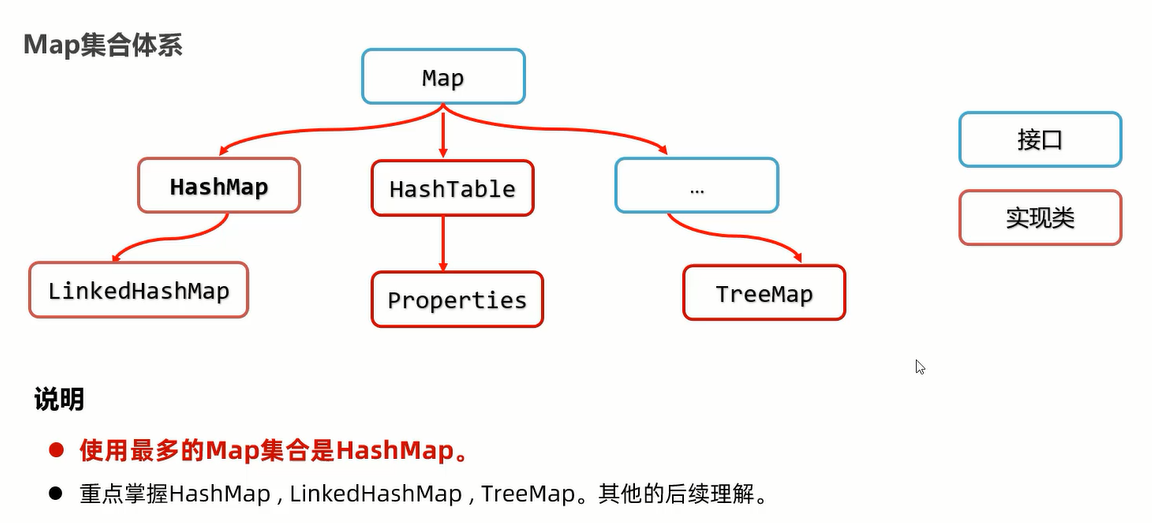
Java 入门 38 Map集合体系 集合的嵌套




package com.ITheima.Map_test; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.LinkedHashMap; import java.util.Map; /** 目标:认识Map体系的特点:按照键无序,不重复,无索引。值不做要求。 */ public class MapDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { //1 创建一个Map集合对象 // Map<String, Integer> maps = new HashMap<>(); // 一行经典代码 Map<String, Integer> maps = new LinkedHashMap<>(); maps.put("鸿星尔克",11); maps.put("java",1); maps.put(null,null); maps.put("枸杞",11); // System.out.println(maps);//{null=null, java=1, 枸杞=11, 鸿星尔克=11} System.out.println(maps);//{鸿星尔克=11, java=1, null=null, 枸杞=11} } }

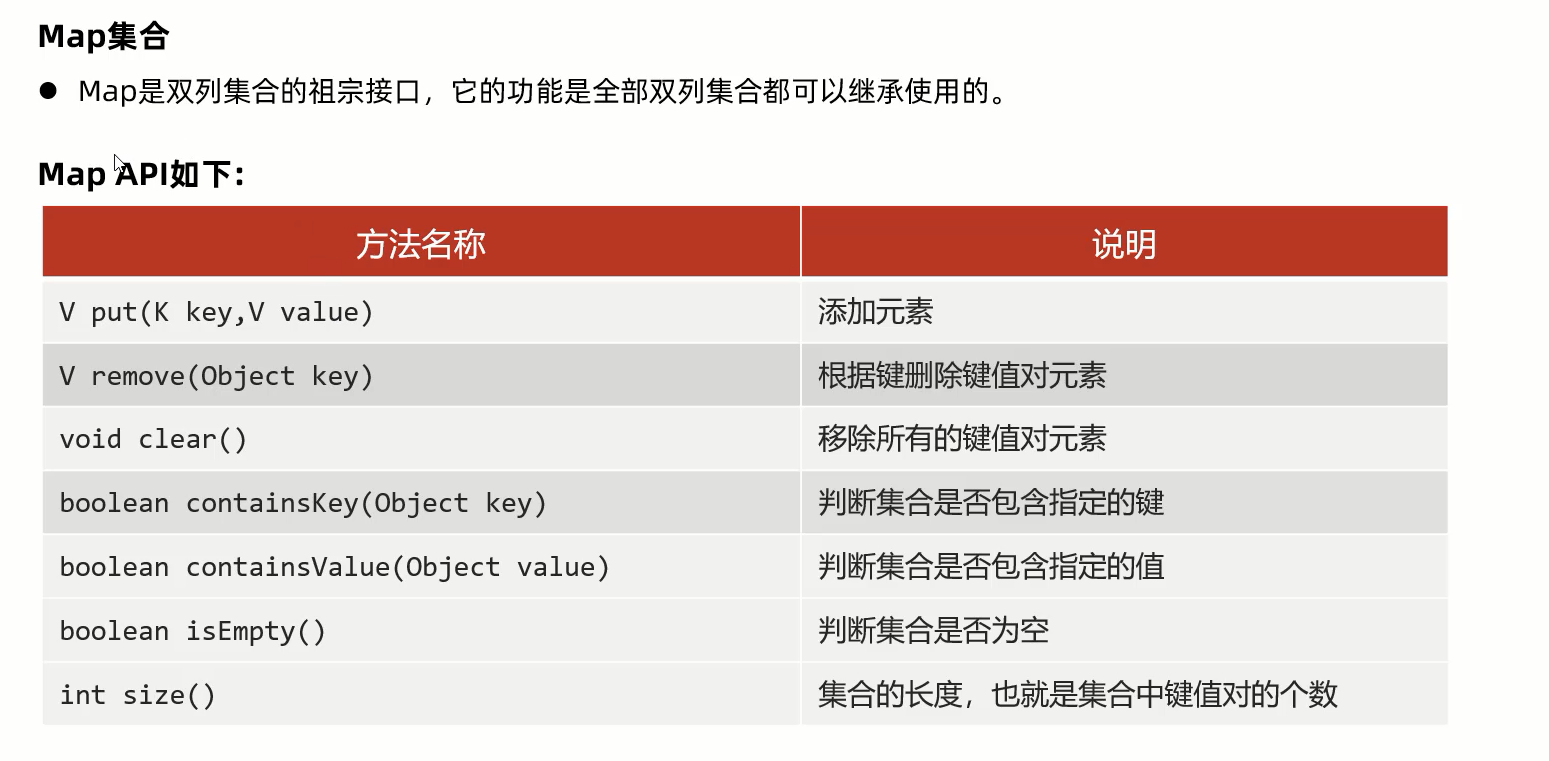

package com.itheima.d6_map_api; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; /** 目标:Map集合的常用API(重点中的重点) - public V put(K key, V value): 把指定的键与指定的值添加到Map集合中。 - public V remove(Object key): 把指定的键 所对应的键值对元素 在Map集合中删除,返回被删除元素的值。 - public V get(Object key) 根据指定的键,在Map集合中获取对应的值。 - public Set<K> keySet(): 获取Map集合中所有的键,存储到Set集合中。 - public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet(): 获取到Map集合中所有的键值对对象的集合(Set集合)。 - public boolean containKey(Object key):判断该集合中是否有此键。 - public boolean containValue(Object value):判断该集合中是否有此值。 */ public class MapDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1.添加元素: 无序,不重复,无索引。 Map<String , Integer> maps = new HashMap<>(); maps.put("iphoneX",10); maps.put("娃娃",20); maps.put("iphoneX",100);// Map集合后面重复的键对应的元素会覆盖前面重复的整个元素! maps.put("huawei",100); maps.put("生活用品",10); maps.put("手表",10); // {huawei=100, 手表=10, 生活用品=10, iphoneX=100, 娃娃=20} System.out.println(maps); // 2.清空集合 // maps.clear(); // System.out.println(maps); // 3.判断集合是否为空,为空返回true ,反之! System.out.println(maps.isEmpty()); // 4.根据键获取对应值:public V get(Object key) Integer key = maps.get("huawei"); System.out.println(key); System.out.println(maps.get("生活用品")); // 10 System.out.println(maps.get("生活用品2")); // null // 5.根据键删除整个元素。(删除键会返回键的值) System.out.println(maps.remove("iphoneX")); System.out.println(maps); // 6.判断是否包含某个键 ,包含返回true ,反之 System.out.println(maps.containsKey("娃娃")); // true System.out.println(maps.containsKey("娃娃2")); // false System.out.println(maps.containsKey("iphoneX")); // false // 7.判断是否包含某个值。 System.out.println(maps.containsValue(100)); // System.out.println(maps.containsValue(10)); // System.out.println(maps.containsValue(22)); // // {huawei=100, 手表=10, 生活用品=10, 娃娃=20} // 8.获取全部键的集合:public Set<K> keySet() Set<String> keys = maps.keySet(); System.out.println(keys); System.out.println("------------------------------"); // 9.获取全部值的集合:Collection<V> values(); Collection<Integer> values = maps.values(); System.out.println(values); // 10.集合的大小 System.out.println(maps.size()); // 4 // 11.合并其他Map集合。(拓展) Map<String , Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>(); map1.put("java1", 1); map1.put("java2", 100); Map<String , Integer> map2 = new HashMap<>(); map2.put("java2", 1); map2.put("java3", 100); map1.putAll(map2); // 把集合map2的元素拷贝一份到map1中去 System.out.println(map1); System.out.println(map2); } }


package com.itheima.d7_map_traversal; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; /** 目标:Map集合的遍历方式一:键找值 Map集合的遍历方式有:3种。 (1)“键找值”的方式遍历:先获取Map集合全部的键,再根据遍历键找值。 (2)“键值对”的方式遍历:难度较大。 (3)JDK 1.8开始之后的新技术:Lambda表达式。(暂时了解) a.“键找值”的方式遍历Map集合。 1.先获取Map集合的全部键的Set集合。 2.遍历键的Set集合,然后通过键找值。 小结: 代码简单,需要记住! */ public class MapDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String , Integer> maps = new HashMap<>(); // 1.添加元素: 无序,不重复,无索引。 maps.put("娃娃",30); maps.put("iphoneX",100); maps.put("huawei",1000); maps.put("生活用品",10); maps.put("手表",10); System.out.println(maps); // maps = {huawei=1000, 手表=10, 生活用品=10, iphoneX=100, 娃娃=30} // 1、键找值:第一步:先拿到集合的全部键。 Set<String> keys = maps.keySet(); // 2、第二步:遍历每个键,根据键提取值 for (String key : keys) { int value = maps.get(key); System.out.println(key + "===>" + value); } } }
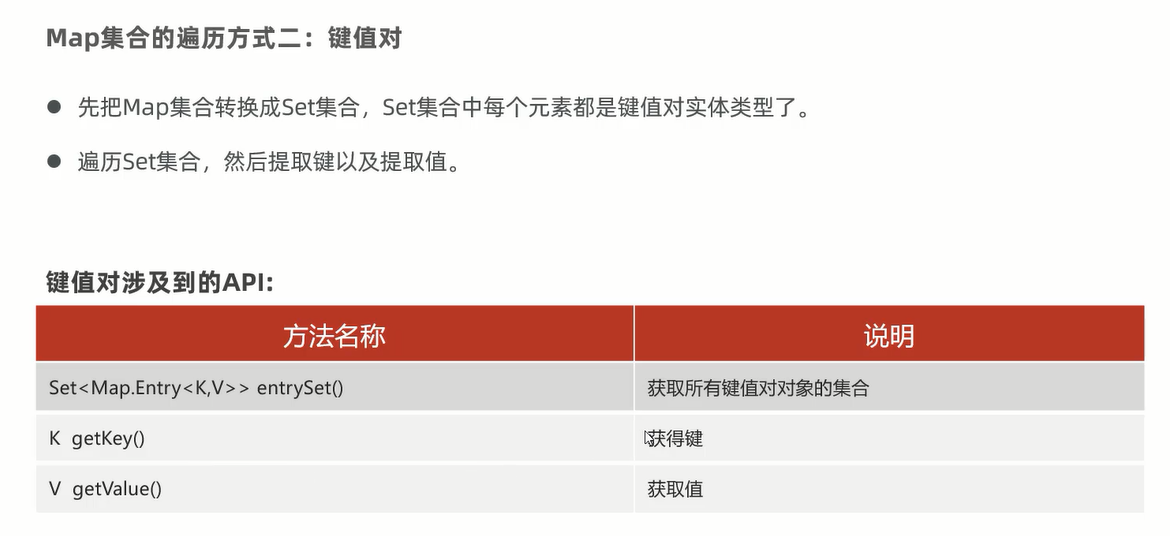

package com.itheima.d7_map_traversal; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; /** 目标:Map集合的遍历方式。 Map集合的遍历方式有:3种。 (1)“键找值”的方式遍历:先获取Map集合全部的键,再根据键找值。 (2)“键值对”的方式遍历:难度较大。 (3)JDK 1.8开始之后的新技术:Lambda表达式。 b.“键值对”的方式遍历: 1.把Map集合转换成一个Set集合:Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet(); 2.此时键值对元素的类型就确定了,类型是键值对实体类型:Map.Entry<K, V> 3.接下来就可以用foreach遍历这个Set集合,类型用Map.Entry<K, V> */ public class MapDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String , Integer> maps = new HashMap<>(); // 1.添加元素: 无序,不重复,无索引。 maps.put("娃娃",30); maps.put("iphoneX",100); maps.put("huawei",1000); maps.put("生活用品",10); maps.put("手表",10); System.out.println(maps); // maps = {huawei=1000, 手表=10, 生活用品=10, iphoneX=100, 娃娃=30} /** maps = {huawei=1000, 手表=10, 生活用品=10, iphoneX=100, 娃娃=30} 👇 使用foreach遍历map集合.发现Map集合的键值对元素直接是没有类型的。所以不可以直接foreach遍历集合。 👇 可以通过调用Map的方法 entrySet把Map集合转换成Set集合形式 maps.entrySet(); 👇 Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> entries = maps.entrySet(); [(huawei=1000), (手表=10), (生活用品=10), (iphoneX=100), (娃娃=30)] entry 👇 此时可以使用foreach遍历 */ // 1、把Map集合转换成Set集合 Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = maps.entrySet(); // 2、开始遍历 for(Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : entries){ String key = entry.getKey(); int value = entry.getValue(); System.out.println(key + "====>" + value); } } }
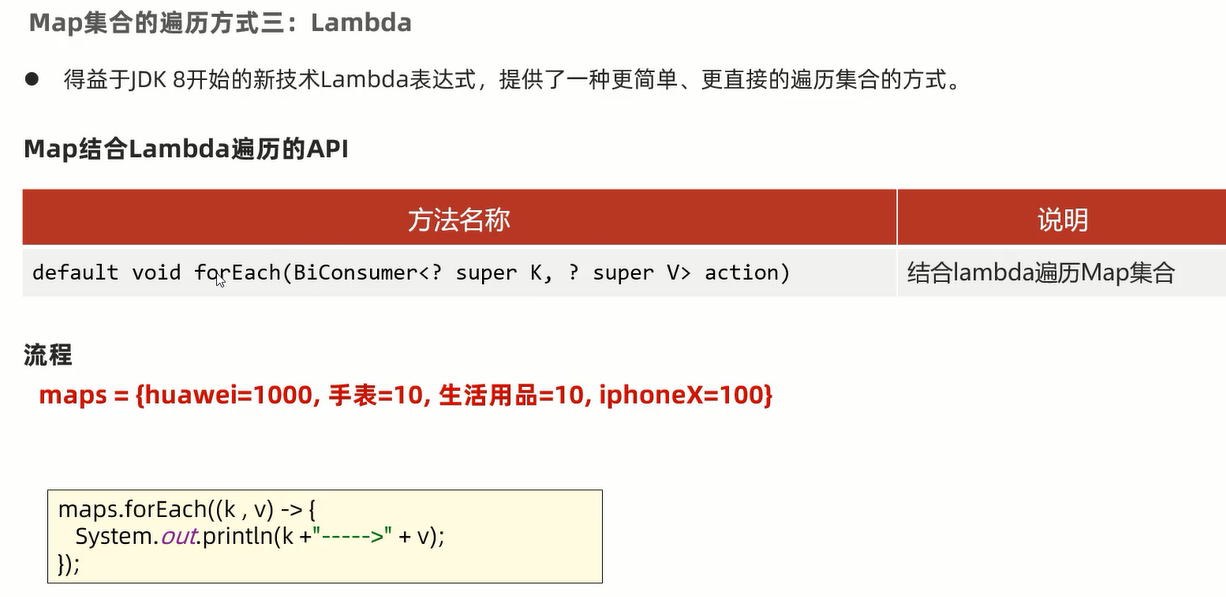

package com.itheima.d7_map_traversal; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.function.BiConsumer; /** 目标:Map集合的遍历方式。 Map集合的遍历方式有:3种。 (1)“键找值”的方式遍历:先获取Map集合全部的键,再根据键找值。 (2)“键值对”的方式遍历:难度较大。 (3)JDK 1.8开始之后的新技术:Lambda表达式。 c.JDK 1.8开始之后的新技术:Lambda表达式。(暂时了解) */ public class MapDemo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String , Integer> maps = new HashMap<>(); // 1.添加元素: 无序,不重复,无索引。 maps.put("娃娃",30); maps.put("iphoneX",100);// Map集合后面重复的键对应的元素会覆盖前面重复的整个元素! maps.put("huawei",1000); maps.put("生活用品",10); maps.put("手表",10); System.out.println(maps); // maps = {huawei=1000, 手表=10, 生活用品=10, iphoneX=100, 娃娃=30} // maps.forEach(new BiConsumer<String, Integer>() { // @Override // public void accept(String key, Integer value) { // System.out.println(key + "--->" + value); // } // }); maps.forEach((k, v) -> { System.out.println(k + "--->" + v); }); } }
案例


package com.itheima.d8_map_test; import java.util.*; /** 需求:统计投票人数 */ public class MapTest1 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1、把80个学生选择的数据拿进来。 String[] selects = {"A" , "B", "C", "D"}; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); Random r = new Random(); for (int i = 0; i < 80; i++) { sb.append(selects[r.nextInt(selects.length)]); } System.out.println(sb); // 2、定义一个Map集合记录最终统计的结果: A=30 B=20 C=20 D=10 键是景点 值是选择的数量 Map<Character, Integer> infos = new HashMap<>(); // // 3、遍历80个学生选择的数据 for (int i = 0; i < sb.length(); i++) { // 4、提取当前选择景点字符 char ch = sb.charAt(i); // 5、判断Map集合中是否存在这个键 if(infos.containsKey(ch)){ // 让其值 + 1 infos.put(ch , infos.get(ch) + 1); }else { // 说明此景点是第一次被选 infos.put(ch , 1); } } // 4、输出集合 System.out.println(infos); } }



package com.itheima.d9_map_impl; import com.itheima.d1_collection_set.Student; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class HashMapDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { // Map集合是根据键去除重复元素 Map<Student, String> maps = new HashMap<>(); Student s1 = new Student("无恙", 20, '男'); Student s2 = new Student("无恙", 20, '男'); Student s3 = new Student("周雄", 21, '男'); maps.put(s1, "北京"); maps.put(s2, "上海"); maps.put(s3, "广州"); System.out.println(maps); } }


package com.itheima.d9_map_impl; import java.util.LinkedHashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.TreeSet; /** 目标:认识Map体系的特点:按照键无序,不重复,无索引。值不做要求。 */ public class LinkedHashMapDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1、创建一个Map集合对象 Map<String, Integer> maps = new LinkedHashMap<>(); maps.put("鸿星尔克", 3); maps.put("Java", 1); maps.put("枸杞", 100); maps.put("Java", 100); // 覆盖前面的数据 maps.put(null, null); System.out.println(maps); } }


package com.itheima.d9_map_impl; import com.itheima.d1_collection_set.Apple; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.Map; import java.util.TreeMap; public class TreeMapDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<Integer, String> maps1 = new TreeMap<>(); maps1.put(13 , "王麻子"); maps1.put(1 , "张三"); maps1.put(3 , "县长"); System.out.println(maps1); // TreeMap集合自带排序。 可排序 不重复(只要大小规则一样就认为重复) 无索引 Map<Apple, String> maps2 = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Apple>() { @Override public int compare(Apple o1, Apple o2) { return Double.compare(o2.getPrice() , o1.getPrice()); // 按照价格降序排序! } }); maps2.put(new Apple("红富士", "红色", 9.9, 500), "山东" ); maps2.put(new Apple("青苹果", "绿色", 15.9, 300), "广州"); maps2.put(new Apple("绿苹果", "青色", 29.9, 400), "江西"); maps2.put(new Apple("黄苹果", "黄色", 9.8, 500), "湖北"); System.out.println(maps2); } }

集合嵌套 案例


package com.itheima.d9_map_impl; import java.util.*; /** 需求:统计投票人数 */ public class MapTest4 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1、要求程序记录每个学生选择的情况。 // 使用一个Map集合存储。 Map<String, List<String>> data = new HashMap<>(); // 2、把学生选择的数据存入进去。 List<String> selects = new ArrayList<>(); Collections.addAll(selects, "A", "C"); data.put("罗勇", selects); List<String> selects1 = new ArrayList<>(); Collections.addAll(selects1, "B", "C" , "D"); data.put("胡涛", selects1); List<String> selects2 = new ArrayList<>(); Collections.addAll(selects2 , "A", "B", "C" , "D"); data.put("刘军", selects2); System.out.println(data); // 3、统计每个景点选择的人数。 Map<String, Integer> infos = new HashMap<>(); // {} // 4、提取所有人选择的景点的信息。 Collection<List<String>> values = data.values(); System.out.println(values); // values = [[A, B, C, D], [B, C, D], [A, C]] // value for (List<String> value : values) { for (String s : value) { // 有没有包含这个景点 if(infos.containsKey(s)){ infos.put(s, infos.get(s) + 1); }else { infos.put(s , 1); } } } System.out.println(infos); } }





