IO流之字节流
字节流:给文件中写数据,或者读取文件中的数据。
字节输出流OutputStream:
OutputStream此抽象类,是表示输出字节流的所有类的超类。操作的数据都是字节,定义了输出字节流的基本共性功能方法。
输出流中定义都是写write方法,如下图:
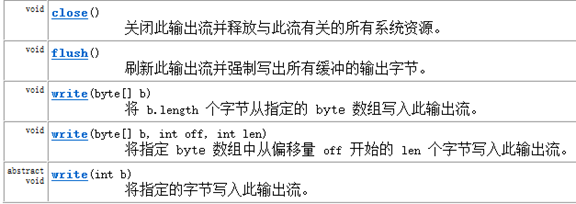
FileOutputStream类:
OutputStream子类FileOutputStream可用来写入数据到文件。
FileOutputStream类,即文件输出流,是用于将数据写入 File的输出流。
l 构造方法

FileOutputStream类写入数据到文件中:
l 将数据写到文件中,代码演示:
public class FileOutputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//需求:将数据写入到文件中。
//创建存储数据的文件。
File file = new File("c:\\file.txt");
//创建一个用于操作文件的字节输出流对象。一创建就必须明确数据存储目的地。
//输出流目的是文件,会自动创建。如果文件存在,则覆盖。
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
//调用父类中的write方法。
byte[] data = "abcde".getBytes();
fos.write(data);
//关闭流资源。
fos.close();
}
}
给文件中续写和换行:
我们直接new FileOutputStream(file)这样创建对象,写入数据,会覆盖原有的文件,那么我们想在原有的文件中续写内容怎么办呢?
继续查阅FileOutputStream的API。发现在FileOutputStream的构造函数中,可以接受一个boolean类型的值,如果值true,就会在文件末位继续添加。
l 构造方法

l 给文件中续写数据和换行,代码演示:
public class FileOutputStreamDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File file = new File("c:\\file.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file, true);
String str = "\r\n"+"aaa";
fos.write(str.getBytes());
fos.close();
}
}
字节输入流InputStream:
通过前面的学习,我们可以把内存中的数据写出到文件中,那如何想把内存中的数据读到内存中,我们通过InputStream可以实现。InputStream此抽象类,是表示字节输入流的所有类的超类。定义了字节输入流的基本共性功能方法。

l int read():读取一个字节并返回,没有字节返回-1.
l int read(byte[]): 读取一定量的字节数,并存储到字节数组中,返回读取到的字节数。
FileInputStream类
InputStream子类FileInputStream可用来读取文件内容。
FileInputStream 从文件系统中的某个文件中获得输入字节。
l 构造方法

FileInputStream类读取数据read方法:
在读取文件中的数据时,调用read方法,实现从文件中读取数据

l 从文件中读取数据,代码演示:
public class FileInputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("c:\\file.txt");
//创建一个字节输入流对象,必须明确数据源,其实就是创建字节读取流和数据源相关联。
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
//读取数据。使用 read();一次读一个字节。
int ch = 0;
while((ch=fis.read())!=-1){
System.out.pr }intln("ch="+(char)ch);
// 关闭资源。
fis.close();
}
}
读取数据read(byte[])方法:
在读取文件中的数据时,调用read方法,每次只能读取一个,太麻烦了,于是我们可以定义数组作为临时的存储容器,这时可以调用重载的read方法,一次可以读取多个字符。

public class FileInputStreamDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
* 演示第二个读取方法, read(byte[]);
*/
File file = new File("c:\\file.txt");
// 创建一个字节输入流对象,必须明确数据源,其实就是创建字节读取流和数据源相关联。
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
//创建一个字节数组。
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];//长度可以定义成1024的整数倍。
int len = 0;
while((len=fis.read(buf))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));
}
fis.close();
}
}
字节流练习:文件的复制
原理;读取一个已有的数据,并将这些读到的数据写入到另一个文件中。

public class CopyFileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1,明确源和目的。
File srcFile = new File("c:\\YesDir\test.JPG");
File destFile = new File("copyTest.JPG");
//2,明确字节流 输入流和源相关联,输出流和目的关联。
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
//3, 使用输入流的读取方法读取字节,并将字节写入到目的中。
int ch = 0;
while((ch=fis.read())!=-1){
fos.write(ch);
}
//4,关闭资源。
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
}
上述代码输入流和输出流之间是通过ch这个变量进行数据交换的。
上述复制文件有个问题,每次都从源文件读取一个,然后在写到指定文件,接着再读取一个字符,然后再写一个,一直这样下去。效率极低。
缓冲数组方式复制文件:
上述代码复制文件效率太低了,并且频繁的从文件读数据,和写数据,能不能一次多把文件中多个数据都读进内容中,然后在一次写出去,这样的速度一定会比前面代码速度快。
public class CopyFileByBufferTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File srcFile = new File("c:\\YesDir\test.JPG");
File destFile = new File("copyTest.JPG");
// 明确字节流 输入流和源相关联,输出流和目的关联。
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
//定义一个缓冲区。
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = fis.read(buf)) != -1) {
fos.write(buf, 0, len);// 将数组中的指定长度的数据写入到输出流中。
}
// 关闭资源。
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
}


