SVM算法应用综合练习-----学习了解数据集和决策函数
SVM算法应用综合练习-----学习了解数据集和决策函数
一.通过LibSVM学习数据集和决策函数格式
1.从LibSVM官方网站下载最新版 LibSVM。
libsvm可以选择主流方式,选择进入官网下载即可,就算不用这个包也需要下载.
2.通过一个最简单的例子开始
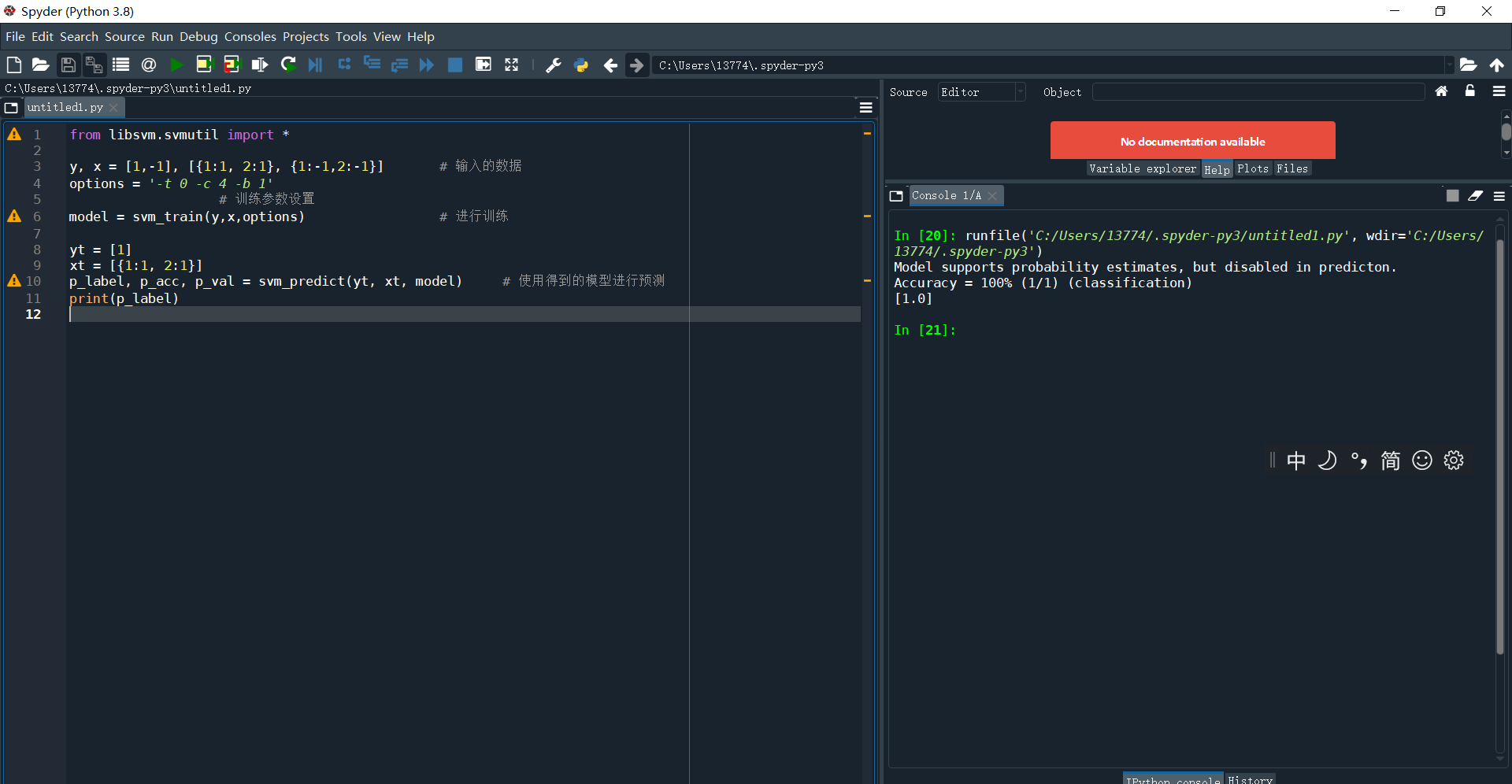
from libsvm.python.svmutil import *
y, x = [1,-1], [{1:1, 2:1}, {1:-1,2:-1}] # 输入的数据
options = '-t 0 -c 4 -b 1' # 训练参数设置
model = svm_train(y,x,options) # 进行训练
yt = [1]
xt = [{1:1, 2:1}]
p_label, p_acc, p_val = svm_predict(yt, xt, model) # 使用得到的模型进行预测
print(p_label)
从文档里获取相关的信息
$$
y: 输入的数据样本对应的标签
x: 输入的样本的属性值,其中每一个样本的格式是一个字典类型,键值对中键是一个索引值,值是对应的数据属性值
options: 训练的一些参数设置,主要有以下的一些设置
-s SVM的类型(svm_type)
0 -- C-SVC(默认) 使用惩罚因子(Cost)的处理噪声的多分类器
1 -- nu-SVC(多分类器) 按照错误样本比例处理噪声的多分类器
2 -- one-class SVM 一类支持向量机,可参见"SVDD"的相关内容
3 -- epsilon-SVR(回归) epsilon支持向量回归 (也就是使用 E-不敏感损失函数进行回归)
4 -- nu-SVR(回归)
-t 核函数类型(kernel_type)
0 -- linear(线性核): u'*v
1 -- polynomial(多项式核): (gammau'v + coef0)^degree
2 -- radial basis function(RBF,径向基核/高斯核): exp(-gamma*|u-v|^2)
3 -- sigmoid(S型核): tanh(gammau'v + coef0)
4 -- precomputed kernel(预计算核): 核矩阵存储在training_set_file中
下面是调整SVM或核函数中参数的选项:
-d 调整核函数的degree参数,默认为3
-g 调整核函数的gamma参数,默认为1/num_features
-r 调整核函数的coef0参数,默认为0
-c 调整C-SVC, epsilon-SVR 和 nu-SVR中的Cost参数,默认为1(就是优化问题中的那个C)
-n 调整nu-SVC, one-class SVM 和 nu-SVR中的错误率nu参数,默认为0.5
-p 调整epsilon-SVR的loss function中的epsilon参数,默认0.1
-m 调整内缓冲区大小,以MB为单位,默认100
-e 调整终止判据,默认0.001
-wi 调整C-SVC中第i个特征的Cost参数
调整算法功能的选项:
-b 是否估算正确概率,取值0 - 1,默认为0
-h 是否使用收缩启发式算法(shrinking heuristics),取值0 - 1,默认为0
-v 交叉校验
-q 静默模式
$$
3.构建数据集并获得决策模型
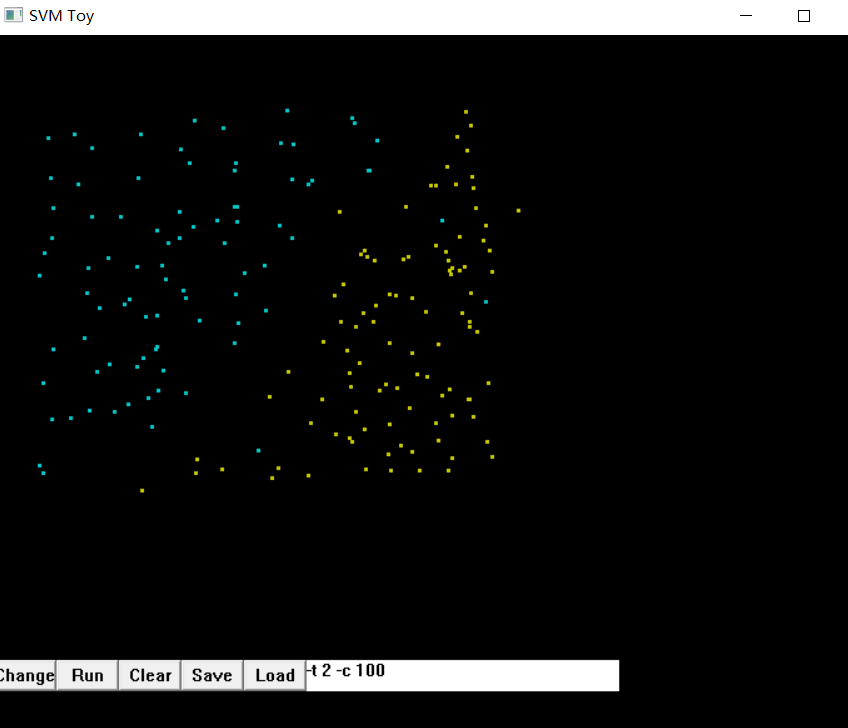
1.从刚刚下载的libsvm中windows文件夹下找到svmtoy,在里面选点,再点击save保存数据
保存下来的文件通过记事本打开发现如下
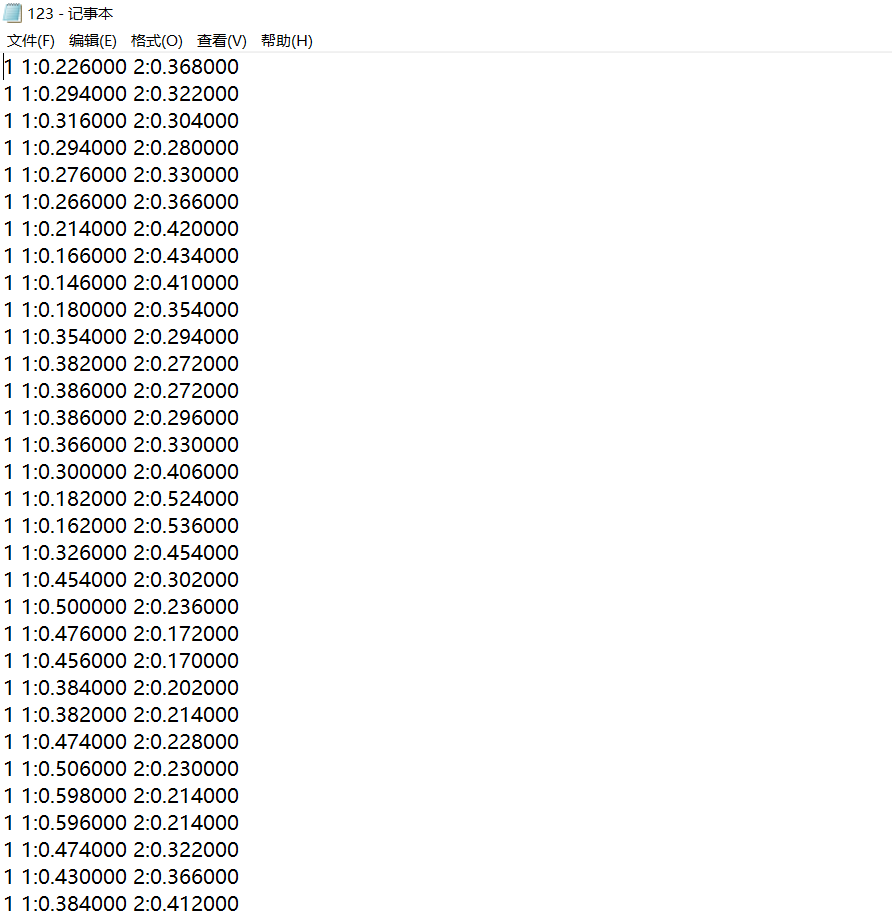
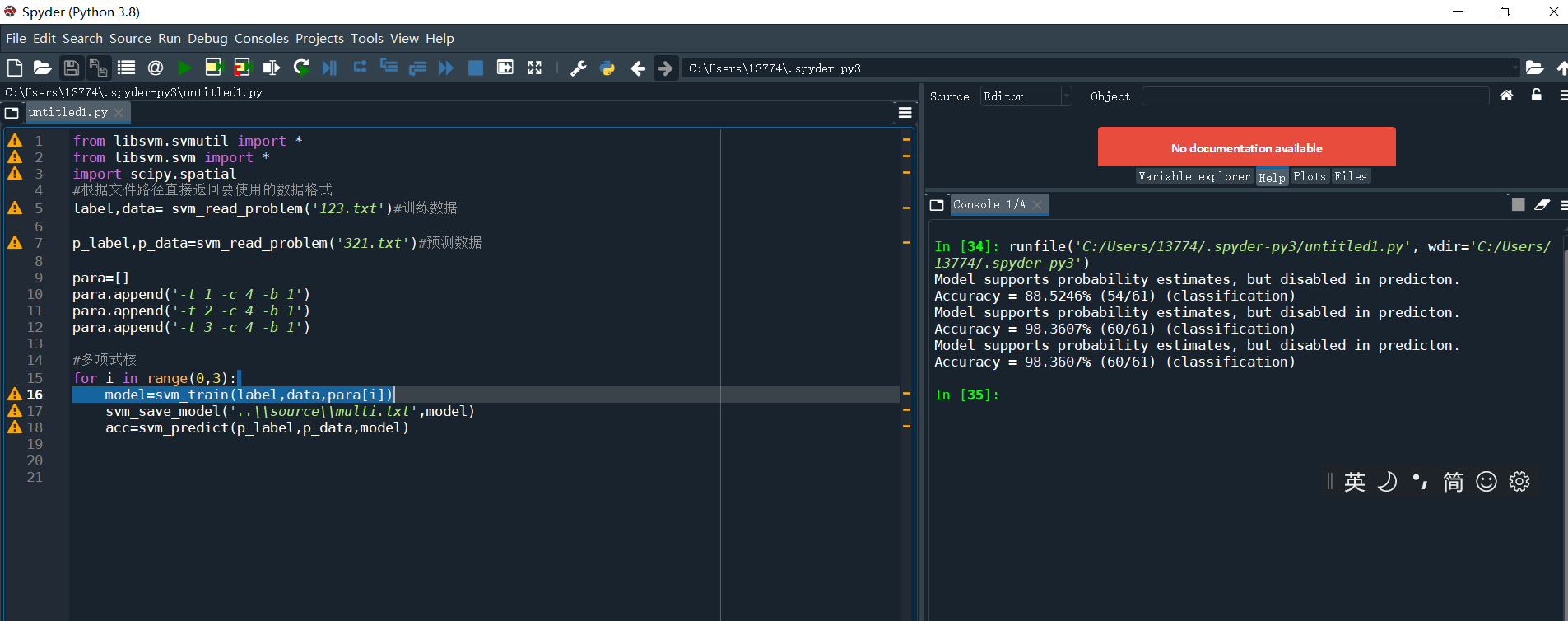
4.用LibSVM工具分别进行线性、多项式、高斯核这三种分类训练
from libsvm.svmutil import *
from libsvm.svm import *
import scipy.spatial
#根据文件路径直接返回要使用的数据格式
label,data= svm_read_problem('123.txt')#训练数据
p_label,p_data=svm_read_problem('321.txt')#预测数据
para=[]
para.append('-t 1 -c 4 -b 1')
para.append('-t 2 -c 4 -b 1')
para.append('-t 3 -c 4 -b 1')
#多项式核
for i in range(0,3):
model=svm_train(label,data,para[i])
svm_save_model('..\\source\\multi.txt',model)
acc=svm_predict(p_label,p_data,model)
3.总结
libsvm的使用与sklearn里的svm使用一样方便,libsvm对于模型的描述相较于sklearn来说更全面一点,不过使用libsvm需要注意数据的格式
二.人脸识别数据集的建立
1.导入包,设置图片存储位置
import cv2
import dlib
import os
import sys
import random
# 存储位置
output_dir = './face/'
size = 64
2.改变图片的亮度与对比度
# 改变图片的亮度与对比度
def relight(img, light=1, bias=0):
w = img.shape[1]
h = img.shape[0]
#image = []
for i in range(0,w):
for j in range(0,h):
for c in range(3):
tmp = int(img[j,i,c]*light + bias)
if tmp > 255:
tmp = 255
elif tmp < 0:
tmp = 0
img[j,i,c] = tmp
return img
3.获取图像或者视频
#使用dlib自带的frontal_face_detector作为我们的特征提取器
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
# 打开摄像头 参数为输入流,可以为摄像头或视频文件
camera = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
#camera = cv2.VideoCapture('C:/Users/CUNGU/Videos/Captures/wang.mp4')
4.定义函数获得人脸检测器和训练好的人脸68特征点检测器,并且获取检测器
#获得默认的人脸检测器和训练好的人脸68特征点检测器
def get_detector_and_predicyor():
#使用dlib自带的frontal_face_detector作为我们的特征提取器
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
"""
功能:人脸检测画框
参数:PythonFunction和in Classes
in classes表示采样次数,次数越多获取的人脸的次数越多,但更容易框错
返回值是矩形的坐标,每个矩形为一个人脸(默认的人脸检测器)
"""
#返回训练好的人脸68特征点检测器
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor('..\\source\\shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat')
return detector,predictor
5.实时读取20张图片,存放到文件夹中
index = 1
while True:
if (index <= 20):#存储15张人脸特征图像
print('Being processed picture %s' % index)
# 从摄像头读取照片
success, img = camera.read()
# 转为灰度图片
gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 使用detector进行人脸检测
dets = detector(gray_img, 1)
for i, d in enumerate(dets):
x1 = d.top() if d.top() > 0 else 0
y1 = d.bottom() if d.bottom() > 0 else 0
x2 = d.left() if d.left() > 0 else 0
y2 = d.right() if d.right() > 0 else 0
face = img[x1:y1,x2:y2]
# 调整图片的对比度与亮度, 对比度与亮度值都取随机数,这样能增加样本的多样性
face = relight(face, random.uniform(0.5, 1.5), random.randint(-50, 50))
face = cv2.resize(face, (size,size))
cv2.imshow('image', face)
cv2.imwrite(output_dir+'/'+str(index)+'.jpg', face)
index += 1
key = cv2.waitKey(30) & 0xff
if key == 27:
break
else:
print('Finished!')
# 释放摄像头 release camera
camera.release()
# 删除建立的窗口 delete all the windows
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
break
6.获取每张图片的特征值计算均值以的到特征数组
# 返回单张图像的 128D 特征,128D特征指的是128维特征向量,是通过68个特征点还原出的人脸计算出的
def return_128d_features(path_img):
img_rd = io.imread(path_img)#读取图片
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_rd, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
faces = detector(img_gray, 1)
print("%-40s %-20s" % ("检测到人脸的图像 / image with faces detected:", path_img), '\n')
# 因为有可能截下来的人脸再去检测,检测不出来人脸了
# 所以要确保是 检测到人脸的人脸图像 拿去算特征
if len(faces) != 0:
shape = predictor(img_gray, faces[0])#获得训练好的人脸68特征点检测器
face_descriptor = face_rec.compute_face_descriptor(img_gray, shape)#获得128维人脸特征向量
else:
face_descriptor = 0
print("no face")
return face_descriptor
# 返回单张图像的 128D 特征
def return_128d_features(path_img):
img_rd = io.imread(path_img)
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_rd, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
faces = detector(img_gray, 1)
print("%-40s %-20s" % ("检测到人脸的图像 / image with faces detected:", path_img), '\n')
# 因为有可能截下来的人脸再去检测,检测不出来人脸了
# 所以要确保是 检测到人脸的人脸图像 拿去算特征
if len(faces) != 0:
shape = predictor(img_gray, faces[0])
face_descriptor = face_rec.compute_face_descriptor(img_gray, shape)
else:
face_descriptor = 0
print("no face")
return face_descriptor
# 将文件夹中照片特征提取出来, 写入 CSV
def return_features_mean_personX(path_faces_personX):
features_list_personX = []
photos_list = os.listdir(path_faces_personX)
if photos_list:
for i in range(len(photos_list)):
# 调用return_128d_features()得到128d特征
print("%-40s %-20s" % ("正在读的人脸图像 / image to read:", path_faces_personX + "/" + photos_list[i]))
features_128d = return_128d_features(path_faces_personX + "/" + photos_list[i])
# print(features_128d)
# 遇到没有检测出人脸的图片跳过
if features_128d == 0:
i += 1
else:
features_list_personX.append(features_128d)
else:
print("文件夹内图像文件为空 / Warning: No images in " + path_faces_personX + '/', '\n')
# 计算 128D 特征的均值
# N x 128D -> 1 x 128D
if features_list_personX:
features_mean_personX = np.array(features_list_personX).mean(axis=0)
else:
features_mean_personX = '0'
return features_mean_personX
7.运行
# 读取某人所有的人脸图像的数据
people = os.listdir(path_images_from_camera)
people.sort()
with open("features2_all.csv", "w", newline="") as csvfile:
writer = csv.writer(csvfile)
for person in people:
print("##### " + person + " #####")
# Get the mean/average features of face/personX, it will be a list with a length of 128D
features_mean_personX = return_features_mean_personX(path_images_from_camera + person)
writer.writerow(features_mean_personX)
print("特征均值 / The mean of features:", list(features_mean_personX))
print('\n')
print("所有录入人脸数据存入 / Save all the features of faces registered into: D:/myworkspace/JupyterNotebook/People/feature/features_all2.csv")
8.运行结果如下图所示