剑指offer第七章&第八章
剑指offer第七章&第八章
1.把字符串转换成整数
将一个字符串转换成一个整数,要求不能使用字符串转换整数的库函数。 数值为0或者字符串不是一个合法的数值则返回0
输入描述:
输入一个字符串,包括数字字母符号,可以为空
输出描述:
如果是合法的数值表达则返回该数字,否则返回0
分析:思路在代码里已经体现
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int StrToInt(string str) 4 { 5 if(str.empty()) 6 return 0; 7 int symbol = 1;//正负号初始化为1表示正数 8 if(str[0] == '-') 9 {//处理负号 10 symbol = -1;//表示是负数 11 str[0] = '0'; //这里是‘0’ 不是0 12 } 13 else if(str[0] == '+') 14 {//处理正号 15 symbol = 1;//表示是正数 16 str[0] = '0'; 17 } 18 int sum = 0; 19 for(int i=0;i<str.size();++i) 20 { 21 if(str[i] < '0' || str[i] > '9') 22 { 23 sum = 0; 24 break; 25 } 26 sum = sum *10 + str[i] - '0'; 27 } 28 return symbol * sum;//正负号乘以sum,即表示字符串所表示的整数 29 } 30 };
2..数组中重复的数字
在一个长度为n的数组里的所有数字都在0到n-1的范围内。 数组中某些数字是重复的,但不知道有几个数字是重复的。也不知道每个数字重复几次。请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字。
例如,如果输入长度为7的数组{2,3,1,0,2,5,3},那么对应的输出是第一个重复的数字2。
分析:注意到数组中的数字都在0——n-1的范围内。如果没有重复数字,那么排序之后数字i将出现在下标为i的位置
从头到尾依次扫描这个数组中的每个数字。当扫描到下标为i的数字时,首先比较这个数字(m)是不是等于i。如果是,接着扫描下一个数字。如果不是,再拿m和第m个数字比较。如果相等,就找到了一个重复数字。如果不等,就把第i个数字和第m个数字交换,把m放到属于它的位置。接下来重复比较,直到找到重复数字。
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 // Parameters: 4 // numbers: an array of integers 5 // length: the length of array numbers 6 // duplication: (Output) the duplicated number in the array number 7 // Return value: true if the input is valid, and there are some duplications in the array number 8 // otherwise false 9 bool duplicate(int numbers[], int length, int* duplication) 10 { 11 if(numbers==NULL||length<=0) 12 return false; 13 for(int i=0;i<length;++i) 14 { 15 if(numbers[i]<0||numbers[i]>length-1) 16 return false; 17 } 18 for(int i=0;i<length;++i) 19 { 20 while(numbers[i]!=i) 21 { 22 if(numbers[i]==numbers[numbers[i]]) 23 { 24 *duplication=numbers[i]; 25 return true; 26 } 27 int temp=numbers[i]; 28 numbers[i]=numbers[temp]; 29 numbers[temp]=temp; 30 } 31 } 32 return false; 33 } 34 };
3.构建乘积数组
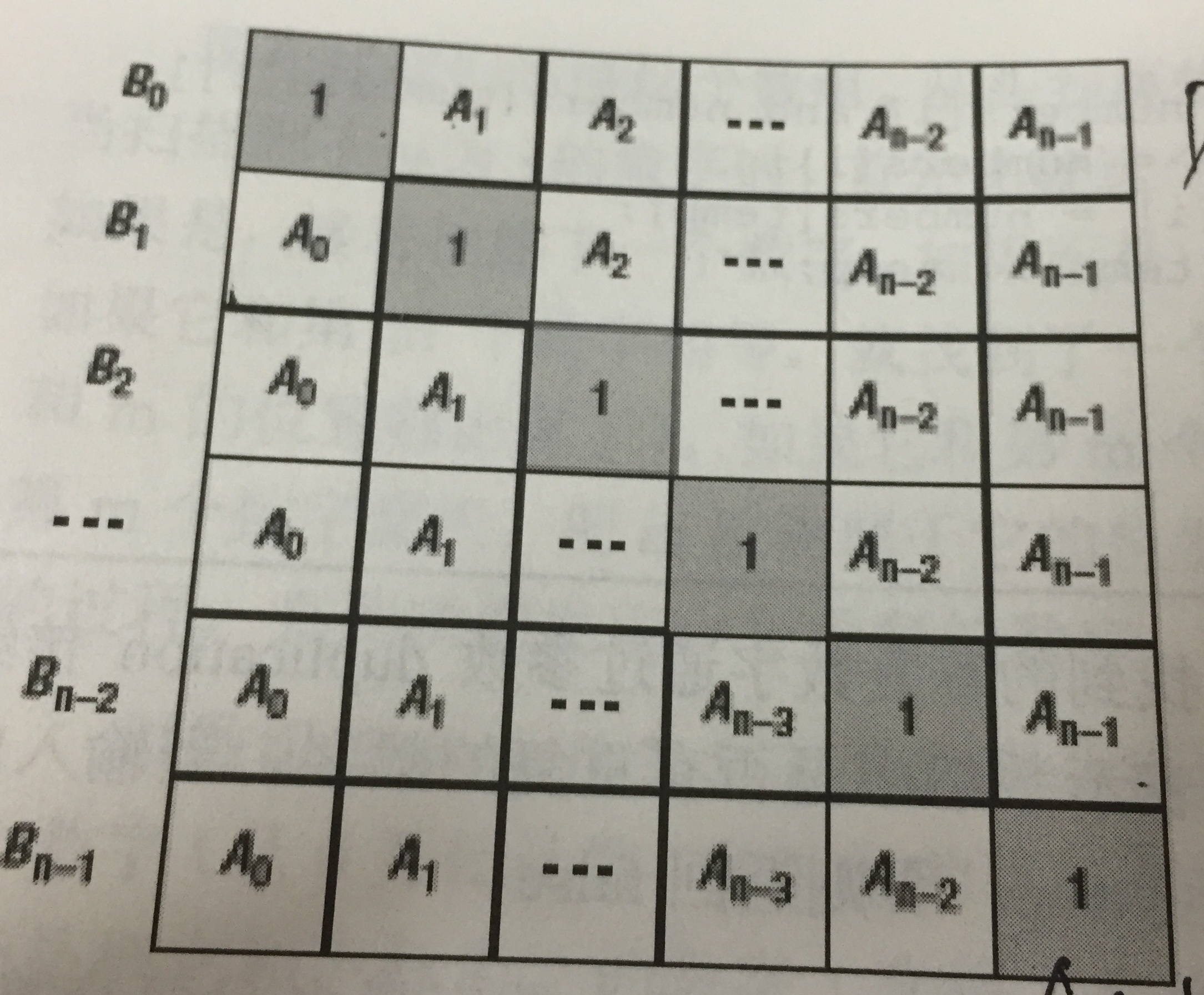
给定一个数组A[0,1,...,n-1],请构建一个数组B[0,1,...,n-1],其中B中的元素B[i]=A[0]*A[1]*...*A[i-1]*A[i+1]*...*A[n-1]。不能使用除法。
分析:
B[i]的值可以看作下图的矩阵中每行的乘积。
下三角用连乘可以很容求得,上三角,从下向上也是连乘。
因此我们的思路就很清晰了,先算下三角中的连乘,即我们先算出B[i]中的一部分,然后倒过来按上三角中的分布规律,把另一部分也乘进去。
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 vector<int> multiply(const vector<int>& A) 4 { 5 int n=A.size(); 6 vector<int> B(n); 7 B[0]=1; 8 for(int i=1;i<n;++i) 9 { 10 B[i]=B[i-1]*A[i-1]; 11 } 12 double temp=1; 13 for(int i=n-2;i>=0;--i) 14 { 15 temp*=A[i+1]; 16 B[i]*=temp; 17 } 18 return B; 19 } 20 };
4.表示数值的字符串
请实现一个函数用来判断字符串是否表示数值(包括整数和小数)。
例如,字符串"+100","5e2","-123","3.1416"和"-1E-16"都表示数值。 但是"12e","1a3.14","1.2.3","+-5"和"12e+4.3"都不是。
分析:在代码里体现
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 bool isNumeric(char* string) 4 { 5 if(string==NULL) 6 return false; 7 if(*string=='+'||*string=='-')//首先判断第一个字符是不是正负号 8 ++string; 9 if(*string=='\0')//边界判断 10 return false; 11 bool numeric=true; 12 scanDigits(&string);//扫描数位 13 if(*string!='\0') 14 { 15 if(*string=='.')//小数 16 { 17 ++string; 18 scanDigits(&string); 19 if(*string=='e'||*string=='E')//科学记数法 20 numeric=isExp(&string); 21 } 22 //整数 23 else if(*string=='e'||*string=='E') 24 numeric=isExp(&string); 25 else 26 numeric=false; 27 } 28 return numeric&&*string=='\0'; 29 } 30 void scanDigits(char** string)//扫描字符串中0到9的数位 31 { 32 while(**string !='\0'&&**string>='0'&&**string<='9') 33 ++(*string); 34 } 35 bool isExp(char** string)//用来匹配用科学记数法表示数值的结尾部分,结尾部分的第一个字符是‘e’或者‘E’,接下来可能有一个正负号 36 { 37 if(**string!='e'&&**string!='E') 38 return false; 39 ++(*string); 40 if(**string=='+'||**string=='-') 41 ++(*string); 42 if(**string=='\0') 43 return false; 44 scanDigits(string); 45 return (**string=='\0') ? true:false; 46 } 47 };
5.字符流中第一个不重复的字符
请实现一个函数用来找出字符流中第一个只出现一次的字符。
例如,当从字符流中只读出前两个字符"go"时,第一个只出现一次的字符是"g"。
当从该字符流中读出前六个字符“google"时,第一个只出现一次的字符是"l"。
输出描述::如果当前字符流没有存在出现一次的字符,返回#字符。
分析:
1 class Solution 2 { 3 public: 4 string s; 5 char hash[256]={0}; 6 //Insert one char from stringstream 7 void Insert(char ch) 8 { 9 s+=ch; 10 hash[ch]++; 11 } 12 //return the first appearence once char in current stringstream 13 char FirstAppearingOnce() 14 { 15 int size=s.size(); 16 for(int i=0;i<size;++i) 17 { 18 if(hash[s[i]]==1) 19 return s[i]; 20 } 21 return '#'; 22 } 23 };
6.链表中环的入口结点
一个链表中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点。
1 /* 2 struct ListNode { 3 int val; 4 struct ListNode *next; 5 ListNode(int x) : 6 val(x), next(NULL) { 7 } 8 }; 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public: 12 //在链表中存在环的前提下找到一快一慢两个指针相遇的结点,一定在环内 13 ListNode* MeetingNode(ListNode* pHead) 14 { 15 if(pHead==NULL) 16 return NULL; 17 ListNode* pSlow=pHead->next; 18 if(pSlow==NULL) 19 return NULL; 20 ListNode* pFast=pSlow->next; 21 while(pFast!=NULL&&pSlow!=NULL) 22 { 23 if(pFast==pSlow) 24 return pFast; 25 pSlow=pSlow->next; 26 pFast=pFast->next; 27 if(pFast!=NULL) 28 pFast=pFast->next; 29 } 30 return NULL; 31 } 32 //找到环中任意一个结点之后,就能得出环中结点的数目,并找到环的入口结点 33 ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead) 34 { 35 ListNode* meetingNode=MeetingNode(pHead); 36 if(meetingNode==NULL)//没有环 37 return NULL; 38 //计算环中结点数 39 int nodesInLoop=1; 40 ListNode* pNode1=meetingNode; 41 //从相遇的结点开始,一边继续向前移动一边计数,当再次回到这个结点,就统计出了环中节点数 42 while(pNode1->next!=meetingNode) 43 { 44 pNode1=pNode1->next; 45 ++nodesInLoop; 46 } 47 //接下来找链表环的入口结点 48 //分三步: 49 //第一步:指针p1和p2初始化时都指向链表头结点 50 //第二步:由于环中有nodesInLoop个结点,指针p1先在链表上向前移动nodesInLoop步 51 //第三步:指针p1和p2以相同速度移动,直到相遇,相遇结点就是环的入口结点 52 pNode1=pHead; 53 for(int i=0;i<nodesInLoop;++i) 54 pNode1=pNode1->next; 55 ListNode* pNode2=pHead; 56 while(pNode1!=pNode2) 57 { 58 pNode1=pNode1->next; 59 pNode2=pNode2->next; 60 } 61 return pNode1; 62 } 63 };
7.删除链表中重复的结点
在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针。
例如,链表1->2->3->3->4->4->5 处理后为 1->2->5
1 /* 2 struct ListNode { 3 int val; 4 struct ListNode *next; 5 ListNode(int x) : 6 val(x), next(NULL) { 7 } 8 }; 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public: 12 ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* pHead) 13 { 14 if(pHead==nullptr) 15 return pHead; 16 ListNode dummy(INT_MIN);//头结点 17 dummy.next=pHead; 18 ListNode *prev=&dummy,*cur=pHead; 19 while(cur!=nullptr){ 20 bool duplicates=false; 21 while(cur->next!=nullptr&&cur->val==cur->next->val) 22 { 23 duplicates=true; 24 ListNode *tmp=cur; 25 cur=cur->next; 26 delete tmp; 27 } 28 if(duplicates) 29 { 30 //删除重复的最后一个元素 31 ListNode *tmp=cur; 32 cur=cur->next; 33 delete tmp; 34 continue; 35 } 36 prev->next=cur; 37 prev=prev->next; 38 cur=cur->next; 39 } 40 prev->next=cur; 41 return dummy.next; 42 } 43 };
8.二叉树的下一个结点
给定一个二叉树和其中的一个结点,请找出中序遍历顺序的下一个结点并且返回。注意,树中的结点不仅包含左右子结点,同时包含指向父结点的指针。
分析二叉树的下一个节点,一共有以下情况:
1.二叉树为空,则返回空;
2.节点右孩子存在,则设置一个指针从该节点的右孩子出发,一直沿着指向左子结点的指针找到的叶子节点即为下一个节点;
3.节点不是根节点。如果该节点是其父节点的左孩子,则返回父节点;否则继续向上遍历其父节点的父节点,重复之前的判断,返回结果。
1 /* 2 struct TreeLinkNode { 3 int val; 4 struct TreeLinkNode *left; 5 struct TreeLinkNode *right; 6 struct TreeLinkNode *next; 7 TreeLinkNode(int x) :val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) { 8 9 } 10 }; 11 */ 12 class Solution { 13 public: 14 TreeLinkNode* GetNext(TreeLinkNode* pNode) 15 { 16 if(pNode==NULL) 17 return NULL; 18 TreeLinkNode* pNext=NULL; 19 if(pNode->right!=NULL) 20 { 21 TreeLinkNode* pRight=pNode->right; 22 while(pRight->left!=NULL) 23 pRight=pRight->left; 24 pNext=pRight; 25 } 26 else if(pNode->next!=NULL) 27 { 28 TreeLinkNode* pCurrent=pNode; 29 TreeLinkNode* pParent=pNode->next; 30 while(pParent!=NULL&&pCurrent==pParent->right) 31 { 32 pCurrent=pParent; 33 pParent=pParent->next; 34 } 35 pNext=pParent; 36 } 37 return pNext; 38 } 39 };
9.对称二叉树
1 /* 2 struct TreeNode { 3 int val; 4 struct TreeNode *left; 5 struct TreeNode *right; 6 TreeNode(int x) : 7 val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { 8 } 9 }; 10 */ 11 12 class Solution { 13 public: 14 bool help(TreeNode *root1,TreeNode *root2) 15 { 16 if(root1==0) 17 return root2==0; 18 if(root2==0) 19 return false; 20 return(root1->val==root2->val)&&help(root1->left,root2->right)&&help(root1->right,root2->left); 21 } 22 bool isSymmetrical(TreeNode *root) 23 { 24 if(root==0){ 25 return true; 26 } 27 return help(root->left,root->right); 28 } 29 };
10.按之字顺序打印二叉树
请实现一个函数按照之字形打印二叉树,即第一行按照从左到右的顺序打印,第二层按照从右至左的顺序打印,第三行按照从左到右的顺序打印,其他行以此类推。
1 /* 2 struct TreeNode { 3 int val; 4 struct TreeNode *left; 5 struct TreeNode *right; 6 TreeNode(int x) : 7 val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { 8 } 9 }; 10 */ 11 class Solution { 12 public: 13 vector<vector<int> > Print(TreeNode* pRoot) 14 { 15 vector<vector<int>> vv; 16 if(pRoot == NULL) 17 return vv; 18 deque<TreeNode *> q; 19 q.push_back(pRoot); 20 bool flag = true;//true表示从左向右存储层次遍历,否则是从右向左 21 int levelCnt = 1;//上一层的节点数目 22 int curLevelCnt = 0;//下一层节点数目 23 vector<int> v; 24 while(!q.empty()) 25 { 26 TreeNode *cur; 27 if(flag) 28 { 29 cur = q.front(); 30 q.pop_front(); 31 } 32 else 33 { 34 cur = q.back(); 35 q.pop_back(); 36 } 37 if(flag) 38 { 39 if(cur->left) 40 { 41 q.push_back(cur->left); 42 ++curLevelCnt; 43 } 44 if(cur->right) 45 { 46 q.push_back(cur->right); 47 ++curLevelCnt; 48 } 49 } 50 else 51 { 52 if(cur->right) 53 { 54 q.push_front(cur->right); 55 ++curLevelCnt; 56 } 57 if(cur->left) 58 { 59 q.push_front(cur->left); 60 ++curLevelCnt; 61 } 62 } 63 v.push_back(cur->val); 64 --levelCnt; 65 if(levelCnt == 0) 66 {//这一层完毕 67 vv.push_back(v); 68 v.clear(); 69 levelCnt = curLevelCnt; 70 curLevelCnt = 0; 71 flag = !flag; 72 } 73 } 74 return vv; 75 } 76 };
11.把二叉树打印成多行
从上到下按层打印二叉树,同一层结点从左至右输出。每一层输出一行。
1 /* 2 struct TreeNode { 3 int val; 4 struct TreeNode *left; 5 struct TreeNode *right; 6 TreeNode(int x) : 7 val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { 8 } 9 }; 10 */ 11 class Solution { 12 public: 13 vector<vector<int> > Print(TreeNode* pRoot) 14 { 15 vector<vector<int> > result; 16 queue<TreeNode*> current,next; 17 if(pRoot==NULL) 18 return result; 19 else 20 current.push(pRoot); 21 while(!current.empty()){ 22 vector<int> level;//元素在一层 23 while(!current.empty()){ 24 TreeNode* node=current.front(); 25 current.pop(); 26 level.push_back(node->val); 27 if(node->left!=NULL) 28 next.push(node->left); 29 if(node->right!=NULL) 30 next.push(node->right); 31 } 32 result.push_back(level); 33 swap(next,current); 34 } 35 return result; 36 } 37 };
12.二叉搜索树的第k个结点
1 /* 2 struct TreeNode { 3 int val; 4 struct TreeNode *left; 5 struct TreeNode *right; 6 TreeNode(int x) : 7 val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { 8 } 9 }; 10 */ 11 class Solution { 12 public: 13 //按照中序遍历的顺序遍历一颗二叉搜索树,遍历序列的数值是递增排序的 14 TreeNode* KthNode(TreeNode* pRoot, int k) 15 { 16 if(pRoot==NULL||k==0) 17 return NULL; 18 return KthNodeCore(pRoot,k); 19 } 20 TreeNode* KthNodeCore(TreeNode* pRoot, int& k) 21 { 22 TreeNode* target=NULL; 23 if(pRoot->left!=NULL) 24 target=KthNodeCore(pRoot->left,k); 25 if(target==NULL) 26 { 27 if(k==1) 28 target=pRoot; 29 k--; 30 } 31 if(target==NULL&&pRoot->right!=NULL) 32 target=KthNodeCore(pRoot->right,k); 33 return target; 34 } 35 };


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号