React中生命周期
1.过时的生命周期(v16.3之前)
1.当前组件初次渲染:
绿色表示执行顺序。
constructor(): 如果不需要初始化,可以直接省略,会自动补全该函数。
可以在这个方法中初始化this.state。也可以直接直接在类的顶部初始化实例属性:state = {}
并且一定要调用super(props);如果只调用super(); 在constructor中无法访问this.props.
另外,属性可以设置默认值,使用静态属性defaultProps.
constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { number: 0 } }
componentWillMount(): render()之前触发。(服务器端渲染唯一会调用的周期函数)
16.3之后改为UNSAFE_componentWillMount,不能和新的周期一起使用。无UNSAFE_前缀的,17.0以后将不能再使用。
UNSAFE不代表不安全,指的是在未来React版本中更可能出错,特别是异步渲染应用后。
原因:
1)如果在该周期中监听或者(订阅)。会出现服务端渲染(永远不调用componentWillUnMount)和
异步渲染(渲染中断而不调用componentWillUnMount),导致内部不能释放,出现内存泄漏。
2)如果进行异步请求。服务器端渲染可能请求的数据不会被使用,异步渲染可能导致发起多次请求。
替代解决方案:
1)如果在该周期中调用setState,因为在render()前触发,不会触发额外渲染。
相当于初始化state。在constructor方法中初始化状态。
2)对于订阅等副作用处理转移至componentDidMount()
this.state.number === 0
render(): 唯一必须存在的方法,且必须返回一个元素或者null。
this.state.number === 0
componentDidMount(): 页面挂载(插入DOM)之后,立即调用。永远只调用一次!!
用法:
1)在此进行针对DOM的操作。 因为在此之前的所有周期都取不到真实的DOM节点。在此之后都可以取到。
2)在此进行订阅。记得UnMount时取消订阅。
3)在此进行网络数据请求。
this.state.number === 0
2.当前组件状态state发生更新
add = () => { this.setState({ number: this.state.number + 1 }) }
shouldComponentUpdate(nextPorps,nextState): 返回布尔值。用于性能优化。
建议直接使用React.PureComponent。 后续版本可能false也不能阻止更新。
此周期范围内,this.state, this.props的值仍未发生变化
this.state.number === 0
componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState): 当组件的state发生变化都会进入该周期,作为render()前的最后准备。
此周期范围内,this.state, this.props 的值仍未发生变化
this.state.number === 0
❎不能在无任何条件的情况下,调用setState或者diapatch修改Redux的状态
16.3之后改为UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate(nextProps,nextState),不能和新周期一起使用。 且无UNSAFE_前缀,17.0以后将不能再使用。
原因:
1)很多人使用该周期函数,是怕来不及更新。
但是,React保证在用户看到UI前(更新屏幕前),确保componentDidMount和componentDidUpdate之间的所有的setState都刷新完。所以在componentDidUpdate中一样。
2)在异步渲染中一次更新可能导致多次调用。但是componentDidMount确保只执行一次。
替代方案: getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()配合componentDidUpdate()
render(); 离开上个周期立即调用,this.state等值发生变化
this.state.number === 1
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState): DOM和Refs更新后被立即调用。
其中的prevProps在props触发的渲染中,是props更改之前的状态,prevState就是当前状态。
在setState触发的渲染中,prevProps就是当前传入的props, prevState是setState之前的state状态。
❎不能在无任何条件的情况下,调用setState或者diapatch修改Redux的状态。会出现死循环。
this.state.number === 1
3.子组件更新(props变化)
<Sub subNumber={this.state.number} />
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps): 只要父组件重新渲染,不论props是否变化,都会进入该生命周期。
组件“挂载阶段”不会触发该方法;本组件setState也不会触发该方法。
16.3之后改为UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate(nextProps,nextState),不能和新周期一起使用。 且无UNSAFE_前缀,17.0以后将不能再使用。
原因: 异步渲染可能会一次更新,多次调用。
替代方案:getDerivedStateFromProps()
this.props ---> {number: 0} nextProps--->{number: 1}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextPorps,nextState);
this.props ---> {number: 0} nextProps--->{number: 1}
componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState);
this.props ---> {number: 0} nextProps--->{number: 1}
render();
this.props ---> {number: 1}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState);
prevProps-->{number: 0} this.props ---> {number: 1}
4. 卸载组件
componentWillUnmount(): 当组件从DOM中移除时触发。
⚠️:在此要清理所有的订阅或者定时器等!!!
{ this.state.show ? <Sub /> : null }// show为false组件卸载
2. 新的生命周期(V16.3+)
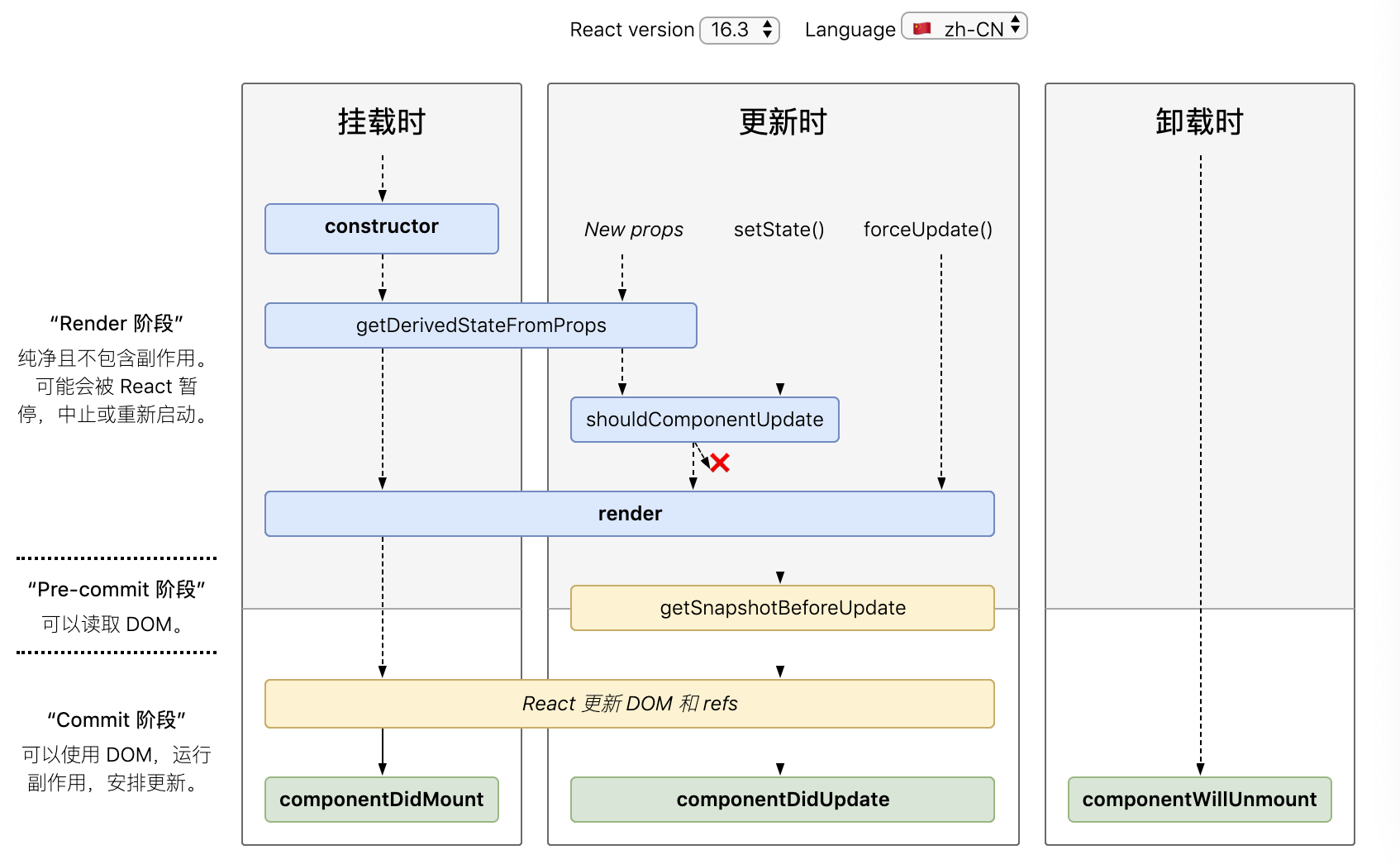
V16.4修复了getDerivedStateFromProps的内容。

1.当前组件初次加载
constructor(props):同上。
static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, state): 根据props的值和state的值,如果有变化返回新的state状态对象。
如果没有变化,返回null; 每次渲染(初次渲染和更新,不论props或者state的值是否有变化)都会调用。
该生命周期设计成静态方法的原因:
静态方法是类上的方法,不是实例上的方法。在该生命周期中取不到this, 不能调用setState等实例方法,保证方法的纯粹;
该方法就是用来通过父组件的props来更新state, 返回增量state对象。
作用:通过props和state计算新的state,用于更新。
❎保守使用该方法。该方法中不能使用this,不能访问组件实例。
保守方案:
1)避免派生状态导致多数据源,使用完全受控,即数据完全由props提供。
2)如果想通过props重置state状态。有三种方案
a. 👍使用key值,重新加载组件
b.在该生命周期中通过判断特殊属性(id)不同,更新state
c.在父组件中使用Ref调用实例方法。
3) 想要通过props更新数据,使用memorization。
使用前置条件:
1)用该生命周期的组件必须有个状态对象(this.state={}),用于接收返回的对象。
2) 该生命周期方法必须返回一个state对象或者null;不能是undefined。
3)因为React的class组件都需要传入ReactDOM.render(<Name />, container)进行组件实例化,所有都会有props属性,默认props是{}。
render();
componentDidMount();
2.当前组件状态state更新
static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState);
shouldComponentUpdate();
render();
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState): 在React更新DOM和Refs之前触发。
可以获取DOM变更前的DOM信息(如滚动位置等)。
必须⚠️返回一个值作为componentDidUpdate()的第三个参数,没有返回null。
其中prevProps代表props触发的渲染中,变更前的props值,
prevState代表setState触发的渲染中,setState之前的state。
应用场景:
UI处理。如获取更新前的滚动位置(scrollHeigth-scrollTop)。

class App extends React.Component{ constructor(props){ super(props); this.state = { lists: Array.from({length: 20}, (item,index) => index) } this.ref = React.createRef(); } componentDidMount() { this.timer = setInterval(() => { this.setState(state => ({ lists: [ 'row'+state.lists.length, ...state.lists] })) },300) } componentWillUnmount() { clearInterval(this.timer) } // 实现在原有数据前增加,但是显示内容不变 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps,prevState) { if (prevState.lists.length < this.state.lists.length) { const dom = this.ref.current; return dom.scrollHeight - dom.scrollTop } return null; } componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) { if (snapshot) { const dom = this.ref.current; dom.scrollTop = dom.scrollHeight - snapshot } } render() { return ( <div ref={this.ref} style={{overflow: 'auto',height: 100, border: '1px solid red'}}> {this.state.lists.map((item,index) => { return ( <div key={item}>Row: {item}</div> ) })} </div> ) } }
替换componentWillUpdate
在异步渲染中,原来的“render阶段”(componentWillUpdate和render)和“提交阶段”(ComponentDIdUpdate)之间可能会有延迟。
所以不再使用componentWillUpdate。
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot);
3. 子组件更新(props)
同2。
4.卸载
同过时周期。




