Socket Programming
| There are two ways to store this value.
- Little Endian.(低位优先)
- Big Endian.(高位优先)
| The complete Client and Server interaction.
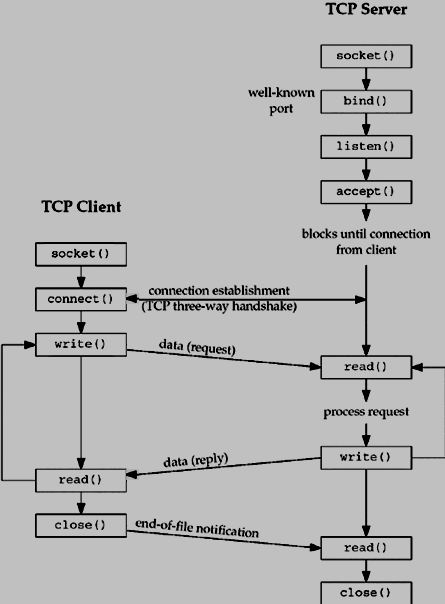
| The simplest way to write a concurrent server under Unix is to fork a child process to handle each client separately.
| Socket Type
- Stream Sockets(TCP)[most commonly used]
- Datagram Sockets (UDP)[most commonly used]
- Raw Sockets (Raw Sockets are not intended for the general user; they have been provided mainly for those interested in developing new communication protocols, of for gaining access to some of the more cryptic facilities of an existing protocol.) [rarely used]
- Sequenced Packet Socket [rarely used]
| Where is socket used?
A Unix socket is used in a client-server application framework.
| In Unix, every I/O action is done by writing or reading a file descriptor.
| Socket allow communication between two different processes on the same or different machines.
| Unix Socket
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/unix_sockets/
| Connection-oriented socket (TCP)

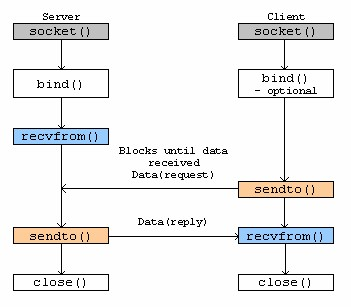
| Connectionless socket (UDP)
| 你一言我一语(Java语言实现):
//: MyServer.java
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class MyServer{
public static void main(String[]args) {
try {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(6666);
Socket s = ss.accept();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(s.getInputStream());
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(s.getOutputStream());
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str = "";
while (!str.equals("stop")) {
str = (String)dis.readUTF();
System.out.println("[client] " + str);
str = br.readLine();
System.out.println("[server] " + str);
dos.writeUTF(str);
dos.flush();
}
s.close();
ss.close();
} catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
//: MyClient.java
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class MyClient {
public static void main (String []args) {
try {
Socket s = new Socket("localhost", 6666);
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(s.getOutputStream());
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(s.getInputStream());
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str = "";
while(!str.equals("stop")) {
str = br.readLine();
dos.writeUTF(str);
dos.flush();
System.out.println("[client] " + str);
System.out.println("[server] " + dis.readUTF());
}
dos.close();
s.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}

