Java 递归(深度优先)寻找迷宫最短路径
有一个数组访问越界的bug,通过连续的递归躲过了一开始的边界检查,记录一下。
public class Maze { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建迷宫,0未走可走,1未走不可走(障碍物), // 2走过可走,3走过不可走 int[][] map = new int[9][8]; int[][] lastPath = new int[9][8]; int[][] thisPath = new int[9][8]; int lastDis; for (int i = 0; i < map[0].length; i++) { map[0][i] = 1; map[8][i] = 1; } for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) { map[i][0] = 1; map[i][7] = 1; } //设置障碍物 map[4][1] = 1; map[4][2] = 1; map[4][3] = 1; map[2][3] = 1; map[2][2] = 1; map[3][3] = 1; map[3][5] = 1; map[6][3] = 1; map[7][5] = 1; T t1 = new T(); //走前迷宫 t1.printMaze(map); //找路 lastPath[0][0] = 8 * 7; t1.findMinWay(map, 1, 1, lastPath, 0); //走后迷宫 t1.printMaze(lastPath); } } class T { public void printMaze(int[][] map) { System.out.println("打印迷宫如下============"); for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < map[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(map[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } } //复制当前的最短路径 public void refreshPath(int[][] map, int[][] lastPath, int nowDepth) { //先清空原有路径 for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < map[i].length; j++) { lastPath[i][j] = 0; } } //再复制新的最短路径 lastPath[0][0] = nowDepth; for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < map[i].length; j++) { if (map[i][j] == 2) { lastPath[i][j] = map[i][j]; } } } } //判断从当前位置map[i][j]是否能找到路到达终点的路 //depth表示递归深度(路的长度) public void findMinWay(int[][] map, int i, int j, int[][] lastPath, int nowDepth) { //比较nowDepth和lastPath[0][0]的大小,如果目前走的距离已经比最短路径长,则返回false //但是,不将当前位置置为2,而是不做处理,只是剪掉了当前路径这种选择 if (nowDepth >= lastPath[0][0]) { System.out.println("剪枝" + nowDepth + ">=" + lastPath[0][0]); return; } else {//继续尝试 if (map[7][6] != 1 && i == 7 && j == 6) {//已经找到出口,并且这条路比之前的最短路径都短,则记录路径,并更新最短距离 lastPath[0][0] = nowDepth; refreshPath(map, lastPath, nowDepth); System.out.println("找到新的最短路径" + lastPath[0][0]); return; } else {//还在找路 System.out.printf("(%d, %d)\n", i, j); if (map[i][j] == 0) {//当前路不是障碍物,可以尝试走 //先假定当前位置可以走通 map[i][j] = 2; //System.out.printf("(%d, %d) %d\n", i, j, nowDepth); //再寻找下一个位置,递归到目标 findMinWay(map, i + 1, j, lastPath, nowDepth + 1); findMinWay(map, i, j + 1, lastPath, nowDepth + 1); findMinWay(map, i - 1, j, lastPath, nowDepth + 1); findMinWay(map, i, j - 1, lastPath, nowDepth + 1); map[i][j] = 0; } } } } }
重点是上面的部分,数组访问越界出现在四周没有路,需要回退的时候,回退一步,就可以获得一次越界的机会,虽然边界用1表示障碍物,做了一层防护,但是当回退两步的时候,还是会出现数组访问越界的情况。
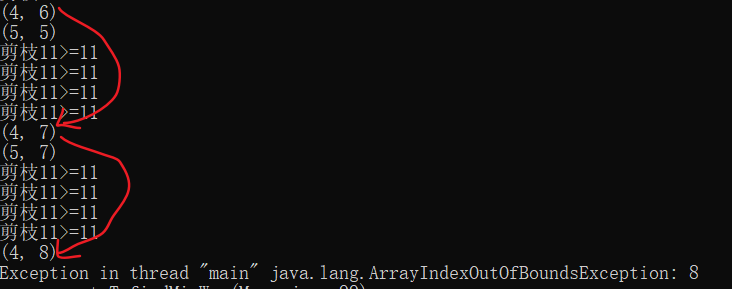
修改后,如下
public class Maze { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建迷宫,0未走可走,1未走不可走(障碍物), // 2走过可走(当前路径中包含该位置) int[][] map = new int[9][8]; //记录最短路径和最短距离 //因为还没学全局变量,所以最短距离记录在lastPath[0][0]中 int[][] lastPath = new int[9][8]; //数组的外围相当于迷宫的围墙,不允许走,初步防止数组访问越界 for (int i = 0; i < map[0].length; i++) { map[0][i] = 1; map[8][i] = 1; } for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) { map[i][0] = 1; map[i][7] = 1; } //设置障碍物 map[4][1] = 1; map[4][2] = 1; map[4][3] = 1; map[2][3] = 1; map[2][2] = 1; map[3][3] = 1; map[3][5] = 1; map[6][3] = 1; map[7][5] = 1; T t1 = new T(); //打印走前迷宫 t1.printMaze(map); //找最短路径 //初始化最短距离为数组全部元素的数量 lastPath[0][0] = 8 * 7; t1.findMinWay(map, 1, 1, lastPath, 0); //打印最短路径 t1.printMinPath(lastPath); } } class T { public void printMaze(int[][] map) { System.out.println("打印迷宫如下============"); for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < map[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(map[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } } //复制当前的最短路径 public void refreshPath(int[][] map, int[][] lastPath, int nowDepth) { //先清空原有路径 for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < map[i].length; j++) { lastPath[i][j] = 0; } } //记录新的最短距离 lastPath[0][0] = nowDepth; //再复制新的最短路径 for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < map[i].length; j++) { if (map[i][j] == 2) { lastPath[i][j] = map[i][j]; } } } } public void printMinPath(int[][] lastPath) { System.out.println("最短路径如下============"); for (int i = 0; i < lastPath.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < lastPath[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(lastPath[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } System.out.println("最短距离为" + lastPath[0][0]); } //判断map[i][j]是否在数组内,防止数组访问越界 public boolean inArr(int[][] map, int i, int j) { return (i >= 0 && i < map.length && j >= 0 && j < map[i].length); //map[i]用到了逻辑与的短路效应,只有i未越界,后面的判断才会继续 } //寻找从当前位置map[i][j]到达终点的最短路径和最短距离 //nowDepth表示递归深度(路的长度) public void findMinWay(int[][] map, int i, int j, int[][] lastPath, int nowDepth) { //比较nowDepth和lastPath[0][0]的大小,如果目前走的距离已经比最短路径长,则直接返回。剪枝,剪掉了当前路径这种选择 //但是,不将当前位置置为2,而是不做处理 if (nowDepth >= lastPath[0][0]) { return; } else {//继续尝试 if (map[7][6] == 0 && i == 7 && j == 6) {//已经找到出口,并且这条路比之前的最短路径都短,则记录路径,并更新最短距离 lastPath[0][0] = nowDepth; map[7][6] = 2; refreshPath(map, lastPath, nowDepth); map[7][6] = 0;//先令终点为2,记录路径。然后置0,表示未走可走,这里也是回退一步的意思。 return; } else {//还在找路 if (map[i][j] == 0) {//当前路不是障碍物,可以尝试走 //先假定当前位置可以走通 map[i][j] = 2; //再寻找下一个位置,递归到目标 if (inArr(map, i + 1, j))//进行边界判断 findMinWay(map, i + 1, j, lastPath, nowDepth + 1); if (inArr(map, i, j + 1)) findMinWay(map, i, j + 1, lastPath, nowDepth + 1); if (inArr(map, i - 1, j)) findMinWay(map, i - 1, j, lastPath, nowDepth + 1); if (inArr(map, i, j - 1)) findMinWay(map, i, j - 1, lastPath, nowDepth + 1); map[i][j] = 0; } } } } }




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!