riscv isa指令(Volume I)
1.Introduction
正如本篇文章所说,在非特权ISA设计中,我们试图消除对
特定微体系结构特性的任何依赖(如如缓存线大小),或特权体系结构细节的任何依赖(如页面翻译)。这既是为了简单,也是为了给可选微架构或可选特权架构提供最大的灵活性。
term
| 名词 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| core | 一个组件如果具有取指单元,则称为core |
| coprocessor | refer to a unit that is attached to a RISC-V core |
| accelerator | refer to either a non-programmable fixed-function unit or a core thatcan operate autonomously but is specialized for certain tasks |
| execution environment interface (EEI) | the number and type of harts,privilege modes,accessibility and attributes of memory and I/O regions,behavior of all legal instructions,handling of any interrupts or exceptions |
| hart | hardware thread |
| XLEN | refer to the width of an integer register in bits (either 32 or 64). |
| Exceptions | refer to an unusual condition occurring(synchronous event) at run time associated with an instruction in the current RISC-V hart |
| interrupt | refer to an external asynchronous event that may cause a RISC-V hart to experience an unexpected transfer of control |
| trap | refer to the transfer of control to a trap handler caused by either an exception or an interrupt |
| IALIGN | (measured in bits) refer to the instruction-address alignment constraint the implementation enforces. |
| ILEN | (measured in bits)refer to the maximum instruction length supported by an implementation, and which is always a multiple of IALIGN |
| word | A word of memory is defined as 32 bits (4 bytes). Correspondingly, a halfword is 16 bits (2 bytes), adoubleword is 64 bits (8 bytes), and a quadword is 128 bits (16 bytes). |
base integer ISA
每个基本整数ISA都可以用一个或多个可选的指令集扩展进行扩展,我们将每个RISCV指令集编码空间(以及相关的编码空间,如csr)划分为三个不相关的类别:标准、保留和自定义。
- RV32I,RV64I,RV32E,RV128I,4个基本整型被视为不同的base ISA
- Standard标准编码由基金会定义,不得与同一基本ISA的其他标准扩展相冲突
- non-standard保留编码目前没有定义,但为将来的标准扩展而保存
- non-conforming自定义编码永远不能用于标准扩展,而只能用于特定于供应商的非标准扩展
| Extension | note |
|---|---|
| I | The base integer ISA is named “I” (prefixed by RV32 or RV64 depending on integer register width), and contains integer computational instructions, integer loads, integer stores, and control flow instructions. |
| M | The standard integer multiplication and division extension is named “M”, and adds instructions to multiply and divide values held in the integer registers. |
| A | The standard atomic instruction extension, denoted by “A”, adds instructions that atomically read, modify, and write memory for inter-processor synchronization. |
| F | The standard single-precision floating-point exten sion, denoted by “F”, adds floating-point registers, single-precision computational instructions, and single-precision loads and stores. |
| D | The standard double-precision floating-point extension, denoted by “D”, expands the floating-point registers, and adds double-precision computational instructions, loads, and stores. |
| C | The standard “C” compressed instruction extension provides narrower 16-bit forms of common instructions. |
Risv-V的指令编码规则
基础的RiscV指令集,比如RV32I,RV64I中,所有指令长度都是固定的32bits,在这些RiscV实施方案中,指令访问必须32bit地址对齐。但是标准的RiscV指令编码方案是支持其它指令长度的,只要指令长度是16bit的倍数,这时候,指令访问是16bit地址对齐的。比如标准的压缩指令RVC,指令长度就是16bit的。在嵌入式系统中,使用16bit的编码可以提高代码密度,减少功耗。我们用IALIGN来表示指令地址必须对齐的位数。在标准指令集中,IALIGN=32,RVC中,IALIGN=16,当然在扩展指令中,你也可以实施16倍数的其它指令编码,比如IALIGN=64等等。
Exceptions, Traps, and Interrupts
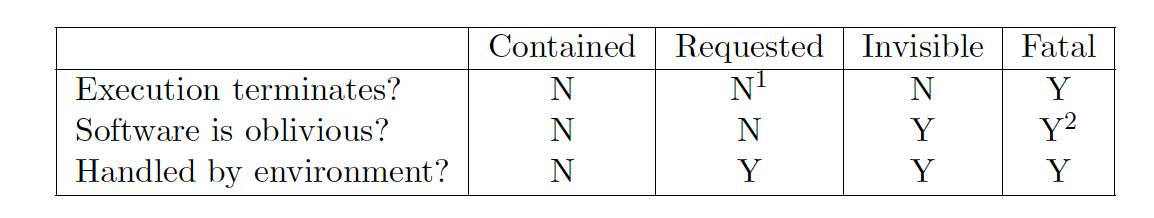
They are four different types of Traps:
- Contained Trap,
- Requested Trap,
- Invisible Trap, and
- Fatal Trap.
是否停止执行环境
业务软件是否察觉?
是否由执行环境处理?
2.RV32I
- RV32I 有
40个指令 - RV32I几乎可以模拟任何其他ISA扩展(除了a扩展,它需要额外的硬件支持原子性)。
- 32个x
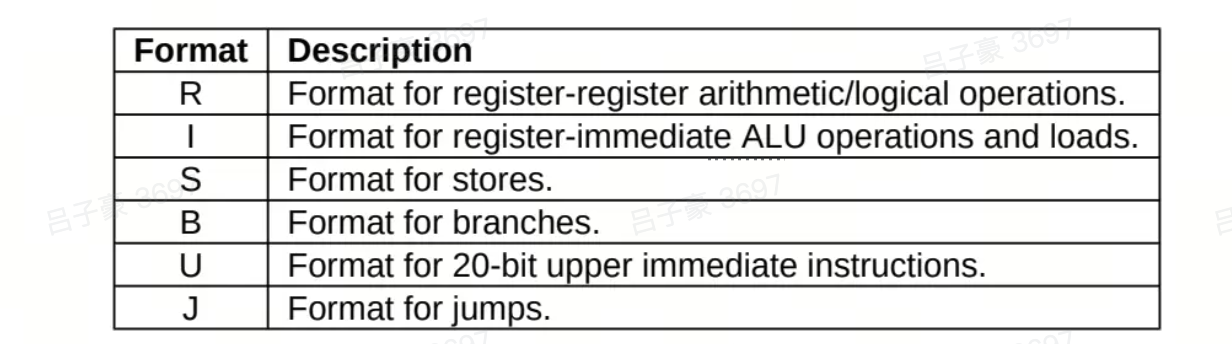
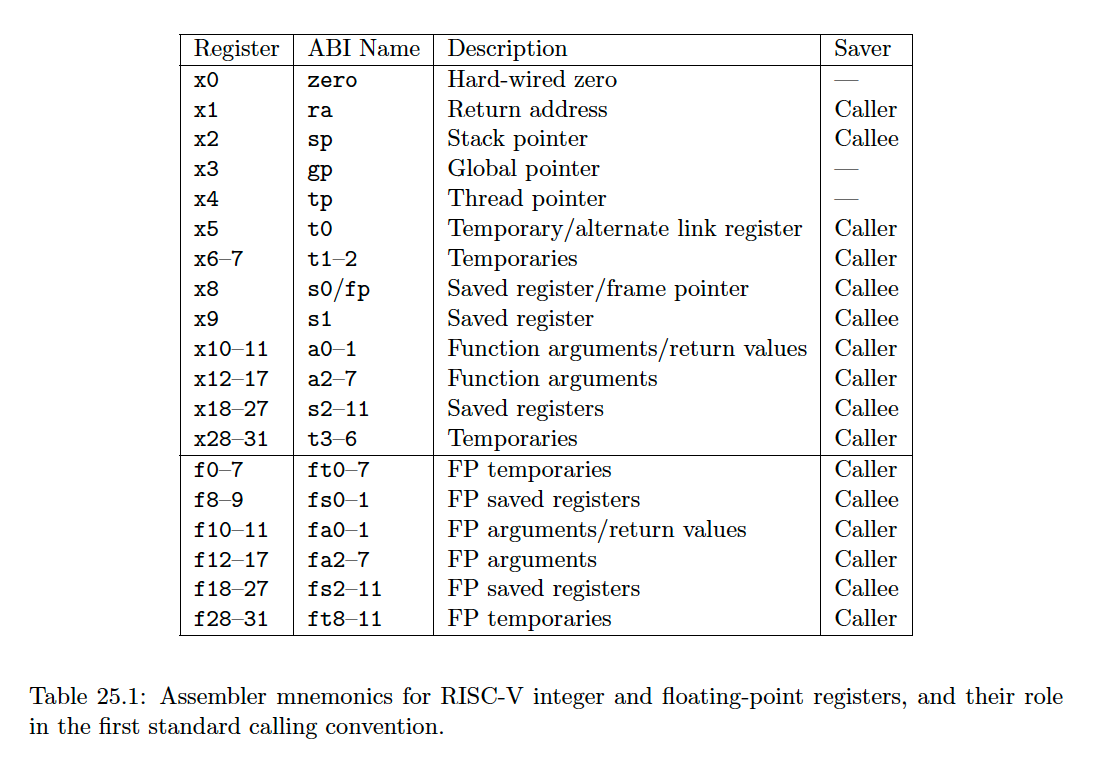
寄存器。一个pc寄存器。其中x0始终为0。 没有专用的栈寄存器和返回地址寄存器 - 有四个指令格式R/I/S/U, rs1,rs2,rd是固定的位置
- 指令必须是4字节对齐,如果RV32E扩展,那么必须是2字节对齐
- 非对齐指令地址将会产生异常(This exception is reported on the branch or jump
instruction, not on the target instruction.)

Ref
-
ISA指令速查
https://msyksphinz-self.github.io/riscv-isadoc/html/index.html -
汇编手册RISC-V Assembly Programmer's Manual
https://github.com/riscv-non-isa/riscv-asm-manual/blob/master/riscv-asm.md




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律