继承与多态
1.请看以下“变态”的类
public class ParentChildTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent=new Parent();
parent.printValue();
Child child=new Child();
child.printValue();
parent=child;
parent.printValue();
parent.myValue++;
parent.printValue();
((Child)parent).myValue++;
parent.printValue();
}
}
class Parent{
public int myValue=100;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
class Child extends Parent{
public int myValue=200;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
截图:

分析:
当子类与父类拥有一样的方法,并且让一个父类变量引用一个子类对象时,到底调用哪个方法,由对象自己的“真实”类型所决定,这就是说:对象是子类型的,它就调用子类型的方法,是父类型的,它就调用父类型的方法。
对于多态,可以总结它为:
一、使用父类类型的引用指向子类的对象;
二、该引用只能调用父类中定义的方法和变量;
三、如果子类中重写了父类中的一个方法,那么在调用这个方法的时候,将会调用子类中的这个方法;(动态连接、动态调用)
四、变量不能被重写(覆盖),”重写“的概念只针对方法,如果在子类中”重写“了父类中的变量,那么在编译时会报错。
2.
class Mammal{}
class Dog extends Mammal {}
class Cat extends Mammal{}
public class TestCast
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Mammal m;
Dog d=new Dog();
Cat c=new Cat();
m=d;
d=m;
d=(Dog)m;
d=c;
c=(Cat)m;
}
}
执行此代码,程序有误,不能正常运行,在main函数里d=m;这句话不合规则,在继承中,基类不能对子类的对象赋值,而子类可以对基类的对象赋值,非继承关系的两个类再赋值应该先进行强制转化,强制转化也不是每次都可以成功,可以使用instanceof运算符判断一个对象是否可以转换为指定的类型,如果可以,则继续进行。
3.方法覆盖
执行代码:
class Parent{
public void Print()
{
System.out.println("test");
}
}
class Child extends Parent{
public void Print()
{
System.out.println("text");
}
}
public class m {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child a=new Child();
a.Print();
}
}
截图:
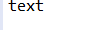
原因分析:在子类中重新声明一个与父类同名同参数的函数,会使父类的函数被子类的覆盖,从而不会被输出出来,
若想调用父类的函数,则必须使用Super来调用。
4.观察输出,注意总结父类与子类之间构造方法的调用关系修改Parent构造方法的代码,显式调用GrandParent的另一个构造函数,注意这句调用代码是否是第一句
class Grandparent
{
public Grandparent()
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");
}
public Grandparent(String string)
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string);
}
}
class Parent1 extends Grandparent
{
public Parent1()
{
super("Hello.Grandparent.");
System.out.println("Parent Created");
// super("Hello.Grandparent.");
}
}
class Child1 extends Parent1
{
public Child1()
{
System.out.println("Child Created");
}
}
public class TestInherits
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Child1 c = new Child1();
}
}
截图:
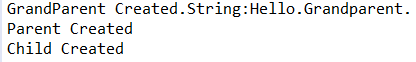
分析:
在类的继承过程中,父类的构造函数也会被子类所继承,当子类创建对象是,会首先调用弗雷德构造函数,随后在调用自身的构造函数。值得注意的是当在子类中显示的调用父类的另一个构造函数是,应该用Super调用,而且,通过 super 调用基类构造方法,必须是子类构造方法中的第一个语句。子类的对象在创建时会先调用父类的构造函数,在调用自身的构造函数,反过来则不行,因为构造函数是用来给类的对象进行初始化的,父类的定义的public和protected函数和变量都会自动被继承到子类中,如果父类不初始化,这些定义在父类的函数和变量不能在子类中使用。



