BIO AIO BIO
BIO
阻塞IO,如果没有连接则会阻塞,如果有连接但是没有发送数据也会阻塞。只能保证一个连接写数据,另一个连接则会被阻塞,无法进行写数据。
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
System.out.println("服务器启动了");
System.out.println("等待连接....");
while (true) {
Socket accept = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("连接到客户端");
handle(accept);
}
private static void handle(Socket clientSocker) throws IOException {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
System.out.println("准备读消息");
int read = clientSocker.getInputStream().read(bytes);
System.out.println("read完毕");
if (read != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, read));
}
}
优化方式是可以使用多线程的方式进行处理数据,主线程用于处理连接,创建新线程来读写客户端发送过来的数据,但是这样做也有问题,如果连接用户过大则创建线程过多,最终导致堆内存耗尽,抛出OOM,可以使用线程池来解决这个问题,不过使用线程池的话,意义不大,如果有五万个用户连接,线程池只有五百,刚好有五百个线程连接了,但是写数据,还是会一直阻塞着其他连接。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
System.out.println("服务器启动了");
System.out.println("等待连接....");
while (true) {
Socket accept = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("连接到客户端");
new Thread(() -> {
try {
handle(accept);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}).start();
}
}
private static void handle(Socket clientSocker) throws IOException {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
System.out.println("准备读消息");
int read = clientSocker.getInputStream().read(bytes);
System.out.println("read完毕");
if (read != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, read));
}
}
NIO
非阻塞IO
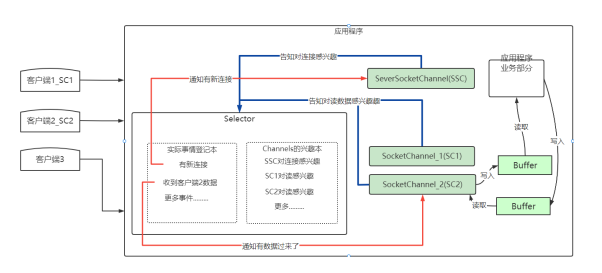
只需要监听事件列表,如有有事件了,在根据不同的事件类型进行不同的处理。
比如以下代码就是先获取到事件集合列表,然后遍历集合,判断集合类型是否是accept,如果是则进行下一步处理。
while (true) {
selector.select(1000);
// 获取事件集合
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
// 遍历事件并根据事件类型进行不同的处理
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey next = iterator.next();
if (next.isValid()) {
if (next.isAcceptable()) {
// 连接成功注册socketChannel 之后注册读事件 读数据进行读操作
ServerSocketChannel channel = (ServerSocketChannel) next.channel();
SocketChannel accept = channel.accept();
accept.configureBlocking(false);
accept.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
// 当对端有数据发送过来时 读取数据
if (next.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) next.channel();
ByteBuffer allocate = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int read = channel.read(allocate);
if (read > 0) {
// 将写模式切换成读模式
allocate.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[allocate.remaining()];
allocate.get(bytes);
System.out.println("客户端接受到的消息为:" + new String(bytes));
}
}
}
iterator.remove();
}
NIO流程
服务端
- 创建selector
selector = Selector.open();
- 创建severSocketChannel并将阻塞模式设置为非阻塞模式
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
- 如果是服务端则需要监听端口完毕之后客户端需要关注客户端发过来的连接,所有需要注册accept接收连接事件。
// 监听端口
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(9797));
// 关注accept事件
serverSocketChannel.register(serverSocketChannelSelector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
- 根据客户端和服务端不同监听不同的事件,因为服务端只用监听客户端的读写事件 对客户端发送过来的数据进行读取然后响应
// 如果有连接过来 则进行连接 连接外部后则注册一个读事件 读取客户端法国来的信息
if (next.isAcceptable()) {
System.out.println("接收到了连接");
ServerSocketChannel clientServerSocketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) next.channel();
SocketChannel accept = clientServerSocketChannel.accept();
accept.configureBlocking(false);
accept.register(serverSocketChannelSelector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
if (next.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel clientSocketChannel = (SocketChannel) next.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 将读到的数据写到buffer中
int read = clientSocketChannel.read(buffer);
if (read > 0) {
// 反转buffer 由写模式切换到读模式
buffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(bytes);
String message = new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("接收到客户端发送的消息:" + message);
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
String str = "HTTP/1.1 302\n"
+ "Content-Type: text/html;charset=UTF-8\n"
+ "\n"
+ "<h1> Hello, Lyra web server! </h1>";
byte[] bytes1 = str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// 创建buffer
ByteBuffer allocate = ByteBuffer.allocate(bytes1.length);
// 在buffer中写数据
allocate.put(bytes1);
// 反转buffer 由写模式切换为读模式
allocate.flip();
// 往客户端写入数据
clientSocketChannel.write(allocate);
clientSocketChannel.close();
}
}
服务端全部代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = null;
Selector serverSocketChannelSelector = null;
try {
serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannelSelector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(9797));
serverSocketChannel.register(serverSocketChannelSelector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true) {
int select = serverSocketChannelSelector.select(1000);
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = serverSocketChannelSelector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey next = iterator.next();
if (next.isValid()) {
// 如果有连接过来 则进行连接 连接外部后则注册一个读事件 读取客户端法国来的信息
if (next.isAcceptable()) {
System.out.println("接收到了连接");
ServerSocketChannel clientServerSocketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) next.channel();
SocketChannel accept = clientServerSocketChannel.accept();
accept.configureBlocking(false);
accept.register(serverSocketChannelSelector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
if (next.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel clientSocketChannel = (SocketChannel) next.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 将读到的数据写到buffer中
int read = clientSocketChannel.read(buffer);
if (read > 0) {
// 反转buffer 由写模式切换到读模式
buffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(bytes);
String message = new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("接收到客户端发送的消息:" + message);
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
String str = "HTTP/1.1 302\n"
+ "Content-Type: text/html;charset=UTF-8\n"
+ "\n"
+ "<h1> Hello, Lyra web server! </h1>";
byte[] bytes1 = str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// 创建buffer
ByteBuffer allocate = ByteBuffer.allocate(bytes1.length);
// 在buffer中写数据
allocate.put(bytes1);
// 反转buffer 由写模式切换为读模式
allocate.flip();
// 往客户端写入数据
clientSocketChannel.write(allocate);
clientSocketChannel.close();
}
}
}
iterator.remove();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (serverSocketChannel != null) {
try {
serverSocketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (serverSocketChannelSelector != null) {
try {
serverSocketChannelSelector.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
客户端
- 开启selection
selector = Selector.open();
- 开启socketChannel并开启非阻塞模式
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
- 与服务端进行连接 客户端则需要知道服务端的IP和端口并与连接服务端进行连接。
// 与服务端进行连接 如果没有延迟 直接连接成功的话则返回true,注册读消息 读取客户端发送过来的消息 如果为false表示还没连接完毕 则注册一个连接消息
if(socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9797))){
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}else{
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}
- 读取客户端发送过来的数据
if (next.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) next.channel();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int read = channel.read(buffer);
if (read > 0) {
buffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(bytes);
String message = new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("接收到客户端发送的消息:" + message);
String serverMessage = new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("接收到服务端端发送的消息,消息:" + serverMessage);
} else if (read < 0) {
next.cancel();
channel.close();
}
}
客户端全部代码
package com.lyra;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class NioClientHandle implements Runnable {
Selector selector = null;
SocketChannel socketChannel = null;
@Override
public void run() {
try {
selector = Selector.open();
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 与服务端进行连接 如果没有延迟 直接连接成功的话则返回true,注册读消息 读取客户端发送过来的消息 如果为false表示还没连接完毕 则注册一个连接消息
if(socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9797))){
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}else{
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}
while (true) {
selector.select(1000);
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey next = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
if (next.isValid()) {
// 表示没有连接完成 执行connect事件
if (next.isConnectable()) {
// 获取socketChannel
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) next.channel();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
// 判断是否连接完成 如果连接完成则注册读消息并往服务端发送数据 如果没有连接完成则直接返回1
if (channel.finishConnect()) {
// 注册读事件
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
// 发送消息 无外乎还是创建buffer 写入数据 反转buffer 发送数据
byte[] clientMessageByte = "Hello Lyra".getBytes();
ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(clientMessageByte.length);
buffer1.put(clientMessageByte);
buffer1.flip();
System.out.println("客户端发送消息.....");
socketChannel.write(buffer1);
} else {
System.exit(1);
}
}
if (next.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) next.channel();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int read = channel.read(buffer);
if (read > 0) {
buffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(bytes);
String message = new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("接收到客户端发送的消息:" + message);
String serverMessage = new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("接收到服务端端发送的消息,消息:" + serverMessage);
} else if (read < 0) {
next.cancel();
channel.close();
}
}
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (selector != null) {
try {
selector.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
public SocketChannel getSocketChannel() {
return socketChannel;
}
public static void sendMessage(String message, SocketChannel socketChannel) {
byte[] clientMessageByte = message.getBytes();
ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(clientMessageByte.length);
buffer1.put(clientMessageByte);
buffer1.flip();
System.out.println("客户端发送消息.....");
try {
socketChannel.write(buffer1);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
一般手动注册OP_WRITE事件
OP_READ和OP_WRITE事件是以下情况才会被注册:
- 当对端有数据过来时,读缓存中有数据了,则会触发OP_READ
- 当写缓存中有空闲空间时,会触发OP_WRITE
写消息会监听发送缓存是否有空闲位 如果有的话则会执行读 一直有则一直读 如果写完写事件没有取消则会一直进行写操作,写操作是主动的,所以一般要往对端进行写数据时,直接调用write写就行了,没必要注册写事件。
直接内存比堆内存要快
HeapBuffer: 堆内存
DirectBuffer:直接内存
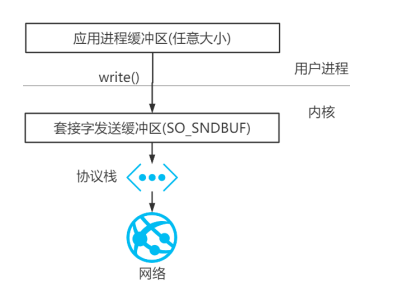
每个TCP socket都有一个读缓存和一个写缓存,应用程序要进行读写操作时,首先将数据读写到应用程序的读写缓存中,之后才会将应用程序的缓存区发送到socket缓存区中,最后才会发送到对端。
具体过程如下图所示
-
如果使用堆外内存的话需要进行二次拷贝,首先会在堆外新建一个DirectBuffer,之后从堆中拿到数据再发送到directBuffer中,然后再由directBuffer发送到socket缓存区再,之后才会发送到对端,多拷贝一次的原因是避免应用程序缓存区读到一半,JVM进行GC时,数据地址变动,原有数据因为地址变动的原因找不到了,所以要在堆外开辟一块不是由JVM管理的内存,将数据直接发送到这个内存上,这样就能避免读一半找不到原有数据的问题了。
JNI调用c库时需要保证地址上的内容不能失效 -
而直接使用直接内存的方式DirectBuffer则不会少拷贝一次,但是使用直接内存的方式发生内存泄露时难以排查。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix