Matplotlib(基本用法)
Matplotlib 是数据分析绘图的常见模块,可以算是 2D-绘图(Python)领域使用最广泛的套件,可以将数据图形化,并且提供多样化的输出格式,利于数据的显示并分析。
接下来展示的是Matplotlib 常见绘制的图形,也是我自己对知识的一种总结。
# 模块的导入
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
matplotlib经常会遇到中文显示不出来的问题,中文乱码设置一般在设置样式之后,之前一直没注意顺序,导致一直没看到效果(😶)
# 设置样式 plt.style.use('seaborn') # 设置中文乱码 plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = 'KaiTi' plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] #用来正常显示中文标签 # 忽视警告 import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
绘制折线图,折线图可以直观得对比数据间的变化
# 构造数据 breakfast = [4,8,8,6,10,4] lunch = [25,10,10,15,50,15] dinner = [20,30,10,30,50,40] # 绘制折线图 plt.plot(breakfast,label='breakfast',linewidth=4,c='green') plt.plot(lunch,label='lunch',linewidth=4,c='blue') plt.plot(dinner,label='dinner',linewidth=4,c='pink')
# 设置样式
x_ticks = [f'星期{i}' for i in range(1,7)]
plt.xticks(ticks=range(6),labels=x_ticks) # x轴刻度值所一一对应的值
plt.ylabel('消费金额:单位(元)')
plt.title('深圳社畜每天三餐的消费')
#添加图例upper right 右上角 边框 透明度 阴影 边框宽度
plt.legend(loc='upper right',fancybox=True,framealpha=1,shadow=True,borderpad=1)
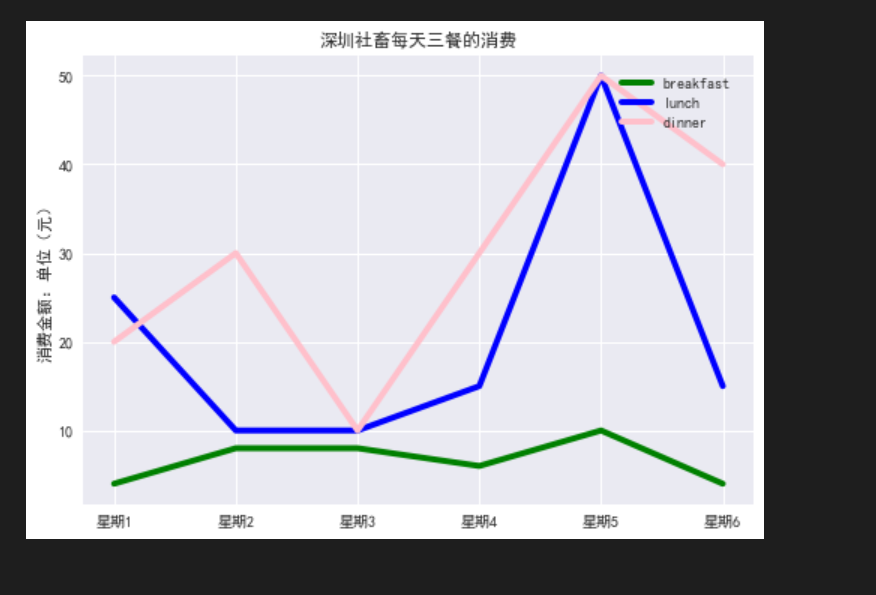
绘制曲线图
# 绘制曲线图 plt.figure(figsize=(15,5)) # 设置画布 x = np.linspace(1,10,num=100) plt.subplot(1,3,1) # 添加分布 1行3列 第1列画布绘制 plt.plot(x,np.sin(x),linewidth='7',color='blue') # 正弦 plt.subplot(1,3,2) # 第2列画布绘制 plt.plot(x,np.cos(x),linewidth='7',color='red') # 余弦 plt.subplot(1,3,3) # 第3列画布绘制 plt.plot(x,np.tanh(x),linewidth='7',color='green') # 正切

绘制散点图 一般用于查看数据是否线性相关 中间可以添加直线分析
# 绘制散点图 x = np.random.rand(100) # rand:服从“0~1”均匀分布的随机样本值均匀分布 y = np.random.rand(100) colors = np.random.rand(100) sizes = np.random.rand(100)*400 plt.scatter(x,y,c=colors,s=sizes)
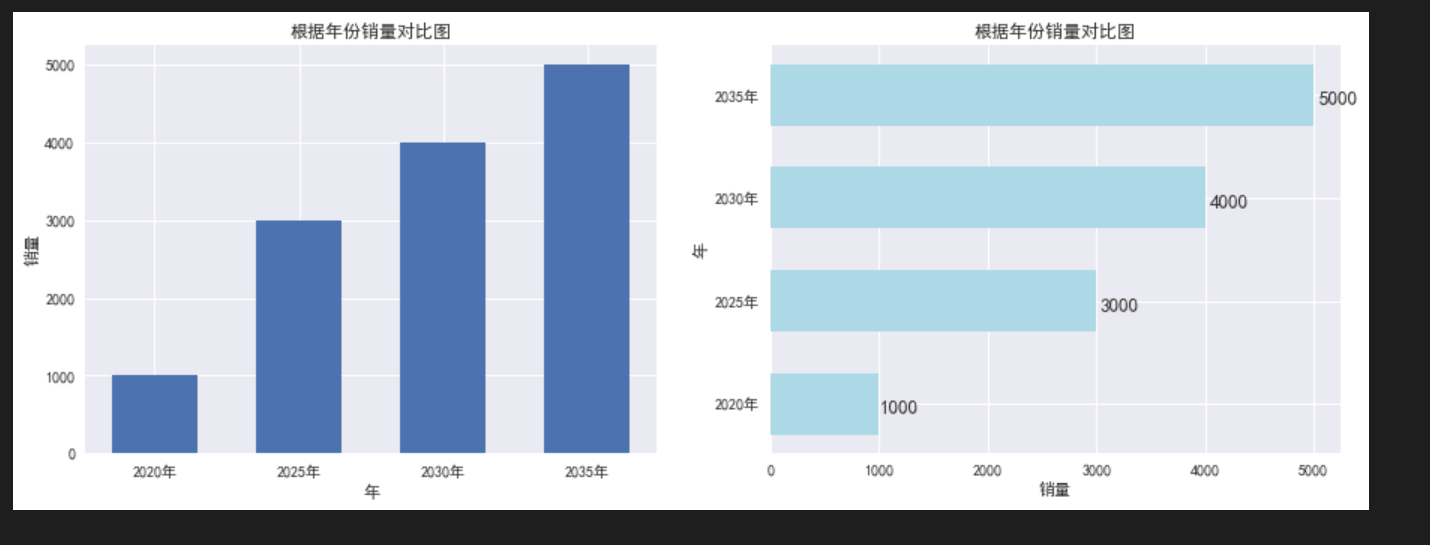
绘制条形图 可以多数据(例如每一年4个季度,一起比较分析)
# 绘制纵向条形图 x=[2020,2025,2030,2035] y=[1000,3000,4000,5000] plt.figure(figsize=(15,5)) # 设置画布 plt.subplot(1,2,1) plt.xticks(x,[f'{x}年' for x in x]) # 横坐标的刻度尺 plt.bar(x,y,width=3) plt.xlabel('年') # 横坐标标签 plt.ylabel('销量') # 纵坐标标签 plt.title('根据年份销量对比图') # 绘制横向条形图 plt.subplot(1,2,2) plt.yticks(x,[f'{x}年' for x in x]) bars = plt.barh(x,y,height=3,color='lightblue') for bar,d in zip(bars,y): x = bar.get_width() + bar.get_width()*0.01 y = bar.get_y() + bar.get_height()/3 text_data = d plt.text(x,y,text_data,fontsize=13) plt.xlabel('销量') plt.ylabel('年') plt.title('根据年份销量对比图')
绘制饼图 直观分辨哪个数据所占比份最重
# 构造数据 全市 = 17560061 福田区 = 1553225/全市 罗湖区 = 1143801/全市 盐田区 = 214225/全市 南山区 = 1795826/全市 宝安区 = 4476554/全市 龙岗区 = 3979037/全市 龙华区 = 2528872/全市 坪山区 = 551333/全市 光明区 = 1095289/全市 大鹏新区 = 156236/全市 explode = (0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0.1, 0, 0, 0, 0) labels = ['福田区','罗湖区','盐田区','南山区','宝安区','龙岗区','龙华区','坪山区','光明区','大鹏新区'] paches,texts,autotexts = plt.pie([福田区,罗湖区,盐田区,南山区,宝安区,龙岗区,龙华区,坪山区,光明区,大鹏新区], autopct='%0.1f%%', labels=labels, explode=explode) plt.title('深圳市第七次全国人口普查——分区人口情况') for text in texts: text.set_fontsize(10) text.set_color('blue') for t in autotexts: t.set_fontsize(10) t.set_color('white')

绘制直方图
# 绘制直方图 x = np.random.rand(100) plt.hist(x,bins=10,align='mid',rwidth=0.8,histtype='barstacked') # rwidth 控制着间隙的宽度

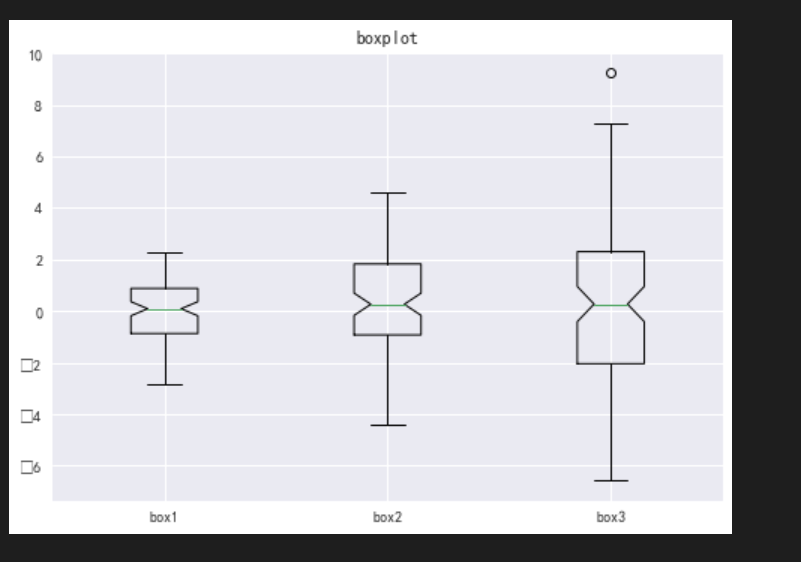
绘制盒图 盒图经常用于观察数据的离散程度 上下两条横线代表最大最小值,上方的空心圆代表异常值
# 绘制盒图 data = [np.random.normal(0,i,100) for i in range(1,4)] # vert:是否需要将箱线图垂直摆放,默认垂直摆放 # notch:是否是凹口的形式展现箱线图,默认非凹口 plt.boxplot(data,vert=True,notch=True) plt.title('boxplot') plt.xticks([1,2,3],['box1','box2','box3']) # 横坐标三个刻度尺,分别对应三个值
# 绘制三维图
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D x = np.linspace(-10,10,100) y = np.linspace(-10,10,100) X,Y = np.meshgrid(x,y) # 网格线 z = np.sqrt(X**2+Y**2) ax = Axes3D(plt.figure()) ax.plot_surface(x,y,z)






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!