java 中 CountDownLatch、CyclicBarrier 和 Semaphore 的简单使用
一、CountDownLatch
1.1 概述
让一些线程阻塞直到另外一些完成后才被唤醒。
该类主要有两个方法,当一个或多个线程调用 await 方法时,调用线程会被阻塞。其他线程调用 countDown方法计数器减1(调用countDown方法时线程不会阻塞),当计数器的值变为0,因调用 await 方法被阻塞的线程会被唤醒继续执行。
1.2 模拟场景
有 6 名学生上完课后,离开教室,但他们离开的时间不相同,班长需要最后一个离开,锁上教室的门。
1.3 程序模拟
1.3.1 使用 CountDownLatch 之前
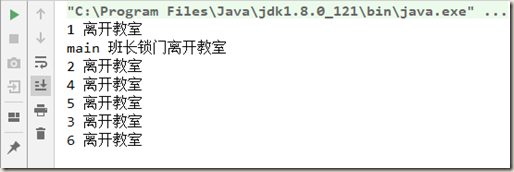
1 public void closeDoor() { 2 3 for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { 4 new Thread(() -> { 5 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 离开教室"); 6 }, String.valueOf(i)).start(); 7 } 8 9 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 班长锁门离开教室"); 10 }
1.3.2 使用 CountDownLatch 之后
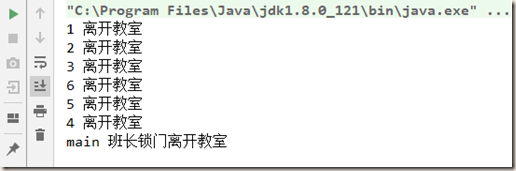
1 public void closeDoor() throws InterruptedException { 2 CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(6); 3 4 for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { 5 new Thread(() -> { 6 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 离开教室"); 7 countDownLatch.countDown(); 8 }, String.valueOf(i)).start(); 9 } 10 11 countDownLatch.await(); 12 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 班长锁门离开教室"); 13 }
1.4 CountDownLatch 配合枚举类的使用
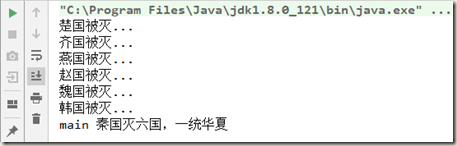
1 private static void nationalUnification() throws InterruptedException { 2 CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(6); 3 4 for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { 5 new Thread(() -> { 6 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "国被灭..."); 7 countDownLatch.countDown(); 8 }, CountryEnum.forEachCountryEnum(i).getCountry()).start(); 9 } 10 11 countDownLatch.await(); 12 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 秦国灭六国,一统华夏"); 13 } 14 15 // 枚举类,存储国家的名字 16 public enum CountryEnum { 17 18 ONE(1, "齐"), 19 TWO(2, "楚"), 20 THREE(3, "燕"), 21 FOUR(4, "赵"), 22 FIVE(5, "魏"), 23 SIX(6, "韩"); 24 25 private Integer code; 26 private String country; 27 28 CountryEnum(Integer code, String country) { 29 this.code = code; 30 this.country = country; 31 } 32 33 public Integer getCode() { 34 return code; 35 } 36 37 public String getCountry() { 38 return country; 39 } 40 41 public static CountryEnum forEachCountryEnum(int index) { 42 CountryEnum[] countryEnums = CountryEnum.values(); 43 for (CountryEnum element : countryEnums) { 44 if (element.getCode() == index) { 45 return element; 46 } 47 } 48 return null; 49 } 50 } 51
二、CyclicBarrier
2.1 概述
CyclicBarrier 的字面意思是可循环(Cyclic),使用的屏障(barrier)。它要做的事情是,让一组线程到达一个屏障(也可以叫做同步点)时被阻塞,直到最后一个线程到达屏障时,屏障才会开门,所有被屏障拦截的线程才会继续干活,线程进入屏障通过 CyclicBarrier 的 await() 方法。
2.2 示例
1 public void meet() { 2 CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(10, () -> { 3 System.out.println("人齐了,准备开会"); 4 }); 5 6 for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { 7 new Thread(() -> { 8 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 来到会议室"); 9 try { 10 cyclicBarrier.await(); 11 } catch (InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e) { 12 e.printStackTrace(); 13 } 14 }, String.valueOf(i)).start(); 15 } 16 }
三、Semaphore
3.1 概述
A counting semaphore. Conceptually, a semaphore maintains a set of permits. Each acquire() blocks if necessary until a permit is available, and then takes it. Each release() adds a permit, potentially releasing a blocking acquirer. However, no actual permit objects are used; the Semaphore just keeps a count of the number available and acts accordingly.
3.2 示例
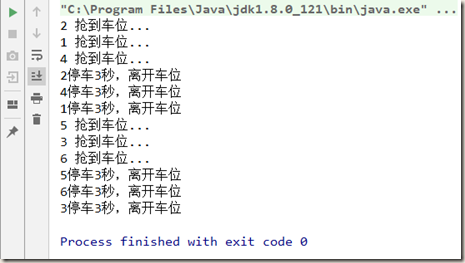
1 public void semaphoreTest() { 2 Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3); 3 4 for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { 5 new Thread(() -> { 6 try { 7 semaphore.acquire(); 8 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 抢到车位..."); 9 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); 10 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "停车3秒,离开车位"); 11 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 12 e.printStackTrace(); 13 } finally { 14 semaphore.release(); 15 } 16 }, String.valueOf(i)).start(); 17 } 18 }