Django~Views
In Django, web pages and other content are delivered by views.
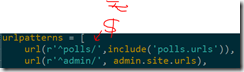
To get from a URL to a view, Django uses what are known as ‘URLconfs’. A URLconf maps URL patterns (described as regular expressions) to views.
write views
add urls
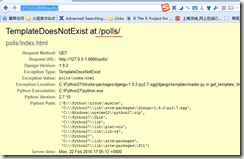
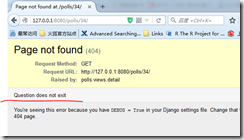
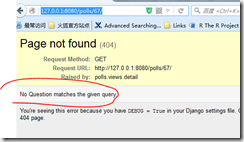
404
Each view is responsible for doing one of two things: returning an HttpResponse object containing the content for the requested page, or raising an exception such as Http404.
PDF,.XML,ZIP ^^^^^^^![]()
Your view can read records from a database, or not. It can use a template system such as Django’s – or a third-party Python template system – or not. It can generate a PDF file, output XML, create a ZIP file on the fly, anything you want, using whatever Python libraries you want.
Create Templates
First, create a directory called templates in your polls directory. Django will look for templates in there
名字空间
路径:polls/templates/polls/index.html. .否则
没有加模板前 添加模板后
templates中内容
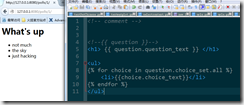
<ul> for 循环</ul>
{% if latest_question_list %} <ul> {% for question in latest_question_list %} <li><a href="/polls/{{question.id}}/">{{question.question_text}}</a></li> {% endfor %} </ul> {% else %} <p>No polls are available.</p> {% endif %}
省事的render
return render(request, 'polls/index.html', context)
The render() function takes the request object as its first argument, a template name as its second argument and a dictionary as its optional third argument. It returns an HttpResponse object of the given template rendered with the given context.
404问题
try except render
加上名字空间
ulsr.py中app_name=’polls’
index 中polls:detail
<li><a href="{% url 'polls:detail' question.id %}">{{question.question_text}}</a></li>