是i2c_adapter,这里初始化i2c_adapter。i2c_adapter的algo成员变量为i2c_imx_algo, 也就是设置 i2c_algorithm,注册 I2C 控制器中断,中断服务函数为 i2c_imx_isr,设置i2c工作频率,内核注册i2c_adapter,申请DMA等。
设备驱动分析:
I2C 设备驱动首先要做的就是初始化 i2c_driver 并向 Linux 内核 注册。当设备和驱动匹配以后 i2c_driver 里面的 probe 函数就会执行,probe 函数里面所做的就是字符设备驱动那一套了。一般需要在 probe 函数里面初始化 I2C 设备,要初始化 I2C 设备就 必须能够对 I2C 设备寄存器进行读写操作,这里就要用到 i2c_transfer 函数了。i2c_transfer 函数 最终会调用 I2C 适配器中 i2c_algorithm 里面的 master_xfer 函数;i2c_transfer 函数原型如下;另外还有两个API函数分别用于I2C数据的收发操作,这两个函数最终都会调用i2c_transfer。
int i2c_transfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num); int i2c_master_send(const struct i2c_client *client, const char *buf, int count); int i2c_master_recv(const struct i2c_client *client, char *buf, int count);
重点来看一下 msgs 这个参数,这是一个 i2c_msg 类型的指针参数,I2C 进行数据收发说白了就是消息的传递,Linux 内核使用 i2c_msg 结构体来描述一个消息。i2c_msg 结构体定义 在 include/uapi/linux/i2c.h 文件中
struct i2c_msg { __u16 addr; /* slave address */ __u16 flags; ...... __u16 len; /* msg length */ __u8 *buf; /* pointer to msg data */ };
核心层:
I2C 核心:drivers/i2c/i2c-core.c ,主要功能如下:
注册一根 i2c 总线,以及虚拟 i2c 设备驱动(dummy_driver里的成员函数都是空的);给设备驱动层提供接口,如提供 I2C 设备驱动的注册、注销方法, I2C 通信方法(即Algorithm);设备与设备驱动之间的匹配检测;
struct bus_type i2c_bus_type = { .name = "i2c", .match = i2c_device_match, .probe = i2c_device_probe, .remove = i2c_device_remove, .shutdown = i2c_device_shutdown, .pm = &i2c_device_pm_ops, }; static int __init i2c_init(void) { int retval; retval = bus_register(&i2c_bus_type); if (retval) return retval; ...... retval = i2c_add_driver(&dummy_driver); if (retval) goto class_err; return 0; ...... } static void __exit i2c_exit(void) { i2c_del_driver(&dummy_driver); #ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT class_compat_unregister(i2c_adapter_compat_class); #endif bus_unregister(&i2c_bus_type); } /* We must initialize early, because some subsystems register i2c drivers * in subsys_initcall() code, but are linked (and initialized) before i2c. */ postcore_initcall(i2c_init); module_exit(i2c_exit);
重点分析一下:i2c_device_match和I2c_device_probe函数,match用来进行device和driver的匹配
static int i2c_device_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv) { /*返回i2c_client的具体参数,它可以防止把一些不是i2c的设备当作是i2c_client*/ struct i2c_client *client = i2c_verify_client(dev); struct i2c_driver *driver; /*i2c_verify_client返回NULL,表示这个设备不是i2c的设备*/ if (!client) return 0; /* 尝试OF风格的匹配 */ if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv)) return 1; driver = to_i2c_driver(drv);//通过device->driver指针获取到对应的i2c_driver指针 /* match on an id table if there is one */ if (driver->id_table) /*如果i2c驱动的id_table存在的话,使用该函数进行匹配,匹配的方法是拿driver-id_table中的 每一项与client进行匹配,如果相同则匹配成功*/ return i2c_match_id(driver->id_table, client) != NULL; return 0; }
probe用于在完成设备和驱动的配对之后调用执行。
static int i2c_device_probe(struct device *dev) { struct i2c_client *client = i2c_verify_client(dev);//通过device指针获取到对应的i2c_client指针 struct i2c_driver *driver; int status; if (!client) return 0; driver = to_i2c_driver(dev->driver);//通过device->driver指针获取到对应的i2c_driver指针 if (!driver->probe || !driver->id_table) return -ENODEV; client->driver = driver;//i2c设备通过i2c_client->driver指针去指向与他匹配成功的设备驱动i2c_driver if (!device_can_wakeup(&client->dev)) device_init_wakeup(&client->dev, client->flags & I2C_CLIENT_WAKE); dev_dbg(dev, "probe\n"); status = driver->probe(client, i2c_match_id(driver->id_table, client));调用设备驱动层的probe函数 if (status) { client->driver = NULL; i2c_set_clientdata(client, NULL); } return status; }
i2c_add_driver调用栈如下;正好符合上面的驱动跟设备的匹配过程
i2c_add_driver -> driver_register -> bus_add_driver -> driver_attach -> bus_for_each_dev -> __driver_attach -> driver_match_device //调用 .match (即i2c_device_match) -> driver_probe_device -> really_probe //调用 .probe (即i2c_device_probe)
i2c-dev.c
i2c-dev.c 文件完全可以被看做是一个 I2C 设备驱动,不过,它实现的 i2c_client 是虚拟、临时的,主要是为了便于从用户空间操作 I2C 外设。i2c-dev.c 针对每个 I2C 适配器生成一个主设备号为89的设备文件,并实现了其文件操作接口
static const struct file_operations i2cdev_fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .llseek = no_llseek, .read = i2cdev_read, .write = i2cdev_write, .unlocked_ioctl = i2cdev_ioctl, .open = i2cdev_open, .release = i2cdev_release, }; static int __init i2c_dev_init(void) { /* 注册主设备号 ,注册硬件操作方法,提供文件操作接口*/ res = register_chrdev(I2C_MAJOR, "i2c", &i2cdev_fops); /* 创建设备类 */ i2c_dev_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "i2c-dev"); /* 绑定适配器,搜索i2c设备链表,每搜索到一个设备都调用i2cdev_attach_adapter函数, * 以生成对应的设备文件。之后再将设备与适配器进行绑定 */ i2c_for_each_dev(NULL, i2cdev_attach_adapter); } static void __exit i2c_dev_exit(void) { bus_unregister_notifier(&i2c_bus_type, &i2cdev_notifier); i2c_for_each_dev(NULL, i2cdev_detach_adapter); class_destroy(i2c_dev_class); unregister_chrdev(I2C_MAJOR, "i2c"); } static int i2cdev_attach_adapter(struct device *dev, void *dummy) { struct i2c_adapter *adap; struct i2c_dev *i2c_dev; ...... /* 创建设备文件: /dev/i2c-0, /dev/i2c-1... */ i2c_dev->dev = device_create(i2c_dev_class, &adap->dev, MKDEV(I2C_MAJOR, adap->nr), NULL, "i2c-%d", adap->nr); res = device_create_file(i2c_dev->dev, &dev_attr_name); }
i2c-dev.c 提供的 i2cdev_read()、i2cdev_write() 函数对应与用户空间要使用的 read() 和 write() 文件操作接口,这两个函数分别调用 I2C 核心的 i2c_master_recv() 和 i2c_master_send() 函数来构造一条 I2C 消息并引发适配器 Algorithm 通信函数的调用,以完成消息的传输
那么对于多条消息的读写,可以在用户空间组织成 i2c_msg 消息数组并通过调用 I2C_RDWR_IOCTL 命令实现。
static long i2cdev_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg) { struct i2c_client *client = file->private_data; unsigned long funcs; dev_dbg(&client->adapter->dev, "ioctl, cmd=0x%02x, arg=0x%02lx\n", cmd, arg); switch (cmd) { case I2C_SLAVE: case I2C_SLAVE_FORCE: if ((arg > 0x3ff) || (((client->flags & I2C_M_TEN) == 0) && arg > 0x7f)) return -EINVAL; if (cmd == I2C_SLAVE && i2cdev_check_addr(client->adapter, arg)) return -EBUSY; /* REVISIT: address could become busy later */ client->addr = arg; return 0; case I2C_TENBIT: if (arg) client->flags |= I2C_M_TEN; else client->flags &= ~I2C_M_TEN; return 0; case I2C_PEC: /* * Setting the PEC flag here won't affect kernel drivers, * which will be using the i2c_client node registered with * the driver model core. Likewise, when that client has * the PEC flag already set, the i2c-dev driver won't see * (or use) this setting. */ if (arg) client->flags |= I2C_CLIENT_PEC; else client->flags &= ~I2C_CLIENT_PEC; return 0; case I2C_FUNCS: funcs = i2c_get_functionality(client->adapter); return put_user(funcs, (unsigned long __user *)arg); case I2C_RDWR: return i2cdev_ioctl_rdwr(client, arg); case I2C_SMBUS: return i2cdev_ioctl_smbus(client, arg); case I2C_RETRIES: if (arg > INT_MAX) return -EINVAL; client->adapter->retries = arg; break; case I2C_TIMEOUT: if (arg > INT_MAX) return -EINVAL; /* For historical reasons, user-space sets the timeout * value in units of 10 ms. */ client->adapter->timeout = msecs_to_jiffies(arg * 10); break; default: /* NOTE: returning a fault code here could cause trouble * in buggy userspace code. Some old kernel bugs returned * zero in this case, and userspace code might accidentally * have depended on that bug. */ return -ENOTTY; } return 0; }
总结:
无论是i2c,spi,pci等总线,以及虚拟总线platforn,
总线的注册究其根本都是通过int bus_register(struct bus_type *bus);这个bus的.name定义为i2c或者platform,其他成员函数也被定义成特定总线的
设备的注册都是通过int device_register(struct device *dev);这个dev被包含到i2c_client或者spi_device等其他xxx_device中
struct i2c_client * i2c_new_device(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_board_info const *info) { struct i2c_client *client; int status; client = kzalloc(sizeof *client, GFP_KERNEL); if (!client) return NULL; client->adapter = adap; client->dev.platform_data = info->platform_data; if (info->archdata) client->dev.archdata = *info->archdata; client->flags = info->flags; client->addr = info->addr; client->irq = info->irq; strlcpy(client->name, info->type, sizeof(client->name)); status = i2c_check_addr_validity(client->addr, client->flags); if (status) { dev_err(&adap->dev, "Invalid %d-bit I2C address 0x%02hx\n", client->flags & I2C_CLIENT_TEN ? 10 : 7, client->addr); goto out_err_silent; } /* Check for address business */ status = i2c_check_addr_ex(adap, i2c_encode_flags_to_addr(client)); if (status != 0) dev_err(&adap->dev, "%d i2c clients have been registered at 0x%02x", status, client->addr); client->dev.parent = &client->adapter->dev; client->dev.bus = &i2c_bus_type; client->dev.type = &i2c_client_type; client->dev.of_node = info->of_node; client->dev.fwnode = info->fwnode; i2c_dev_set_name(adap, client, status); status = device_register(&client->dev); if (status) goto out_err; dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "client [%s] registered with bus id %s\n", client->name, dev_name(&client->dev)); return client; out_err: dev_err(&adap->dev, "Failed to register i2c client %s at 0x%02x " "(%d)\n", client->name, client->addr, status); out_err_silent: kfree(client); return NULL; } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(i2c_new_device);
驱动的注册都是通过int driver_register(struct device_driver *drv),这个driver被包含到i2c_driver中
int i2c_register_driver(struct module *owner, struct i2c_driver *driver) { int res; /* Can't register until after driver model init */ if (unlikely(WARN_ON(!i2c_bus_type.p))) return -EAGAIN; /* add the driver to the list of i2c drivers in the driver core */ driver->driver.owner = owner; driver->driver.bus = &i2c_bus_type; INIT_LIST_HEAD(&driver->clients); /* When registration returns, the driver core * will have called probe() for all matching-but-unbound devices. */ res = driver_register(&driver->driver); if (res) return res; pr_debug("i2c-core: driver [%s] registered\n", driver->driver.name); /* Walk the adapters that are already present */ i2c_for_each_dev(driver, __process_new_driver); return 0; }



