计算机视觉(一)
1. CV背景介绍

两个项目整理:
OpenBR http://openbiometrics.org/ 人脸识别
http://git.oschina.net/easypr/EasyPR 车牌定位
2.opencv库的完全解析
Clion + opencv3.2
安装方法
https://blog.csdn.net/bskfnvjtlyzmv867/article/details/78940472
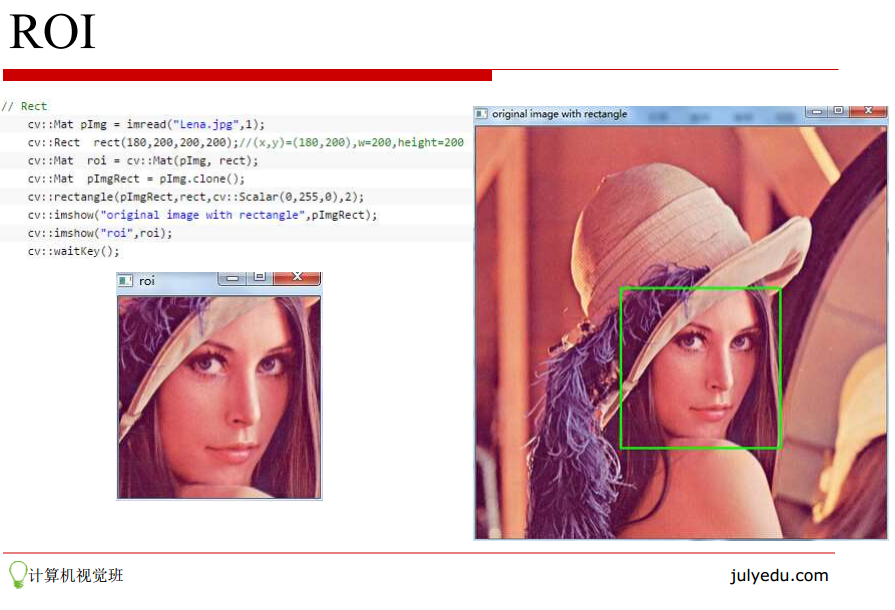
3.图像的基本操作:遍历图像、ROI选取
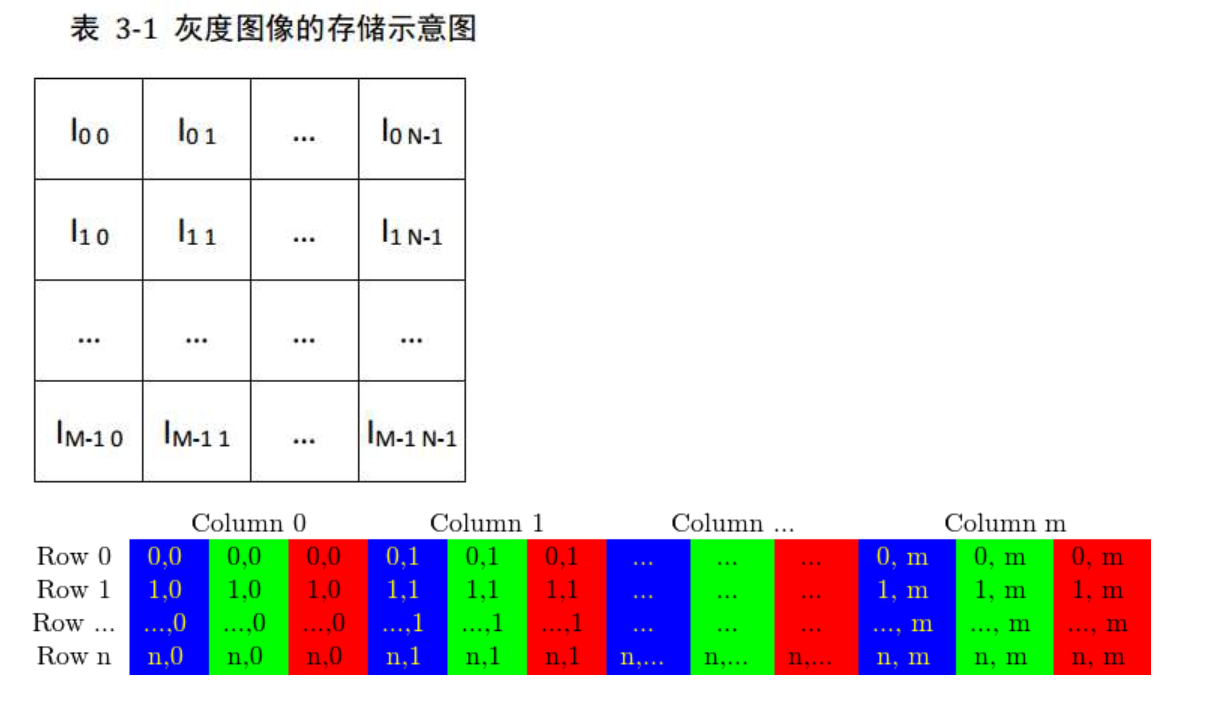
Opencv 中都是用Mat进行矩阵管理
#include "cv.hpp" using namespace cv; using namespace std; #include <iostream> int main() { Mat M(3,2,CV_8UC3,Scalar(0,0,255)); // cout << "Hello, World!" <<endl; cout << M <<endl; return 0; }
M=
[ 0, 0, 255, 0, 0, 255;
0, 0, 255, 0, 0, 255;
0, 0, 255, 0, 0, 255]

遍历图像的六种方法: 1. uchar value = grayim.at<uchar>(i,j); for( int i = 0; i < grayim.rows; ++i) for( int j = 0; j < grayim.cols; ++j ) grayim.at<uchar>(i,j) = (i+j)%255;
for( int i = 0; i < colorim.rows; ++i) for( int j = 0; j < colorim.cols; ++j ) { Vec3b pixel; pixel[0] = i%255; //Blue pixel[1] = j%255; //Green pixel[2] = 0; //Red colorim.at<Vec3b>(i,j) = pixel; } 2.
彩色图像:
cv::Mat Iterator_<uchar> grayit, grayend; for( colorit = colorbegin = im.begin<uchar>(), colorend = colorim.end<uchar>(); colorit != colorend; ++colorit) {
*colorit[0] = rand()%255;
*colorit[1] = rand()%255;
*colorit[2] = rand()%255;
}
灰度图像:
cv::Mat Iterator_<uchar> grayit, grayend;
for( grayit = grayim.begin<uchar>(), grayend =
grayim.end<uchar>(); grayit != grayend; ++grayit)
*grayit = rand()%255;
3. for( int i = 0; i < grayim.rows; ++i) { //获取第 i 行首像素指针 uchar * p = grayim.ptr<uchar>(i); //对第 i 行的每个像素(byte)操作 for( int j = 0; j < grayim.cols; ++j ) p[j] = (i+j)%255; } 4. Mat M(600, 800, CV_8UC1); for( int i = 0; i < M.rows; ++i) { uchar * p = M.ptr<uchar>(i); for( int j = 0; j < M.cols; ++j ) { double d1 = (double) ((i+j)%255); M.at<uchar>(i,j) = d1; double d2 = M.at<double>(i,j); } } 5.
查找表的方式 int divideWith=10; uchar table[256]; for (int i = 0; i < 256; ++i) table[i] = divideWith* (i/divideWith); Mat lookUpTable(1, 256, CV_8U); uchar* p = lookUpTable.data; for( int i = 0; i < 256; ++i) p[i] = table[i]; LUT(I, lookUpTable, Out); 6.
地址寻址去访问 addr(Mi0,i1,…im-1) = M.data + M.step[0] * i0 + M.step[1] * i1 + … + M.step[m-1] * im-1 (其中 m = M.dims M的维度)
4.Python环境搭建+语法
python基础教程:
http://www.runoob.com/python/python-tutorial.html
5.机器学习在CV中的应用: Kmeans与KNN
监督学习
回归、分类
无监督学习
聚类
KNN:
目标:分类未知类别案例。
输入:待分类未知类别案例项目。已知类别案例集合D ,其中包含 j个已知类别的案例。
输出:项目可能的类别
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<cv.h> #include<highgui.h> #include<ml.h> #include<time.h> using namespace cv; int readFlippedInteger(FILE *); int main() { FILE *fp = fopen("..\\data\\train-images.idx3-ubyte", "rb"); FILE *fp2 = fopen("..\\data\\train-labels.idx1-ubyte", "rb"); if (!fp || !fp2) { // cout << "Files not Found" << endl; return 0; } int magicNumber = readFlippedInteger(fp); int numImages = readFlippedInteger(fp); int numRows = readFlippedInteger(fp); int numCols = readFlippedInteger(fp); fseek(fp2, 0x08, SEEK_SET); int size = numRows*numCols; Mat trainingVectors(numImages, size, CV_32FC1); Mat trainingLabels(numImages, 1, CV_32FC1); //CvMat *trainingVectors = cvCreateMat(numImages, size, CV_32FC1); //CvMat *trainingLabels = cvCreateMat(numImages, 1, CV_32FC1); uchar *temp = new uchar[size]; //unsigned char *temp = new unsigned char[size]; uchar tempClass = 0; for (int i = 0; i < numImages; i++) { fread((void*)temp, size, 1, fp); fread((void*)(&tempClass), sizeof(uchar), 1, fp2); trainingLabels.at<float>(i, 0) = tempClass; Mat img(numRows, numCols, CV_32FC1); for (int k = 0; k < size; k++) { trainingVectors.at<float>(i, k) = temp[k]; img.at<float>(k / numCols, k%numCols) = temp[k]; } imshow("data", img); //waitKey(2); } KNearest knn(trainingVectors, trainingLabels); printf("Maximum k: %d\n", knn.get_max_k()); fclose(fp); fclose(fp2); delete[] temp; fp = fopen("..\\data\\t10k-images.idx3-ubyte", "rb"); fp2 = fopen("..\\data\\t10k-labels.idx1-ubyte", "rb"); magicNumber = readFlippedInteger(fp); numImages = readFlippedInteger(fp); numRows = readFlippedInteger(fp); numCols = readFlippedInteger(fp); fseek(fp2, 0x08, SEEK_SET); CvMat *testVectors = cvCreateMat(numImages, size, CV_32FC1); CvMat *testLabels = cvCreateMat(numImages, 1, CV_32FC1); CvMat *actualLabels = cvCreateMat(numImages, 1, CV_32FC1); temp = new uchar[size]; tempClass = 1; CvMat *currentTest = cvCreateMat(1, size, CV_32FC1); CvMat *currentLabel = cvCreateMat(1, 1, CV_32FC1); int totalCorrect = 0; for (int i = 0; i<numImages; i++) { fread((void*)temp, size, 1, fp); fread((void*)(&tempClass), sizeof(uchar), 1, fp2); actualLabels->data.fl[i] = (float)tempClass; for (int k = 0; k<size; k++) { testVectors->data.fl[i*size + k] = temp[k]; currentTest->data.fl[k] = temp[k]; } knn.find_nearest(currentTest, 5, currentLabel); testLabels->data.fl[i] = currentLabel->data.fl[0]; if (currentLabel->data.fl[0] == actualLabels->data.fl[i]) totalCorrect++; } printf("Time: %d Accuracy: %f ", (int)time, (double)totalCorrect * 100 / (double)numImages); } int readFlippedInteger(FILE *fp) { int ret = 0; uchar *temp; temp = (uchar*)(&ret); fread(&temp[3], sizeof(uchar), 1, fp); fread(&temp[2], sizeof(uchar), 1, fp); fread(&temp[1], sizeof(uchar), 1, fp); fread(&temp[0], sizeof(uchar), 1, fp); return ret; }
K-means:
欧式距离进行计算。数据集取与分类之间欧式距离的平均值作为新的分类点,一直到循环迭代,中心变化很小便停止了。
// colorReduce.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application. // #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> #include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp> void colorReduce(cv::Mat& image, int div = 64) { int nl = image.rows; // number of lines int nc = image.cols * image.channels(); // number of elements per line for (int j = 0; j < nl; j++) { // get the address of row j uchar* data = image.ptr<uchar>(j); for (int i = 0; i < nc; i++) { // process each pixel data[i] = data[i] / div * div; } } } void keamsCplus(cv::Mat& input, cv::Mat& output, int clusterCount = 4){ cv::Mat src; input.copyTo(src); //step 1 : map the src to the samples cv::Mat samples = src.reshape(1, src.total()); samples.convertTo(samples, CV_32F); //step 2 : apply kmeans to find labels and centers cv::Mat labels; int attempts = 5;//try 5 times, choose the best result cv::Mat centers; cv::kmeans(samples, clusterCount, labels, cv::TermCriteria(CV_TERMCRIT_ITER | CV_TERMCRIT_EPS, 10, 0.01), attempts, cv::KMEANS_PP_CENTERS, centers); //step 3 : map the centers to the output // Now convert back into uint8, and make original image cv::Mat new_image(src.size(), src.type()); cv::Mat red_samples(src.total(), 3, CV_8U); centers.convertTo(centers, CV_8U); for (int i = 0; i < src.total(); i++) { int clusterIdx = labels.at<int>(i); centers.row(clusterIdx).copyTo(red_samples.row(i)); } new_image = red_samples.reshape(3, src.rows); new_image.copyTo(output); } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { // Load input image (colored, 3-channel, BGR) cv::Mat input = cv::imread("boldt.jpg"); if (input.empty()) { std::cout << "!!! Failed imread()" << std::endl; return -1; } int divideWith = 64; uchar table[256]; for (int i = 0; i < 256; ++i) table[i] = (uchar)(divideWith * (i / divideWith)); cv::Mat lookUpTable(1, 256, CV_8U); uchar*p = lookUpTable.data; for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) p[i] = table[i]; cv::Mat result; LUT(input, lookUpTable, result); /////////////////// //kmeans cv::Mat resultKmeans; keamsCplus(input, resultKmeans,8); ////////////////////// colorReduce(input); /////////////////////// cv::imshow("Color Reduction", input); cv::imwrite("output.jpg", input); cv::waitKey(0); return 0; }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号