连接池的复习
数据库连接池的概念
用池来管理Connection,这可以重复使用Connection。有了池,所以我们就不用自己来创建Connection,而是通过池来获取Connection对象。当使用完Connection后,调用Connection的close()方法也不会真的关闭Connection(因为连接池对Connection使用了装饰模式),而是把Connection“归还”给池。池就可以再利用这个Connection对象了。
JDBC数据库连接池接口(DataSource)
Java为数据库连接池提供了公共的接口:javax.sql.DataSource,各个厂商可以让自己的连接池实现这个接口(必须)。这样应用程序可以方便的切换不同厂商的连接池。当我们不指定连接池参数时,会使用默认值
DBCP
DBCP是Apache提供的一款开源免费的数据库连接池!
Hibernate3.0之后不再对DBCP提供支持!因为Hibernate声明DBCP有致命的缺欠!DBCP因为Hibernate的这一毁谤很是生气,并且说自己没有缺欠
在Java代码中配置:
public void fun1() throws SQLException { BasicDataSource ds = new BasicDataSource(); ds.setUsername("root"); ds.setPassword("123"); ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb1"); ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); ds.setMaxActive(20); ds.setMaxIdle(10); ds.setInitialSize(10); ds.setMinIdle(2); ds.setMaxWait(1000); Connection con = ds.getConnection(); System.out.println(con.getClass().getName()); con.close(); }
这个BasicDataSource类就是DBCPjar包中的
C3P0
C3P0也是开源免费的连接池,较为常用
C3P0连接池的配置可以使用在Java代码中硬编码的方式设置,但是为后期维护修改带来不便,这里我是用的是xml配置文件的方式
配置文件要求:
- 文件名称:必须叫c3p0-config.xml
- 文件位置:必须在src下
c3p0-config.xml :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <c3p0-config> <!--默认参数--> <default-config> <!--四大参数--> <property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb1</property> <property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> <property name="user">root</property> <property name="password">root</property> <property name="acquireIncrement">3</property> <property name="initialPoolSize">10</property> <property name="minPoolSize">2</property> <property name="maxPoolSize">10</property> </default-config> <!--命名配置,这里还使用的是Mysql的四大参数,只是连接池配置有些修改--> <named-config name="mysql-config"> <property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb1</property> <property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> <property name="user">root</property> <property name="password">root</property> <property name="acquireIncrement">3</property> <property name="initialPoolSize">10</property> <property name="minPoolSize">2</property> <property name="maxPoolSize">10</property> </named-config> </c3p0-config>
c3p0的配置文件中可以配置多个连接信息,可以给每个配置起个名字,这样可以方便的通过配置名称来切换配置信息。上面文件中有一个默认配置和一个名为mysql-config配置(在这里其实都一样)
使用默认配置:
public void fun2() throws PropertyVetoException, SQLException { ComboPooledDataSource ds = new ComboPooledDataSource(); //不用定配置文件名称,因为配置文件名必须是c3p0-config.xml,这里使用的是默认配置 Connection con = ds.getConnection(); System.out.println(con); con.close(); }
使用名为mysql-config的配置:
public void fun2() throws PropertyVetoException, SQLException { ComboPooledDataSource ds = new ComboPooledDataSource("mysql-config"); //使用名为mysql-config配置 Connection con = ds.getConnection(); System.out.println(con); con.close(); }
JNDI
JNDI(Java Naming and Directory Interface),Java命名和目录接口。JNDI的作用就是:在服务器上配置资源,然后通过统一的方式来获取配置的资源。
我们这里要配置的资源当然是连接池了,这样项目中就可以通过统一的方式来获取连接池对象
需要在Tomcat的apache-tomcat-8.5.12\conf\Catalina路径下放入配置文件,该配置文件是以项目名为名称的xml文件,只对当前项目有效
配置JNDI资源文件需要到<Context>元素中配置<Resource>子元素:
- name:指定资源的名称,这个名称可以随便给,在获取资源时需要这个名称;
- factory:用来创建资源的工厂,这个值基本上是固定的,不用修改;
- type:资源的类型,我们要给出的类型当然是我们连接池的类型了;
- bar:表示资源的属性,如果资源存在名为bar的属性,那么就配置bar的值。对于DBCP连接池而言,你需要配置的不是bar,因为它没有bar这个属性,而是应该去配置url、username等属性
DBCP的配置:
<Context> <Resource name="mydbcp" type="org.apache.tomcat.dbcp.dbcp.BasicDataSource" factory="org.apache.naming.factory.BeanFactory" username="root" password="123" driverClassName="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" <!--需改为实际项目的数据库名--> url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb1" maxIdle="3" maxWait="5000" maxActive="5" initialSize="3"/> </Context>
C3P0的配置:
<Context> <Resource name="myc3p0" type="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" factory="org.apache.naming.factory.BeanFactory" user="root" password="123" classDriver="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" <!--需修改为实际项目的数据库--> jdbcUrl="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb1" maxPoolSize="20" minPoolSize ="5" initialPoolSize="10" acquireIncrement="2"/> </Context>
这就是以项目名为名称的xml文件的内容
获取资源
配置资源的目的当然是为了获取资源了。只要你启动了Tomcat,那么就可以在项目中任何类中通过JNDI获取资源的方式来获取资源了
获取资源:
- Context:javax.naming.Context;
- InitialContext:javax.naming.InitialContext;
- lookup(String):获取资源的方法,其中”java:comp/env”是资源的入口(这是固定的名称),获取过来的还是一个Context,这说明需要在获取到的Context上进一步进行获取。”bean/MyBeanFactory”对应<Resource>中配置的name值,这回获取的就是资源对象了
Context cxt = new InitialContext(); DataSource ds = (DataSource)cxt.lookup("java:/comp/env/myc3p0"); //使用的是myc3p0 Connection con = ds.getConnection(); System.out.println(con); con.close();
JdbcUtils.java
import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.SQLException; import javax.sql.DataSource; import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource; /** * 使用本类的方法,必须提供c3p0-copnfig.xml文件 */ public class JdbcUtils { private static DataSource ds = new ComboPooledDataSource(); /** * 它为null表示没有事务 * 它不为null表示有事务 * 当开启事务时,需要给它赋值 * 当结束事务时,需要给它赋值为null * 并且在开启事务时,让dao的多个方法共享这个Connection */ private static ThreadLocal<Connection> tl = new ThreadLocal<Connection>(); public static DataSource getDataSource() { return ds; } /** * dao使用本方法来获取连接 * @return * @throws SQLException */ public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { /* * 如果有事务,返回当前事务的con * 如果没有事务,通过连接池返回新的con */ Connection con = tl.get();//获取当前线程的事务连接 if(con != null) return con; return ds.getConnection(); } /** * 开启事务 * @throws SQLException */ public static void beginTransaction() throws SQLException { Connection con = tl.get();//获取当前线程的事务连接 if(con != null) throw new SQLException("已经开启了事务,不能重复开启!"); con = ds.getConnection();//给con赋值,表示开启了事务 con.setAutoCommit(false);//设置为手动提交 tl.set(con);//把当前事务连接放到tl中 } /** * 提交事务 * @throws SQLException */ public static void commitTransaction() throws SQLException { Connection con = tl.get();//获取当前线程的事务连接 if(con == null) throw new SQLException("没有事务不能提交!"); con.commit();//提交事务 con.close();//关闭连接 con = null;//表示事务结束! tl.remove(); } /** * 回滚事务 * @throws SQLException */ public static void rollbackTransaction() throws SQLException { Connection con = tl.get();//获取当前线程的事务连接 if(con == null) throw new SQLException("没有事务不能回滚!"); con.rollback(); con.close(); con = null; tl.remove(); } /** * 释放Connection * @param con * @throws SQLException */ public static void releaseConnection(Connection connection) throws SQLException { Connection con = tl.get();//获取当前线程的事务连接 if(connection != con) {//如果参数连接,与当前事务连接不同,说明这个连接不是当前事务,可以关闭! if(connection != null &&!connection.isClosed()) {//如果参数连接没有关闭,关闭之! connection.close(); } } } }
ThreadLocal类
这个是标准JDK中的类,在lang包下
ThreadLocal类只有三个方法:
- void set(T value):保存值;
- T get():获取值;
- void remove():移除值。
ThreadLocal的内部是Map
ThreadLocal内部其实是个Map来保存数据。虽然在使用ThreadLocal时只给出了值,不给出键,因为它内部使用了当前线程做为键
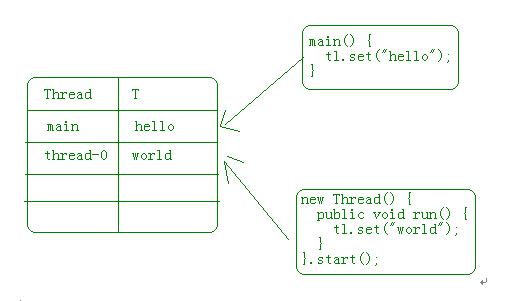
在介绍完使用commons-dbutils.jar后,会提供一个TxQueryRunner类方便操作(这是使用Jdbc的方式操作,使用框架操作数据库的时候就没有这么麻烦,毕竟这些东西框架都是封装好的)
BaseServlet
在开始客户管理系统之前,我们先写一个工具类:BaseServlet。
我们知道,写一个项目可能会出现N多个Servlet,而且一般一个Servlet只有一个方法(doGet或doPost),如果项目大一些,那么Servlet的数量就会很惊人。
为了避免Servlet的“膨胀”,我们写一个BaseServlet。它的作用是让一个Servlet可以处理多种不同的请求。不同的请求调用Servlet的不同方法。我们写好了BaseServlet后,让其他Servlet继承BaseServlet。(注意在页面调用Servlet的时候,需要给个method值作为说明调用Servlet中的哪个方法,不论是通过hidden隐藏表单项,还是使用url传值,一定要给这个参数,因为我们的BaseServlet是这样设计的,有点类似Struts2的Action调用方式)
BaseServlet.java:
import java.io.IOException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; /** * BaseServlet用来作为其它Servlet的父类 * 一个类多个请求处理方法,每个请求处理方法的原型与service相同! 原型 = 返回值类型 + 方法名称 + 参数列表 */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class BaseServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override public void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");//处理响应编码 request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8"); /** * 1. 获取method参数,它是用户想调用的方法 2. 把方法名称变成Method类的实例对象 3. 通过invoke()来调用这个方法 */ String methodName = request.getParameter("method"); Method method = null; /** * 2. 通过方法名称获取Method对象 */ try { method = this.getClass().getMethod(methodName, HttpServletRequest.class, HttpServletResponse.class); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException("您要调用的方法:" + methodName + "它不存在!", e); } /** * 3. 通过method对象来调用它 */ try { String result = (String)method.invoke(this, request, response); if(result != null && !result.trim().isEmpty()) {//如果请求处理方法返回不为空 int index = result.indexOf(":");//获取第一个冒号的位置 if(index == -1) {//如果没有冒号,使用转发 request.getRequestDispatcher(result).forward(request, response); } else {//如果存在冒号 String start = result.substring(0, index);//分割出前缀 String path = result.substring(index + 1);//分割出路径 if(start.equals("f")) {//前缀为f表示转发 request.getRequestDispatcher(path).forward(request, response); } else if(start.equals("r")) {//前缀为r表示重定向 response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + path); } } } } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }
这个BaseServlet还对forword和重定向进行了简化,可以在我们编写的Servlet中分别使用f:或r: 当然什么都不写,只给出页面路径是以forword方式转跳。注意:我们自己编写的Servlet继承BaseServlet还是需要在web.xml文件中配置的(或者你使用注解)
commons-dbutils.jar
DBUtils是Apache Commons组件中的一员,开源免费!
DBUtils是对JDBC的简单封装,但是它还是被很多公司使用。
QueryRunner类:
QueryRunner的update()方法可以用来执行insert、update、delete语句
QueryRunner的query()方法用于查询
ResultSetHandler接口:
我们知道在执行select语句之后得到的是ResultSet,然后我们还需要对ResultSet进行转换,得到最终我们想要的数据。你可以希望把ResultSet的数据放到一个List中,也可能想把数据放到一个Map中,或是一个Bean中
DBUtils提供了一个接口ResultSetHandler,它就是用来ResultSet转换成目标类型的工具。你可以自己去实现这个接口,把ResultSet转换成你想要的类型
事实上DBUtils提供了很多个ResultSetHandler接口的实现,这些实现已经基本够用了,我们通常不用自己去实现ResultSet接口了。
- MapHandler:单行处理器!把结果集转换成Map<String,Object>,其中列名为键!
- MapListHandler:多行处理器!把结果集转换成List<Map<String,Object>>;
- BeanHandler:单行处理器!把结果集转换成Bean,该处理器需要Class参数,即Bean的类型;
- BeanListHandler:多行处理器!把结果集转换成List<Bean>;
- ColumnListHandler:多行单列处理器!把结果集转换成List<Object>,使用ColumnListHandler时需要指定某一列的名称或编号,例如:new ColumListHandler(“name”)表示把name列的数据放到List中。
- ScalarHandler:单行单列处理器!把结果集转换成Object。一般用于聚集查询,例如select count(*) from tab_student。
配合使用DBUtils工具和上面的JdbcUtils类,编写一个TxQueryRunner类继承于QueryRunner,来简化操作:
TxQueryRunner.java:
import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.SQLException; import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner; import org.apache.commons.dbutils.ResultSetHandler; public class TxQueryRunner extends QueryRunner { @Override public int[] batch(String sql, Object[][] params) throws SQLException { Connection con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); int[] result = super.batch(con, sql, params); JdbcUtils.releaseConnection(con); return result; } @Override public <T> T query(String sql, ResultSetHandler<T> rsh, Object... params) throws SQLException { Connection con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); T result = super.query(con, sql, rsh, params); JdbcUtils.releaseConnection(con); return result; } @Override public <T> T query(String sql, ResultSetHandler<T> rsh) throws SQLException { Connection con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); T result = super.query(con, sql, rsh); JdbcUtils.releaseConnection(con); return result; } @Override public int update(String sql) throws SQLException { Connection con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); int result = super.update(con, sql); JdbcUtils.releaseConnection(con); return result; } @Override public int update(String sql, Object param) throws SQLException { Connection con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); int result = super.update(con, sql, param); JdbcUtils.releaseConnection(con); return result; } @Override public int update(String sql, Object... params) throws SQLException { Connection con = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); int result = super.update(con, sql, params); JdbcUtils.releaseConnection(con); return result; } }
最后提供一个CommonUtils来用于生成UUID和封装页面传递的数据
UUID通过算法生成一个唯一的值(显示出来是32位),可以作为主键,即使在分布式环境中也可以保持id唯一。使用这个类的uuid()方法可生成
这个类还有一个toBean()方法,用于将页面传递的数据封装成Bean组件,注意,这个方法的第一个参数使用的是map,我们可以在Servlet中使用request.getParameterMap()方法将页面(表单)传递的数据生成map类型作为toBean的第一参数就行了,toBean()的第二个参数就是你想转换的类型(使用泛型)
CommonUtils.java(需要commons-beanutils.jar):
import java.util.Map; import java.util.UUID; import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils; import org.apache.commons.beanutils.ConvertUtils; import org.apache.commons.beanutils.converters.DateConverter; /** * 小工具 * */ public class CommonUtils { /** * 返回一个不重复的字符串 * @return */ public static String uuid() { return UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "").toUpperCase(); } /** * 把map转换成对象 * @param map * @param clazz * @return * * 把Map转换成指定类型 */ @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") public static <T> T toBean(Map map, Class<T> clazz) { try { /* * 1. 通过参数clazz创建实例 * 2. 使用BeanUtils.populate把map的数据封闭到bean中 */ T bean = clazz.newInstance(); ConvertUtils.register(new DateConverter(), java.util.Date.class); BeanUtils.populate(bean, map); return bean; } catch(Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }


