Spring系统学习--3AOP
解决什么样的问题?
@Override
public void transfer(String sourceName,String targetName,Float money){ //1.根据名称查询转出账户 Account source=accountDao.findByName(sourceName); //2.根据名称查询转入账户 Account target=accountDao.findByName(targetName); //3.转出账户减钱 source.setMoney(source.getMoney()-money); //4.转入账户加钱 target.setMoney(target.getMoney()+money); //5.更新转出账户 accountDao.update(source); //模拟转账异常 int i=1/0;//6.更新转入账户 accountDao.update(target);
动态代理
1.基于接口
/*创建一个被代理的类(这里加入是笔记本电脑生产厂家),被代理类要实现代理类接口*/ public class ComputerFactory implements IAgent{ public void sale(Float money){ System.out.println("一手交钱"+money+"一手交货"); } public void afterService(Float money){ System.out.println("维想修,拿钱来"+money); } } /*创建一个代理类(接口),(这里假设是生产厂家的代理,帮着买电脑等...)*/ public interface IAgent { public void sale(Float money); public void afterService(Float money); } /*下面是如何使用代理类代理处理业务的*/ package spring.day03.agent; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; public class Demo { /** * 动态代理 * 特点:字节码随用随创建,随用随加载 * 分类: * 基于接口的 * 基于子类的 * 作用: * 在不改变源码的基础上对已有方法增强 * 此类讲解的是基于接口的动态代理 * 提供者:JDK官方
* 涉及的类:Proxy * 创建代理对象的方法:newProxyInstance
* 方法的参数: * ClassLoader:类加载器。和被代理象使用相同的类加载器。该参数是固定写法。 * Class[]:字节码数组。和被代理对象具有相同的行为,实现相同的接口。 * InvocationHandler:它是一个接口。提供如何代理的代码。也就是增强的代码。该参数一般都成名内部类。 * 并且它是策略模式的体现。 * 策略模式: * 要求:数据已经有了,目的明确。 * 达成目标的过程就是策略。 * 该参数是谁用谁写。 * 使用要求:被代理类最少实现一个接口。 */ public static void main(String[] args) { final ComputerFactory factory = new ComputerFactory(); IAgent proxyFactory = (IAgent) Proxy.newProxyInstance(factory.getClass().getClassLoader(), factory.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { /** *该方法的特征: *执行被代理对象的任何方法,都会经过该方法。该方法有拦截的特点 *方法的参数: *Object proxy:代理对象的引用。 *Method method:当前执行的方法 *Object[]args:当前执行方法所需的参数 *方法的返回值: *Object:和被代理对象的方法返回值一致。 * */ @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { Object rtValue = null; //1.获取正在执行方法的参数 Float money = (Float) args[0]; //2.判断正在执行的方法 if ("sale".equals(method.getName())) { //经销商最少一台电脑挣2000元钱 if (money > 7000) { rtValue = method.invoke(factory, money / 2); } } if ("afterservice".equals(method.getName())) { //经销商最少一台电脑正600元 if (money > 1600) { rtValue = method.invoke(factory, money / 4 * 3); } } return rtValue; // return method.invoke(factory,args); } }); // factory.sale(5000f); // factory.afterService(100f); proxyFactory.sale(10000f); proxyFactory.afterService(100f); } }
2.基于子类
<!--所需依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>cglib</groupId> <artifactId>cglib</artifactId> <version>2.2.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>asm</groupId> <artifactId>asm</artifactId> <version>3.3.1</version> </dependency>
/*被代理的类*/ public class ComputerFactory { public void sale(Float money){ System.out.println("一手交钱"+money+"一手交货"); } public void afterService(Float money){ System.out.println("维想修,拿钱来"+money); } } /*执行代理的代码*/ public class Demo { /** * 动态代理 * 特点:字节码随用随创建,随用随加载 * 分类: * 基于接口的 * 基于子类的 * 作用: * 在不改变源码的基础上对已有方法增强 * 此类讲解的是基于子类的动态代理 * 提供者:cglib * 依赖外部jar:cglib;asm; * 涉及的类:Enhancer * 创建代理对象的方法:create * 方法的参数: * Class:字节码。指定被代理文件的字节码文件 * CallBack:如何代理。 * <p> * 使用要求:被代理类不能是最终类 */ public static void main(String[] args) { ComputerFactory factory = new ComputerFactory(); ComputerFactory cglibfactory = (ComputerFactory) Enhancer.create(factory.getClass(), new MethodInterceptor() { /** *它和InvocationHandler中的invoke方法作用是一样的 *该方法的前3个参数和invoke方法的三个参数作用是一样的。 *该方法的返回值和invoke方法的返回值作用也是一样的。 * *MethodProxy参数:它是当前执行方法的代理对象,一般用不到。 */ @Override public Object intercept(Object Proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable { Object rtValue = null; //1.获取正在执行方法的参数 Float money = (Float) args[0]; //2.判断正在执行的方法 if ("sale".equals(method.getName())) { //经销商最少一台电脑挣2000元钱 if (money > 7000) { rtValue = method.invoke(factory, money / 2); } } if ("afterService".equals(method.getName())) { //经销商最少一台电脑正600元 if (money > 1600) { rtValue = method.invoke(factory, money / 4 * 3); } } return rtValue; // return method.invoke(factory,args); } }); cglibfactory.sale(10000f); cglibfactory.afterService(5000f); } }
AOP概述
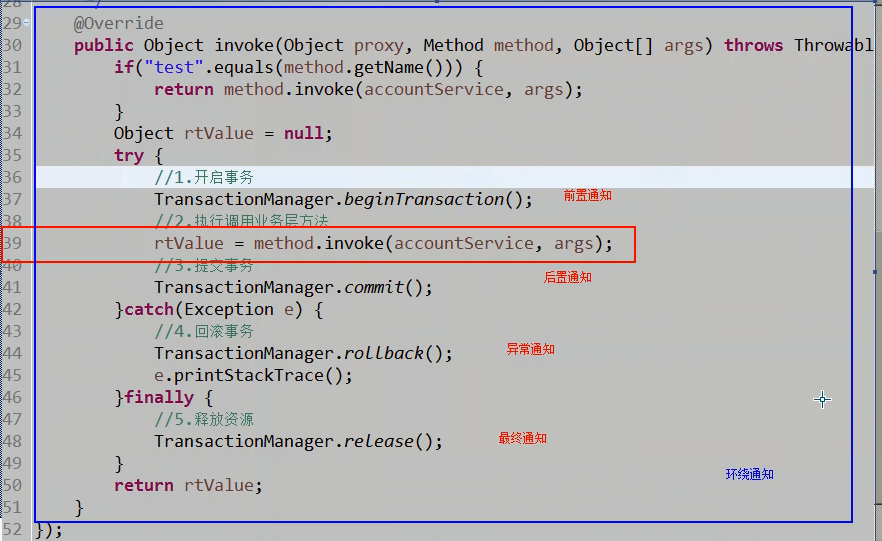
简单的说它就是把我们程序重复的代码抽取出来,在需要执行的时候,使用动态代理的技术,在不修改源码的基础上,对我们的已有方法进行增强。
作用:
在程运行期间:不修改源码对已有方法进行增强。
优点:
减少重复代码
提高开发效案
维护方便
基于XML的AOP配置
项目依赖:
<!-- junit:方便我们进行方法的测试--> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <!-- <scope>test</scope>--> </dependency> <!-- spring-context:导入spring核心jar包 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.0.7.RELEASE</version> <!-- <scope>test</scope>--> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.46</version> </dependency> <!-- 导入日志jar包--> <dependency> <groupId>commons-logging</groupId> <artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId> <version>1.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>jakarta.annotation</groupId> <artifactId>jakarta.annotation-api</artifactId> <version>1.3.4</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>cglib</groupId> <artifactId>cglib</artifactId> <version>2.2.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>asm</groupId> <artifactId>asm</artifactId> <version>3.3.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.9.2</version> </dependency>
SpringXML配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!-- 配置业务逻辑层--> <bean id="AccountService" class="main.java.spring.day03.aop.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean> <!--spring基于xml的aop配置步骤: 前期准备: 1.拷贝aop的jar包 2.在配置文件中导入aop的约束 配置步骤: 1.把通知bean也交给spring来管理 2.使用aop名称空间下的aop:config标签开始aop的配置 3.使用aop:aspect标签,开始配置切面。 id属性:用于给切面提供一个唯一标识 ref属性:用于引用通知bean的id。 4.使用aop:before标签配置前置通知 method属性:用于指定通知类中的哪个方法是前置通知 pointcut属性:用于指定切入点表达式。 切入点表达式: 关键字:execution(表达式) 表达式的写法: 访问修饰符返回值包名。包名...类名.方法名(参数列表) 全匹配方式: public vdid main.java.spring.day03.aop.impl.AccountServiceImpl.saveAccount() 访问修饰符可以省略: void main.java.spring.day03.aop.impl.AccountServiceImpl.saveAccount() 返回值可以使用*,表示任意返回值类型 * main.java.spring.day03.aop.impl.AccountServiceImpl.saveAccount() 包名可以使用*,表示任意包。但是有几级包,需要写几个* * *,*,*,*,*,*.AccountServiceImpl.saveAccount() 包名可以使用..表示当前包及其子包: * *..AccountServiceImpl.saveAccount() 类名可以使用*,表示任意类 **..*.saveAccount() 方法名可以使用*,表示任意方法 *main.java.spring..*.*() 参数列表可以指定具体类型: 基本类型直接写类型名称:*main.java.spring..*.*(int) 引用类型必须是包名,类名的方式:*main.java.spring..*.*(java.lang.String) 参数列表可以使用*,表示任意参数类型,但是必须有参数 *main.java.spring..*.*(*) 参数列表可以使用..,表示有无参数均可: *main.java.spring..*.*(..) --> <bean id="logger" class="main.java.spring.day03.aop.Logger"></bean> <aop:config> <!--使用aop:pointcut标签可以配置通用切入点表达式 ;写在切面aop:aspect标签内部,只能当前切面使用。 如果要想所有切面使用,请写到aop:aspect标签外面--> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* main.java.spring..*.*(..)) " id="pt"/> <aop:aspect id="logerAop" ref="logger"> <!-- 配置前置通知:她永远都会在切入点方法执行之前执行--> <aop:before method="beforeprintLog" pointcut="execution(public void main.java.spring.day03.aop.impl.AccountServiceImpl.saveAccount())"></aop:before> <!--配置后置通知:当切入点方法正常执行之后,后置通知执行。它和异常通知只能有一个执行--> <aop:after-returning method="afterReturningPrintLog" pointcut="execution(* main.java.spring..*.*(..))"/> <!--配置异常通知:当切入点方法执行产生异常后执行。它和后置通知是互斥的--> <aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowingPrintLog" pointcut="execution(* main.java.spring..*.*(..))"/> <!--配置最终通知:无论切入点方法是否正常执行,它都会在其后面执行--> <aop:after method="afterPrintLog" pointcut="execution (* main.java.spring..*.*(..))"/> <!--配置环绕通知:详细注释写到Logger类里了--> <aop:around method="aroundPrintLog" pointcut-ref="pt"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> </beans>
/* 业务层代码 */ public interface AccountService { /** * 保存账户 */ void saveAccount(); } /* 业务层实现类 */ public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { private AccountDao accountDao; public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) { this.accountDao = accountDao; } @Override public void saveAccount() { System.out.println("保存账户!!!"); // int a=1/0;//模拟异常 } }
/*****************切面类*************************/ package main.java.spring.day03.aop; import org.springframework.aop.aspectj.MethodInvocationProceedingJoinPoint; public class Logger { /** *计划让其在切入点方法执行之前执行 */ public void beforeprintLog() { System.out.println("Logger类中的beforePrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。前置"); } /** * 后置通知 */ public void afterReturningPrintLog(){ System.out.println("Logger类中的afterReturningPrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。后置"); } /** *异常通知 */ public void afterThrowingPrintLog(){ System.out.println("Logger类中的afterThrowingPrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。异常"); } /** *最终通知 */ public void afterPrintLog() { System.out.println("Logger类中的afterPrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。最终"); } /** *环绕通知 * 问题: * 当我们配置了环绕通知之后,执行切入点方法时,最终的结果是环绕通知的代码执行了,而切入点方法却没有执行。 * 分析: * 根据动态代理的代码分析,可以看到invoke方法中有一个明确调用切入点方法的代码。而我们spring中的环绕通知目前没有调用切入点方法 * 解决办法: * 思路:我们也需要在环绕通知中明确调用一下切入点方法。 * Spring框架为我们提供了一个接口:ProceedingJoinPoint。该接口可以作为环绕通知的方法参数来使用。 * 在程序运行时spring框架会为我们注入该接口的实现类供我们使用。I * 该接口有个方法: * proceed()方法,它就相当于明确调用切入点方 * 环绕通知:它是spring为我们提供的一种可以在代码中手动控制通知何时执行的方式方式。 */ public Object aroundPrintLog(MethodInvocationProceedingJoinPoint pjp) { //获取方法所需参数 Object[] args = pjp.getArgs(); Object rtValue = null; try { System.out.println("Logger类中的aroundPrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。前置"); rtValue = pjp.proceed(args); System.out.println("Logger类中的aroundPrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。后置"); } catch (Throwable throwable) { System.out.println("Logger类中的aroundPrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。异常"); throwable.printStackTrace(); }finally { System.out.println("Logger类中的aroundPrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。最终"); } return rtValue; } }
/******************测试类**************/ public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("config/bean_aop.xml"); AccountServiceImpl accountService = context.getBean("AccountService", AccountServiceImpl.class); accountService.saveAccount(); context.close(); } }
基于注解的AOP配置
项目依赖:
<!-- junit:方便我们进行方法的测试--> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <!-- <scope>test</scope>--> </dependency> <!-- spring-context:导入spring核心jar包 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.1.2.RELEASE</version> <!-- <scope>test</scope>--> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.46</version> </dependency> <!-- 导入日志jar包--> <dependency> <groupId>commons-logging</groupId> <artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId> <version>1.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>jakarta.annotation</groupId> <artifactId>jakarta.annotation-api</artifactId> <version>1.3.4</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>cglib</groupId> <artifactId>cglib</artifactId> <version>2.2.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>asm</groupId> <artifactId>asm</artifactId> <version>3.3.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.9.2</version> </dependency>
spring配置类
/** * 创建spring的配置类,相当于原来的bean.xml */ @Configuration @ComponentScan("spring")//配置要扫描的包 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy//开启spring对注解AOP的支持 public class SpringConfigtion { }
业务层实现类
/* 业务层实现类 */ @Service("accountService") public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { @Override public void saveAccount() { System.out.println("保存账户!!!"); // int a=1/0;//模拟异常 } }
切面类
@Component("logger")
@Aspect//把此类配置成一个切面
public class Logger {
@Pointcut("execution(* spring..*.*(..))")
public void pt(){
}
/**
* 前置通知
*计划让其在切入点方法执行之前执行
*/
@Before(value = "pt()")
public void beforeprintLog() {
System.out.println("Logger类中的beforePrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。前置");
}
/**
* 后置通知
*/
@AfterReturning(value = "pt()")
public void afterReturningPrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的afterReturningPrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。后置");
}
/**
*异常通知
*/
@AfterThrowing(value = "pt()")
public void afterThrowingPrintLog(){
System.out.println("Logger类中的afterThrowingPrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。异常");
}
/**
*最终通知
*/
@After(value = "pt()")
public void afterPrintLog() {
System.out.println("Logger类中的afterPrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。最终");
}
// @Around(value = "pt()")
public Object aroundPrintLog(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) {
//获取方法所需参数
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
Object rtValue = null;
try {
System.out.println("Logger类中的aroundPrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。前置");
rtValue = pjp.proceed(args);
System.out.println("Logger类中的aroundPrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。后置");
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("Logger类中的aroundPrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。异常");
throwable.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("Logger类中的aroundPrintLog方法开始记录日志了。。。最终");
}
return rtValue;
}
}
测试类
public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfigtion.class); AccountService accountService = (AccountService)context.getBean("accountService"); accountService.saveAccount(); context.close(); } }

