react
pc端开发 先统一所有浏览器的样式
https://meyerweb.com/eric/tools/css/reset/
安装react-cli
npx create-react-app my-react-app
安装 axios
yarn add axios --save
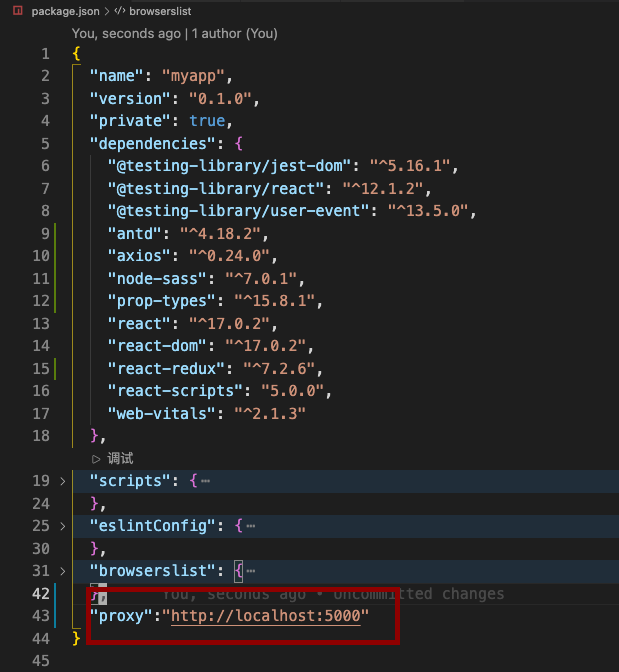
axios的使用 及 react代理服务器的配置
配置单个代理

import React, { Component } from 'react'
import axios from 'axios';
import './index.scss';
export default class TodoList extends Component {
//发送axios 获取数据
getAxiosState=()=>{
/*
记住添加http:// 端口号还是本身3000的端口号
在package中添加代理 请求代理服务器3000转发到5000端口的服务器
"proxy":"http://localhost:5000"
*/
axios.get('http://localhost:3000/login')
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
});
}
render() {
return (
<div >
{/* 发送axios请求 */}
<button onClick={this.getAxiosState}>点击获取数据</button>
</div>
)
}
}
图
配置多个代理 就不许用在package中配置,需要在src文件下建立一个文件setupProxy.js(不允许改名)
setupProxy.js配置

const proxy=require('http-proxy-middleware')
module.exports = function (app) {
app.use(
proxy.createProxyMiddleware('/api1', { //遇/api前缀的请求,就会出发该代理配置
target: 'http://localhost:5000', //服务器转发目标
changeOrigin: true, //控制服务器收到的请求头中的‘HOST’值
/*
changeOrigin:trur 服务器 收到的请求头的host就是5000开头
changeOrigin:false 服务器 收到的请求头的host就是3000开头(默认false)
我们一般设置为true
*/
pathRewrite: {
'^/api1': ''
} //重写请求路径 将/api1的路径替换成空字符串(必须配置)
}),
proxy.createProxyMiddleware('/api2', { //遇/api前缀的请求,就会出发该代理配置
target: 'http://localhost:5001', //服务器转发目标
changeOrigin: true, //控制服务器收到的请求头中的‘HOST’值
pathRewrite: {
'^/api2': ''
} //重写请求路径
})
)
}
用法

import React, { Component } from 'react'
import axios from 'axios';
import './index.scss';
export default class TodoList extends Component {
//发送axios 获取数据
getAxiosState=()=>{
/*
记住添加http:// 端口号还是本身3000的端口号
在package中添加代理 请求代理服务器3000转发到5000端口的服务器
只有3000端口没有的资源才会找5000端口的服务器要
必须带上setupProxy.js中的自己设置的/api1 前缀
*/
axios.get('http://localhost:3000/api1/login')
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
});
}
//第二个代理请求
getAxiosState1=()=>{
axios.get('http://localhost:3000/api2/cors')
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
});
}
render() {
return (
<div >
{/* 发送axios请求 */}
<button onClick={this.getAxiosState}>点击获取数据0</button>
<button onClick={this.getAxiosState1}>点击获取数据1</button>
</div>
)
}
}
使用fatch发送 请求(特点 不许用下载安装 老版本浏览器可能不支持)
promise写法

getMsg=()=>{ /* fatch用法 window自带的方法 fatch第一个then 返回的res是请求服务器成功,res原型链上的json()方法返回的是一个promise状态 之后才可以then()获取成功失败的参数 */ fetch(`http://localhost:3000/api1/login`) // res中原型上的json()方法返回的是promise()pending的一个状态 // .then(res=>{console.log(res.json());return res.json()}) .then(res=>res.json()) .then((data)=>console.log(data)).catch(err=>{ console.log(err) }) }
ES7 async await写法

//async await 优化 promise()写法 getMsg = async () => { try { const res = await fetch(`http://localhost:3000/api1/login`); const data = await res.json(); console.log(data,'success'); } catch (e) { console.log(e,'error'); } }
安装 styled-components (使各个模块的css独立出来) (如果使用scss之类的就不许用这样css模块化)
yarn add styled-components
第一步 把css文件改成js文件
第二部 import {createGlobalStyle } from 'styled-components'; (全局样式组件方法)
style.js//1引入全局样式方法 import {createGlobalStyle } from 'styled-components'; //2定义并暴露全局样式 export const GlobalStyled =createGlobalStyle` body{ margin:0; padding:0; background:blue; }APP.js//3引入全局样式 并以组件的形式使用 import {GlobalStyled} from './style' function App() { return ( <div className="App"> <GlobalStyled/> hello world </div> ); } export default App;
第三部 import styled from 'styled-components'; (局部样式组件方法)
common公用的组件 中的index.js
import styled from 'styled-components'; export const HeaderWrapper=styled.div` height:56px; background:red; `common公用的组件的样式
import React,{Component} from 'react'; import {HeaderWrapper} from './style'; class Header extends Component{ render(){ return ( <HeaderWrapper>hello world</HeaderWrapper> ) } } export default Header;
安装scss
yarn add node-sass
scss用法

import React ,{Component} from 'react';
import './index.scss';
class TodoList extends Component{
render(){
return (
<div>
<ul>
<li>hello world</li>
<li>happy</li>
</ul>
</div>
)
}
}
export default TodoList;
安装ant-design PC端
yarn add antd --save
ant-design库的用法

import React ,{Component} from 'react';
import 'antd/dist/antd.min.css';
import './index.scss';
import {Button} from 'antd';
class TodoList extends Component{
render(){
return (
<div>
<Button type="primary" className="btn">Button</Button>
</div>
)
}
}
export default TodoList;
安装 antd-mobile 移动端
yarn add antd-mobile@next
使用 不需要引入样式 antd-mobile会自动加载样式

import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { Button } from 'antd-mobile'
export default class Login extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<Button color='primary'>Primary</Button>
</div>
)
}
}
安装prop-types库
yarn add prop-types --save
prop-types 库的用法

import React,{Component} from 'react';
//1引入prop-types库
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
class Child extends Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state={
item:this.props.content
}
this.handleClick=this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
handleClick(){
this.props.delmethods(this.props.index)
}
render(){
return (
<div onClick={this.handleClick}>
{this.state.item}
</div>
)
}
}
//2数据类型校验
Child.propTypes= {
// 表示content类型要是string 且必须要传递
content:PropTypes.string.isRequired,
delmethods:PropTypes.func,
index:PropTypes.index,
test:PropTypes.string
}
//3如果父组件没传递数据 可以定义默认值
Child.defaultProps={
test:'hello'
}
export default Child;
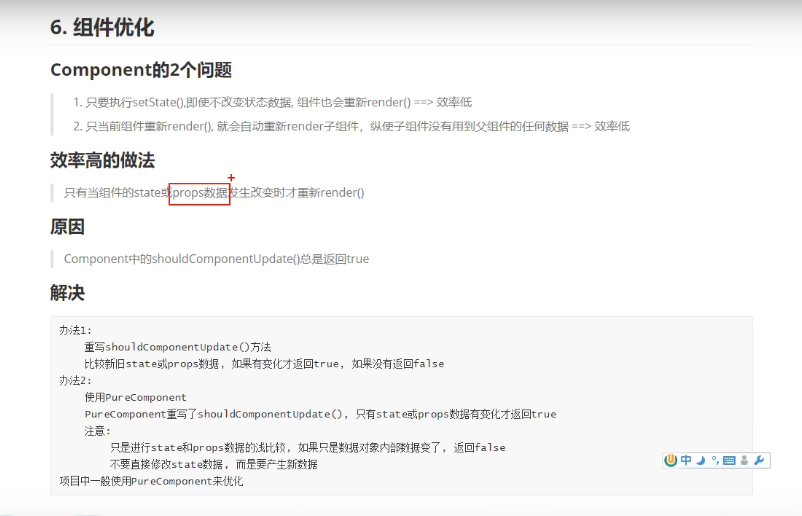
shouldComponentUpdate用法

shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps,nextState){ if(nextProps.content!==this.props.content){ return true; } else{ return false; } }
安装react-redux
yarn add react-redux --save
react-redux的用法
用法 主要就两部
- 第一步 被Provider包裹的子组件 内部可以直接调用store中的数据
- 第二部 connect(mapStateToProps,mapDispatchToProps)(TodoList)
- mapStateToProps 主要负责 将store中的state数据映射到TodoList的props属性中
- mapDidpatchToProps 主要负责将props中的方法可以通过dispatch方法发送action到store中的reducer内 修改store中的state数据
挂载节点 第一步使用Provider组件
index.js

import React from 'react'; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'; import './index.css'; import reportWebVitals from './reportWebVitals'; import TodoList from './TodoList/index'; import store from './store/index'; //Provider组件 可以是内部的所有子组件都可以获得store的数据 import {Provider} from 'react-redux'; const App=( <Provider store={store}> <TodoList></TodoList> </Provider> ) ReactDOM.render( App, document.getElementById('root') ); // If you want to start measuring performance in your app, pass a function // to log results (for example: reportWebVitals(console.log)) // or send to an analytics endpoint. Learn more: https://bit.ly/CRA-vitals reportWebVitals();
store中的index.js

//引入redux createStore 创建store //applyMiddleware 方法允许redux 使用中间件 import { createStore, applyMiddleware, compose } from "redux"; import reducer from "./reducer"; import thunk from "redux-thunk"; const composeEnhancers = window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__ ? window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__({ // Specify extension’s options like name, actionsBlacklist, actionsCreators, serialize... }) : compose; const enhancer = composeEnhancers( applyMiddleware(thunk) // other store enhancers if any ); //创建store 并把reducer存入store中 const store = createStore( reducer, enhancer // applyMiddleware(thunk) // rudex dev tools chrome 插件 使用 // window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ && window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__() ); export default store;
store中的reducer.js

const defaultState={ inputValue:'', list:[1,3,4,5,5] } export default (state=defaultState,action)=>{ if(action.type==='change_input_value'){ const newState=JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(state)); newState.inputValue=action.value; console.log(newState) return newState; } if(action.type==='add_todo_list'){ const newState=JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(state)); if(newState.inputValue===''){ return newState; } newState.list.push(newState.inputValue); newState.inputValue=''; return newState; } if(action.type==="delete_todo_list"){ console.log(1) const newState=JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(state)); newState.list.splice(action.value,1); return newState; } return state; }
TodoList组件中的index.js

import React, { Component } from "react";
import { connect } from "react-redux";
//无状态组件是一个函数
const TodoList = (props) => {
const { inputValue, changeInputValue, handleClick, handleDel } = props;
return (
<div>
<div>
<input type="text" onChange={changeInputValue} value={inputValue} />
<button type="button" className="btn" onClick={handleClick}>
输入
</button>
</div>
<ul className="list">
{props.list.map((item, index) => {
return (
<li onClick={handleDel.bind(this, index)} key={index}>
{item}
</li>
);
})}
</ul>
</div>
);
};
// class TodoList extends Component {
// constructor(props) {
// super(props);
// }
// render() {
// const { inputValue, changeInputValue, handleClick, handleDel } = this.props;
// return (
// <div>
// <div>
// <input type="text" onChange={changeInputValue} value={inputValue} />
// <button type="button" className="btn" onClick={handleClick}>
// 输入
// </button>
// </div>
// <ul className="list">
// {this.props.list.map((item, index) => {
// return (
// <li onClick={handleDel.bind(this,index)} key={index}>
// {item}
// </li>
// );
// })}
// </ul>
// </div>
// );
// }
// }
const mapStateToProps = (state) => {
return {
inputValue: state.inputValue,
list: state.list,
};
};
const mapDispatchToprops = (dispatch) => {
return {
changeInputValue(e) {
const action = {
type: "change_input_value",
value: e.target.value,
};
// console.log(e.target.value)
dispatch(action);
},
handleClick() {
const action = {
type: "add_todo_list",
};
dispatch(action);
},
handleDel(index) {
const action = {
type: "delete_todo_list",
value: index,
};
dispatch(action);
},
};
};
//connect(mapStateToProps,mapDispatchToprops) 方法的作用使TodoList和store链接
//并按照mapStateToProps的规则下将store中的数据映射到TodoList的props中
//store.dispatch映射到TodoList组件的props上 可以让props上的方法能够调用dispatch来操作store中的数据
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToprops)(TodoList);
Ref的使用
第一种 字符串类写法 (不推荐 现在还可以使用 将来可能废弃 )
第二种 回调函数式写法(最为推荐)

import React, { Component } from 'react'
export default class home extends Component {
showData=(c)=>{
//函数
this.input2=c;
console.log(this.input2)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{/* ref 方式1 string形式 目前还可以用 未来可能废弃 */}
<button onClick={()=>{console.log(this.refs.input1)}}>点击提示</button>
<input ref='input1' type="text" onBlur={this.handleClick} placeholder='左侧侧提示' />
{/* ref 方式2 callback 形式 */}
<button onClick={()=>{console.log(this.input2)}}>点击提示</button>
{/* <input type="text" placeholder='右侧提示' ref={(currentNode)=>{this.input2=currentNode}} /> */}
{/* 箭头函数简写(内联函数写法,更新时会出发两次 功能不收影响 第一次值为null 第二次才为Dom节点;(每次函数执行完毕后会清空传入的currentNode 之后在重新执行)) */}
{/* <input type="text" placeholder='右侧提示' ref={(c)=>this.input2=c} /> */}
{/* 推荐写法 */}
<input type="text" placeholder='右侧提示' ref={this.showData} />
</div>
)
}
}
第三种 使用最新Api React.createRef 调用后返回一个容器,改容器可以存储ref所表示的节点

import React, { Component } from 'react'
export default class home extends Component {
//1调用React.createRef()创造myRef容器(单个容器)
myRef1=React.createRef();
myRef2=React.createRef();
//3 使用ref容器的方式
showDate=()=>{
console.log(this.myRef1);
console.log(this.myRef2);
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={this.showDate}>点击提示</button>
{/* ref 方式3 Api React.create()创建ref容器形式 */}
<input type="text" placeholder='右侧提示' ref={this.myRef1} />
<input type="text" placeholder='右侧提示' ref={this.myRef2} />
</div>
)
}
}
受控组件和非受控组件

// 非受控组件 // 受控组件的作用 可以少写ref 随用随取 import React, { Component } from 'react' export default class Login extends Component { state={ username:'', password:'' } //非受控组件使用ref LoginUser = (event) => { const { username, password } = this event.preventDefault();//阻止表单默认提交 console.log(`你的账号是${username.value},你的密码是${password.value}`) } //受控组件方法 实时获取状态 saveUserName = (e) => { console.log(e) this.setState({ username: e.target.value }) } savePassword = (e) => { this.setState({ password:e.target.value }) } render() { return ( <div> {/* 非受控组件 */} <form action="" onSubmit={this.LoginUser}> <div className="item"> <label htmlFor="">账号</label> <input type="text" placeholder='请输入账号' ref={c => this.username = c} /> </div> <div className="item"> <label htmlFor="">密码</label> <input type="password" placeholder='请输入密码' ref={c => this.password = c} /> </div> <div className="item"> <button>登录</button> </div> </form> {/* 受控组件 */} <form action="" onSubmit={this.LoginUser}> <div className="item"> <label htmlFor="">账号</label> <input type="text" placeholder='请输入账号' onChange={this.saveUserName} /> </div> <div className="item"> <label htmlFor="">密码</label> <input type="password" placeholder='请输入密码' onChange={this.savePassword} /> </div> <div className="item"> <button>登录</button> </div> </form> </div> ) } }
高阶函数及柯理化函数应用(简写表单绑定数据)

import React, { Component } from 'react'
export default class Reg extends Component {
/*
高阶函数:如果一个函数符合下面两个规范中的任何一个,那该函数就是高阶函数
1 若A函数,接收的参数是一个函数,那么A久可以称之为高阶函数
2 若A函数,调用的返回值依然是一个函数,那么A久可以称之为高阶函数
常见的高阶函数:Promise,setTimeout,arr.map()等
函数的柯理化 :通过函数调用继续返回函数的方式,实现多次接收参数最后统一处理的函数编码形式;
*/
LoginUser = (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
}
//函数的柯理化
saveFormDate=(dataType)=>{
const that=this;
return (event)=>{
//[]会解析变量
that.setState({
[dataType]:event.target.value
})
}
}
notSaveFormDate=(dataType,e)=>{
this.setState({
[dataType]:e.target.value
})
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{/* 使用柯理化 */}
<form action="" onSubmit={this.LoginUser}>
<div className="item">
<label htmlFor="">账号</label>
<input type="text" onChange={this.saveFormDate('username')} placeholder='账号' />
</div>
<div className="item"><label htmlFor="">密码</label>
<input type="password" placeholder='密码' onChange={this.saveFormDate('password')}/>
</div>
<div className="item"><button className="btn">登录</button></div>
</form>
{/*不使用柯理化 (通用方法) */}
<form action="" onSubmit={this.LoginUser}>
<div className="item">
<label htmlFor="">账号</label>
<input type="text" onChange={(e)=>{this.notSaveFormDate('username',e)}} placeholder='账号' />
</div>
<div className="item"><label htmlFor="">密码</label>
<input type="password" placeholder='密码' onChange={(e)=>{this.notSaveFormDate('password',e)}}/>
</div>
<div className="item"><button className="btn">登录</button></div>
</form>
</div>
)
}
}
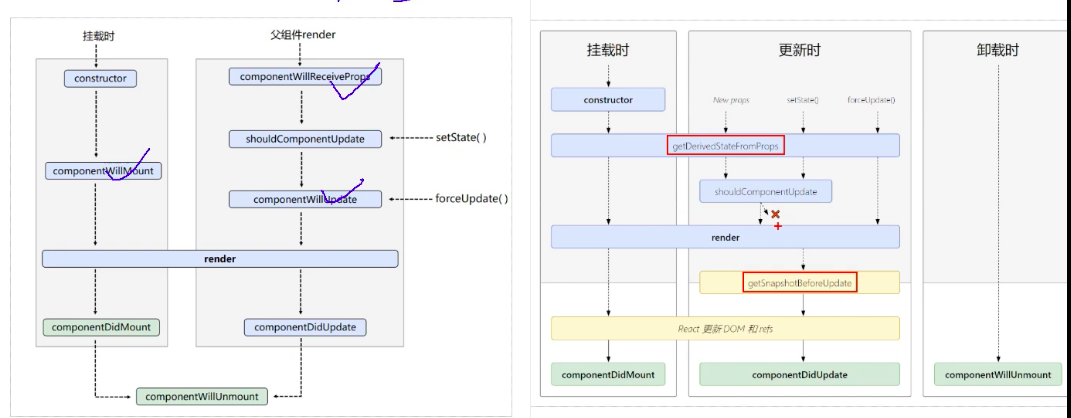
react 生命周期 旧
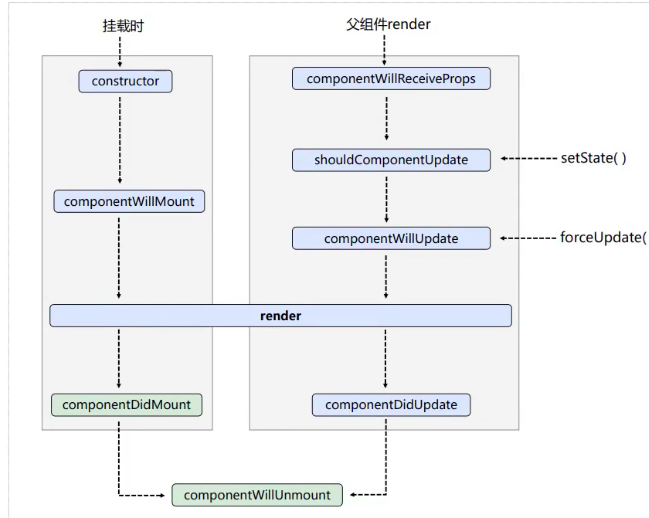

新生命周期

react新生命周期与旧生命周期对比
diff 算法


虚拟DOM相关

消息订阅-发布机制 实现组件之间的通信
下载库PubSubsJS
npm install pubsub-js --save
使用

/* 1) import PubSub from 'pubsub-js'; 2) token=PubSub.subscribe("delete",function(data){});//订阅 在收到消息的组件中的componentDidmount(){使用} //用法 componentDidMount() { this.token = PubSub.subscribe('msg', (_, data) => { //接收到的信息 console.log(data) this.setState({ List: data }) }) } 3) PubSub.publish("msg",data);//发布 在发布消息的组件中使用 4) PubSub.unsubscribe(token);//卸载 在收到消息的组件中的componentWillUnmount(){使用} //用法:组件卸载时 componentWillUnmount() { //卸载订阅消息 PubSub.unsubscribe(this.token) } */
路由
1 什么叫路由
- 一个路由就是一个 映射关系(key,value)
- key为path路径,value可能是function或component
2路由的分类
- 后端路由
- 理解:value是function,用来处理客户端提交的请求
- 注册路由 router.get(path,function(req,res)=>{})
- 工作过程: 当node接收到一个请求时,根据请求路径找到匹配的路由,调用路由种的函数来处理请求,返回相应数据
- 前端路由
- 浏览器路由,value是component,用于展示页面内容
- 注册路由:<Router path="/test" component={Test} >
- 工作过程:当浏览器的path变为test时,当前路由组件就会变为Test组件
- 后端路由
react-router-dom (react web 路由库)
安装 yarn add react-router-dom --save
- react 的一个插件库
- 专门用来实现一个SPA应用
- 基本react的项目基本会用到此库
路由的基本使用
- 明确好界面中的导航区,展示区
- 导航区的a标签改为Link标签: <Link to="/xxx">Demo</Link>
- 展示区写Route标签进行路径的匹配 : <Route path="/xxx" element={<Demo />} />
- <App>最外侧包裹了一个<BrowserRouter>或<HashRouter>
react-router-dom 相关的API
内置组件
- <BrowserRouter/> 整个路由 只能通过一个路由器管理

import React from 'react'; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'; import './index.css'; import App from './App'; import 'antd/dist/antd.min.css'; import reportWebVitals from './reportWebVitals'; // 引入全局路由器 import {BrowserRouter} from 'react-router-dom' ReactDOM.render( <React.StrictMode> {/* 路由器全局只能有一个 BroswerRouter*/} <BrowserRouter> <App /> </BrowserRouter> </React.StrictMode>, document.getElementById('root') ); // If you want to start measuring performance in your app, pass a function // to log results (for example: reportWebVitals(console.log)) // or send to an analytics endpoint. Learn more: https://bit.ly/CRA-vitals reportWebVitals();
- <HashRouter/>
- <Router/> 注册路由
- <Link/>
- <NavLink/> 使用和Link 一样 只是点击时可以添加需要的类名

import "./App.css"; import Home from "./views/Home"; import About from "./views/About"; import { Routes, Route, Link, NavLink } from "react-router-dom"; function App() { return ( <div className="App"> <h1>hello world</h1> <hr></hr> {/* 原生a标签跳转 React通过link标签(to 后面不识别大小写 建议小写) */} <Link to="/about" className="link"> got to Aboout </Link> <hr></hr> <Link to="/" className="link"> got to Home </Link> <hr></hr> {/* 点击NavLink时 会添上类名 在className中使用函数({isActive})=>isActive?'className':''*/} <NavLink to="/" className={({ isActive }) => (isActive ? "link clickActive" : "link")} > got to Home </NavLink> <hr></hr> <NavLink to="/about" className={({ isActive }) => (isActive ? "link clickActive" : "link")} > got to Aboout </NavLink> {/* routes 表现 内部嵌套 具体的route路由页面 */}{" "} <Routes> <Route path="/" element={<Home />}></Route>{" "} <Route path="/about" element={<About />}></Route>{" "} </Routes> </div> ); } export default App;
自己利用NavLink封装的MyNavLink组件 避免多写样式之类的内容

//封装组件 import React, { Component } from 'react' import {NavLink} from 'react-router-dom' export default class MyNavLink extends Component { render() { console.log(this) return ( <div> <NavLink className={({isActive})=>isActive?"link clickActive":"link"} {...this.props} /> </div> ) } } // 使用组件 import MyNavLink from "./components/myNavLink"; <MyNavLink to="/about" >About</MyNavLink> <MyNavLink to="/" >Home</MyNavLink>
- <Switch/> 旧版本 新版本 修改成了<Routes /> 为了 提高匹配效率 匹配到了路由 就停止匹配

{/* 旧版本是<Switch/> 新版本是<Routes /> */}
<Routes>
{/* 注册路由 */}
<Route path="/" element={<Home />}></Route>{" "}
<Route path="/about" element={<About />}></Route>{" "}
<Route path="/about" element={<About />}></Route>{" "}
</Routes>
- <Redirect/> 重定向 当 前面的Route 都匹配不到的时候 按<Redirect />的来
其他
- history对象
- match对象
- withRouter函数
路由组件与一般组件

react中解决多级路径刷新页面样式丢失问题(即用绝对路径 或者将BroswerRouter换成HashRouter)
路由的模糊匹配与严格匹配


<MyNavLink to="/about/a/b">About</MyNavLink>
<MyNavLink to="/">Home</MyNavLink>
{/* routes 表现 内部嵌套 具体的route路由页面 */}{" "}
{/* 旧版本是<Switch/> 新版本是<Routes /> */}
<Routes>
{/* 注册路由 */}
<Route path="/" element={<Home />}></Route>{" "}
{/* exact 默认模糊匹配 exact={true}精准匹配 必须path与Link或NavLink 的to属性值一致才会匹配到*/}
<Route exact={true} path="/about" element={<About />}></Route>{" "}
</Routes>
自定义路由规则文件router.js

//改文件专门用于同一路由管理 import Login from '../pages/Login' import User from '../pages/User' import Home from '../pages/Home/' //routes 数组中存储者所有的路由配置,每个路由配置都是一个对象 const routes = [ { path: '/login', element: < Login / > }, { path: '/user', element: < User / > }, { path: '/', element: < Home / > }, ] export default routes;
使用

import "./App.css"; import { Routes, Route } from "react-router-dom"; import routes from "./config/router"; function App() { return ( <div className="App"> <Routes> {routes.map((item) => { // 全写 // return <Route path={item.path} element={item.element} key={item.path}></Route> // 简写 批量传递 return <Route {...item} key={item.path}></Route>; })} </Routes>{" "} </div> ); } export default App;
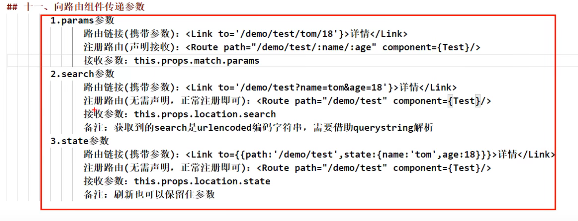
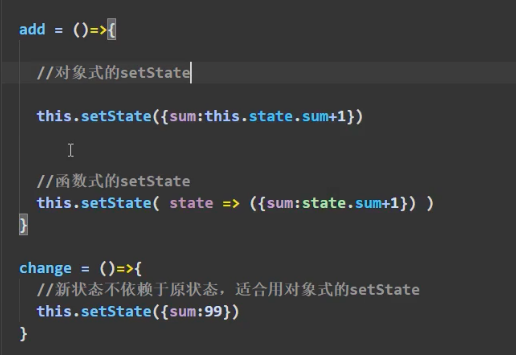
深入了解setState

lazyLoad 懒加载
路由组件的lazyLoad

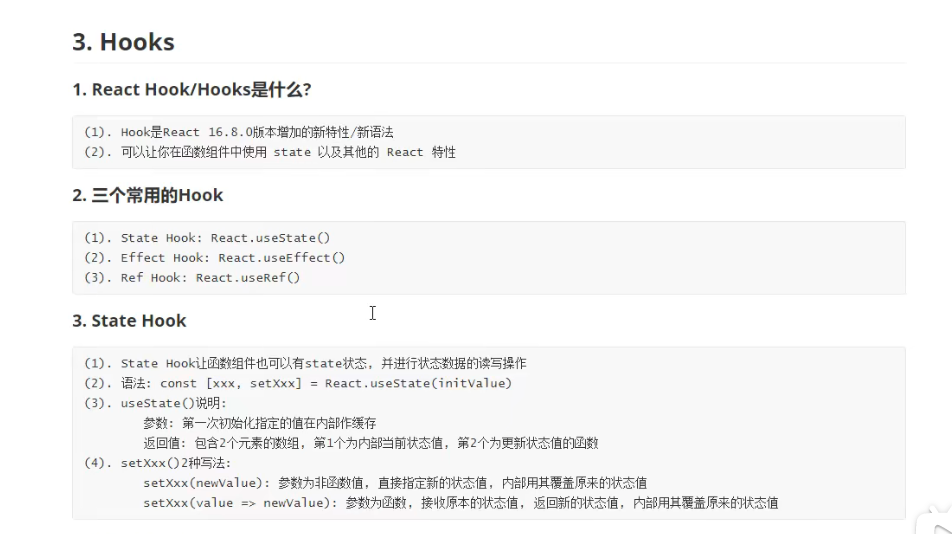
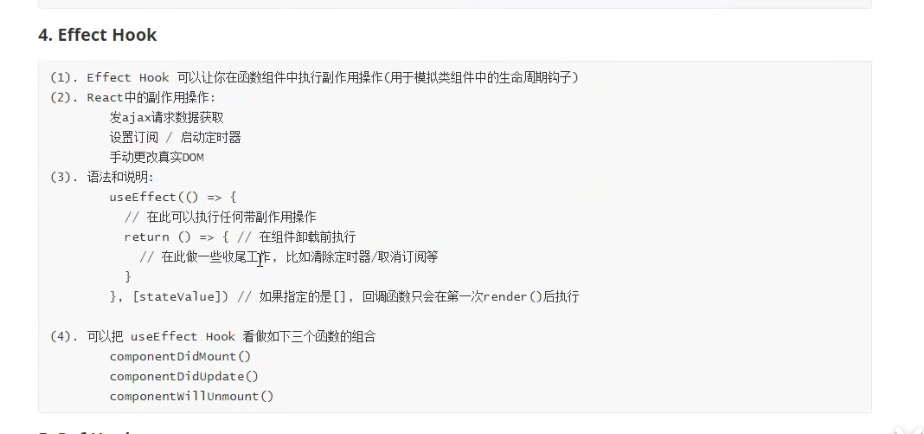
HooKs

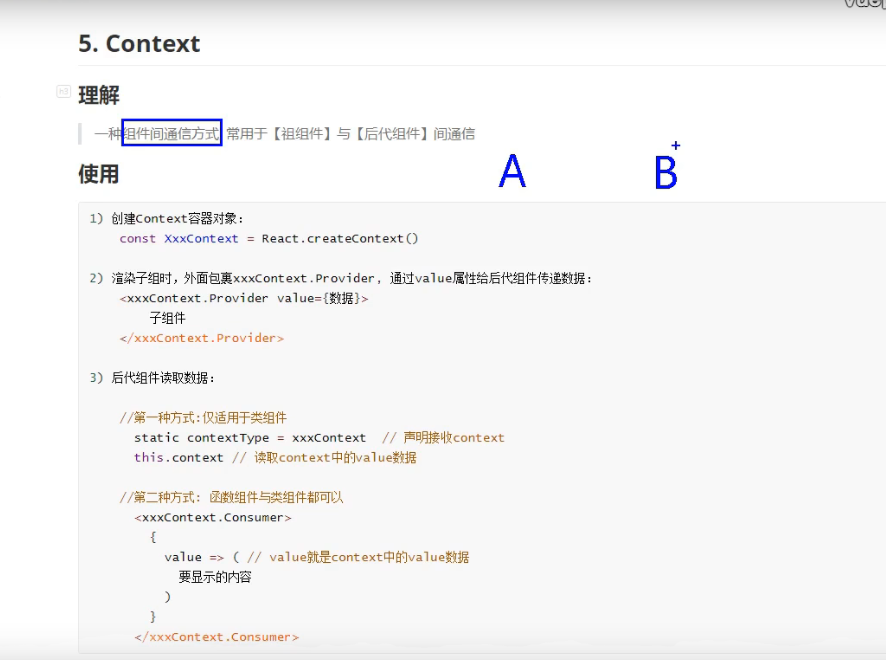
Context