2021.1 java集合框架1
JAVA集合框架1
一.集合的概念
1.集合的概念
对象的容器,定义了对多个对象进行操作的常用方法。可实现数组的功能
2.集合与数组的区别
- 数组长度固定,集合长度不固定
- 数组可以存储基本类型和引用类型,集合只能存储引用类型
- 位置位于java.util.*;
二.Collection接口
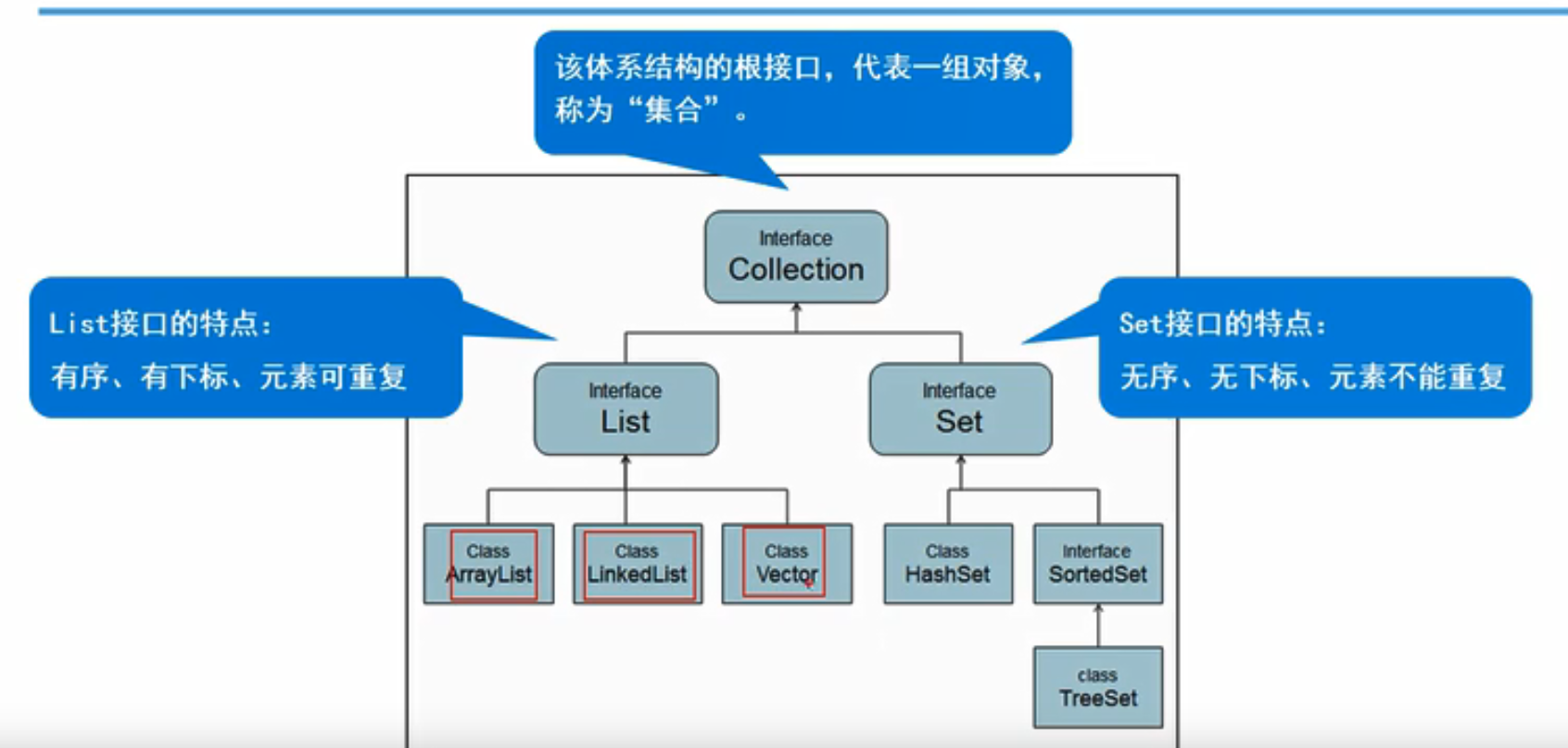
-
实现类
ArrayList数组
LinkedList链表
SortedSet排序
1. Collection父接口的特点
- 特点:代表一组类型的对象,一些collection允许有重复的元素(List),而另一些不允许(Set)。一些collection是有序的(List),一些collection是无序的(Set)。
2.Collection接口的使用(方法)----处理元素
/*
Collection接口的使用---处理元素
1.添加元素
2.删除元素
3.遍历元素(重点)
4.判断
*/
public class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合,接口不能实例化,但是能创建对象;需要利用实现类
Collection collection=new ArrayList();
//1.添加元素
collection.add("aaa");//添加字符串
collection.add("bbb");
collection.add("ccc");
collection.add(123);//添加数据
System.out.println("元素个数:"+collection.size());//集合长度(个数)
System.out.println(collection.toString());
System.out.println("=================================");
//2.删除元素
collection.remove("aaa");//删除一个元素
System.out.println("元素个数:"+collection.size());//集合长度(个数)
System.out.println(collection.toString());
//collection.clear();//清空元素
//System.out.println("元素个数:"+collection.size());//集合长度(个数)
//System.out.println(collection.toString());
System.out.println("=================================");
//3.遍历元素(重点)
//(1)使用增强for循环,collection集合没有显示下标,无法使用普通for来遍历
System.out.println("使用增强for循环遍历集合");
for (Object object:collection){
System.out.println(object.toString());
}
System.out.println("=================================");
//(2)使用迭代器遍历,迭代器是个接口,方法如下
//hasNext();判断有没有下一个元素
//next();获取下一个元素
//remove();删除当前元素
System.out.println("使用迭代器遍历集合");
Iterator it=collection.iterator();//这是一个接口
while(it.hasNext()){
Object o=it.next();
System.out.println(o.toString());
//在迭代过程中不能使用collection的删除方法:collection.remove();
//迭代里面有自己的删除方法
//it.remove();
}
System.out.println("元素个数:"+collection.size());
System.out.println("=================================");
//4.判断
System.out.println(collection.contains("bbb"));//存不存在这个元素
System.out.println(collection.isEmpty());//是不是空
}
}
/*结果:
元素个数:4
[aaa, bbb, ccc, 123]
=================================
元素个数:3
[bbb, ccc, 123]
=================================
使用增强for循环遍历集合
bbb
ccc
123
=================================
使用迭代器遍历集合
bbb
ccc
123
元素个数:3
=================================
true
false
*/
3. Collection接口的使用(方法)----处理信息(已有类的信息)
/*
Collection接口的使用---处理已有类的信息
此处处理学生类的信息
*/
public class B {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合,不接口能实例化,但是能创建对象;需要利用实现类
//1.处理信息
Collection collection=new ArrayList();
Student s1=new Student();
s1.setAge(10);
s1.setName("aaa");
Student s2=new Student();
s1.setAge(11);
s1.setName("bbb");
Student s3=new Student();
s1.setAge(12);
s1.setName("ccc");
//1.添加信息
collection.add(s1);
collection.add(s2);
collection.add(s3);
System.out.println("元素个数"+collection.size());
System.out.println(collection.toString());
System.out.println("===================");
//2.删除信息
collection.remove(s1);
System.out.println("删除之后元素个数:"+collection.size());
System.out.println(collection.toString());
//collection.clear();全部清除
//清除只是集合里面清除,对象本身不会清除,添加信息时只是传地址进集合
System.out.println("===================");
//3.遍历信息
//(1)增强for循环遍历
System.out.println("使用增强for循环遍历集合");
for (Object object:collection){
System.out.println(object.toString());
}
System.out.println("=================================");
//(2)使用迭代器遍历,迭代器是个接口,方法如下
//hasNext();判断有没有下一个元素
//next();获取下一个元素
//remove();删除当前元素
System.out.println("使用迭代器遍历集合");
Iterator it=collection.iterator();//这是一个接口
while(it.hasNext()){
Object o=it.next();
System.out.println(o.toString());
//在迭代过程中不能使用collection的删除方法:collection.remove();
//迭代里面有自己的删除方法
//it.remove();
}
System.out.println("元素个数:"+collection.size());
System.out.println("=================================");
//4.判断
System.out.println(collection.contains(s2));//存不存在这个信息
System.out.println(collection.isEmpty());//是不是空
}
}
/*结果:
元素个数3
[aaa 10, bbb 11, ccc 12]
===================
删除之后元素个数:2
[bbb 11, ccc 12]
===================
使用增强for循环遍历集合
bbb 11
ccc 12
=================================
使用迭代器遍历集合
bbb 11
ccc 12
元素个数:2
=================================
true
false
*/
//学生类
public class Student{
//封装属性
private int age;
private String name;
//构造器,new之后,程序先运行构造器再生成对象
public Student(){
}
public Student(String name,int age) {
super();
this.age=age;
this.name=name;
}
//可以通过快捷键Alt+Insert:重写常用的方法
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int n1=this.name.hashCode();
int n2=this.age;
return n1+n2;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
// 1.判断这两个对象是不是同一个引用
if(this==obj){
return true;
}
// 2.判断obj是否为null
if(obj==null){
return false;
}
// 3.判断两个对象是否为同一类型
if(obj instanceof Student)//左边为对象,右边为类;
//obj所指的实际类型是Student的子类型,则true
{
// 4.强制转换
Student student=(Student) obj;
// 5.
if(this.name==student.name&&this.age==student.age)
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "name:"+name+" "+"age:"+age;
}
}
三.List接口与实现类
1.List接口的概念
-
为collection接口的子接口
-
特点:有序、有下标、元素可以重复
注意:有序的意思是添加的顺序与遍历或者获取的顺序是一致的
-
List因为有序,可以利用下标来访问,而Collection不行,它没有下标
-
List方法除了包含Collection的方法外,还有自己的方法
2.List接口的使用
//List接口的使用
public class C {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合,接口不能实例化,但是能创建对象;需要利用实现类
List list=new ArrayList();
//1.添加元素(可以添加下标)
list.add(520);//添加数据
list.add("aaa");//添加字符串
list.add(0,"111");
list.add("bbb");
list.add(0,"000");
System.out.println("元素个数:"+list.size());//集合长度(个数)
System.out.println(list.toString());
System.out.println("====================================");
//2.删除元素
list.remove(3);//利用角标删除
list.remove("111");
System.out.println("删除之后,元素个数:"+list.size());//集合长度(个数)
System.out.println(list.toString());
//list.clear();全部清除
System.out.println("====================================");
//3.遍历元素
//(1)使用for来遍历
System.out.println("使用for来遍历");
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
//(2)使用增强for来遍历
System.out.println("使用增强for来遍历");
for (Object object:list){
System.out.println(object.toString());
}
//(3)使用迭代器Iterator遍历,迭代器是个接口,方法如下
//hasNext();判断有没有下一个元素
//next();获取下一个元素
//remove();删除当前元素
System.out.println("使用迭代器Iterator来遍历");
Iterator it=list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Object o=it.next();
System.out.println(o.toString());
//在迭代过程中不能使用collection的删除方法:collection.remove();
//迭代里面有自己的删除方法
//it.remove();
}
//(4)使用列表迭代器ListIterator遍历,列表迭代器是个接口
//列表迭代器与迭代器的区别:
// 多了许多方法
// 可以向前或者向后遍历
// 可以在遍历的时候添加、删除、修改元素
System.out.println("使用列表迭代器ListIterator来遍历:从前往后遍历");
ListIterator lit=list.listIterator();
while(lit.hasNext()){
System.out.println(lit.nextIndex()+":"+lit.next());
}
System.out.println("使用列表迭代器ListIterator来遍历:从后往前遍历");
//此时指针,经过上面从前往后遍历,已到最后一个,故不用修改指针
while(lit.hasPrevious()){
System.out.println(lit.previousIndex()+":"+lit.previous());
}
System.out.println("====================================");
//4.判断元素是否存在
System.out.println(list.contains("000"));
System.out.println(list.isEmpty());
//5.获取位置
System.out.println(list.indexOf("000"));
}
}
/*结果:
元素个数:5
[000, 111, 520, aaa, bbb]
====================================
删除之后,元素个数:3
[000, 520, bbb]
====================================
使用for来遍历
000
520
bbb
使用增强for来遍历
000
520
bbb
使用迭代器Iterator来遍历
000
520
bbb
使用列表迭代器ListIterator来遍历:从前往后遍历
0:000
1:520
2:bbb
使用列表迭代器ListIterator来遍历:从后往前遍历
2:bbb
1:520
0:000
====================================
true
false
0
*/
3.List接口的补充
- 注意1:集合是没办法存储基本类型的,当你添加一个基本类型进集合时,如底下:list.add(520),其实系统已经帮你自动装箱,变成了包装类
- 注意2:当你要删除集合里面520这个数据时,利用
list.remove(520)是不行的,因为remove(index),删除的是下标的数据。需要将他转为list.remove((Object)520);或者list.remove((Integer)520);或者list.remove(new Integer(520));
//List接口的补充
public class D {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合,接口不能实例化,但是能创建对象;需要利用实现类
List list=new ArrayList();
//1.添加数据(可以添加下标)
list.add(520);//添加数据
list.add(101);//添加数据
list.add(102);//添加数据
list.add(103);//添加数据
list.add(104);//添加数据
list.add(105);//添加数据
list.add(106);//添加数据
list.add(1,100);//添加数据
System.out.println("元素个数:"+list.size());//集合长度(个数)
System.out.println(list.toString());
//2.删除数据
list.remove(3);
list.remove((Object)520);
list.remove((Integer)100);
//list.remove(new Integer(100));
System.out.println("删除之后元素个数:"+list.size());//集合长度(个数)
System.out.println(list.toString());
//3.subList(a,b)方法,返回子集合,截取的位置为集合的[a,b)位置
System.out.println("子集合元素个数:"+list.subList(1,4).size());//集合长度(个数)
System.out.println(list.subList(1,4));
}
}
/*结果:
元素个数:8
[520, 100, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106]
删除之后元素个数:5
[101, 103, 104, 105, 106]
子集合元素个数:3
[103, 104, 105]
*/
4.List接口的实现类
- ArrayList(重点):数组结构实现,查询遍历快、增删慢,运行效率快,线程不安全
- Vector:数组结构实现,查询遍历快、增删慢 ,运行效率慢,线程安全
- LinkedList:链表结构实现,增删快,查询遍历慢
- ArrayList的用法
//AllayList是List接口的实现类
public class E {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
ArrayList arrayList=new ArrayList();
//1.添加元素
//在Student类中进行有参构造
Student s1=new Student("aaa",5);
Student s2=new Student("bbb",10);
Student s3=new Student("ccc",15);
Student s4=new Student("ddd",20);
arrayList.add(s1);
arrayList.add(s2);
arrayList.add(s3);
arrayList.add(s4);
System.out.println("元素个数:"+arrayList.size());//集合长度(个数)
System.out.println(arrayList.toString());//此处的toString方法需要重写
System.out.println("===================================");
//2.删除元素
//删除元素需要用到equals()方法先进行比较
//不重写equals()方法,没法删除下面(元素相同,对象不同)的集合元素
arrayList.remove(new Student("aaa",5));
System.out.println("元素个数:"+arrayList.size());//集合长度(个数)
System.out.println(arrayList.toString());
System.out.println("====================================");
//3.遍历元素
//(1)使用for循环遍历
//(2)使用增强for循环遍历
//(3)使用迭代器遍历
System.out.println("使用迭代器Iterator来遍历");
Iterator it=arrayList.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Object o=it.next();
System.out.println(o.toString());
}
//(4)使用列表迭代器遍历
System.out.println("使用列表迭代器ListIterator来遍历:从前往后遍历");
ListIterator lit=arrayList.listIterator();
while(lit.hasNext()){
System.out.println(lit.nextIndex()+":"+lit.next());
}
System.out.println("使用列表迭代器ListIterator来遍历:从后往前遍历");
//此时指针,经过上面从前往后遍历,已到最后一个,故不用修改指针
while(lit.hasPrevious()){
System.out.println(lit.previousIndex()+":"+lit.previous());
}
System.out.println("====================================");
//4.判断元素是否存在
//也需要用到equals()方法,此处方法已被重写
System.out.println(arrayList.contains(s2));
System.out.println(arrayList.contains(new Student("ccc",15)));
System.out.println(arrayList.isEmpty());
System.out.println("====================================");
//5.获取位置
//也需要用到equals()方法,此处方法已被重写
System.out.println(arrayList.indexOf(s2));
System.out.println(arrayList.indexOf(new Student("ccc",15)));
}
}
/*结果:
元素个数:4
[name:aaa age:5, name:bbb age:10, name:ccc age:15, name:ddd age:20]
===================================
元素个数:3
[name:bbb age:10, name:ccc age:15, name:ddd age:20]
====================================
使用迭代器Iterator来遍历
name:bbb age:10
name:ccc age:15
name:ddd age:20
使用列表迭代器ListIterator来遍历:从前往后遍历
0:name:bbb age:10
1:name:ccc age:15
2:name:ddd age:20
使用列表迭代器ListIterator来遍历:从后往前遍历
2:name:ddd age:20
1:name:ccc age:15
0:name:bbb age:10
====================================
true
true
false
====================================
0
1
*/
public class Student{
//封装属性
private int age;
private String name;
//构造器,new之后,程序先运行构造器再生成对象
public Student(){
}
public Student(String name,int age) {
super();
this.age=age;
this.name=name;
}
//可以通过快捷键Alt+Insert:重写常用的方法
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int n1=this.name.hashCode();
int n2=this.age;
return n1+n2;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
// 1.判断这两个对象是不是同一个引用
if(this==obj){
return true;
}
// 2.判断obj是否为null
if(obj==null){
return false;
}
// 3.判断两个对象是否为同一类型
if(obj instanceof Student)//左边为对象,右边为类;
//obj所指的实际类型是Student的子类型,则true
{
// 4.强制转换
Student student=(Student) obj;
// 5.
if(this.name==student.name&&this.age==student.age)
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "name:"+name+" "+"age:"+age;
}
}
-
ArrayList类的源码分析
-
默认容量DEFAULT_CAPACITY=10
-
存放元素的数组elementDate
-
实际元素的个数size<=容量
-
ArrayList的无参构造
注意:new一个ArrayList对象,在没有向集合中添加元素之前,容量为0,实际元素个数为0
-
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
-
- 在使用add()方法添加一个元素后,容量变为10
-
- 每次扩容的大小为原来的1.5倍
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
-
Vector类(向量类)
-
可以实现可增长的对象数组。与数组一样,它包含可以使用整数索引进行访问的组件。有下标
-
存储结构:数组
-
Vector类用的很少,使用方法和上面的ArrayList类类似,它的方法也差不多
-
在遍历上面除了前面说的四种方式
(1)使用for循环遍历
(2)使用增强for循环遍历
(3)使用迭代器遍历
(4)使用列表迭代器遍历还有 (5)使用枚举器elements(),它的返回值类型是**Enumeration **,使用方法和迭代器也类似
-
-
LinkedList类
- 存储结构:双项链表-----有从头指到尾,也有从尾指到头
- 使用方法
//LinkedList是List接口的实现类
//LinkedList的使用
public class F {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
//1.添加元素
//在Student类中进行有参构造
Student s1=new Student("aaa",5);
Student s2=new Student("bbb",10);
Student s3=new Student("ccc",15);
Student s4=new Student("ddd",20);
Student s5=new Student("eee",25);
linkedList.add(s1);
linkedList.add(s2);
linkedList.add(s3);
linkedList.add(s4);
linkedList.add(s5);
System.out.println("元素个数:"+linkedList.size());//集合长度(个数)
System.out.println(linkedList.toString());//此处的toString方法需要重写
System.out.println("===================================");
//2.删除元素
//删除元素需要用到equals()方法先进行比较
//不重写equals()方法,没法删除下面(元素相同,对象名不同)的集合元素
linkedList.remove(new Student("aaa",5));
linkedList.remove(1);
System.out.println("元素个数:"+linkedList.size());//集合长度(个数)
System.out.println(linkedList.toString());
System.out.println("====================================");
//3.遍历元素
//(1)使用for来遍历
System.out.println("使用for来遍历");
for(int i=0;i<linkedList.size();i++){
System.out.println(linkedList.get(i));
}
//(2)使用增强for来遍历
System.out.println("使用增强for来遍历");
for (Object object:linkedList){
System.out.println(object.toString());
}
//(3)使用迭代器遍历
System.out.println("使用迭代器Iterator来遍历");
Iterator it=linkedList.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Object o=it.next();
System.out.println(o.toString());
}
//(4)使用列表迭代器遍历
System.out.println("使用列表迭代器ListIterator来遍历:从前往后遍历");
ListIterator lit=linkedList.listIterator();
while(lit.hasNext()){
System.out.println(lit.nextIndex()+":"+lit.next());
}
System.out.println("使用列表迭代器ListIterator来遍历:从后往前遍历");
//此时指针,经过上面从前往后遍历,已到最后一个,故不用修改指针
while(lit.hasPrevious()){
System.out.println(lit.previousIndex()+":"+lit.previous());
}
System.out.println("====================================");
//4.判断元素是否存在
//也需要用到equals()方法,此处方法已被重写
System.out.println(linkedList.contains(s2));
System.out.println(linkedList.contains(new Student("ccc",15)));
System.out.println(linkedList.isEmpty());
System.out.println("====================================");
//5.获取位置
//也需要用到equals()方法,此处方法已被重写
System.out.println(linkedList.indexOf(s2));
System.out.println(linkedList.indexOf("name:ddd age:20"));//这样子找不到需要找的字符串位置
System.out.println(linkedList.indexOf(new Student("eee",25)));
}
}
/*结果:
元素个数:5
[name:aaa age:5, name:bbb age:10, name:ccc age:15, name:ddd age:20, name:eee age:25]
===================================
元素个数:3
[name:bbb age:10, name:ddd age:20, name:eee age:25]
====================================
使用for来遍历
name:bbb age:10
name:ddd age:20
name:eee age:25
使用增强for来遍历
name:bbb age:10
name:ddd age:20
name:eee age:25
使用迭代器Iterator来遍历
name:bbb age:10
name:ddd age:20
name:eee age:25
使用列表迭代器ListIterator来遍历:从前往后遍历
0:name:bbb age:10
1:name:ddd age:20
2:name:eee age:25
使用列表迭代器ListIterator来遍历:从后往前遍历
2:name:eee age:25
1:name:ddd age:20
0:name:bbb age:10
====================================
true
false
false
====================================
0
-1
2
*/
所用的Student类同上
- LinkedList类的源码分析
- int size:集合大小,默认为0
- Node first:链表的头节点,默认为null
- Node last:链表的尾节点,默认为null
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
private static class Node<E>{
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev,E element,Node<E> next){
this.item=element;
this.next=next;
this.prev=prev;
}
}
-
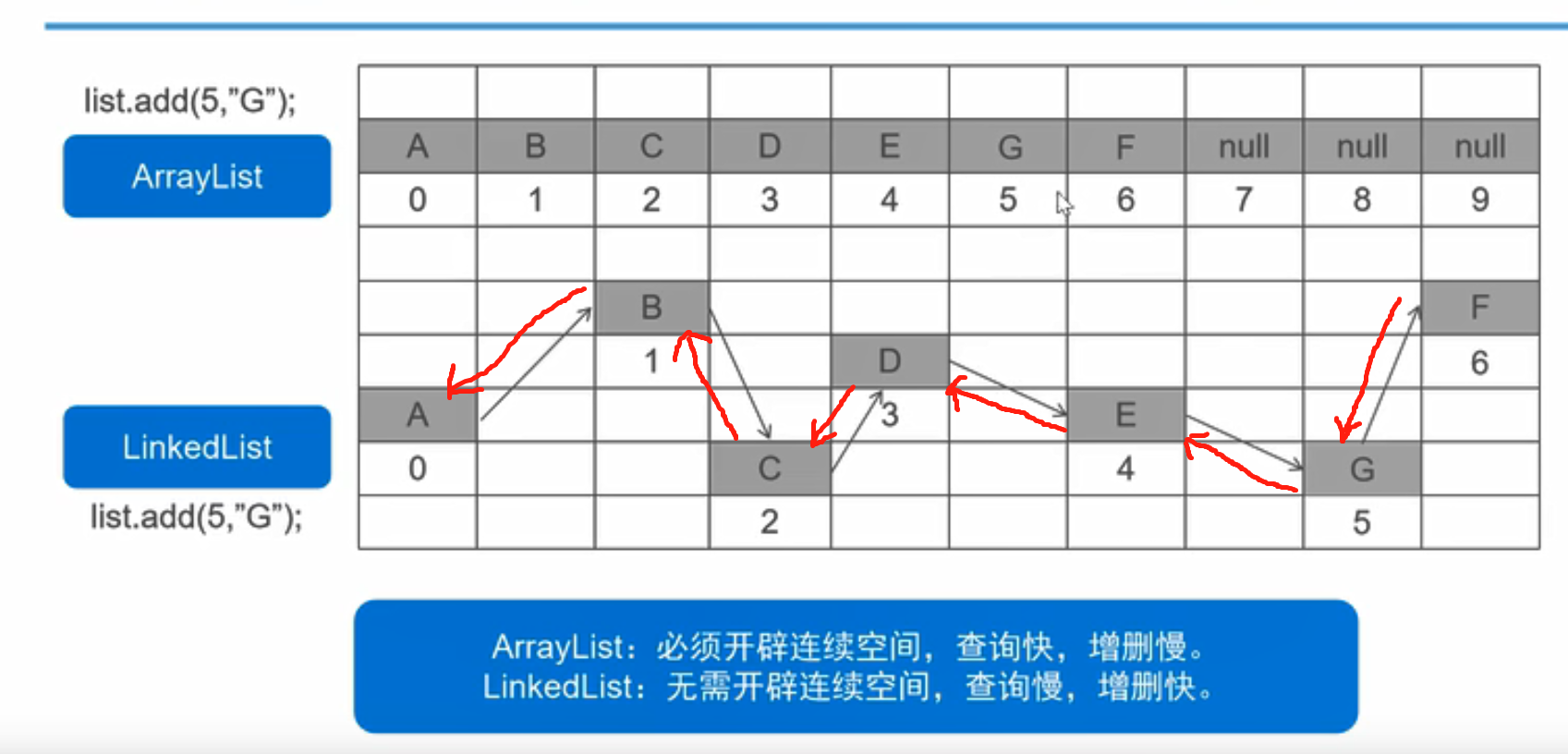
ArrayList和LinkedList区别
![ArrayList和LinkedList区别]()
链表:增删快是因为,可以直接改变指针指向,如可以让B.next---->D,D.previous----->B从而达到删除C的效果
查询慢是因为,链表开辟的空间不是连续的,不能像数组一样定位,只能通过指针指到需要的数据



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号