influxDB 入门教程及使用过程中遇到的问题
一、安装与使用
1、下载地址
GitHUb: https://github.com/Muscleape/influxdb_demo
64位程序: https://dl.influx data.com/influxdb/releases/influxdb-1.7.4_windows_amd64.zip
2、解压安装包
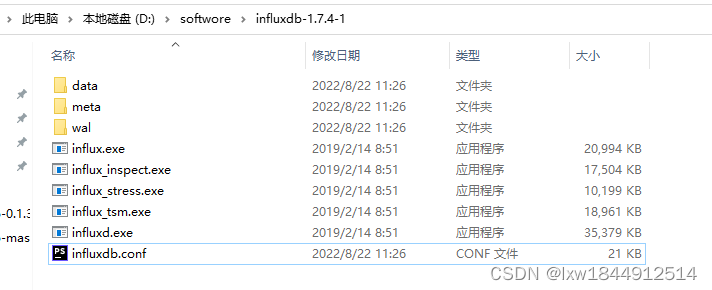 3、修改配置文件
3、修改配置文件
InfluxDB 的数据存储主要有三个目录。默认情况下是 meta, wal 以及 data 三个目录,服务器运行后会自动生成。
meta
用于存储数据库的一些元数据,meta 目录下有一个 meta.db 文件。
wal
目录存放预写日志文件,以 .wal 结尾。
data
目录存放实际存储的数据文件,以 .tsm 结尾。
如果不使用 influxdb.conf 配置的话,那么直接双击打开 influxd.exe 就可以使用influx,此时上面三个文件夹的目录则存放在Windows系统的C盘User目录下的.Influx目录下,默认端口为8086,以下为修改文件夹地址,以及端口号方法。
(1)修改以下部分路径

(2)如果修改端口号,则修改以下部分配置
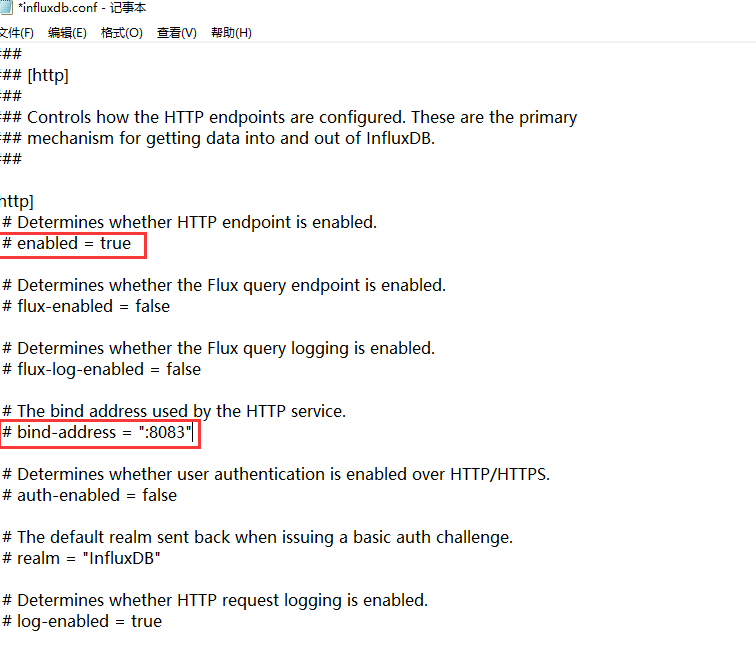
(3)修改配置后启动方式
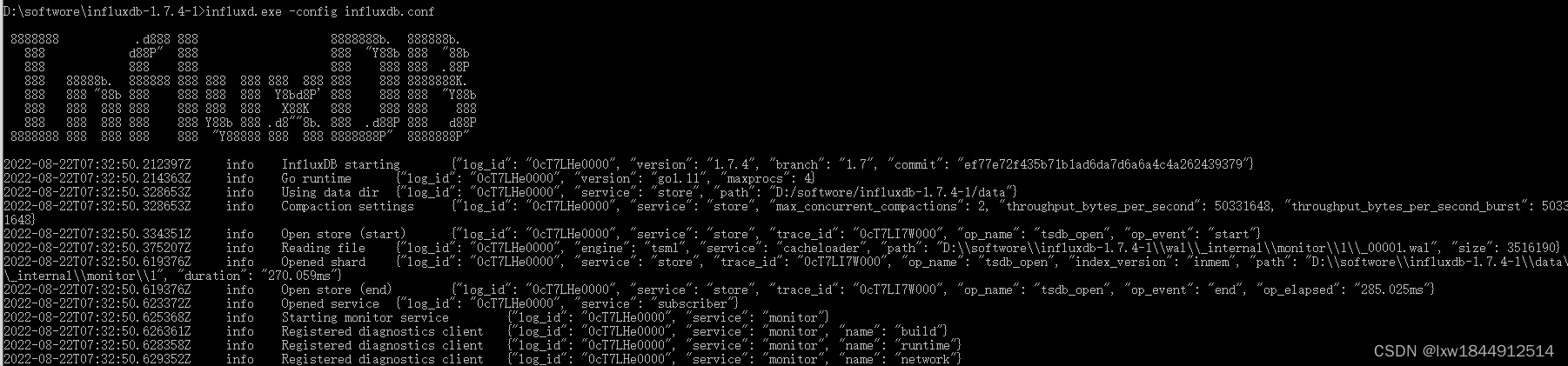
InfluxDB 使用时需要首先打开Influxd.exe,直接打开会使用默认配置,需要使用已配置的配置文件的话,需要指定conf文件进行启动,启动命令:influxd --config influxdb.conf
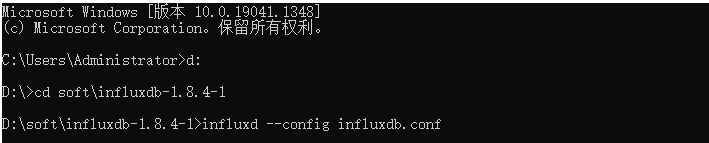
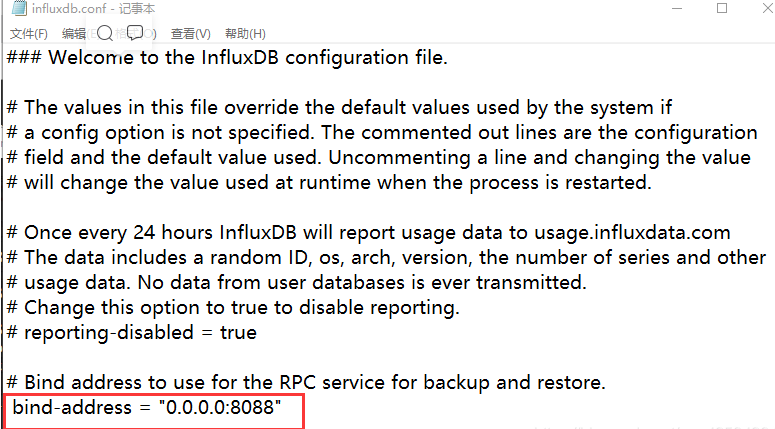
如果出现下列情况,启动失败,还需要修改influxdb.con
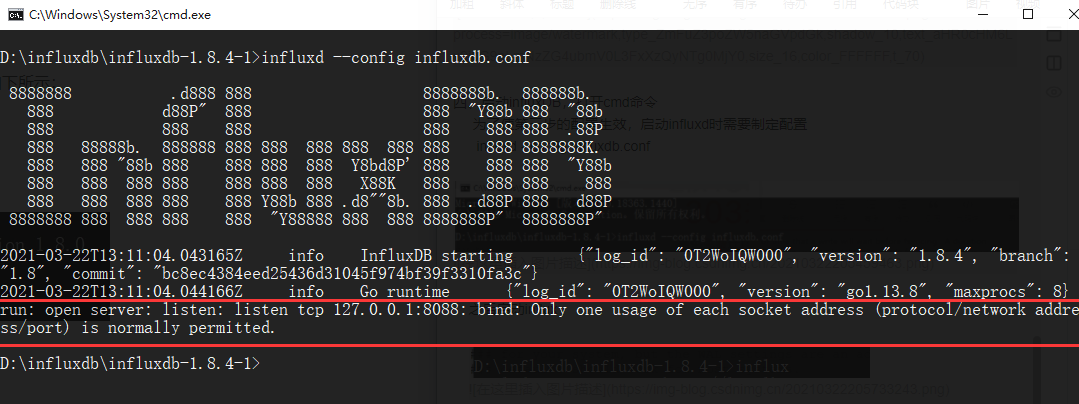
在influxdb.conf中修改如下一行,修改地址并且打开注释,修改后保存
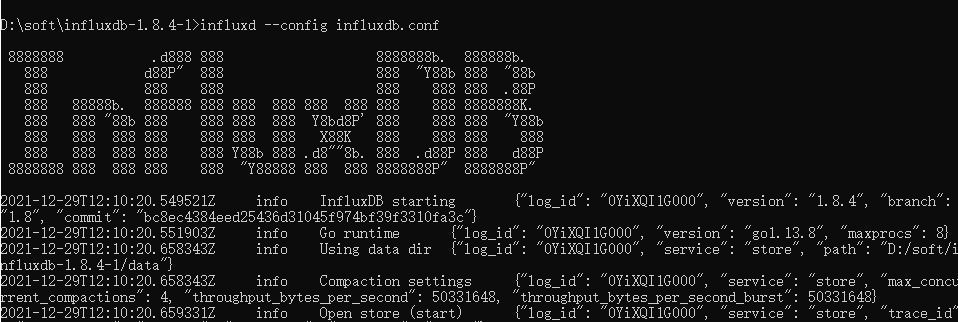
再次运行 influxd --config influxdb.conf 命令;出现如下信息启动成功
(4)、启动influx后,窗口不要关闭,在启动一个cmd窗口,执行如下命令 influx
InfluxDB自带一个客户端程序influx,可用来增删改查等操作数据库。
influx 客户端指定端口号访问,-port是使用特定port号启动
influx.exe -port 8083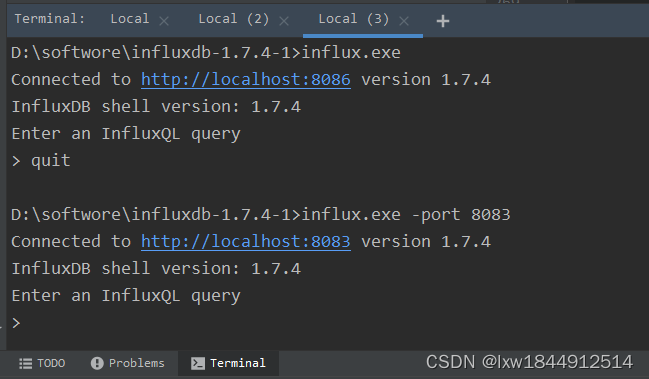
4、开启InfluxDb
可以直接打开Influxd.exe,也可以采用命令启动,
使用命令时可以指定配置文件和端口号。( 运行influx.exe 时,influxd.exe不可关闭。)
启动成功
5、其他配置
官方文档:https://archive.docs.influxdata.com/influxdb/v1.2/administration/config/
一些配置项的汉化注释已加在文件中
6、常用操作(使用)
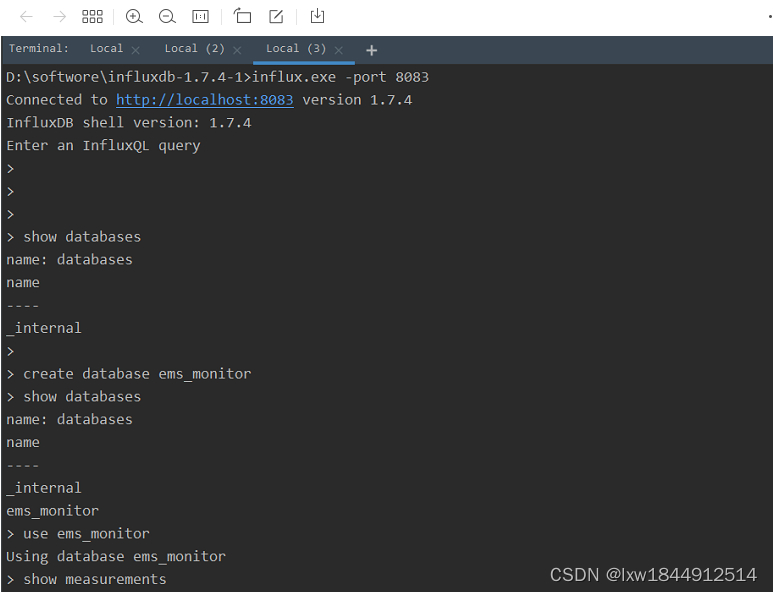
在 Influxd.exe 正常运行的情况下打开 Influx.exe,链接成功后如图所示,若链接失败需要检查地址和端口是否一致
1. influxdb数据库操作
show databases 查看有什么数据库
create database shijiange 创建数据库,数据库名称为shijiange
drop database shijiange 删除数据库,数据库名称为shijiange
2.measurement(类似于表)操作
use shijiange #操作哪个库需要用use
show measurements #查询所有measurement (没有表则不返回)
insert cpuinfo,item=shijiange_47.105.99.75_cpu.idle value=90
select * from cpuinfo #查询所有cpuinfo的数据
drop measurement cpuinfo #删除measurement
update更新语句没有,不过有alter命令,在influxdb中,删除操作用和更新基本不用到 。在针对数据保存策略方面,有一个特殊的删除方式,这个后面再提。
例子:插入数据的格式
insert cpuinfo(measurement:表名),item=shijiange_1.1.1.1_cpu.idle(tags:数据标识) value=90(fields:数据)
其中item和value名字都可以变化
3.influxdb常用查询和删除操作
select * from cpuinfo
select * from cpuinfo limit 2 #如果数据量太大,得使用limit,限制输出多少行
delete from cpuinfo where time=1531992939634316937 删除一条数据
delete from cpuinfo 删除所有数据
4.influxdb中数据保留时间的设置
SHOW RETENTION POLICIES ON shijiange 查看数据库shijiange 中表的保留策略
CREATE RETENTION POLICY rp_shijiange ON shijiange DURATION 30d REPLICATION 1 DEFAULT #数据要保留一个月
alter RETENTION POLICY rp_shijiange ON shijiange DURATION 90d REPLICATION 1 DEFAULT 改变保留策略
DROP RETENTION POLICY rp_shijiange on shijiange #删除保存时间和策略,同时会删除该表,一般来说是不删除
5.influxdb使用易看的时间格式
用标准时间格式展示数据,使time更容易看:precision rfc3339
数据保存策略
一般情况下基于时间序列的point数据不会进行直接删除操作,一般我们平时只关心当前数据,历史数据不需要一直保存,不然会占用太多空间。这里可以配置数据保存策略(Retention Policies),当数据超过了指定的时间之后,就会被删除。
SHOW RETENTION POLICIES ON "testDB" //查看当前数据库的Retention Policies CREATE RETENTION POLICY "rp_name" ON "db_name" DURATION 30d REPLICATION 1 DEFAULT //创建新的Retention Policies #注释如下: rp_name:策略名 db_name:具体的数据库名 30d:保存30天,30天之前的数据将被删除 它具有各种时间参数,比如:h(小时),w(星期) REPLICATION 1:副本个数,这里填1就可以了 DEFAULT 设为默认的策略 也可以通过如下命令修改和删策略: ALTER RETENTION POLICY "rp_name" ON db_name" DURATION 3w DEFAULT DROP RETENTION POLICY "rp_name" ON "db_name"
name--名称,此示例名称为 defaultduration--数据可以持久化数据库的时间,0代表无限制
shardGroupDuration--shardGroup的存储时间,shardGroup是InfluxDB的一个基本储存结构,应该大于这个时间的数据在查询效率上应该有所降低。
replicaN--全称是REPLICATION,副本个数
default--是否是默认策略
新建表和插入数据 ( 新建表没有具体的语法,只是增加第一条数据时,会自动建立表 )
语法:
<measurement>
[,<tag-key>=<tag-value>...]
<field-key>=<field-value>[,<field2-key>=<field2-value>...]
[unix-nano-timestamp]
下面给出一个简单的实例:
insert add_test,name=YiHui,phone=110 user_id=20,email="b**zewu@126.com"新增一条数据,measurement为add_test, tag为name,phone, field为user_id,email
空格前的为tag,空格后的为field
insert sensor_data,sensor_type="风速",sensor_id="1" sensor_data=12.12
insert Battery_Level,Change="处于充电状态",Device_ID="01" Battery_Level=1.0注意:插入数据时,如果插入的字段的类型为字符型,那么要用" "包括,不包含或者用' '都是错误的
> insert maintest,temperature=35.6 cputype=cpu001
ERR: {"error":"unable to parse 'maintest,temperature=35.6 cputype=cpu001': invalid boolean"}
> insert maintest,temperature=35.6 cputype="cpu001"
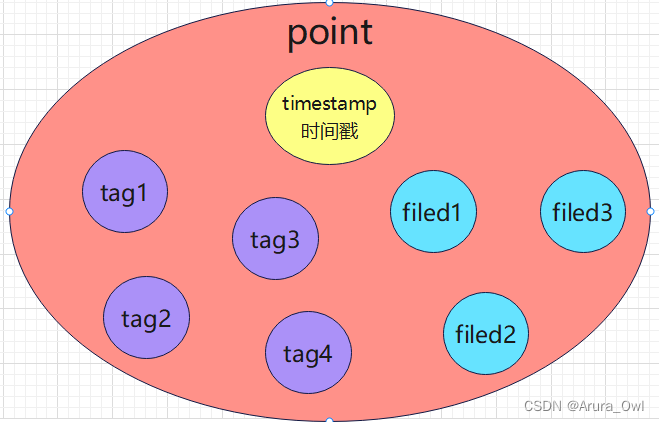
>influxdb的point比较特殊,一个point(行)包括了timestamp(时间戳),tags(带索引),fields(不带索引)这几种属性
influxdb数据的构成:
Point由时间戳(time)、数据(field)、标签(tags)组成。
Point属性
传统数据库中的概念
time:每个数据记录时间,是数据库中的主索引(会自动生成)
fields:各种记录值(没有索引的属性)也就是记录的值:温度, 湿度
tags:各种有索引的属性:地区,海拔
这里不得不提另一个名词:series:所有在数据库中的数据,都需要通过图表来展示,而这个series表示这个表里面的数据,可以在图表上画成几条线:通过tags排列组合算出来。具体可以通过
SHOW SERIES FROM "表名" 进行查询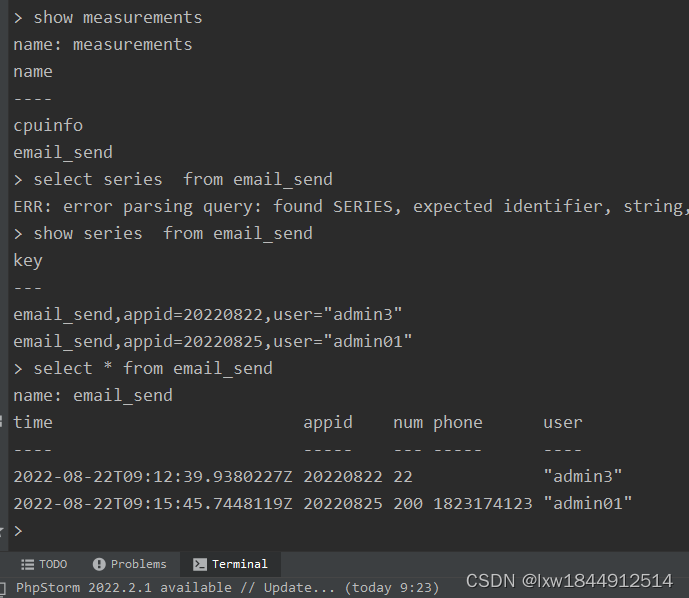
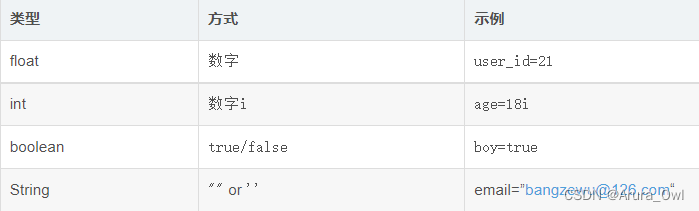
field中有四种存储类型,分别是int, float, string, boolean,用法为
显示所有用户
show users创建 普通用户:
create user "..." with password '...'
create user "ems" with password 'ems123' # 密码用单引号创建 管理员用户:
create user "..." with password '...' with all privileges
create user "ems33" with password '1234' with all privileges删除用户:
drop user "..."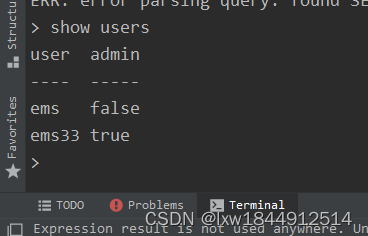
influxdb的权限设置比较简单,只有读、写、ALL几种。更多用户权限设置可以参看官方文档:https://docs.influxdata.com/influxdb/v1.0/query_language/authentication_and_authorization/ 。
默认情况下,influxdb类似与mongodb,是不开启用户认证的,可以修改其
conf文件,配置http块内容如下:
[http]
enable = true
bind-address = ":8086"
auth-enabled = true # 开启认证参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/vtnews/article/details/80197045
https://www.cnblogs.com/stone-s/p/16457720.html
https://www.likecs.com/show-306856081.html
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43135178/article/details/108733373
二、遇到问题
1.关于influxDB,修改过端口号无法连接的问题
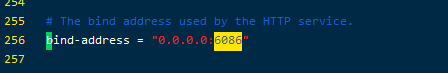
再启动influxdb的时候,可能会遇到端口被占用等情况,此时便需要修改influx的配置文件来更换端口。
但是当修改过influxdb.config文件的路径之后,再本地输入influx时发现,他所连接的端口并不是我所更改后的端口。当我输入show databases时,报401错。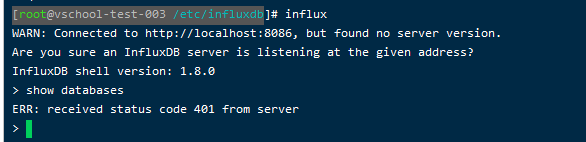
从网上找了一大堆资料,发现只需要再启动的时候输入指定端口即可:
influx -host localhost -port 6086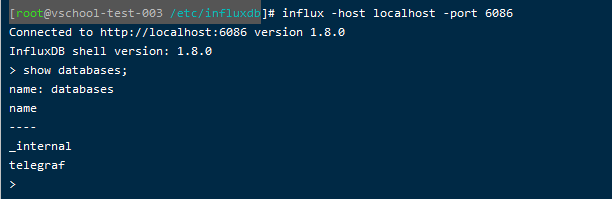
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39770653/article/details/119808573
https://blog.csdn.net/ColorfulChen/article/details/125946615
三、 Influxdb配置文件详解---influxdb.conf
官方介绍:Database Configuration | InfluxData Documentation Archive
全局配置
reporting-disabled = false # 该选项用于上报influxdb的使用信息给InfluxData公司,默认值为false
bind-address = ":8088" # 备份恢复时使用,默认值为80881、meta相关配置
[meta]
dir = "/var/lib/influxdb/meta" # meta数据存放目录
retention-autocreate = true # 用于控制默认存储策略,数据库创建时,会自动生成autogen的存储策略,默认值:true
logging-enabled = true # 是否开启meta日志,默认值:true2、data相关配置
[data]
dir = "/var/lib/influxdb/data" # 最终数据(TSM文件)存储目录
wal-dir = "/var/lib/influxdb/wal" # 预写日志存储目录
query-log-enabled = true # 是否开启tsm引擎查询日志,默认值: true
cache-max-memory-size = 1048576000 # 用于限定shard最大值,大于该值时会拒绝写入,默认值:1000MB,单位:byte
cache-snapshot-memory-size = 26214400 # 用于设置快照大小,大于该值时数据会刷新到tsm文件,默认值:25MB,单位:byte
cache-snapshot-write-cold-duration = "10m" # tsm引擎 snapshot写盘延迟,默认值:10Minute
compact-full-write-cold-duration = "4h" # tsm文件在压缩前可以存储的最大时间,默认值:4Hour
max-series-per-database = 1000000 # 限制数据库的级数,该值为0时取消限制,默认值:1000000
max-values-per-tag = 100000 # 一个tag最大的value数,0取消限制,默认值:1000003、coordinator查询管理的配置选项
[coordinator]
write-timeout = "10s" # 写操作超时时间,默认值: 10s
max-concurrent-queries = 0 # 最大并发查询数,0无限制,默认值: 0
query-timeout = "0s # 查询操作超时时间,0无限制,默认值:0s
log-queries-after = "0s" # 慢查询超时时间,0无限制,默认值:0s
max-select-point = 0 # SELECT语句可以处理的最大点数(points),0无限制,默认值:0
max-select-series = 0 # SELECT语句可以处理的最大级数(series),0无限制,默认值:0
max-select-buckets = 0 # SELECT语句可以处理的最大"GROUP BY time()"的时间周期,0无限制,默认值:04、retention旧数据的保留策略
[retention]
enabled = true # 是否启用该模块,默认值 : true
check-interval = "30m" # 检查时间间隔,默认值 :"30m"5、shard-precreation分区预创建
[shard-precreation]
enabled = true # 是否启用该模块,默认值 : true
check-interval = "10m" # 检查时间间隔,默认值 :"10m"
advance-period = "30m" # 预创建分区的最大提前时间,默认值 :"30m"6、monitor 控制InfluxDB自有的监控系统。 默认情况下,InfluxDB把这些数据写入_internal 数据库,如果这个库不存在则自动创建。 _internal 库默认的retention策略是7天,如果你想使用一个自己的retention策略,需要自己创建。
[monitor]
store-enabled = true # 是否启用该模块,默认值 :true
store-database = "_internal" # 默认数据库:"_internal"
store-interval = "10s # 统计间隔,默认值:"10s"7、admin web管理页面
[admin]
enabled = true # 是否启用该模块,默认值 : false
bind-address = ":8083" # 绑定地址,默认值 :":8083"
https-enabled = false # 是否开启https ,默认值 :false
https-certificate = "/etc/ssl/influxdb.pem" # https证书路径,默认值:"/etc/ssl/influxdb.pem"8、http API
[http]
enabled = true # 是否启用该模块,默认值 :true
bind-address = ":8086" # 绑定地址,默认值:":8086"
auth-enabled = false # 是否开启认证,默认值:false
realm = "InfluxDB" # 配置JWT realm,默认值: "InfluxDB"
log-enabled = true # 是否开启日志,默认值:true
write-tracing = false # 是否开启写操作日志,如果置成true,每一次写操作都会打日志,默认值:false
pprof-enabled = true # 是否开启pprof,默认值:true
https-enabled = false # 是否开启https,默认值:false
https-certificate = "/etc/ssl/influxdb.pem" # 设置https证书路径,默认值:"/etc/ssl/influxdb.pem"
https-private-key = "" # 设置https私钥,无默认值
shared-secret = "" # 用于JWT签名的共享密钥,无默认值
max-row-limit = 0 # 配置查询返回最大行数,0无限制,默认值:0
max-connection-limit = 0 # 配置最大连接数,0无限制,默认值:0
unix-socket-enabled = false # 是否使用unix-socket,默认值:false
bind-socket = "/var/run/influxdb.sock" # unix-socket路径,默认值:"/var/run/influxdb.sock"9、subscriber 控制Kapacitor接受数据的配置
[subscriber]
enabled = true # 是否启用该模块,默认值 :true
http-timeout = "30s" # http超时时间,默认值:"30s"
insecure-skip-verify = false # 是否允许不安全的证书
ca-certs = "" # 设置CA证书
write-concurrency = 40 # 设置并发数目,默认值:40
write-buffer-size = 1000 # 设置buffer大小,默认值:100010、graphite 相关配置
[[graphite]]
enabled = false # 是否启用该模块,默认值 :false
database = "graphite" # 数据库名称,默认值:"graphite"
retention-policy = "" # 存储策略,无默认值
bind-address = ":2003" # 绑定地址,默认值:":2003"
protocol = "tcp" # 协议,默认值:"tcp"
consistency-level = "one" # 一致性级别,默认值:"one
batch-size = 5000 # 批量size,默认值:5000
batch-pending = 10 # 配置在内存中等待的batch数,默认值:10
batch-timeout = "1s" # 超时时间,默认值:"1s"
udp-read-buffer = 0 # udp读取buffer的大小,0表示使用操作系统提供的值,如果超过操作系统的默认配置则会出错。 该配置的默认值:0
separator = "." # 多个measurement间的连接符,默认值: "."11、collectd
[[collectd]]
enabled = false # 是否启用该模块,默认值 :false
bind-address = ":25826" # 绑定地址,默认值: ":25826"
database = "collectd" # 数据库名称,默认值:"collectd"
retention-policy = "" # 存储策略,无默认值
typesdb = "/usr/local/share/collectd" # 路径,默认值:"/usr/share/collectd/types.db"
auth-file = "/etc/collectd/auth_file"
batch-size = 5000
batch-pending = 10
batch-timeout = "10s"
read-buffer = 0 # udp读取buffer的大小,0表示使用操作系统提供的值,如果超过操作系统的默认配置则会出错。默认值:012、opentsdb
[[opentsdb]]
enabled = false # 是否启用该模块,默认值:false
bind-address = ":4242" # 绑定地址,默认值:":4242"
database = "opentsdb" # 默认数据库:"opentsdb"
retention-policy = "" # 存储策略,无默认值
consistency-level = "one" # 一致性级别,默认值:"one"
tls-enabled = false # 是否开启tls,默认值:false
certificate= "/etc/ssl/influxdb.pem" # 证书路径,默认值:"/etc/ssl/influxdb.pem"
log-point-errors = true # 出错时是否记录日志,默认值:true
batch-size = 1000
batch-pending = 5
batch-timeout = "1s"13、udp
[[udp]]
enabled = false # 是否启用该模块,默认值:false
bind-address = ":8089" # 绑定地址,默认值:":8089"
database = "udp" # 数据库名称,默认值:"udp"
retention-policy = "" # 存储策略,无默认值
batch-size = 5000
batch-pending = 10
batch-timeout = "1s"
read-buffer = 0 # udp读取buffer的大小,0表示使用操作系统提供的值,如果超过操作系统的默认配置则会出错。 该配置的默认值:0 14、continuous_queries
[continuous_queries]
enabled = true # enabled 是否开启CQs,默认值:true
log-enabled = true # 是否开启日志,默认值:true
run-interval = "1s" # 时间间隔,默认值:"1s"我的配置文件
### Welcome to the InfluxDB configuration file.
# The values in this file override the default values used by the system if
# a config option is not specified. The commented out lines are the configuration
# field and the default value used. Uncommenting a line and changing the value
# will change the value used at runtime when the process is restarted.
# Once every 24 hours InfluxDB will report usage data to usage.influxdata.com
# The data includes a random ID, os, arch, version, the number of series and other
# usage data. No data from user databases is ever transmitted.
# Change this option to true to disable reporting.
# reporting-disabled = false
# Bind address to use for the RPC service for backup and restore.
bind-address = "0.0.0.0:8088"
###
### [meta]
###
### Controls the parameters for the Raft consensus group that stores metadata
### about the InfluxDB cluster.
###
[meta]
# Where the metadata/raft database is stored
dir = "D:/softwore/influxdb-1.7.4-1/meta"
# Automatically create a default retention policy when creating a database.
# retention-autocreate = true
# If log messages are printed for the meta service
# logging-enabled = true
###
### [data]
###
### Controls where the actual shard data for InfluxDB lives and how it is
### flushed from the WAL. "dir" may need to be changed to a suitable place
### for your system, but the WAL settings are an advanced configuration. The
### defaults should work for most systems.
###
[data]
# The directory where the TSM storage engine stores TSM files.
dir = "D:/softwore/influxdb-1.7.4-1/data"
# The directory where the TSM storage engine stores WAL files.
wal-dir = "D:/softwore/influxdb-1.7.4-1/wal"
# The amount of time that a write will wait before fsyncing. A duration
# greater than 0 can be used to batch up multiple fsync calls. This is useful for slower
# disks or when WAL write contention is seen. A value of 0s fsyncs every write to the WAL.
# Values in the range of 0-100ms are recommended for non-SSD disks.
# wal-fsync-delay = "0s"
# The type of shard index to use for new shards. The default is an in-memory index that is
# recreated at startup. A value of "tsi1" will use a disk based index that supports higher
# cardinality datasets.
# index-version = "inmem"
# Trace logging provides more verbose output around the tsm engine. Turning
# this on can provide more useful output for debugging tsm engine issues.
# trace-logging-enabled = false
# Whether queries should be logged before execution. Very useful for troubleshooting, but will
# log any sensitive data contained within a query.
# query-log-enabled = true
# Validates incoming writes to ensure keys only have valid unicode characters.
# This setting will incur a small overhead because every key must be checked.
# validate-keys = false
# Settings for the TSM engine
# CacheMaxMemorySize is the maximum size a shard's cache can
# reach before it starts rejecting writes.
# Valid size suffixes are k, m, or g (case insensitive, 1024 = 1k).
# Values without a size suffix are in bytes.
# cache-max-memory-size = "1g"
# CacheSnapshotMemorySize is the size at which the engine will
# snapshot the cache and write it to a TSM file, freeing up memory
# Valid size suffixes are k, m, or g (case insensitive, 1024 = 1k).
# Values without a size suffix are in bytes.
# cache-snapshot-memory-size = "25m"
# CacheSnapshotWriteColdDuration is the length of time at
# which the engine will snapshot the cache and write it to
# a new TSM file if the shard hasn't received writes or deletes
# cache-snapshot-write-cold-duration = "10m"
# CompactFullWriteColdDuration is the duration at which the engine
# will compact all TSM files in a shard if it hasn't received a
# write or delete
# compact-full-write-cold-duration = "4h"
# The maximum number of concurrent full and level compactions that can run at one time. A
# value of 0 results in 50% of runtime.GOMAXPROCS(0) used at runtime. Any number greater
# than 0 limits compactions to that value. This setting does not apply
# to cache snapshotting.
# max-concurrent-compactions = 0
# CompactThroughput is the rate limit in bytes per second that we
# will allow TSM compactions to write to disk. Note that short bursts are allowed
# to happen at a possibly larger value, set by CompactThroughputBurst
# compact-throughput = "48m"
# CompactThroughputBurst is the rate limit in bytes per second that we
# will allow TSM compactions to write to disk.
# compact-throughput-burst = "48m"
# If true, then the mmap advise value MADV_WILLNEED will be provided to the kernel with respect to
# TSM files. This setting has been found to be problematic on some kernels, and defaults to off.
# It might help users who have slow disks in some cases.
# tsm-use-madv-willneed = false
# Settings for the inmem index
# The maximum series allowed per database before writes are dropped. This limit can prevent
# high cardinality issues at the database level. This limit can be disabled by setting it to
# 0.
# max-series-per-database = 1000000
# The maximum number of tag values per tag that are allowed before writes are dropped. This limit
# can prevent high cardinality tag values from being written to a measurement. This limit can be
# disabled by setting it to 0.
# max-values-per-tag = 100000
# Settings for the tsi1 index
# The threshold, in bytes, when an index write-ahead log file will compact
# into an index file. Lower sizes will cause log files to be compacted more
# quickly and result in lower heap usage at the expense of write throughput.
# Higher sizes will be compacted less frequently, store more series in-memory,
# and provide higher write throughput.
# Valid size suffixes are k, m, or g (case insensitive, 1024 = 1k).
# Values without a size suffix are in bytes.
# max-index-log-file-size = "1m"
# The size of the internal cache used in the TSI index to store previously
# calculated series results. Cached results will be returned quickly from the cache rather
# than needing to be recalculated when a subsequent query with a matching tag key/value
# predicate is executed. Setting this value to 0 will disable the cache, which may
# lead to query performance issues.
# This value should only be increased if it is known that the set of regularly used
# tag key/value predicates across all measurements for a database is larger than 100. An
# increase in cache size may lead to an increase in heap usage.
series-id-set-cache-size = 100
###
### [coordinator]
###
### Controls the clustering service configuration.
###
[coordinator]
# The default time a write request will wait until a "timeout" error is returned to the caller.
# write-timeout = "10s"
# The maximum number of concurrent queries allowed to be executing at one time. If a query is
# executed and exceeds this limit, an error is returned to the caller. This limit can be disabled
# by setting it to 0.
# max-concurrent-queries = 0
# The maximum time a query will is allowed to execute before being killed by the system. This limit
# can help prevent run away queries. Setting the value to 0 disables the limit.
# query-timeout = "0s"
# The time threshold when a query will be logged as a slow query. This limit can be set to help
# discover slow or resource intensive queries. Setting the value to 0 disables the slow query logging.
# log-queries-after = "0s"
# The maximum number of points a SELECT can process. A value of 0 will make
# the maximum point count unlimited. This will only be checked every second so queries will not
# be aborted immediately when hitting the limit.
# max-select-point = 0
# The maximum number of series a SELECT can run. A value of 0 will make the maximum series
# count unlimited.
# max-select-series = 0
# The maxium number of group by time bucket a SELECT can create. A value of zero will max the maximum
# number of buckets unlimited.
# max-select-buckets = 0
###
### [retention]
###
### Controls the enforcement of retention policies for evicting old data.
###
[retention]
# Determines whether retention policy enforcement enabled.
# enabled = true
# The interval of time when retention policy enforcement checks run.
# check-interval = "30m"
###
### [shard-precreation]
###
### Controls the precreation of shards, so they are available before data arrives.
### Only shards that, after creation, will have both a start- and end-time in the
### future, will ever be created. Shards are never precreated that would be wholly
### or partially in the past.
[shard-precreation]
# Determines whether shard pre-creation service is enabled.
# enabled = true
# The interval of time when the check to pre-create new shards runs.
# check-interval = "10m"
# The default period ahead of the endtime of a shard group that its successor
# group is created.
# advance-period = "30m"
###
### Controls the system self-monitoring, statistics and diagnostics.
###
### The internal database for monitoring data is created automatically if
### if it does not already exist. The target retention within this database
### is called 'monitor' and is also created with a retention period of 7 days
### and a replication factor of 1, if it does not exist. In all cases the
### this retention policy is configured as the default for the database.
[monitor]
# Whether to record statistics internally.
# store-enabled = true
# The destination database for recorded statistics
# store-database = "_internal"
# The interval at which to record statistics
# store-interval = "10s"
###
### [http]
###
### Controls how the HTTP endpoints are configured. These are the primary
### mechanism for getting data into and out of InfluxDB.
###
[http]
# Determines whether HTTP endpoint is enabled.
enabled = true
# Determines whether the Flux query endpoint is enabled.
# flux-enabled = false
# Determines whether the Flux query logging is enabled.
# flux-log-enabled = false
# The bind address used by the HTTP service.
bind-address = ":8083"
# Determines whether user authentication is enabled over HTTP/HTTPS.
# auth-enabled = false
# The default realm sent back when issuing a basic auth challenge.
# realm = "InfluxDB"
# Determines whether HTTP request logging is enabled.
# log-enabled = true
# Determines whether the HTTP write request logs should be suppressed when the log is enabled.
# suppress-write-log = false
# When HTTP request logging is enabled, this option specifies the path where
# log entries should be written. If unspecified, the default is to write to stderr, which
# intermingles HTTP logs with internal InfluxDB logging.
#
# If influxd is unable to access the specified path, it will log an error and fall back to writing
# the request log to stderr.
# access-log-path = ""
# Filters which requests should be logged. Each filter is of the pattern NNN, NNX, or NXX where N is
# a number and X is a wildcard for any number. To filter all 5xx responses, use the string 5xx.
# If multiple filters are used, then only one has to match. The default is to have no filters which
# will cause every request to be printed.
# access-log-status-filters = []
# Determines whether detailed write logging is enabled.
# write-tracing = false
# Determines whether the pprof endpoint is enabled. This endpoint is used for
# troubleshooting and monitoring.
# pprof-enabled = true
# Enables a pprof endpoint that binds to localhost:6060 immediately on startup.
# This is only needed to debug startup issues.
# debug-pprof-enabled = false
# Determines whether HTTPS is enabled.
# https-enabled = false
# The SSL certificate to use when HTTPS is enabled.
# https-certificate = "/etc/ssl/influxdb.pem"
# Use a separate private key location.
# https-private-key = ""
# The JWT auth shared secret to validate requests using JSON web tokens.
# shared-secret = ""
# The default chunk size for result sets that should be chunked.
# max-row-limit = 0
# The maximum number of HTTP connections that may be open at once. New connections that
# would exceed this limit are dropped. Setting this value to 0 disables the limit.
# max-connection-limit = 0
# Enable http service over unix domain socket
# unix-socket-enabled = false
# The path of the unix domain socket.
# bind-socket = "/var/run/influxdb.sock"
# The maximum size of a client request body, in bytes. Setting this value to 0 disables the limit.
# max-body-size = 25000000
# The maximum number of writes processed concurrently.
# Setting this to 0 disables the limit.
# max-concurrent-write-limit = 0
# The maximum number of writes queued for processing.
# Setting this to 0 disables the limit.
# max-enqueued-write-limit = 0
# The maximum duration for a write to wait in the queue to be processed.
# Setting this to 0 or setting max-concurrent-write-limit to 0 disables the limit.
# enqueued-write-timeout = 0
###
### [logging]
###
### Controls how the logger emits logs to the output.
###
[logging]
# Determines which log encoder to use for logs. Available options
# are auto, logfmt, and json. auto will use a more a more user-friendly
# output format if the output terminal is a TTY, but the format is not as
# easily machine-readable. When the output is a non-TTY, auto will use
# logfmt.
# format = "auto"
# Determines which level of logs will be emitted. The available levels
# are error, warn, info, and debug. Logs that are equal to or above the
# specified level will be emitted.
# level = "info"
# Suppresses the logo output that is printed when the program is started.
# The logo is always suppressed if STDOUT is not a TTY.
# suppress-logo = false
###
### [subscriber]
###
### Controls the subscriptions, which can be used to fork a copy of all data
### received by the InfluxDB host.
###
[subscriber]
# Determines whether the subscriber service is enabled.
# enabled = true
# The default timeout for HTTP writes to subscribers.
# http-timeout = "30s"
# Allows insecure HTTPS connections to subscribers. This is useful when testing with self-
# signed certificates.
# insecure-skip-verify = false
# The path to the PEM encoded CA certs file. If the empty string, the default system certs will be used
# ca-certs = ""
# The number of writer goroutines processing the write channel.
# write-concurrency = 40
# The number of in-flight writes buffered in the write channel.
# write-buffer-size = 1000
###
### [[graphite]]
###
### Controls one or many listeners for Graphite data.
###
[[graphite]]
# Determines whether the graphite endpoint is enabled.
# enabled = false
# database = "graphite"
# retention-policy = ""
# bind-address = ":2003"
# protocol = "tcp"
# consistency-level = "one"
# These next lines control how batching works. You should have this enabled
# otherwise you could get dropped metrics or poor performance. Batching
# will buffer points in memory if you have many coming in.
# Flush if this many points get buffered
# batch-size = 5000
# number of batches that may be pending in memory
# batch-pending = 10
# Flush at least this often even if we haven't hit buffer limit
# batch-timeout = "1s"
# UDP Read buffer size, 0 means OS default. UDP listener will fail if set above OS max.
# udp-read-buffer = 0
### This string joins multiple matching 'measurement' values providing more control over the final measurement name.
# separator = "."
### Default tags that will be added to all metrics. These can be overridden at the template level
### or by tags extracted from metric
# tags = ["region=us-east", "zone=1c"]
### Each template line requires a template pattern. It can have an optional
### filter before the template and separated by spaces. It can also have optional extra
### tags following the template. Multiple tags should be separated by commas and no spaces
### similar to the line protocol format. There can be only one default template.
# templates = [
# "*.app env.service.resource.measurement",
# # Default template
# "server.*",
# ]
###
### [collectd]
###
### Controls one or many listeners for collectd data.
###
[[collectd]]
# enabled = false
# bind-address = ":25826"
# database = "collectd"
# retention-policy = ""
#
# The collectd service supports either scanning a directory for multiple types
# db files, or specifying a single db file.
# typesdb = "/usr/local/share/collectd"
#
# security-level = "none"
# auth-file = "/etc/collectd/auth_file"
# These next lines control how batching works. You should have this enabled
# otherwise you could get dropped metrics or poor performance. Batching
# will buffer points in memory if you have many coming in.
# Flush if this many points get buffered
# batch-size = 5000
# Number of batches that may be pending in memory
# batch-pending = 10
# Flush at least this often even if we haven't hit buffer limit
# batch-timeout = "10s"
# UDP Read buffer size, 0 means OS default. UDP listener will fail if set above OS max.
# read-buffer = 0
# Multi-value plugins can be handled two ways.
# "split" will parse and store the multi-value plugin data into separate measurements
# "join" will parse and store the multi-value plugin as a single multi-value measurement.
# "split" is the default behavior for backward compatability with previous versions of influxdb.
# parse-multivalue-plugin = "split"
###
### [opentsdb]
###
### Controls one or many listeners for OpenTSDB data.
###
[[opentsdb]]
# enabled = false
# bind-address = ":4242"
# database = "opentsdb"
# retention-policy = ""
# consistency-level = "one"
# tls-enabled = false
# certificate= "/etc/ssl/influxdb.pem"
# Log an error for every malformed point.
# log-point-errors = true
# These next lines control how batching works. You should have this enabled
# otherwise you could get dropped metrics or poor performance. Only points
# metrics received over the telnet protocol undergo batching.
# Flush if this many points get buffered
# batch-size = 1000
# Number of batches that may be pending in memory
# batch-pending = 5
# Flush at least this often even if we haven't hit buffer limit
# batch-timeout = "1s"
###
### [[udp]]
###
### Controls the listeners for InfluxDB line protocol data via UDP.
###
[[udp]]
# enabled = false
# bind-address = ":8089"
# database = "udp"
# retention-policy = ""
# InfluxDB precision for timestamps on received points ("" or "n", "u", "ms", "s", "m", "h")
# precision = ""
# These next lines control how batching works. You should have this enabled
# otherwise you could get dropped metrics or poor performance. Batching
# will buffer points in memory if you have many coming in.
# Flush if this many points get buffered
# batch-size = 5000
# Number of batches that may be pending in memory
# batch-pending = 10
# Will flush at least this often even if we haven't hit buffer limit
# batch-timeout = "1s"
# UDP Read buffer size, 0 means OS default. UDP listener will fail if set above OS max.
# read-buffer = 0
###
### [continuous_queries]
###
### Controls how continuous queries are run within InfluxDB.
###
[continuous_queries]
# Determines whether the continuous query service is enabled.
# enabled = true
# Controls whether queries are logged when executed by the CQ service.
# log-enabled = true
# Controls whether queries are logged to the self-monitoring data store.
# query-stats-enabled = false
# interval for how often continuous queries will be checked if they need to run
# run-interval = "1s"
###
### [tls]
###
### Global configuration settings for TLS in InfluxDB.
###
[tls]
# Determines the available set of cipher suites. See https://golang.org/pkg/crypto/tls/#pkg-constants
# for a list of available ciphers, which depends on the version of Go (use the query
# SHOW DIAGNOSTICS to see the version of Go used to build InfluxDB). If not specified, uses
# the default settings from Go's crypto/tls package.
# ciphers = [
# "TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305",
# "TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256",
# ]
# Minimum version of the tls protocol that will be negotiated. If not specified, uses the
# default settings from Go's crypto/tls package.
# min-version = "tls1.2"
# Maximum version of the tls protocol that will be negotiated. If not specified, uses the
# default settings from Go's crypto/tls package.
# max-version = "tls1.2"
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/guyeshanrenshiwoshifu/p/9188368.html
赞赏码


非学,无以致疑;非问,无以广识


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号