mongodb 学习笔记
1 //验证环境是否支持 2 if( !extension_loaded( 'mongo' ) ) 3 exit( ' not fonud mongo extentions' . "\n" ); 4 5 if( !class_exists( 'MongoClient' ) ) 6 exit( 'not support mongo' . "\n" );
1 //连接数据库 2 //http://php.net/manual/zh/mongoclient.construct.php 3 try { 4 $mongo = new MongoClient('mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017'); 5 }catch ( \Exception $e ) { 6 exit( $e->getMessage() ); 7 } 8 //选择数据库test,选择test1 ; 不存在在插入数据自动创建 9 $collections = $mongo->selectDB( 'test' )->selectCollection( 'test1' );
1 //具体操作,看手册 http://php.net/manual/zh/mongocollection.insert.php 2 //新增数据 3 $arr = [ 4 'name' => 'joe', 5 'age' => 40, 6 'pages' => 10 7 ]; 8 //通过设置 insert 的第二个参数 [ 'w' => 0 ],res 返回的是布尔值, 9 $res = $collections->insert( $arr ); 10 11 var_dump( $res );
返回值: 服务器之间查看:
服务器之间查看: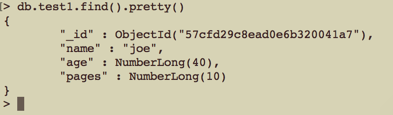
1 //修改 2 //直接修改,即找到对应信息,将其直接替换为 new_data; w => 0 也是返回为布尔值,但感觉不好用,第三个参数 upsert 匹配到了则更新,否则新增; multiple 批量 3 $where = [ 'name' => 'joe' ]; 4 $new_data = [ 'name' => 'joe modify' ]; 5 $res = $collections->update( $where, $new_data, ['w' => 0] ); 6 var_dump( $res );
原数据: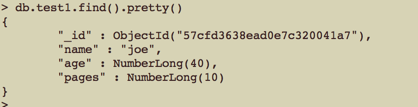 更新后
更新后 
1 //使用 $set “用来指定一个键的值,如果这个键不存在,则创建它,这对更新模式或者增加用户定义键 非常方便” 2 $where = [ 'name' => 'joe modify' ]; 3 $new_data = [ '$set' => ['name' => 'joe', 'age' => 39, 'pages' => "10"]]; 4 $res = $collections->update( $where, $new_data, ['w' => 0] ); 5 var_dump( $res );
原数据: 更新后:
更新后:
1 //使用 $inc "用来增加已有键的值,或者在键不存在时创建一个键,对于分析数据,因果关系,投票或者其他数据变化的地方,都非常有用" 对int类型结果进行增减 3/+3 是一样的;对字符串类型的进行inc操作,会报异常 2 $where = [ 'name' => 'joe' ]; 3 $new_data = [ '$inc' => ['age' => +3 ] ]; 4 $res = $collections->update( $where, $new_data ); 5 var_dump( $res );
更新前: 更新后:
更新后: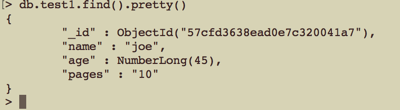
1 //数组修改器 $push “会向已有的数组末尾加入一个元素,要是没有就会创建一个新的数组” 2 $where = [ 'name' => 'joe' ]; 3 $new_data = [ '$push' => [ 'friends' => ['lily','angly', 'mike'] ] ]; 4 $res = $collections->update( $where, $new_data ); 5 var_dump( $res );
更新前: 更新后:
更新后: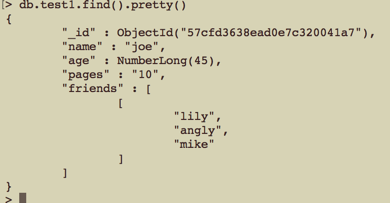
1 //如果一个值不在数组中就把它添加进去 2 $where = [ 'name' => 'joe' ]; 3 $new_data = [ '$addToSet' => ['friends'=> 'oby' ] ]; 4 $res = $collections->update( $where, $new_data ); 5 var_dump( $res );
更新前: 更新后:
更新后: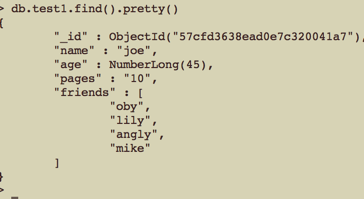
1 //如果想一次添加多个不存在的值,可以使用each 2 $where = ['name'=> 'joe']; 3 $new_data = [ '$addToSet' => [ 'friends' => [ '$each' => ['a','b','c','oby','lily'] ] ]]; 4 $res = $collections->update( $where, $new_data ); 5 var_dump( $res );
更新前: 更新后:
更新后: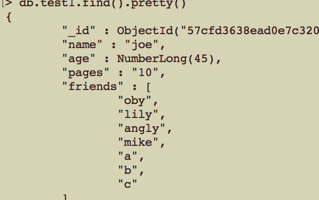
1 //$pop 从数组的任何一端删除元素 1 表示从数组的尾部剔除一个;-1 表示从数组的头部 2 $where = ['name' => 'joe']; 3 $new_data = [ '$pop' => ['friends' => 1] ]; 4 $res = $collections->update( $where, $new_data ); 5 var_dump( $res );
更新前: 更新后:
更新后: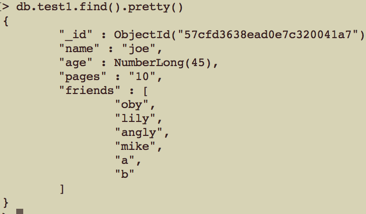
1 //$pull 根据指定条件,删除数组的成员,pull会将所匹配的成员全部删掉,[1,2,1,1] 如果匹配1,那么数组最后只剩2 2 $where = [ 'name' => 'joe' ]; 3 $new_data = [ '$pull' => ['friends' => 'lily'] ]; 4 $res = $collections->update( $where, $new_data ); 5 var_dump( $res );
更新前: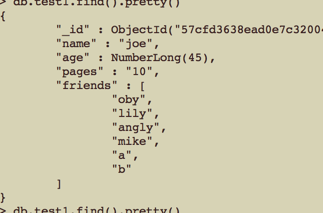 更新后:
更新后:
1 //数组定位器 ,用来定位查询文档已经匹配的元素,并进行更新 ,定位符只能更新第一个匹配的元素,如果有多少,只更新第一个 2 $where = [ 'arrs.a' => 4]; 3 $new_data = [ '$set' => ['arrs.$.a' => 3] ]; 4 $res = $collections->update( $where, $new_data ); 5 var_dump( $res );
更新前: 更新后:
更新后: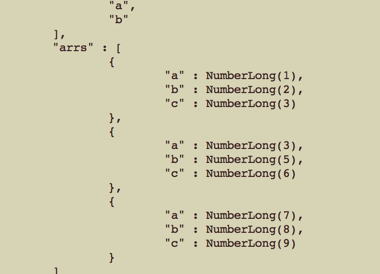
1 //findandmodify 更新/删除 一个文档 并返回文档 2 //remove false 表示不删除;new false 表示返回更新前数据,之前没有数据 返回 null;upsert true 如果条件没有找到,则新增 3 //执行的是新增操作 4 $where = [ 'name' => 'joe' ]; 5 $new_data = [ '$set' => ['pages' => 400] ]; 6 $res = $collections->findAndModify( $where, $new_data, [], ['new' => false, 'remove' => false,'upsert' => true] ); 7 var_dump( $res );
更新前: 更新后:
更新后:
1 //执行的是更新操作 2 $where = [ 'name' => 'joe' ]; 3 $new_data = [ '$set' => ['pages' => 4] ]; 4 $res = $collections->findAndModify( $where, $new_data, ['name' => 1, 'pages' => 1] ); 5 var_dump( $res );
更新前: 更新后:
更新后:
1 //执行的是删除操作 2 $where = [ 'name' => 'joe' ]; 3 $res = $collections->findAndModify( $where, null, null, ['remove' => true] ); 4 var_dump( $res );
更新前: 更新后:
更新后:
1 //find 查询操作 http://php.net/manual/zh/mongocollection.find.php 2 //根据条件查找所有 3 $where = ['gender' => 'female']; 4 $res = $collections->find( $where ); 5 var_dump( $res->count() ); 6 7 //指定返回的键 8 $where = ['name' => 'joe']; 9 $fields = ['name' => 1, '_id' => 0]; 10 $res = $collections->find( $where, $fields ); 11 if( $res->hasNext() ) 12 var_dump( $res->getNext() ); 13 14 //$lt $lte $gt $gte $ne 比较操作符 分别是 < <= > >= != 15 $where = ['age' => ['$gt' => 27] ]; 16 $res = $collections->find( $where ); 17 var_dump( $res->count() ); 18 19 $where = ['name' => ['$gt' => 'z']];//字母排序 20 $res = $collections->find( $where ); 21 var_dump( iterator_to_array( $res ) ); 22 23 //$in $nin 范围查询 24 $where = [ 'age' => ['$in' => [29,32,27,28] ] ]; 25 $res = $collections->find( $where ); 26 var_dump( iterator_to_array( $res ) );
1 //$or 查询 2 $where = ['$or' => [ ['age' => 27],['name' => 'lili'] ]]; 3 $res = $collections->find( $where ); 4 var_dump( iterator_to_array( $res ) ); 5 6 7 //$or 可以包含其他条件语句 8 $where = [ '$or' => [ ['age' => ['$in' => [32,33,34] ] ], ['name' => 'joe'] ]]; 9 $res = $collections->find( $where ); 10 var_dump( iterator_to_array( $res ) ); 11 12 //$mod 余数 将查询的值跟第一个数求余,等于第二个数的就被帅选处理 例如 age 为1,6,11 的 13 $where = ['age' => [ '$mod' => [5,1] ] ]; 14 $res = $collections->find( $where ); 15 var_dump( iterator_to_array( $res ) ); 16 17 //$not 是元条件j句,即可以用在其他条件之上 18 $where = [ 'age' => ['$not' => ['$mod' => [5,1]]]]; 19 $res = $collections->find( $where ); 20 var_dump( iterator_to_array( $res ) );
条件句的规则:
如果比较更新修改器跟查询文档,会发现以“$”开头的键处在不同的位置。在查询中,“$lt”在内层文档,而在更新中"$inc"则是外层文档的键。基本可以肯定:条件句是内层文档的键,而修改器是外层文档的键。
可对一个键应用多个条件,例如,查找年龄在20-30直接的用户,可以在age上使用$lt,$gt: $where = [ 'age' => [ '$lt' => 30, '$gt' => 20] ];
一个键可以有多个条件,但是不能对应多个更新修改器。例如 修改文档不能同时包含 [ '$inc' => ['age' => 1], '$set' => [ 'age' => 40] ]
1 // null null 不仅仅匹配自身,而且匹配“不存在的”,所以这种匹配会返回缺少这个键的文档;如果仅仅匹配值为null,既要检查该键是否为null,还要通过“$exists”p判断该键是否存在 2 $where = [ 'frind' => [ '$in' => [null], '$exists' => true]]; 3 $res = $collections->find( $where ); 4 var_dump( iterator_to_array( $res ) ); 5 6 //正则表达式 7 $where = [ 'name' => new MongoRegex( '/joe/i' )]; 8 $res = $collections->find( $where ); 9 var_dump( iterator_to_array( $res ) ); 10 11 //查询数组 f是数组的键;a 数组的值;同时也查询出有相关条件的信息 12 $where = [ 'f' => 'a' ]; 13 $res = $collections->find( $where ); 14 var_dump( iterator_to_array( $res ) ); 15 16 //$all 通过多个元素匹配数组 ['f' => ['$all'=>['c']]] = ['f'=>'c'] 17 $where = [ 'f' => ['$all' => ['c','d'] ] ]; 18 $res = $collections->find( $where ); 19 var_dump( iterator_to_array( $res ) ); 20 21 22 //精准匹配数组的元素 23 $where = [ 'f' => ['a','b','c']]; 24 $res = $collections->find( $where ); 25 var_dump( iterator_to_array( $res ) ); 26 27 //查询数组指定位置的元素 28 $where = [ 'f.2' => 'c']; 29 $res = $collections->find( $where ); 30 var_dump( iterator_to_array( $res ) ); 31 32 33 //查询数组的个数 size不能跟其他查询子句组合(比如"$gt")但这种查询可以通过文档中增加一个size键来实现 34 $where = ['f' => ['$size' => 4]]; 35 $res = $collections->find( $where ); 36 var_dump( iterator_to_array( $res ) ); 37 38 39 //$slice 返回数组的一个子集合; 2 表示 前2个;-2 表示 后两个;[1,2] 表示从第一个开始,取两个 40 $where = [ 'name' => 'joe' ]; 41 $res = $collections->find( $where, ['f' => ['$slice' => [2,2]]] ); 42 var_dump( iterator_to_array( $res ) );
来源:mongodb权威指南


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号