Thesis-一文看尽语义分割中的non-local
一文看尽语义分割中的non-local
Non-local或者说self-attention,由于可以较好的刻画全局信息, 在多种任务中都有不错的表现,在语义分割中也是如此,这里我们列举了13篇相关论文。
包含:
- DANet
- OCNet
- CCNet
- OCRNet
- Interlaced sparse self-attention for semantic segmentation
- Asymmetric non-local neural networks for semantic segmentation
- Co-occurrent features in semantic segmentation
- ACFNet: Attentional class feature network for semantic segmentation
- Dual graph convolutional network for semantic segmentation
- GcNet
- Disentangled non-local neural networks
- ORDNet: Capturing Omni-Range Dependencies for Scene Parsing
- SETR
0 non-local的基本结构
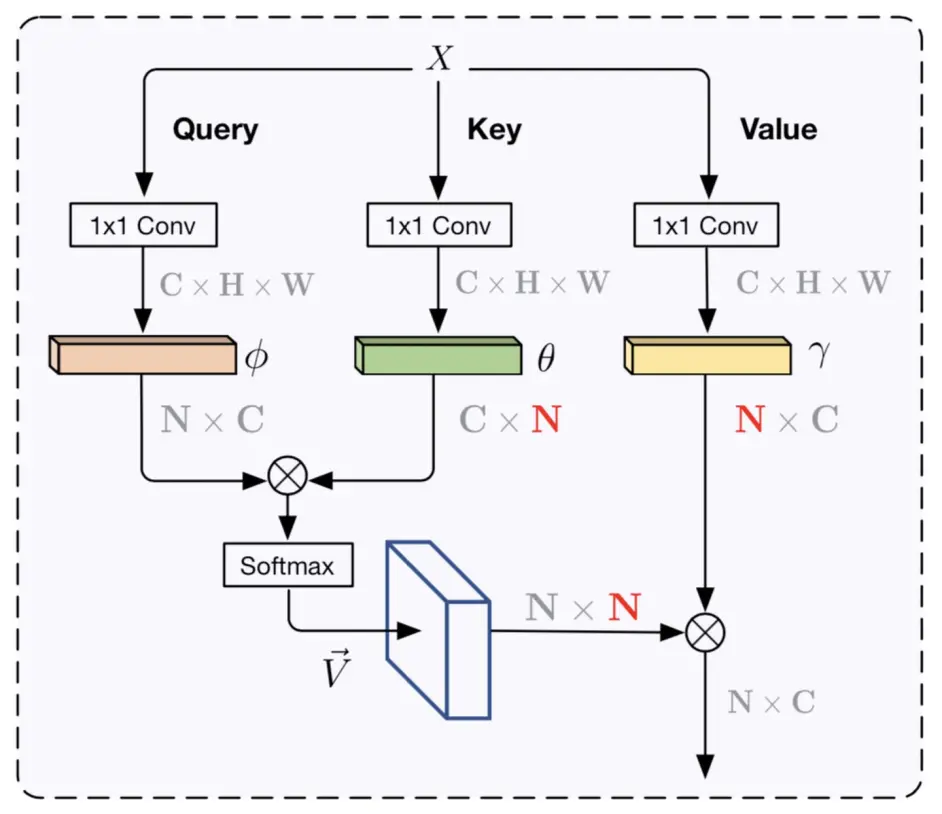 non-local结构[6]
non-local结构[6]
如上图(取自[6]),输入 X 经过三个conv之后 分别得到 value/key/query三个分支, query与key分支reshape之后矩阵乘得到shape为(hw)x(hw)的关系矩阵,然后用softmax得到每一个点与其他所有位置点的关系(attention map或者成为affinity map),value分支reshape之后与attention map相乘即可,输出的结果中每个点的特征都通过attention map与其他所有的点相关,故有了全局的上下文信息。
1. DANET

arxiv.org/pdf/1809.0298
github.com/junfu1115/DA
使用self attention分别对channel 及 spatial两个维度进行特征聚合,以使网络获得所谓的context
网络的结构比较简明,如下图,是将non local用在semantic segmentation方面的早期工作之一
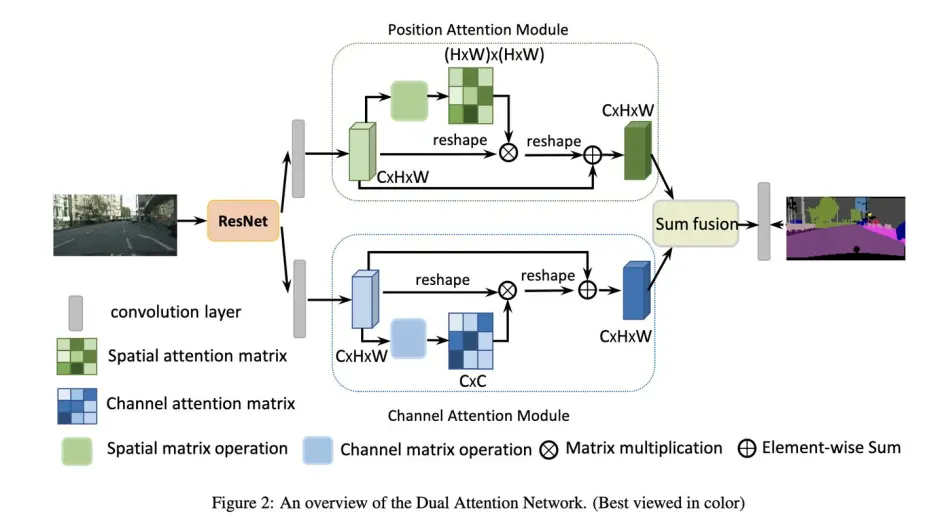
其中的位置注意力和通道注意力结构如下:
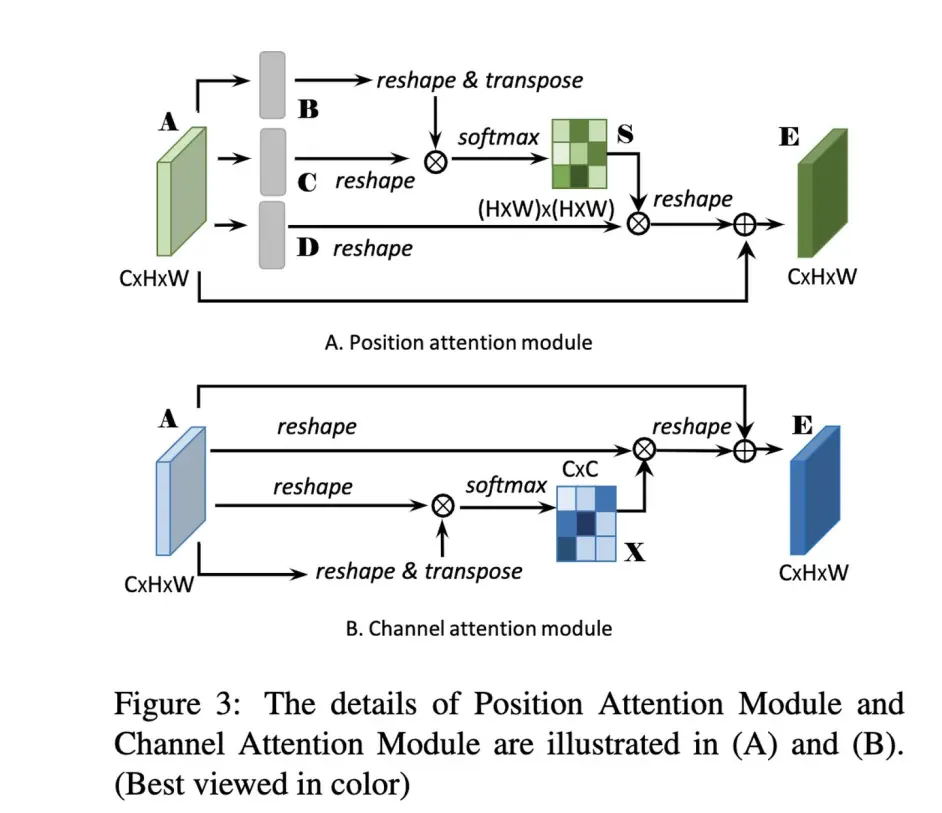
这里就是近似于原本的self-attention实现,在上图中的softmax之前没有除以variance,另外在于A相加之前学了一个比例gamma
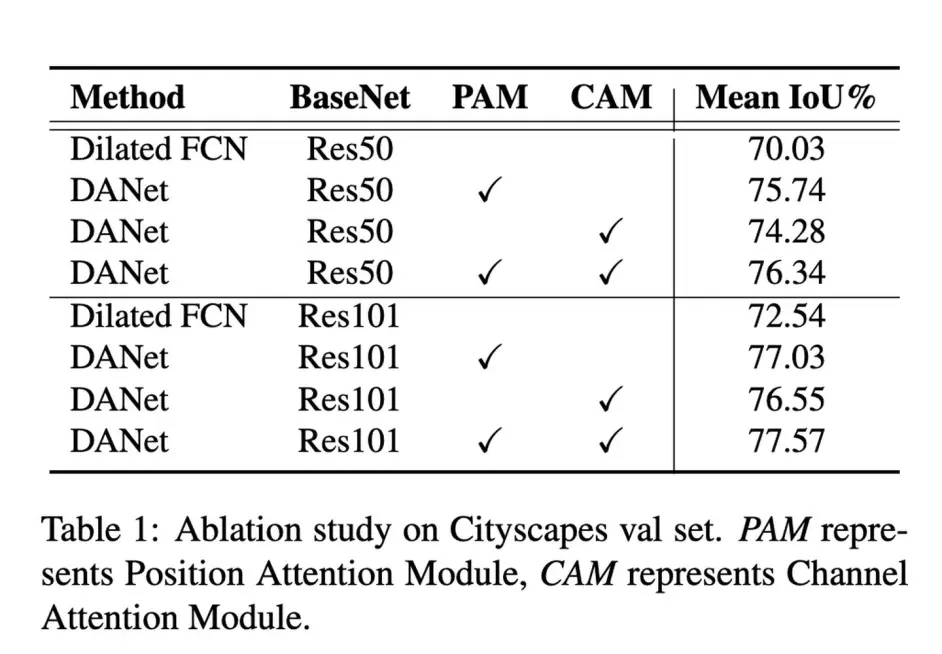
效果如下提升5个点:
2 OCNet

github.com/openseg-grou
arxiv.org/pdf/1809.0091
OCNet是与DAnet同期的文章,也是self-attention的应用,不同之处是探索了与psp及aspp等模块的结合效果

ocp就是self-attention, Pyramid-OC是类似于psp的方法先划分成不同的区域后单独做 self-attention,后面的结果显示这样没有明显的提升,但也没有下降,asp-oc是用ocp代替了原来的gap,效果有提升,具体如下:

3 CCNet

arxiv.org/abs/1811.1172
github.com/speedinghzl/
ccnet是对non-local的加速,non-local中每个位置都会计算与全局的关系,ccnet 通过多次计算当前位置与其同行或者同列的feature的关系,逐步propagation到全局。
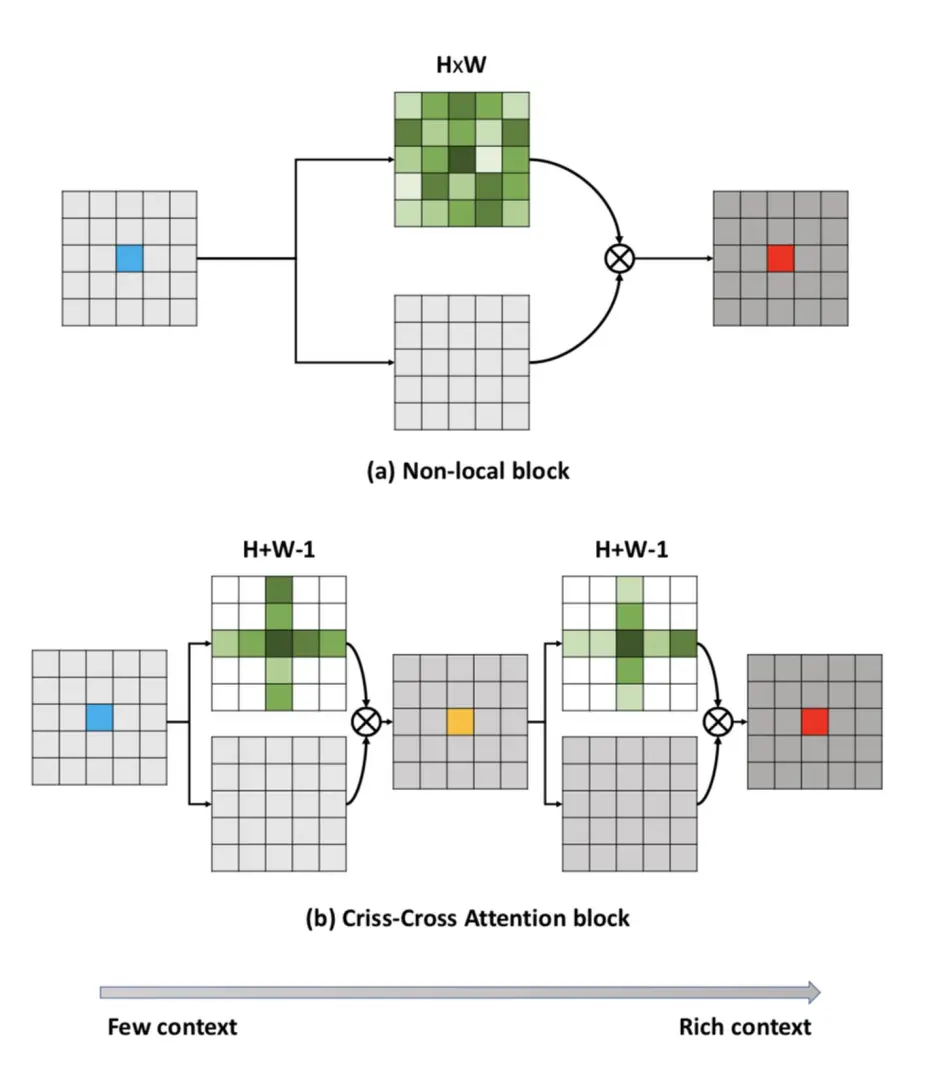
其中criss-cross attention block的结构如下:
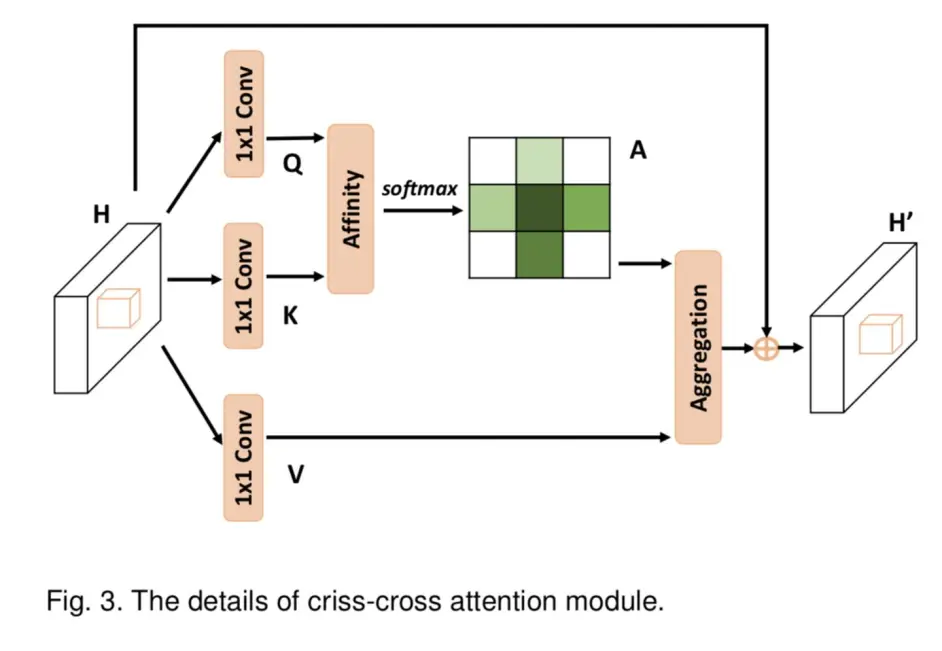
多次叠加使用时信息的传递方式:

蓝色位置的信息第一次loop的时候被传递给浅绿色的位置,第二次loop的时候这些信息传递给了深绿色位置。
由于每个点只关注与(H+W-1)个点的关系,所以计算量会少。
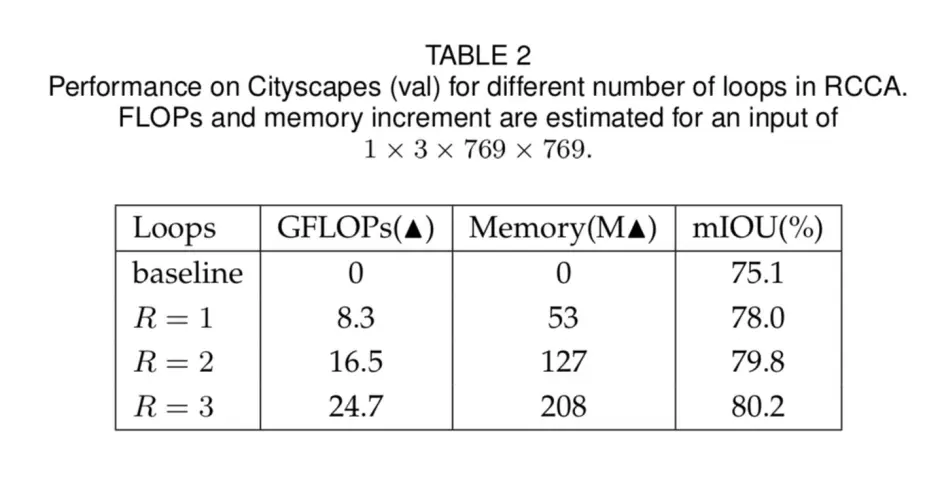
另外叠加criss-cross attention次数越多,效果越好
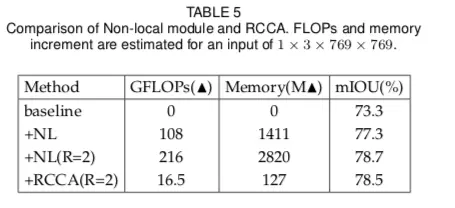
另外CCNET的实现也可以关注下
4 OCRNet

arxiv.org/abs/1909.1106
git.io/HRNet.OCR
通过获取pixel与object region之间的关系得到 object-contextual representation,具体看下图

可能只看上面的pipeline并不能直接与non-local联系起来,但是如果结合下图来看,就可以明白,这里可以看成是改了key,value的纬度,原来(hw)x(hw)的affinity map 变成了现在的(hw)xc,故而计算量也是大大减少了,原来是点两两之间的关系,现在成为了pixel与每个region的关系,这里的region可以理解为不同channel表达特定类别的region
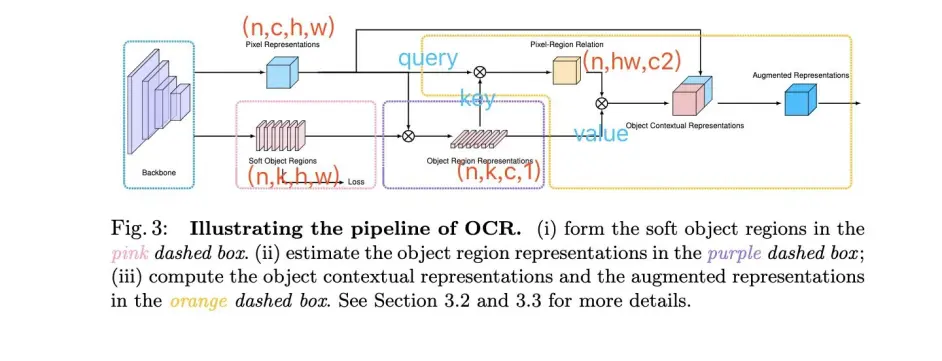
结合上图论文中提出的三个部分就好理解了
- 红色虚线框部分,提取soft object regions
红色部分采用celoss监督,这里的loss有两个点的提升,还是很重要的。feature上在每个channel上做softmax ,得到特定类别(对应channel)的相应区域 - 紫色虚线框部分,估计object region representations
使用上一步经过softmax normalize的结果,对每个位置的representation 做aggregation,也就是矩阵乘 得到object region representation - 黄色框计算object contextual representations 然后augmented representations (non-local)
首先通过query和key得到,每个pixel与region之间的关系(affinity map,也是通过softmax来做norm),然后通过value与affinity map矩阵乘得到object contextual representation
看下结果
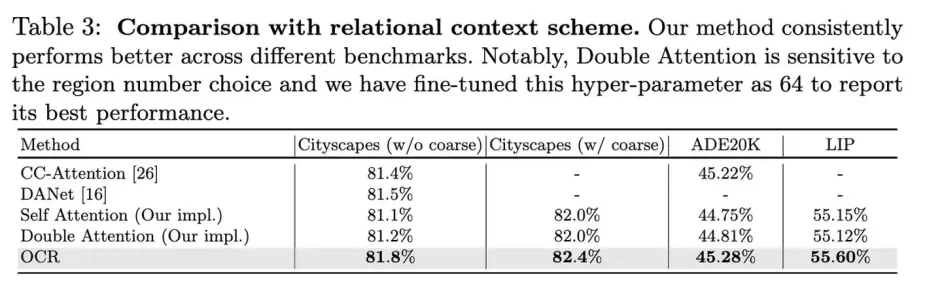
上面提到了double attention,也是可以和non-local对比一下的,原文没做语义分割,就暂且不写了,可以参照下文【文献阅读】A2-Nets: Double Attention Networks
5 Interlaced Sparse Self-Attention for Semantic Segmentation

arxiv.org/abs/1907.1227
这篇文章依然是通过将non-local中费时费力的affinity map分解为多个便于得到的小affinity map,从而起到加速效果

这个图形象的说明了本文将dense的两两之间的关系,转换为了两步:long range和short range
具体如下
实现代码如下:
效果如何呢:
6 Asymmetric Non-local Neural Networks for Semantic Segmentation
arxiv.org/abs/1908.0767
github.com/MendelXu/ANN
同样是通过降低non-local中query和value的纬度降低计算量
作者提出了asymmetric non-local,如下:
简洁明了,主要在如何sample,作者用了多尺度金字塔的方式:
另外还用不同深度的特征结合在一起做花式non-local
看下效果:
7 Co-occurrent Features in Semantic Segmentation
openaccess.thecvf.com/c
在non-local的基础上加了一个gap, 也是早期文章
看图就知道怎么做的了,直接看结果
gap进一步提升了0.5个点
8 ACFNet: Attentional Class Feature Network for Semantic Segmentation

arxiv.org/abs/1909.0940
文章通过引入class-level的context来提升效果
先看整体结构
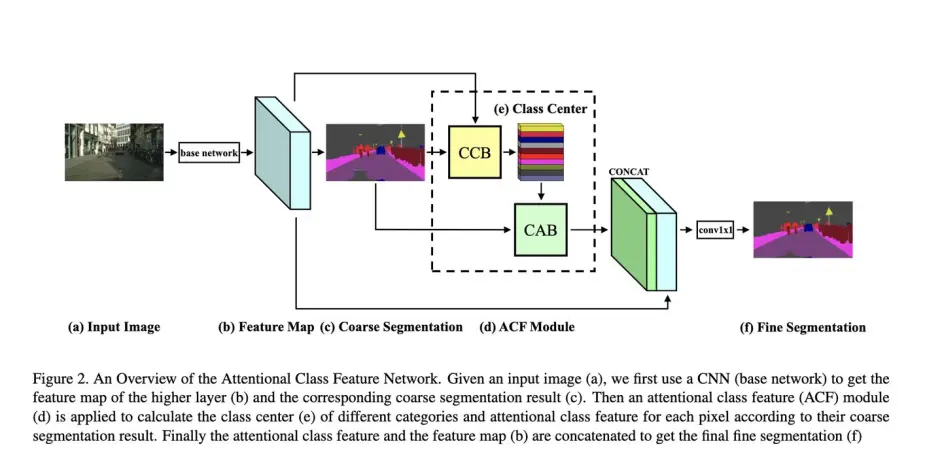
其中部件结构如下:
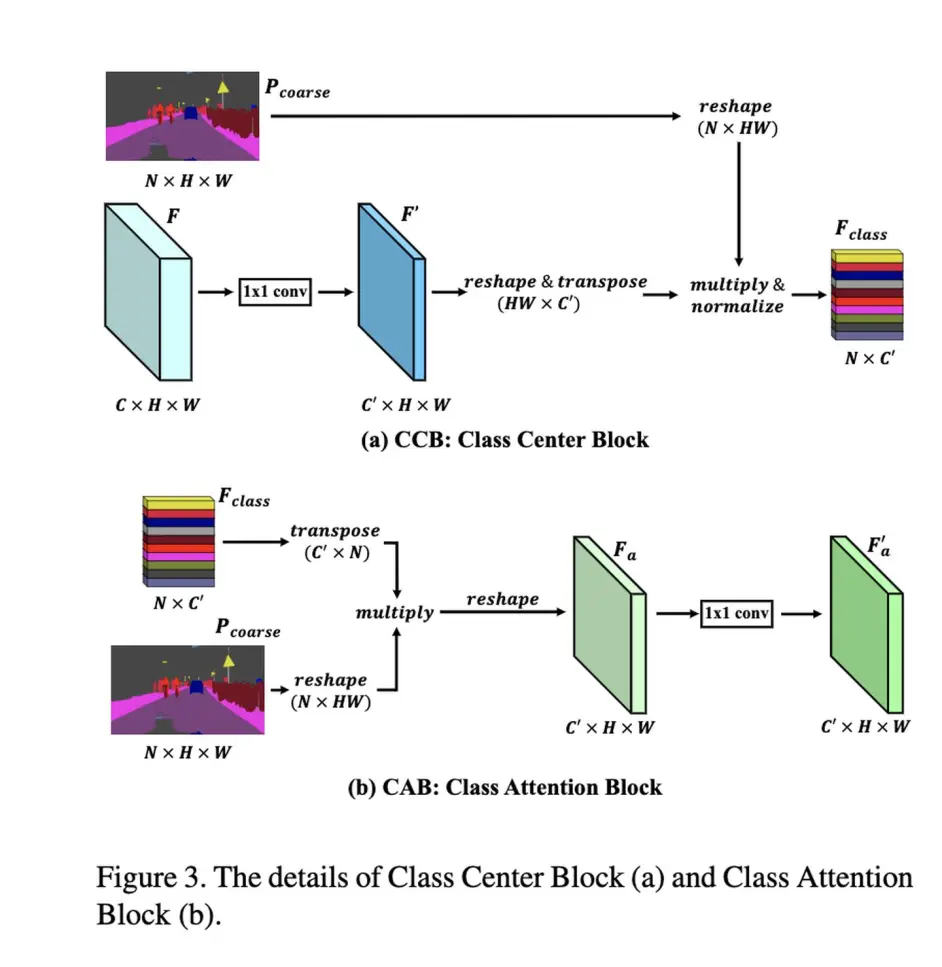
其中Pcoarse是预测的score map,ccb这样得到的每个class center是与全局所有的pixel相关的,这样每个pixel对于其对应的class 就有了对应的关系,利于feature consistency。
这里的normalize就不是softmax了。
与本文不同的是OCR中计算的是Pixel到Region的relation map,这里的attention只是用了class center。
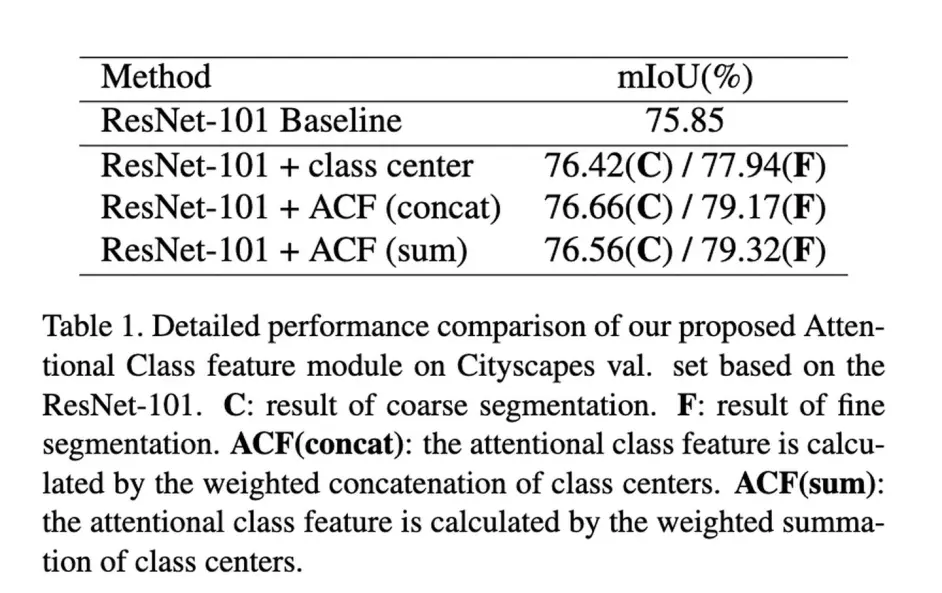
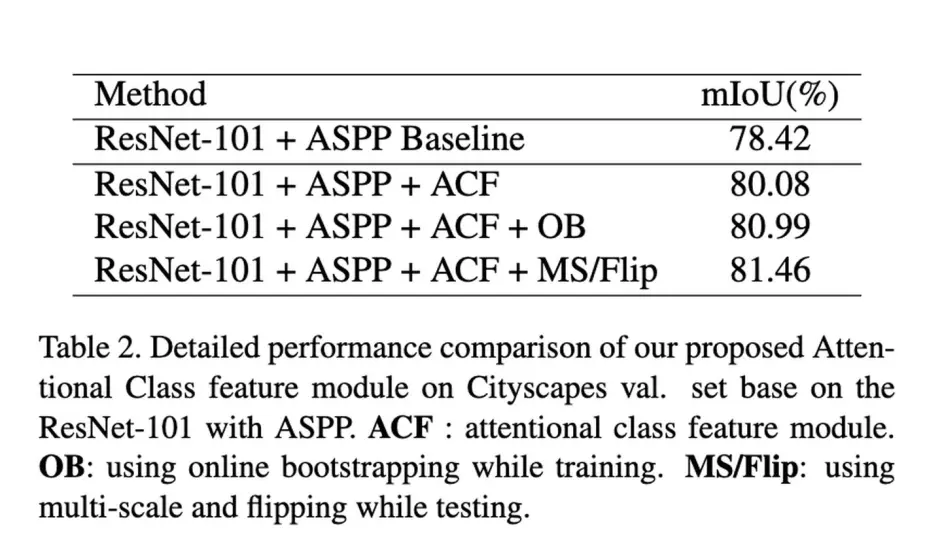
来看下结果,也是有不错的提升,其中表1中的+class center是指直接将其append到每个pixel之后得到的结果。
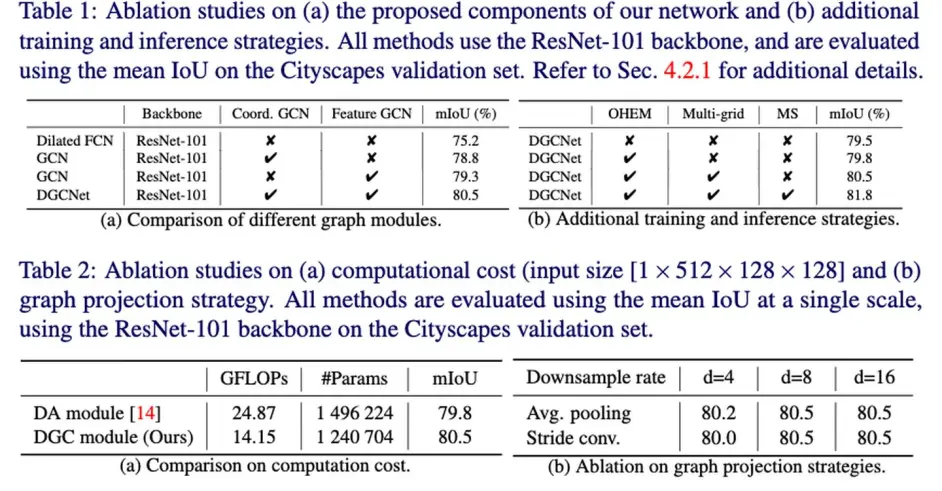
9 Dual Graph Convolutional Network for Semantic Segmentation
arxiv.org/abs/1909.0612
github.com/lxtGH/GALD-D
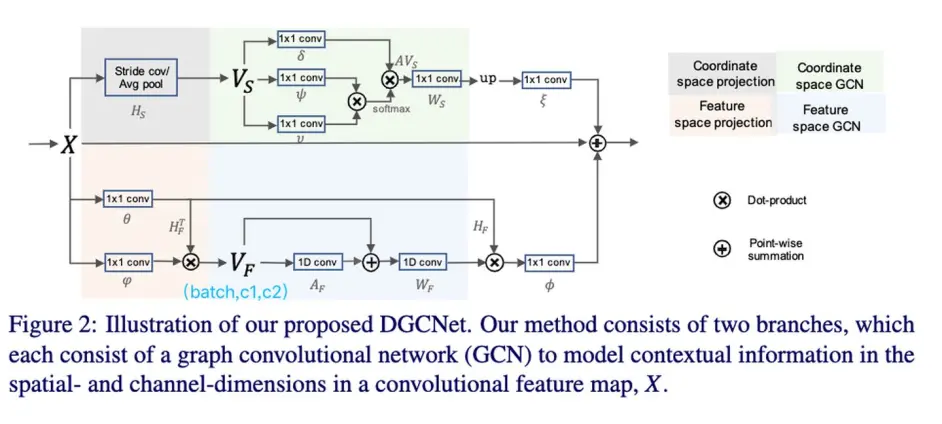
这篇文章可以对照DAnet来看,都是在space和channel两个维度做non-local

non-local就是Gcn中的特例,文中只是downsample之后再进行non-local,而且效果更好。但是channel维度上并不是先进行降维。channel(也就是文章中说的feature space)加了一个laplacian smoothing(Wf作为训练的权重),似乎没有关于这个laplacian smoothing的 ablation。
10 Global Context Networks

arxiv.org/pdf/2012.1337
github.com/xvjiarui/GcN
本文观察到在出segmentation之外的任务中,non-local呈现出的attention 在不同位置都近似,因而改进了non-local
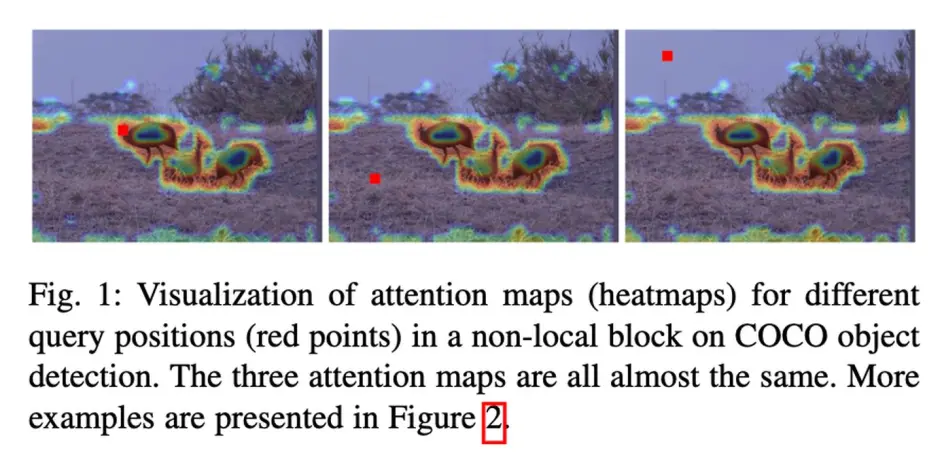

以检测任务为例在,在上图三个不同位置的attention map都呈现相同的pattern
于是作者提出了以下结构:
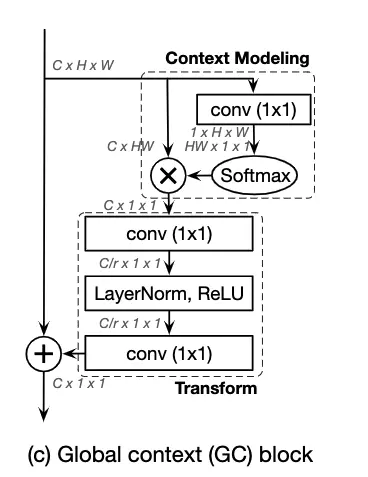
可以看到最后的输出与senet相同变成了cx1x1;值得注意的是作者在实验中发现fusion的方式(相加或者相乘)对效果影响很大,因为这里主要探讨segmentation,所以只贴一下segmentation的结果

11 Disentangled Non-Local Neural Networks

arxiv.org/abs/2006.0666
github.com/yinmh17/DNL-
该文继承自上一篇GcN,认为non-local除了刻画像素间的两两关系也刻画了像素的显著性,分别记为pairwise与unary,并且证明了两者同时学习的时候会造成相互影响,于是对其进行了解耦
该文提出的结构如下:
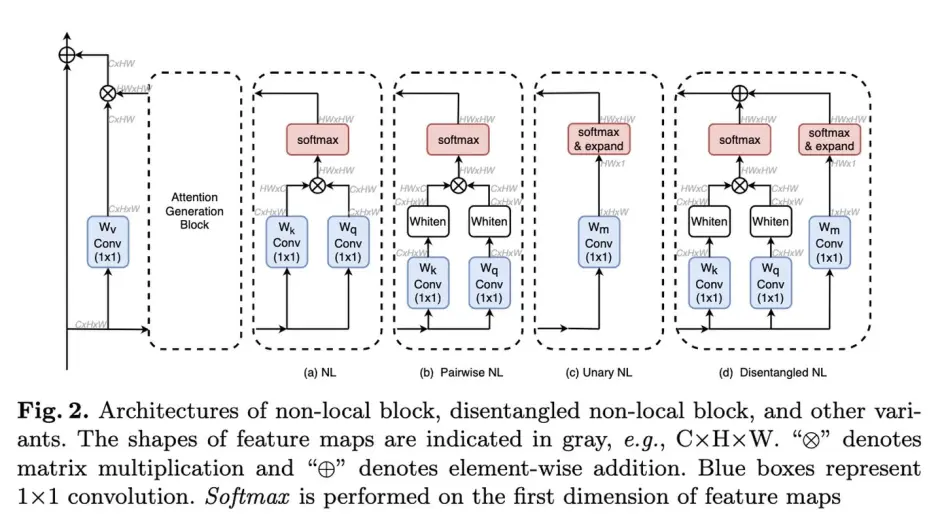
其中whiten是指减去均值
在各任务的可视化结果如下:
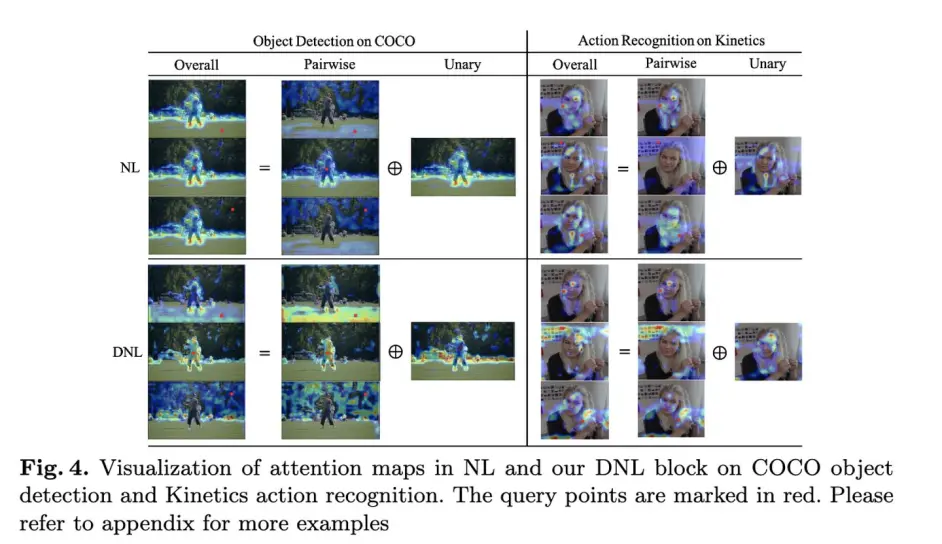
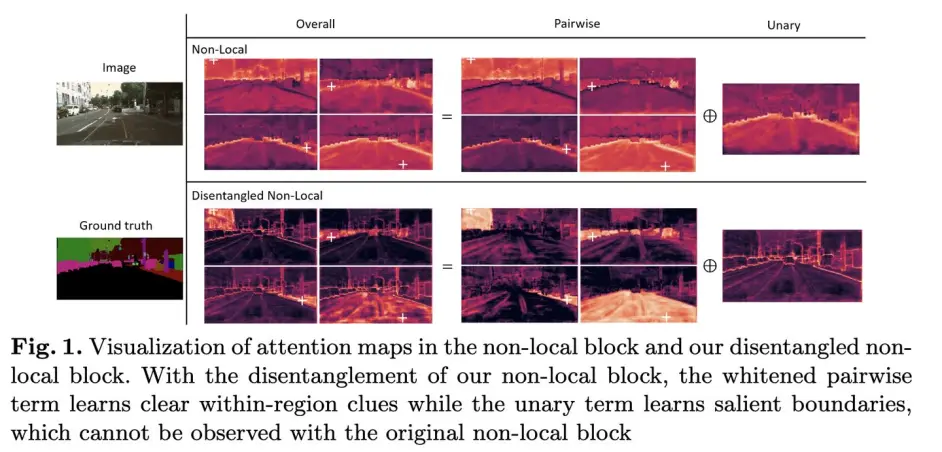

segmentation上的提升效果:
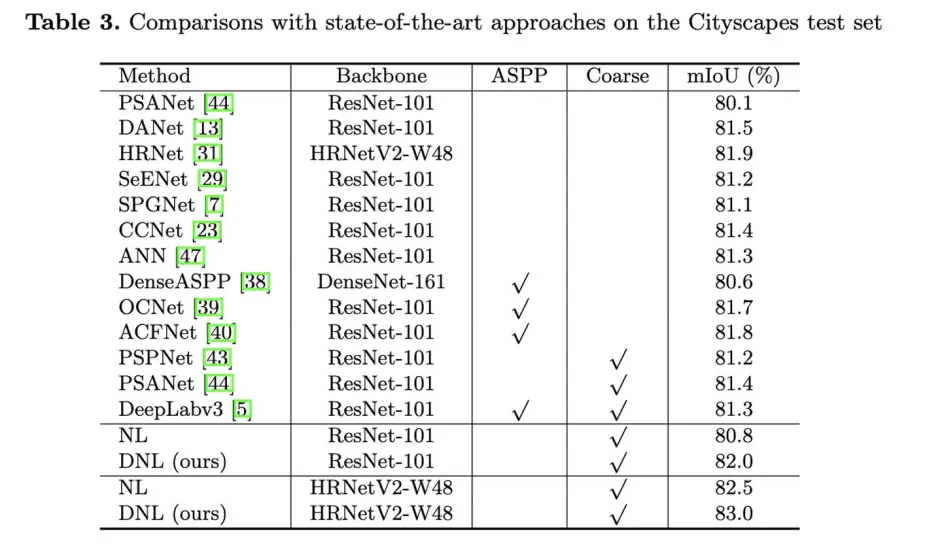
(其实好奇NL+unary效果会如何?
12 ORDNet: Capturing Omni-Range Dependencies for Scene Parsing

arxiv.org/abs/2101.0392
作者观察到self-attention中很多点的响应范围过大,于是提出了Middle-Range的self-attention以及Reweighed Long-Range

如上图,作者认为绿色的点的attention响应范围过大,太远处的响应会不利于feature aggregation,于是提出下面的两个branch
MR就是将原来的图分为4块,分别做non-local
RlR就是将attention map沿着col的方向求和后经过sigmoid做weight
结果中没跑cityscapes
13 SETR
Rethinking Semantic Segmentation from a Sequence-to-Sequence Perspective with Transformers
fudan-zvg.github.io/SET
类似于ViT,该文用transformer搞segmentation
如上图a,将图像分为若干小格子,每个小格字做linear projection,加上position embedding 之后concat一起做transformer,文中用了24层。
之后接一个decoder,作者试了两种1是图b中逐步上采的(PUP),另外一种是c中融合了不同level的transformer输出(MLA)
结果还是挺好的
参考文献:
[1] Fu J, Liu J, Tian H, et al. Dual attention network for scene segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2019: 3146-3154.
[2] Yuan Y, Wang J. Ocnet: Object context network for scene parsing[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.00916, 2018.
[3] Huang Z, Wang X, Huang L, et al. Ccnet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. 2019: 603-612.
[4] Yuan Y, Chen X, Wang J. Object-contextual representations for semantic segmentation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.11065, 2019.
[5] Huang L, Yuan Y, Guo J, et al. Interlaced sparse self-attention for semantic segmentation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.12273, 2019.
[6] Zhu Z, Xu M, Bai S, et al. Asymmetric non-local neural networks for semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. 2019: 593-602.
[7] Zhang H, Zhang H, Wang C, et al. Co-occurrent features in semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2019: 548-557.
[8] Zhang F, Chen Y, Li Z, et al. Acfnet: Attentional class feature network for semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. 2019: 6798-6807.
[9] Zhang L, Li X, Arnab A, et al. Dual graph convolutional network for semantic segmentation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.06121, 2019.
[10] Cao Y, Xu J, Lin S, et al. Gcnet: Non-local networks meet squeeze-excitation networks and beyond[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. 2019: 0-0.
[11] Yin M, Yao Z, Cao Y, et al. Disentangled non-local neural networks[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, Cham, 2020: 191-207.
[12] Huang S, Liu S, Hui T, et al. ORDNet: Capturing Omni-Range Dependencies for Scene Parsing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 8251-8263.
[13] Zheng S, Lu J, Zhao H, et al. Rethinking Semantic Segmentation from a Sequence-to-Sequence Perspective with Transformers[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.15840, 2020.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号