源码之Integer
一、由Integer对象的比较引出的一系列深思
public static void main(String[] args) { Integer i1 = 127; Integer i2 = 127; Integer i3 = 128; Integer i4 = 128; Integer i5 = new Integer(127); Integer i6 = new Integer(128); System.out.println(i1==i2); System.out.println(i3==i4); System.out.println(i3.equals(i4)); System.out.println(i1.equals(i5)); System.out.println(i1==i5); System.out.println(i3==i6); System.out.println(i3.equals(i6)); }

true false true true false false true
是不是很疑惑?答案和我想的也不太一样
1、首先要了解一下java的装箱和拆箱,
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer i = 10; int n = i; } }
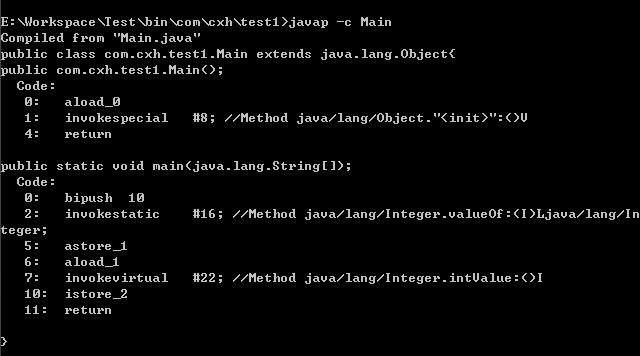
从反编译得到的字节码内容可以看出,在装箱的时候自动调用的是Integer的valueOf(int)方法。而在拆箱的时候自动调用的是Integer的intValue方法。
其他的也类似,比如Double、Character,不相信的朋友可以自己手动尝试一下。
因此可以用一句话总结装箱和拆箱的实现过程:
装箱过程是通过调用包装器的valueOf方法实现的,而拆箱过程是通过调用包装器的 xxxValue方法实现的。(xxx代表对应的基本数据类型)。海子的原文

1 //boolean原生类型自动装箱成Boolean 2 public static Boolean valueOf(boolean b) { 3 return (b ? TRUE : FALSE); 4 } 5 6 7 //byte原生类型自动装箱成Byte 8 public static Byte valueOf(byte b) { 9 final int offset = 128; 10 return ByteCache.cache[(int)b + offset]; 11 } 12 13 14 //short原生类型自动装箱成Short 15 public static Short valueOf(short s) { 16 final int offset = 128; 17 int sAsInt = s; 18 if (sAsInt >= -128 && sAsInt <= 127) { // must cache 19 return ShortCache.cache[sAsInt + offset]; 20 } 21 return new Short(s); 22 } 23 24 //char原生类型自动装箱成Character 25 public static Character valueOf(char c) { 26 if (c <= 127) { // must cache 27 return CharacterCache.cache[(int)c]; 28 } 29 return new Character(c); 30 } 31 32 //int原生类型自动装箱成Integer 33 public static Integer valueOf(int i) { 34 if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high) 35 return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)]; 36 return new Integer(i); 37 } 38 39 //long原生类型自动装箱成Long 40 public static Long valueOf(long l) { 41 final int offset = 128; 42 if (l >= -128 && l <= 127) { // will cache 43 return LongCache.cache[(int)l + offset]; 44 } 45 return new Long(l); 46 } 47 48 //double原生类型自动装箱成Double 49 public static Double valueOf(double d) { 50 return new Double(d); 51 } 52 53 54 //float原生类型自动装箱成Float 55 public static Float valueOf(float f) { 56 return new Float(f); 57 }
2、Integer的valueOf
public static Integer valueOf(int i) { if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high) return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)]; return new Integer(i); } //low = -128 //high = 127 好像可以通过 JVM 的启动参数 -XX:AutoBoxCacheMax=size 修改
//当valueOf入参在[-128,127]时直接从IntegerCache返回一个Integer对象,其他则直接new一个
//IntegerCache就是Integer的缓存,把经常用到的对象([-128,127])先new出来,方便直接取

1 private static class IntegerCache { 2 static final int low = -128; 3 static final int high; 4 static final Integer cache[]; 5 6 static { 7 // high value may be configured by property 8 int h = 127; 9 String integerCacheHighPropValue = 10 sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high"); 11 if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) { 12 try { 13 int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue); 14 i = Math.max(i, 127); 15 // Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE 16 h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1); 17 } catch( NumberFormatException nfe) { 18 // If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it. 19 } 20 } 21 high = h; 22 23 cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1]; 24 int j = low; 25 for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++) 26 cache[k] = new Integer(j++); 27 28 // range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7) 29 assert IntegerCache.high >= 127; 30 } 31 32 private IntegerCache() {} 33 }
其他包装类也有类似的情况
| 基本类型 | 装箱类型 | 取值范围 | 是否缓存 | 缓存范围 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| boolean | Boolean | true, false | 是 | true, false |
| char | Character | \u0000 ~ \uffff | 是 | \u0000 ~ \u007f |
| long | Long | -2^63 ~ (2^63 - 1) | 是 | -128~127 |
| int | Integer | -2^31 ~ (2^31 - 1) | 是 | -128 ~ 127 |
| short | Short | -2^15 ~ (2^15 - 1) | 是 | -128 ~ 127 |
| byte | Byte | -128 ~ 127 | 是 | -128 ~ 127 |
| double | Double | -- | 否 | -- |
| float | Float | -- | 否 | -- |
3、Integer的equals方法
public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (obj instanceof Integer) { return value == ((Integer)obj).intValue(); } return false; }
//Integer重写了Object的equals方法,可见它比较的是Integer的值,而非地址
4、所以开头的答案是不是明了了?
public static void main(String[] args) { Integer i1 = 127; Integer i2 = 127; Integer i3 = 128; Integer i4 = 128; Integer i5 = new Integer(127); Integer i6 = new Integer(128); System.out.println(i1==i2); //对象的==比较的是地址,i1、i2都在[-128,127]内,所以是直接从缓存中取得,当然就是同一个了,地址自然一样 true System.out.println(i3==i4); //128不在缓存中,自己设置high的话就另说了,所以每次都是new的新的对象,所以不是同一个对象 false System.out.println(i3.equals(i4)); //Integer的equals比较的是对象的value值 都是128 所以 true System.out.println(i1.equals(i5)); //i1从缓存中取得,而i5是new的新的对象 然而equals比较的值 所以 true System.out.println(i1==i5); //i1从缓存中取得,而i5是new的新的对象 ==比较的是地址 所以 false System.out.println(i3==i6); //i3和i6都是new的新的对象 false System.out.println(i3.equals(i6)); //比较值 都是128 true }
5、为什么要引入包装类?
1)java是面向对象的语言,所以要为基本数据类型提供包装类,方便调用对象的一些方法
2)方法泛型的使用
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();//正确 ArrayList<int> list1 = new ArrayList<>();//错误



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号