找出字符串中的最长回文子串 - 马拉车算法
问题:
找出字符串中的最长回文子串
思路:
举例分析下,例如 ”abadaba“ 这个字符串的计算
1、从左往右遍历,整个字符串,把每个字符和字符间的空隙当作回文的中心,然后向两边扩展来找到最长回文串,这种情况下默认得对每一个字符进行计算,计算量比较大,而且有部分计算其实能通过之前的计算得到答案,后面第2点开始讨论下如何减少计算次数
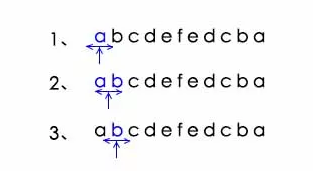
2、利用回文的特性,结合已经计算的部分,尽量减少后面的计算次数。比如下图,当我们计算到第5位的时候,通过前面的计算可以知道2-4位是一个回文子串,由于5也是回文子串,且跨幅度是2-8,因为4位不是回文子串,所以与4对应的6位也不是回文子串,同理可以推断出6-8是一个回文子串

3、由于之前的计算已经知道了第5位为中心的abadaba是回文,而第4位为中心的a的回文长度是1,所以第6位为中心的回文长度只能是1,不用再去计算了。

4、以第7位为中心的回文串的计算,由之前分析已经知道最小长度是3了,但是还是需要进行扩展,因为第9位是什么根据之前的信息无法得知,需要扩展进行探索。

5、考虑到回文子串可能是复数,这里得在字符之间加多个标记进行特殊处理

总结下步骤:
1、先对字符串进行预处理,两个字符之间加上特殊符号#
2、然后遍历整个字符串,用一个数组来记录以该字符为中心的回文长度,为了方便计算右边界,在数组中记录长度的一半(覆盖半径)
3、每一次遍历的时候,如果该字符在已知回文串最右边界的覆盖下,那么就计算其相对最右边界回文串中心对称的位置,得出已知回文串的长度
4、判断该长度和右边界,如果达到了右边界,那么需要进行中心扩展探索。当然,如果第3步该字符没有在最右边界的“半径”下,则直接进行中心扩展探索。进行中心扩展探索的时候,同时又更新右边界
5、最后得到最长回文之后,去掉其中的特殊符号即可
实现:
C++:
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cstdio> #include <sstream> #include <vector> using namespace std; string changeString(string source){ int length = 2*source.length()+1; char root[length]; root[0] = '#'; for(int i=0,j=1;i<source.length();i++){ root[j++] = source[i]; root[j++] = '#'; } string new_source = root; return new_source.substr(0,length); } void printArray(int a[],int size){ for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){ cout<<a[i]<<" "; } cout<<endl; } void printMaxString(int center,int half_size,string source){ cout<<"Max string is: "; for(int k=center-half_size;k<center+half_size;k++){ if(source[k]!='#'){ cout<<source[k]; } } cout<<endl; } void calculate(string source){ int left = 0,right = source.length();//记录字符串的最左最右边界 int center = 0,half_size = 0;//记录最长回文子串的中心以及半径 int cur_center = 0;//当前回文串在左侧半径内的中心位置 int max_right = 0;//计算当前访问位置回文子串右半径最大覆盖范围 int cover[right];//记录字符串每个位置回文子串的覆盖半径 bool flag = true; int times = 0; for(int i=0;i<source.length();i++){ flag = true; //判断要不要计算 if(i<max_right){ //因为在覆盖的右半径内,由于回文的特性,右半径任何位置的回文子串覆盖半径在前面已经算出来了,这里仅需要找出对应的左半径位置 cur_center = 2*center-i; //该位置的回文子串的半径 cover[i] = cover[cur_center]; //当前位置加上回文覆盖的半径未超过当前回文子串右半径最大覆盖范围,无需重新计算 if(cover[cur_center]+i<max_right){ flag = false; } } if(flag){ times++; int step = 1; while(i-step>=left && i+step<right){ if(source[i-step]==source[i+step]){ step++; }else{ break; } } cover[i] = step-1; } if(cover[i]>=half_size){ half_size = cover[i]; center = i; } if(i+cover[i]>=max_right){ max_right = cover[i]+i; } } printArray(cover,source.length()); printMaxString(center,half_size,source); cout<<"Calculate times is: "<<times<<endl; } int main(){ string source_array[] = { "abcdcef", "adaelele", "cabadabae", "aaaabcdefgfedcbaa", "aaba", "aaaaaaaaa" }; for(int i =0;i<6;i++){ // string source = "adaelele"; string source = source_array[i]; string new_source = changeString(source); cout<<"Source string is: "<<source<<endl; cout<<"New_source string is: "<<new_source<<endl; calculate(new_source); cout<<endl; } return 0; }
输出:
Source string is: abcdcef New_source string is: #a#b#c#d#c#e#f# 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 3 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 Max string is: cdc Calculate times is: 14 Source string is: adaelele New_source string is: #a#d#a#e#l#e#l#e# 0 1 0 3 0 1 0 1 0 3 0 5 0 3 0 1 0 Max string is: elele Calculate times is: 13 Source string is: cabadabae New_source string is: #c#a#b#a#d#a#b#a#e# 0 1 0 1 0 3 0 1 0 7 0 1 0 3 0 1 0 1 0 Max string is: abadaba Calculate times is: 14 Source string is: aaaabcdefgfedcbaa New_source string is: #a#a#a#a#b#c#d#e#f#g#f#e#d#c#b#a#a# 0 1 2 3 4 3 2 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 15 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 2 1 0 Max string is: aabcdefgfedcbaa Calculate times is: 23 Source string is: aaba New_source string is: #a#a#b#a# 0 1 2 1 0 3 0 1 0 Max string is: aba Calculate times is: 8 Source string is: aaaaaaaaa New_source string is: #a#a#a#a#a#a#a#a#a# 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Max string is: aaaaaaaaa Calculate times is: 19
分析:
这算法也就是”马拉车“算法,精妙程度可以与KMP算法相媲美,利用回文的特征以及之前的计算结果,最大程度上减少后面的计算次数,由于只进行一次遍历,时间复杂度上是O(n)





