GUI编程基础
学一个东西:
- 它是什么
- 怎么运行
- 如何应用
组件
- 窗口
- 弹窗
- 面板
- 文本框
- 列表框
- 按钮
- 图片
- 监听事件
- 鼠标
- 键盘事件
- 破解工具
1 简介
GUI核心技术:Swing AWT
但并不流行,甚至快要被淘汰:
- 界面不美观
- 需要JRE环境
为什么我们还要学习?
- 自娱自乐
- 了解MVC框架,了解监听
2 AWT
2.1 AWT介绍
AWT Abstract Windows Tools 抽象窗口工具
GUI Graphical User Interface 图形用户接口
- 包含了许多类和接口
- 元素:窗口,文本框,按钮
- java.awt包
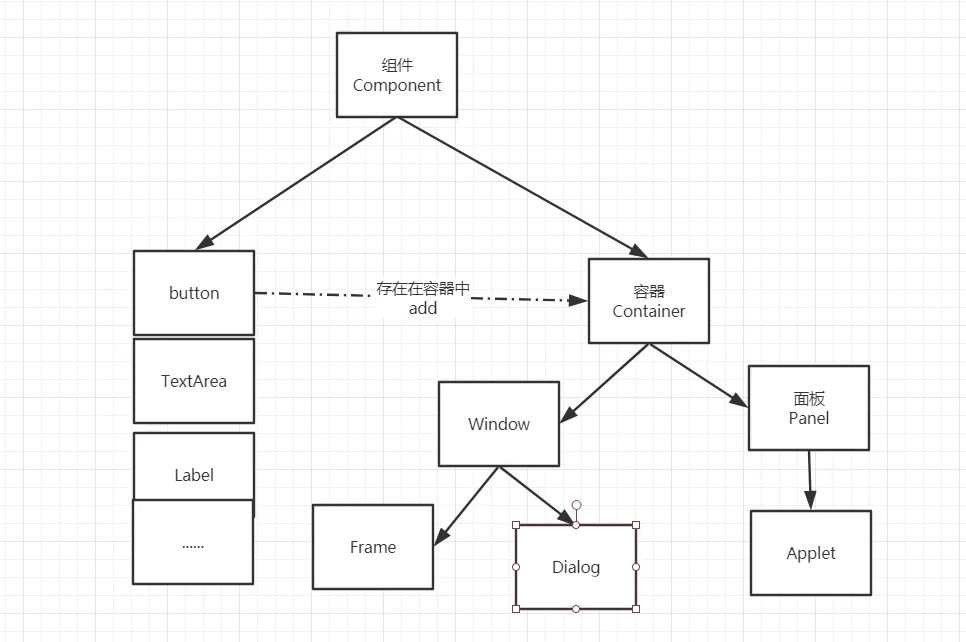
2.2 组件和容器
Frame
//GUI的第一个界面
public class TestFrame {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用时要学会点进去看源码
Frame frame = new Frame("我的第一个Java图像界面");
//需要设置可见性
frame.setVisible(true);
//设置窗口大小
frame.setSize(400,400);
//设置背景颜色
//new Color(1,1,1);//自定义颜色
frame.setBackground(Color.BLACK);
//弹出的初始位置,(0,0)在左上角
frame.setLocation(200,200);
//设置大小固定
frame.setResizable(false);
}
}
发现问题:程序无法关掉。方法:停止程序运行。
回顾封装:产生多个窗口
public class TestFrame2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyFrame myFrame1 = new MyFrame(100, 100, 200, 200, Color.BLUE);
MyFrame myFrame2 = new MyFrame(300, 100, 200, 200, Color.CYAN);
MyFrame myFrame3 = new MyFrame(100, 300, 200, 200, Color.GREEN);
MyFrame myFrame4 = new MyFrame(300, 300, 200, 200, Color.ORANGE);
}
}
class MyFrame extends Frame{
//可能存在多个窗口,我们需要一个计数器
static int count = 0;
public MyFrame(int x,int y,int w,int h,Color color){
super("MyFrame"+(++count));
setBounds(x, y, w, h);
setVisible(true);
setBackground(color);
}
}
Panel
面板不能单独存在,在容器里面,可以看成是一个空间
下面的代码解决了关闭事件
//Panel可以看成是一个空间,但不能单独存在
public class TestPanel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame();
//布局的概念
Panel panel = new Panel();
//设置布局
frame.setLayout(null);
//坐标
frame.setBounds(300,300,500,500);
frame.setBackground(new Color(96, 255, 29, 255));
//Panel设置坐标,相对于frame
panel.setBounds(50,50,400,400);
panel.setBackground(new Color(0, 82, 255));
//放进frame
frame.add(panel);
frame.setVisible(true);
//监听事件,监听窗口关闭事件 System.exit(0);
//适配器模式 不去new WindowListener 实现太全部的接口
//而是去继承它的一个子类,子类有默认的实现,我们只写我们需要的那个功能
//这是AWT的解决方式,后面还有swing的解决方式
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
//窗口点击关闭的时候需要做的事情
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
//结束程序
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
2.3 布局管理器
三种布局
-
流式布局
public class TestFlowLayout { public static void main(String[] args) { Frame frame = new Frame(); //组件 按钮 Button button1 = new Button("button1"); Button button2 = new Button("button2"); Button button3 = new Button("button3"); //设置流式布局 居中 靠左 靠右 等等 frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout()); //frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT)); //frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.RIGHT)); frame.setSize(200,200); //添加按钮 frame.add(button1); frame.add(button2); frame.add(button3); frame.setVisible(true); } } -
东西南北中
public class TestBorderLayout { public static void main(String[] args) { Frame frame = new Frame("BorderLayout"); Button button1 = new Button("East"); Button button2 = new Button("West"); Button button3 = new Button("South"); Button button4 = new Button("North"); Button button5 = new Button("Center"); frame.add(button1,BorderLayout.EAST); frame.add(button2,BorderLayout.WEST); frame.add(button3,BorderLayout.SOUTH); frame.add(button4,BorderLayout.NORTH); frame.add(button5,BorderLayout.CENTER); frame.setSize(200,200); frame.setVisible(true); } } -
表格布局 Gird
public class TestGirdLayout { public static void main(String[] args) { Frame frame = new Frame(); Button button1 = new Button("1"); Button button2 = new Button("2"); Button button3 = new Button("3"); Button button4 = new Button("4"); Button button5 = new Button("5"); Button button6 = new Button("6"); frame.setLayout(new GridLayout(3,2)); frame.add(button1); frame.add(button2); frame.add(button3); frame.add(button4); frame.add(button5); frame.add(button6); frame.pack(); // Java方法,自动选择最优布局 也无需设计大小 //frame.setSize(200,200); frame.setVisible(true); } }
布局练习
通过不同布局的嵌套我们可以设计出我们想要的布局,下面是一个练习

布局解答
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame();
frame.setSize(400,300);
frame.setLocation(300,400);
frame.setBackground(Color.BLACK);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,1));
//4个面板
Panel panel1 = new Panel(new BorderLayout());
Panel panel2 = new Panel(new GridLayout(2,1));
Panel panel3 = new Panel(new BorderLayout());
Panel panel4 = new Panel(new GridLayout(2,1));
//上面
panel1.add(new Button("East-1"),BorderLayout.EAST);
panel1.add(new Button("East-2"),BorderLayout.WEST);
panel2.add(new Button("p2-btn-1"));
panel2.add(new Button("p2-btn-2"));
panel1.add(panel2,BorderLayout.CENTER);
//下面
panel3.add(new Button("East-1"),BorderLayout.EAST);
panel3.add(new Button("East-2"),BorderLayout.WEST);
//中间的四个
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
panel4.add(new Button("btn"+i));
}
panel3.add(panel4,BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.add(panel1);
frame.add(panel3);
}
}
总结
- Frame是一个顶级窗口
- Panel无法单独显示,必须添加到某个容器中。
- 三种布局管理器
- 设置 大小,颜色,位置,可见性,监听
2.4 事件监听
事件监听
按下按钮打印一行字符串
public class TestAction {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//按下按钮,触发一些事件
Frame frame = new Frame();
Button button = new Button();
//addActionListener()方法需要一个ActionListener,我们构建了一个MyActionListener类
MyActionListener myActionListener = new MyActionListener();
button.addActionListener(myActionListener);
frame.add(button,BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.pack();
windowClose(frame);//窗口可以关闭
frame.setVisible(true);
}
//关闭窗体的事件
private static void windowClose(Frame frame){
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
//事件监听
class MyActionListener implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println("aaa");
}
}
两个按钮,共享一个事件
public class TestAction02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//两个按钮实现同一个监听
//开始 结束
Frame frame = new Frame();
Button button1 = new Button("start");
Button button2 = new Button("stop");
//可以显示地定义触发返回的命令
//设置行为命令前button2参数为stop,设置后变更为button-2-stop
button2.setActionCommand("button-2-stop");
MyMonitor myMonitor = new MyMonitor();
button1.addActionListener(myMonitor);
button2.addActionListener(myMonitor);
frame.add(button1,BorderLayout.NORTH);
frame.add(button2,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
class MyMonitor implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
//System.out.println("按钮被点击了:msg=> "+e.getActionCommand());
if(e.getActionCommand().equals("start")){
System.out.println("开始");
}else{
System.out.println("停止");
}
}
}
2.5 输入框
TextField
public class TextField01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyFrame myFrame = new MyFrame();
}
}
class MyFrame extends Frame{
public MyFrame(){
//new TextArea();//多行文本
TextField textField = new TextField();//单行文本
add(textField);
//监听这个文本框输入的文字
MyActionListener myActionListener = new MyActionListener();
//按下Enter 触发输入框的事件
textField.addActionListener(myActionListener);
//设置替换编码
textField.setEchoChar('*');
pack();
setVisible(true);
}
class MyActionListener implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
//获得一些资源,返回的一个对象Object 监听谁就转为谁
TextField field = (TextField) e.getSource();
System.out.println(field.getText());// 获得输入框中的文本
field.setText("");//Enter后清空输入框
}
}
}
2.6 计算器及回顾
实现一个简易的计算器,顺便回顾组合,内部类
组合是继承的另一种方式,OOP原则:组合大于继承
public A extends B{
//继承
}
public A{
public B b;
//组合,耦合性降低
}
加法计算器
//简易计算器
public class Calculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Calc();
}
}
//计算器类
class Calc extends Frame{
public Calc(){
//三个文本框
TextField textField1 = new TextField(10);//最多写多少字符
TextField textField2 = new TextField(10);
TextField textField3 = new TextField(20);//比前两个长
//一个按钮
Button button = new Button("=");
button.addActionListener(new MyCalculatorListener(textField1,textField2,textField3));
//一个标签 展示+
Label label = new Label("+");
//布局 流式
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
add(textField1);
add(label);
add(textField2);
add(button);
add(textField3);
pack();
setVisible(true);
}
}
//监听器类
class MyCalculatorListener implements ActionListener{
//获取三个变量
private TextField field1,field2,field3;
public MyCalculatorListener(TextField field1,TextField field2,TextField field3){
this.field1 = field1;
this.field2 = field2;
this.field3 = field3;
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
//获得加数和被加数
int i1 = Integer.parseInt(field1.getText());
int i2 = Integer.parseInt(field2.getText());
//相加后,放到第三个框
field3.setText(""+(i1+i2));//暴力拼接成字符串
//清除前两个框
field1.setText("");
field2.setText("");
}
}
优化
//简易计算器
public class Calculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Calc().loadFrame();
}
}
//计算器类
class Calc extends Frame{
//属性
TextField textField1,textField2,textField3;
//方法
public void loadFrame(){
//三个文本框
textField1 = new TextField(10);//最多写多少字符
textField2 = new TextField(10);
textField3 = new TextField(20);//比前两个长
//一个按钮
Button button = new Button("=");
button.addActionListener(new MyCalculatorListener(this));
//一个标签 展示+
Label label = new Label("+");
//布局 流式
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
add(textField1);
add(label);
add(textField2);
add(button);
add(textField3);
pack();
setVisible(true);
}
}
//监听器类
class MyCalculatorListener implements ActionListener{
//在一个类中组合另一个类
Calc calc = null;
//没必要依次获取三个变量,直接把计算器类拿过来
public MyCalculatorListener(Calc calc){
this.calc = calc;
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
//获得加数和被加数
int i1 = Integer.parseInt(calc.textField1.getText());
int i2 = Integer.parseInt(calc.textField2.getText());
//相加后,放到第三个框
calc.textField3.setText(""+(i1+i2));
//清除前两个框
calc.textField1.setText("");
calc.textField2.setText("");
}
}
完全改造为OOP
多态,继承什么三大特性都不建议使用,在企业开发中:继承增强了耦合性,多态让代码更麻烦,理解可能有错误
更应该使用内部类
内部类:
- 更好的包装
- 内部类最大的好处就是可以畅通无阻地访问外部类的属性和方法
//简易计算器
public class Calculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Calc().loadFrame();
}
}
//计算器类
class Calc extends Frame{
//属性
TextField textField1,textField2,textField3;
//方法
public void loadFrame(){
//三个文本框
textField1 = new TextField(10);//最多写多少字符
textField2 = new TextField(10);
textField3 = new TextField(20);//比前两个长
//一个按钮
Button button = new Button("=");
button.addActionListener(new MyCalculatorListener());
//一个标签 展示+
Label label = new Label("+");
//布局 流式
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
add(textField1);
add(label);
add(textField2);
add(button);
add(textField3);
pack();
setVisible(true);
}
//内部类最大的好处就是可以畅通无阻地访问外部类的属性和方法
private class MyCalculatorListener implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
//获得加数和被加数
int i1 = Integer.parseInt(textField1.getText());
int i2 = Integer.parseInt(textField2.getText());
//相加后,放到第三个框
textField3.setText(""+(i1+i2));
//清除前两个框
textField1.setText("");
textField2.setText("");
}
}
}
2.7 画笔
public class TestPaint {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//我们只调用了loadFrame,但是子类重写父类的方法也被执行了
new MyPaint().loadFrame();
}
}
class MyPaint extends Frame {
public void loadFrame(){
setBounds(200,200,600,500);
setVisible(true);
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics g){
//画笔可以有颜色,可以画画
g.setColor(Color.red);
//空心圆
g.drawOval(100,100,100,100);
//实心圆
g.fillOval(100,100,100,100);
g.setColor(Color.BLUE);
g.fillRect(150,200,200,200);
//养成习惯画笔用完,将它还原到最初的颜色 黑色
g.setColor(Color.BLACK);
}
}
每隔一段时间就重写画,可以构成动画
2.8 鼠标监听
目标:实现鼠标画画(点)
public class TestMouseListener {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyFrame("画图");
}
}
class MyFrame extends Frame{
//画画需要画笔,需要监听鼠标当前的位置,需要集合来存储这个点
private ArrayList points;
public MyFrame(String title){
super(title);
setBounds(200,200,400,300);
setVisible(true);
//存鼠标点击的点
points = new ArrayList<>();
//鼠标监听器,针对这个窗口
this.addMouseListener(new MyMouseListener());
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics g) {
//画画,监听鼠标事件
Iterator iterator = points.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
Point point = (Point) iterator.next();//返回当前并指向下一个
g.setColor(Color.BLUE);
//点表示出来是实心圆形
g.fillOval(point.x,point.y,10,10);
}
}
//添加一个点到界面上
public void addPoint(Point point){
points.add(point);
}
//适配器模式,不去实现MouseListener的所有接口
//而是去继承一个实现好的类,只重写我们需要的
private class MyMouseListener extends MouseAdapter{
//鼠标有三种状态 按下 弹起 按住不放
@Override
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) {
MyFrame myFrame = (MyFrame) e.getSource();
//这里我们点击的时候就会在界面上产生一个点
//这个点就是鼠标的点
myFrame.addPoint(new Point(e.getX(),e.getY()));
//每次点击鼠标都需要重新画一次
myFrame.repaint();
}
}
}
2.9 窗口监听
public class TestWindow {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new WindowFrame();
}
}
class WindowFrame extends Frame{
public WindowFrame(){
setBackground(Color.BLUE);
setBounds(100,100,200,200);
setVisible(true);
this.addWindowListener(
//匿名内部类
new WindowAdapter() {
//其中的关闭窗口激活窗口较为常用
@Override
public void windowOpened(WindowEvent e) {
System.out.println("windowOpened");
}
@Override
public void windowClosed(WindowEvent e) {
System.out.println("windowClosed");
}
@Override
public void windowActivated(WindowEvent e) {
System.out.println("windowActivated");
}
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.out.println("关闭");
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
2.10 键盘监听
public class TestKeyListener {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new KeyFrame();
}
}
class KeyFrame extends Frame{
public KeyFrame(){
setBounds(1,1,200,200);
setVisible(true);
this.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter() {
//键盘按下
@Override
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {
//获得按下的键是哪一个,当前的码
int keyCode = e.getKeyCode();
System.out.println(keyCode);
//可以根据不同的操作,产生不同的结果
if(keyCode == KeyEvent.VK_ENTER){
System.out.println("Enter");
}
}
});
}
}
3 Swing
AWT是底层的,Swing是封装好的
3.1 窗口,面板
public class TestJFrame {
public void init(){
//JFrame是一个顶级窗口
JFrame jFrame = new JFrame("这是一个JFrame窗口");
jFrame.setVisible(true);
jFrame.setBounds(100,100,200,200);
//直接设置没有颜色,需要一个容器
//jFrame.setBackground(Color.CYAN);
//设置文字
JLabel label = new JLabel("欢迎来到英雄联盟",SwingConstants.CENTER);
//让文本标签居中,设置水平对齐,上面已经做过了
//label.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER);
jFrame.add(label);
//容器实例化
jFrame.getContentPane().setBackground(Color.CYAN);
//关闭事件
jFrame.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//建立一个窗口
new TestJFrame().init();
}
}
3.2 弹窗
JDialog用来被弹出,默认就有关闭事件
//主窗口
public class DialogDemo extends JFrame {
public DialogDemo(){
super("title");
this.setVisible(true);
this.setSize(700,500);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
//JFrame放东西需要一个容器
Container contentPane = getContentPane();
//绝对布局,自己去决定放在什么位置
contentPane.setLayout(null);
//按钮
JButton button = new JButton("欢迎来到王者荣耀");//创建
button.setBounds(30,30,200,50);
contentPane.add(button);
//点击这个按钮的时候弹出一个弹窗
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {//匿名内部类 监听器
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
//弹窗
MyDialog myDialog = new MyDialog();
myDialog.setVisible(true);
}
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new DialogDemo();
}
}
//弹出的窗口
class MyDialog extends JDialog{
public MyDialog() {
this.setTitle("Dialog");
this.setBounds(100,100,500,500);
//无需,默认可关
//setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
Container container = this.getContentPane();
container.setLayout(null);
container.add(new JButton("敌军还有30秒到达战场"));
this.setVisible(true);
}
}
//不能显示
3.3 标签
label
new Jlabel("文字")
icon图标
public class IconDemo extends JFrame implements Icon {
private int width;
private int height;
public IconDemo() throws HeadlessException {
}
public IconDemo(int width, int height) throws HeadlessException {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
public void init(){
IconDemo iconDemo = new IconDemo(15, 15);
//图标放在标签上,也可以放在按钮上...
JLabel label = new JLabel("iconText", iconDemo, SwingConstants.CENTER);
Container container = getContentPane();
container.add(label);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new IconDemo().init();
}
@Override
public void paintIcon(Component c, Graphics g, int x, int y) {
g.fillOval(x,y,width,height);
}
@Override
public int getIconWidth() {
return this.width;
}
@Override
public int getIconHeight() {
return this.height;
}
}
Icon及ImageIcon标签
public class ImageIconDemo extends JFrame {
public ImageIconDemo() throws HeadlessException {
JLabel label = new JLabel("ImageIcon");
//获取图片的地址
//通过类来获取类路径当前目录下的资源
URL url = ImageIconDemo.class.getResource("1.jpeg");//找的是src下的
ImageIcon imageIcon = new ImageIcon(url);
label.setIcon(imageIcon);
label.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER);
Container container = getContentPane();
container.add(label);
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setBounds(100,100,200,200);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ImageIconDemo();
}
}
3.4 面板
JPanel
public class JPanelTest extends JFrame {
public JPanelTest() throws HeadlessException {
Container container = this.getContentPane();
//后面参数 间距
container.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,1,10,10));
JPanel panel1 = new JPanel(new GridLayout(1,3));
JPanel panel2 = new JPanel(new GridLayout(1,3));
JPanel panel3 = new JPanel(new GridLayout(1,3));
JPanel panel4 = new JPanel(new GridLayout(1,3));
panel1.add(new JButton("1"));
panel1.add(new JButton("1"));
panel1.add(new JButton("1"));
panel2.add(new JButton("1"));
panel2.add(new JButton("1"));
panel2.add(new JButton("1"));
panel3.add(new JButton("1"));
panel3.add(new JButton("1"));
panel3.add(new JButton("1"));
panel4.add(new JButton("1"));
panel4.add(new JButton("1"));
panel4.add(new JButton("1"));
this.setVisible(true);
this.setSize(500,500);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
container.add(panel1);
container.add(panel2);
container.add(panel3);
container.add(panel4);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JPanelTest();
}
}
JScrollPanel
文本域
public class JScrollDemo extends JFrame {
public JScrollDemo() throws HeadlessException {
Container container = this.getContentPane();
//文本域
JTextArea area = new JTextArea(20, 50);
area.setText("welcome");
//scroll面板
JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane(area);
container.add(scrollPane);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setBounds(100,100,300,350);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JScrollDemo();
}
}
3.5 按钮
图片按钮
public class JButtonDemo extends JFrame {
public JButtonDemo() throws HeadlessException {
Container container = this.getContentPane();
//将一个图片变成图标
URL url = JButtonDemo.class.getResource("1.jpeg");
Icon icon = new ImageIcon(url);
//将图片放在按钮上
JButton button = new JButton();
button.setIcon(icon);
button.setToolTipText("图片按钮");
container.add(button);
this.setSize(500,300);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JButtonDemo();
}
}
单选按钮
public class JButtonDemo2 extends JFrame {
public JButtonDemo2() throws HeadlessException {
Container container = this.getContentPane();
//单选框,三个不能同时选择
JRadioButton jRadioButton1 = new JRadioButton("01");
JRadioButton jRadioButton2 = new JRadioButton("02");
JRadioButton jRadioButton3 = new JRadioButton("03");
//分组,组里只能选一个,三个选一个
ButtonGroup buttonGroup = new ButtonGroup();
buttonGroup.add(jRadioButton1);
buttonGroup.add(jRadioButton2);
buttonGroup.add(jRadioButton3);
container.add(jRadioButton1,BorderLayout.CENTER);
container.add(jRadioButton2,BorderLayout.NORTH);
container.add(jRadioButton3,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
this.setSize(500,300);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JButtonDemo2();
}
}
复选按钮
public class JButtonDemo3 extends JFrame {
public JButtonDemo3() throws HeadlessException {
Container container = this.getContentPane();
JCheckBox jCheckBox1 = new JCheckBox("jCheckBox1");
JCheckBox jCheckBox2 = new JCheckBox("jCheckBox2");
container.add(jCheckBox1,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
container.add(jCheckBox2,BorderLayout.NORTH);
this.setSize(500,300);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JButtonDemo3();
}
}
3.6 列表
下拉框
public class ComboBoxDemo extends JFrame {
public ComboBoxDemo() throws HeadlessException {
Container contentPane = this.getContentPane();
JComboBox comboBox = new JComboBox();
comboBox.addItem(null);
comboBox.addItem("正在热映");
comboBox.addItem("下架");
comboBox.addItem("即将上映");
contentPane.add(comboBox);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setSize(500,500);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ComboBoxDemo();
}
}
列表
public class ComboBoxDemo2 extends JFrame {
public ComboBoxDemo2() throws HeadlessException {
Container contentPane = this.getContentPane();
//生成列表的内容
//String[] contents = {"1","2","3"};
Vector contents = new Vector();
//列表中需要放入内容
JList jList = new JList(contents);
contents.add("zhang");
contents.add("li");
contents.add("wu");
contentPane.add(jList);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setSize(500,500);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ComboBoxDemo2();
}
}
应用场景
- 选择地区或一些单个选项
- 列表,展示信息,一般是动态扩容
3.7 文本框
文本框
public class TextDemo extends JFrame {
public TextDemo() throws HeadlessException {
Container contentPane = this.getContentPane();
JTextField jTextField1 = new JTextField("hello",20);
JTextField jTextField2 = new JTextField("world",20);
contentPane.add(jTextField1,BorderLayout.NORTH);
contentPane.add(jTextField2,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setSize(500,500);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TextDemo();
}
}
密码框
public class TextDemo2 extends JFrame{
public TextDemo2() throws HeadlessException {
Container contentPane = this.getContentPane();
JPasswordField jPasswordField = new JPasswordField();
jPasswordField.setEchoChar('*');
contentPane.add(jPasswordField);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setSize(500,500);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TextDemo2();
}
}
文本域
public class JScrollDemo extends JFrame {
public JScrollDemo() throws HeadlessException {
Container container = this.getContentPane();
//文本域
JTextArea area = new JTextArea(20, 50);
area.setText("welcome");
//scroll面板
JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane(area);
container.add(scrollPane);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setBounds(100,100,300,350);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JScrollDemo();
}
}
4 贪吃蛇
帧,如果时间片足够小,就是动画,一秒30帧
连起来是动画,拆开是静态托图片
键盘监听
定时器 Timer
四部曲
定义数据
画上去
监听它
Swing来做界面
AWT来做监听



