Py4j的简单使用
一、
Py4j官网:https://www.py4j.org/,介绍大家可以到官网进行了解。
二、
本次介绍的是通过java调用python的函数,以及python的返回值给到java。
三、
演示:
java代码
import py4j.GatewayServer;
import java.net.InetAddress;
public class ExampleClientApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
for(int i =0;i<3;i++) {
GatewayServer.turnLoggingOff();
GatewayServer.GatewayServerBuilder builder = new GatewayServer.GatewayServerBuilder();
GatewayServer server = builder.javaAddress(InetAddress.getByName("10.252.218.147")).build();
// GatewayServer server = new GatewayServer();
server.start();
IHello hello = (IHello) server.getPythonServerEntryPoint(new Class[] { IHello.class });
try {
// System.out.println(hello.sayHello());
// System.out.println(hello.sayHello(2, "Hello World", "/Users/admin/Downloads/临时文件/pycharmProject/标签分析_0_2023-04-24+18_32_16.xlsx"));
// System.out.println(hello.sayHello());
System.out.println(hello.sayHello2("a", "b", "c"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
server.shutdown();
Thread.sleep(1000L);
}
}
}
public interface IHello { public String sayHello(); public String sayHello(int i, String s, String path); public String sayHello2(String s1, String s2, String s3); }
其中:IHello是一个java的接口,调用的是sayHello方法(带3个参数),实质调用的是python侧的该函数,java没有写其实现类。
python代码
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier, plot_tree from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, accuracy_score, recall_score, precision_score, f1_score import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from sklearn.datasets import load_iris import pandas as pd import json from sklearn import tree import graphviz import pydotplus import matplotlib matplotlib.use('agg') class SimpleHello(object): def sayHello2(self, s1, s2, s3): return s1 + '_' + s2 + '_' + s3 def sayHello(self, int_value=None, string_value=None, path=None): # print(int_value, string_value) # return "Said hello to {0}".format(string_value) # Load the iris dataset # X = np.array([[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]]) # y = np.array([0, 1, 1, 0]) m = {} # iris = load_iris() # X = iris.data # y = iris.target # df = pd.read_excel("/Users/admin/Downloads/临时文件/pycharmProject/标签分析_0_2023-04-24+18_32_16.xlsx") df = pd.read_excel(path) df1 = df df2 = df.drop(columns=['flag', 'boss_id', 'ds']) X = np.array(df2) # print(X) y = np.array(df['flag']) # print(y) # Train the decision tree model dt = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=4, min_samples_leaf=1, criterion='entropy') dt.fit(X, y) # Calculate feature importance importance = dt.feature_importances_ print("Feature Importance:", importance) m['Importance'] = importance.tolist() print(type(importance)) # Make predictions on the test data y_pred = dt.predict(X) # Calculate confusion matrix cm = confusion_matrix(y, y_pred) print(type(cm)) print("Confusion Matrix:\n", cm) m["matrix"] = cm.tolist() # Calculate accuracy accuracy = accuracy_score(y, y_pred) print("Accuracy:", accuracy) m["Accuracy"] = accuracy # Calculate recall recall = recall_score(y, y_pred, average="macro") print("Recall:", recall) m["Recall"] = recall # Calculate precision precision = precision_score(y, y_pred, average="macro") print("Precision:", precision) m["Precision"] = precision # Calculate F1 score f1 = f1_score(y, y_pred, average="macro") print("F1 Score:", f1) m["F"] = f1 # Plot the decision tree and save it # plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) # mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # print(iris.feature_names) # print(type(iris.feature_names)) # print(iris.target_names) # print(type(iris.target_names)) # plot_tree(dt, filled=True, feature_names=np.array(df1.columns), class_names=np.array(['1', '0'])) # plt.savefig("./decision_tree1.png", dpi=300) with open("./model.dot", 'w') as f: f = tree.export_graphviz(dt, out_file=f) # # 画图,保存到pdf文件 # # 设置图像参数 dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(dt, out_file=None, feature_names=np.array(df2.columns), filled=True, rounded=True, special_characters=True) dot_data = dot_data.replace("helvetica", "MicrosoftYaHei") graph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data) # # 保存图像到pdf文件 # graph.write_pdf("./model_4.pdf") graph.write_svg("./model_5.svg") return json.dumps(m) class Java: implements = ["org.example.java_call_python.IHello"] # Make sure that the python code is started first. # Then execute: java -cp py4j.jar py4j.examples.SingleThreadClientApplication from py4j.java_gateway import JavaGateway, CallbackServerParameters, GatewayParameters # simple_hello = SimpleHello() gateway_param = GatewayParameters(address="10.252.218.147") gateway = JavaGateway( gateway_parameters=gateway_param, callback_server_parameters=CallbackServerParameters(), python_server_entry_point=simple_hello)
使用方式:先执行python程序,在运行java程序,二者通过GatewayServer进行通信。
效果展示:
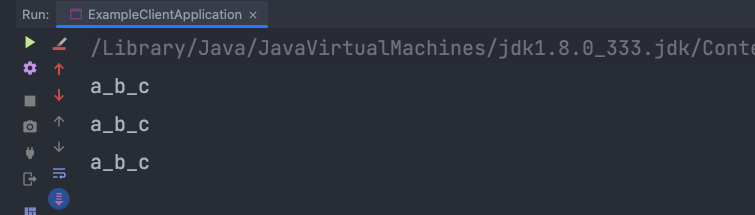
这样就达到了在java调用python的函数进行返回,博主的场景是在java中调用python的决策树算法,大家可以自行进行函数内部逻辑封装即可。

