光流法
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/crzy_sparrow/article/details/7407604
本文目录:
一.基于特征点的目标跟踪的一般方法
二.光流法
三.opencv中的光流法函数
四.用类封装基于光流法的目标跟踪方法
五.完整代码
六.参考文献
一.基于特征点的目标跟踪的一般方法
基于特征点的跟踪算法大致可以分为两个步骤:
1)探测当前帧的特征点;
2)通过当前帧和下一帧灰度比较,估计当前帧特征点在下一帧的位置;
3)过滤位置不变的特征点,余下的点就是目标了。
很显然,基于特征点的目标跟踪算法和1),2)两个步骤有关。特征点可以是Harris角点(见我的另外一篇博文),也可以是边缘点等等,而估计下一帧位置的方法也有不少,比如这里要讲的光流法,也可以是卡尔曼滤波法(咱是控制系的,上课经常遇到这个,所以看光流法看着看着就想到这个了)。
本文中,用改进的Harris角点提取特征点(见我另一篇博文:http://blog.csdn.net/crzy_sparrow/article/details/7391511),用Lucas-Kanade光流法实现目标跟踪。
二.光流法
这一部分《learing opencv》一书的第10章Lucas-Kanade光流部分写得非常详细,推荐大家看书。我这里也粘帖一些选自书中的内容。
另外我对这一部分附上一些个人的看法(谬误之处还望不吝指正):
1.首先是假设条件:
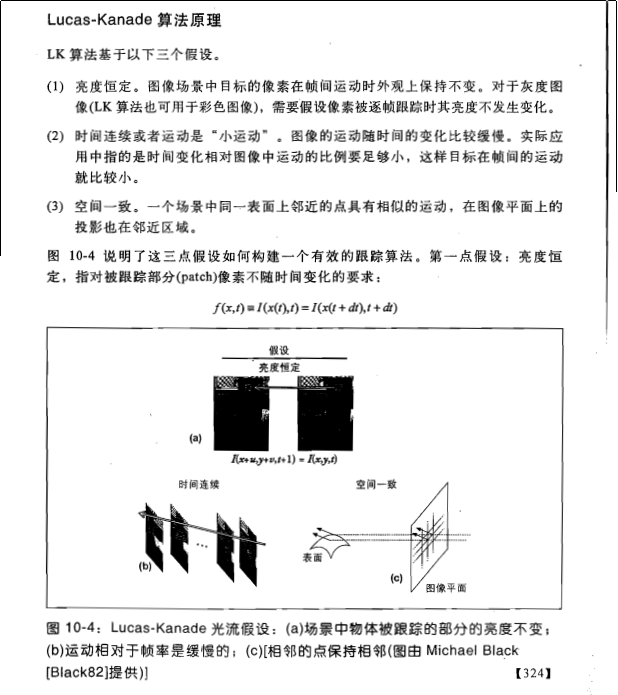
(1)亮度恒定,就是同一点随着时间的变化,其亮度不会发生改变。这是基本光流法的假定(所有光流法变种都必须满足),用于得到光流法基本方程;
(2)小运动,这个也必须满足,就是时间的变化不会引起位置的剧烈变化,这样灰度才能对位置求偏导(换句话说,小运动情况下我们才能用前后帧之间单位位置变化引起的灰度变化去近似灰度对位置的偏导数),这也是光流法不可或缺的假定;
(3)空间一致,一个场景上邻近的点投影到图像上也是邻近点,且邻近点速度一致。这是Lucas-Kanade光流法特有的假定,因为光流法基本方程约束只有一个,而要求x,y方向的速度,有两个未知变量。我们假定特征点邻域内做相似运动,就可以连立n多个方程求取x,y方向的速度(n为特征点邻域总点数,包括该特征点)。
2.方程求解
多个方程求两个未知变量,又是线性方程,很容易就想到用最小二乘法,事实上opencv也是这么做的。其中,最小误差平方和为最优化指标。
3.好吧,前面说到了小运动这个假定,聪明的你肯定很不爽了,目标速度很快那这货不是二掉了。幸运的是多尺度能解决这个问题。首先,对每一帧建立一个高斯金字塔,最大尺度图片在最顶层,原始图片在底层。然后,从顶层开始估计下一帧所在位置,作为下一层的初始位置,沿着金字塔向下搜索,重复估计动作,直到到达金字塔的底层。聪明的你肯定发现了:这样搜索不仅可以解决大运动目标跟踪,也可以一定程度上解决孔径问题(相同大小的窗口能覆盖大尺度图片上尽量多的角点,而这些角点无法在原始图片上被覆盖)。






#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
#include <sstream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
class FrameProcessor;
//帧处理基类
class FrameProcessor{
public:
virtual void process(Mat &input,Mat &ouput)=0;
};
//特征跟踪类,继承自帧处理基类
class FeatureTracker : public FrameProcessor{
Mat gray; //当前灰度图
Mat gray_prev; //之前的灰度图
vector<Point2f> points[2];//前后两帧的特征点
vector<Point2f> initial;//初始特征点
vector<Point2f> features;//检测到的特征
int max_count; //要跟踪特征的最大数目
double qlevel; //特征检测的指标
double minDist;//特征点之间最小容忍距离
vector<uchar> status; //特征跟踪状态
vector<float> err; //跟踪时的错误
public:
FeatureTracker():max_count(500),qlevel(0.01),minDist(10.){}
void process(Mat &frame,Mat &output){
//得到灰度图
cvtColor (frame,gray,CV_BGR2GRAY);
frame.copyTo (output);
//特征点太少了,重新检测特征点
if(addNewPoint()){
detectFeaturePoint ();
//插入检测到的特征点
points[0].insert (points[0].end (),features.begin (),features.end ());
initial.insert (initial.end (),features.begin (),features.end ());
}
//第一帧
if(gray_prev.empty ()){
gray.copyTo (gray_prev);
}
//根据前后两帧灰度图估计前一帧特征点在当前帧的位置
//默认窗口是15*15
calcOpticalFlowPyrLK (
gray_prev,//前一帧灰度图
gray,//当前帧灰度图
points[0],//前一帧特征点位置
points[1],//当前帧特征点位置
status,//特征点被成功跟踪的标志
err);//前一帧特征点点小区域和当前特征点小区域间的差,根据差的大小可删除那些运动变化剧烈的点
int k = 0;
//去除那些未移动的特征点
for(int i=0;i<points[1].size ();i++){
if(acceptTrackedPoint (i)){
initial[k]=initial[i];
points[1][k++] = points[1][i];
}
}
points[1].resize (k);
initial.resize (k);
//标记被跟踪的特征点
handleTrackedPoint (frame,output);
//为下一帧跟踪初始化特征点集和灰度图像
std::swap(points[1],points[0]);
cv::swap(gray_prev,gray);
}
void detectFeaturePoint(){
goodFeaturesToTrack (gray,//图片
features,//输出特征点
max_count,//特征点最大数目
qlevel,//质量指标
minDist);//最小容忍距离
}
bool addNewPoint(){
//若特征点数目少于10,则决定添加特征点
return points[0].size ()<=10;
}
//若特征点在前后两帧移动了,则认为该点是目标点,且可被跟踪
bool acceptTrackedPoint(int i){
return status[i]&&
(abs(points[0][i].x-points[1][i].x)+
abs(points[0][i].y-points[1][i].y) >2);
}
//画特征点
void handleTrackedPoint(Mat &frame,Mat &output){
for(int i=0;i<points[i].size ();i++){
//当前特征点到初始位置用直线表示
line(output,initial[i],points[1][i],Scalar::all (0));
//当前位置用圈标出
circle(output,points[1][i],3,Scalar::all(0),(-1));
}
}
};
class VideoProcessor{
private:
VideoCapture caputure;
//写视频流对象
VideoWriter writer;
//输出文件名
string Outputfile;
int currentIndex;
int digits;
string extension;
FrameProcessor *frameprocessor;
//图像处理函数指针
void (*process)(Mat &,Mat &);
bool callIt;
string WindowNameInput;
string WindowNameOutput;
//延时
int delay;
long fnumber;
//第frameToStop停止
long frameToStop;
//暂停标志
bool stop;
//图像序列作为输入视频流
vector<string> images;
//迭代器
public:
VideoProcessor() : callIt(true),delay(0),fnumber(0),stop(false),digits(0),frameToStop(-1){}
//设置图像处理函数
void setFrameProcessor(void (*process)(Mat &,Mat &)){
frameprocessor = 0;
this->process = process;
CallProcess ();
}
//打开视频
bool setInput(string filename){
fnumber = 0;
//若已打开,释放重新打开
caputure.release ();
return caputure.open (filename);
}
//设置输入视频播放窗口
void displayInput(string wn){
WindowNameInput = wn;
namedWindow (WindowNameInput);
}
//设置输出视频播放窗口
void displayOutput(string wn){
WindowNameOutput = wn;
namedWindow (WindowNameOutput);
}
//销毁窗口
void dontDisplay(){
destroyWindow (WindowNameInput);
destroyWindow (WindowNameOutput);
WindowNameInput.clear ();
WindowNameOutput.clear ();
}
//启动
void run(){
Mat frame;
Mat output;
if(!isOpened())
return;
stop = false;
while(!isStopped()){
//读取下一帧
if(!readNextFrame(frame))
break;
if(WindowNameInput.length ()!=0)
imshow (WindowNameInput,frame);
//处理该帧
if(callIt){
if(process)
process(frame,output);
else if(frameprocessor)
frameprocessor->process (frame,output);
}
else{
output = frame;
}
if(Outputfile.length ()){
cvtColor (output,output,CV_GRAY2BGR);
writeNextFrame (output);
}
if(WindowNameOutput.length ()!=0)
imshow (WindowNameOutput,output);
//按键暂停,继续按键继续
if(delay>=0&&waitKey (delay)>=0)
waitKey(0);
//到达指定暂停键,退出
if(frameToStop>=0&&getFrameNumber()==frameToStop)
stopIt();
}
}
//暂停键置位
void stopIt(){
stop = true;
}
//查询暂停标志位
bool isStopped(){
return stop;
}
//返回视频打开标志
bool isOpened(){
return caputure.isOpened ()||!images.empty ();
}
//设置延时
void setDelay(int d){
delay = d;
}
//读取下一帧
bool readNextFrame(Mat &frame){
if(images.size ()==0)
return caputure.read (frame);
else{
if(itImg!=images.end()){
frame = imread (*itImg);
itImg++;
return frame.data?1:0;
}
else
return false;
}
}
void CallProcess(){
callIt = true;
}
void dontCallProcess(){
callIt = false;
}
//设置停止帧
void stopAtFrameNo(long frame){
frameToStop = frame;
}
// 获得当前帧的位置
long getFrameNumber(){
long fnumber = static_cast<long>(caputure.get ((CV_CAP_PROP_POS_FRAMES)));
return fnumber;
}
//获得帧大小
Size getFrameSize() {
if (images.size()==0) {
// 从视频流获得帧大小
int w= static_cast<int>(caputure.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH));
int h= static_cast<int>(caputure.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT));
return Size(w,h);
}
else {
//从图像获得帧大小
cv::Mat tmp= cv::imread(images[0]);
return (tmp.data)?(tmp.size()):(Size(0,0));
}
}
//获取帧率
double getFrameRate(){
return caputure.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FPS);
}
vector<string>::const_iterator itImg;
bool setInput (const vector<string> &imgs){
fnumber = 0;
caputure.release ();
images = imgs;
itImg = images.begin ();
return true;
}
void setFrameProcessor(FrameProcessor *frameprocessor){
process = 0;
this->frameprocessor = frameprocessor;
CallProcess ();
}
//获得编码类型
int getCodec(char codec[4]) {
if (images.size()!=0)
return -1;
union { // 数据结构4-char
int value;
char code[4];
} returned;
//获得编码值
returned.value= static_cast<int>(
caputure.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FOURCC));
// get the 4 characters
codec[0]= returned.code[0];
codec[1]= returned.code[1];
codec[2]= returned.code[2];
codec[3]= returned.code[3];
return returned.value;
}
bool setOutput(const string &filename,int codec = 0,double framerate = 0.0,bool isColor = true){
//设置文件名
Outputfile = filename;
//清空扩展名
extension.clear ();
//设置帧率
if(framerate ==0.0){
framerate = getFrameRate ();
}
//获取输入原视频的编码方式
char c[4];
if(codec==0){
codec = getCodec(c);
}
return writer.open(Outputfile,
codec,
framerate,
getFrameSize(),
isColor);
}
//输出视频帧到图片fileme+currentIndex.ext,如filename001.jpg
bool setOutput (const string &filename,//路径
const string &ext,//扩展名
int numberOfDigits=3,//数字位数
int startIndex=0 ){//起始索引
if(numberOfDigits<0)
return false;
Outputfile = filename;
extension = ext;
digits = numberOfDigits;
currentIndex = startIndex;
return true;
}
//写下一帧
void writeNextFrame(Mat &frame){
//如果扩展名不为空,写到图片文件中
if(extension.length ()){
stringstream ss;
ss<<Outputfile<<setfill('0')<<setw(digits)<<currentIndex++<<extension;
imwrite (ss.str (),frame);
}
//反之,写到视频文件中
else{
writer.write (frame);
}
}
};
//帧处理函数:canny边缘检测
void canny(cv::Mat& img, cv::Mat& out) {
//灰度变换
if (img.channels()==3)
cvtColor(img,out,CV_BGR2GRAY);
// canny算子求边缘
Canny(out,out,100,200);
//颜色反转,看起来更舒服些
threshold(out,out,128,255,cv::THRESH_BINARY_INV);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
VideoProcessor processor;
FeatureTracker tracker;
//打开输入视频
processor.setInput ("bike.avi");
processor.displayInput ("Current Frame");
processor.displayOutput ("Output Frame");
//设置每一帧的延时
processor.setDelay (1000./processor.getFrameRate ());
//设置帧处理函数,可以任意
processor.setFrameProcessor (&tracker);
// processor.setOutput ("./bikeout.avi");
// processor.setOutput ("bikeout",".jpg");
processor.run ();
return 0;
}
运行结果:


六.参考文献
【1】The classic article by B. Lucas and T. Kanade, An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision in Int. Joint Conference in Artificial Intelligence, pp. 674-679,1981, that describes the original feature point tracking algorithm.
【2】The article by J. Shi and C. Tomasi, Good Features to Track in IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 593-600, 1994, that describes an improved version of the original feature point tracking algorithm.





