jaonpath
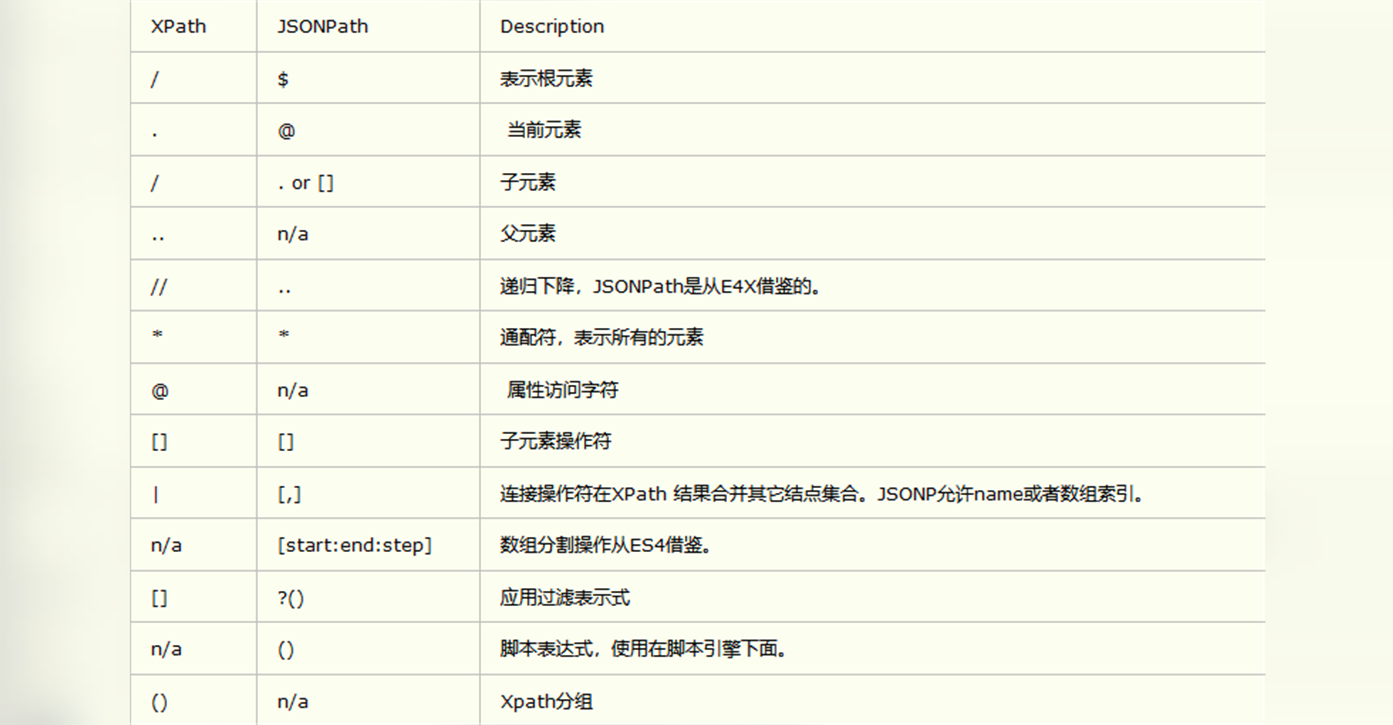

数据提取
使用普通查找:
print(data["store"]["book"][0]["author"] # 找到book下的第一个author
使用jsonpath查找:
print(jsonpath.jsonpath(data, "$..author")) # 所有author节点
print(jsonpath.jsonpath(data, "$.store.book[*].author")) # 所有book的authoe节点
print(jsonpath.jsonpath(data, "$.store.*")) # store下的所有节点,book数组和bicycle节点
print(jsonpath.jsonpath(data, "$.store..price")) # store下的所有price节点
print(jsonpath.jsonpath(data, "$..book[2]")) # 匹配第3个book节点
print(jsonpath.jsonpath(data, "$..book[@. length-1]")) # 匹配倒数第1个book节点 写法一
print(jsonpath.jsonpath(data, "$..book[-1:]")) # 匹配倒数第1个book节点 写法二
print(jsonpath.jsonpath(data, "$..book[:2]")) # 匹配前两个book节点
print(jsonpath.jsonpath(data, "$..book[?(@. isbn]")) # 过滤含isbn字段的节点,找到所有含ISBN的数据
print(jsonpath.jsonpath(data, "$.store.book[?. price<10)]")) # 过滤price<10的节点,找到价格低于10的数据
BS4 https://www.crummy.com/software/BeautifulSoup/bs4/doc/index.zh.html
beautifulsoup bs 是一个从网页中提取数据的包。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html_doc = """ <html> <head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <body> <a href="https://www.baidu.com">百度</a> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <span>this is span tag!</span> <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well. </p> <p class="story science">this is a story</p> </body> """ bs = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, "html.parser") """ 通过标签获取数据 """ # 获取文档的标题 title = bs.title # Tag类型对象 # print(title, type(title)) # print(title.text) # print(bs.title.text) # p = bs.p # 只会拿到文档中的第一个p标签 # print(p, type(p)) # a = bs.a # attrs = a.attrs # 会返回属性的字典 # 链接地址(href对应的值) # print(attrs["href"]) # href的值 # 通过特定的方法来获取标签 find_all # p_list = bs.find_all("p") # # # print(p_list, type(p_list)) # p = p_list[-1] # # print(p, type(p)) # print(p.text, p.attrs["class"]) # p_list = bs.find_all("p", class_="story") # p_list = bs.find_all("p", class_="science") # p = bs.find("p", class_="science") # print(p.text) """ 通过选择器的方式去找到自己想要的标签 """ p = bs.select("p.story.science") #返回的结果是一个列表 p = bs.select_one("p.story.science") # print(p, type(p)) print(p.text, p.attrs["class"])
正则 re https://www.runoob.com/regexp/regexp-metachar.html

xpath https://www.w3school.com.cn/xpath/index.asp









【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理