48.反射
1.类加载器
1.1类加载


1.2类加载器


public static void main(String[] args) { // static ClassLoader getSystemClassLoader() 返回用于委派的系统类加载器。 // ClassLoader getParent() 返回委托的父类加载器。(返回父类加载器进行委派) ClassLoader c1 = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();//返回用于委派的系统类加载器。 System.out.println(c1);//AppClassLoader ClassLoader c2 = c1.getParent(); System.out.println(c2);//ExtClassLoader ClassLoader c3 = c2.getParent(); System.out.println(c3);//null } }
2.反射
2.1反射概述


2.2获取Class类的对象

public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException { // 1.使用类的Class获取对应类的class Class<Student> c1 = Student.class; System.out.println(c1);//class fanshe.Student Class<Student> c2 = Student.class; System.out.println(c1==c2);//true // 2.调用对象的getClass()方法,获取该对象所属类的Class对象 Student student = new Student(); Class<? extends Student> c3 = student.getClass(); System.out.println(c1==c3);//true // 3.通过Class类的静态方法forName(String className) Class<?> c4 = Class.forName("fanshe.Student"); System.out.println(c1==c4);//true }
2.3反射获取构造方法并使用
Class<?> c4 = Class.forName("fanshe.Student");
System.out.println(c1==c4);//true
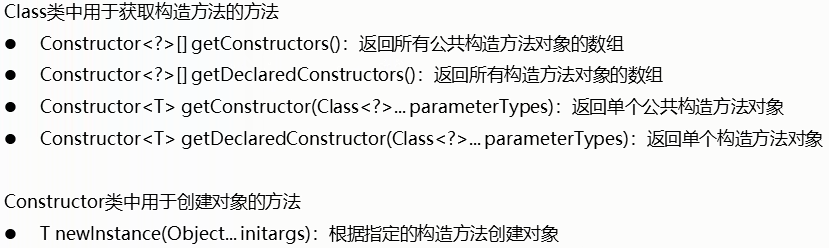
// Constructor<?>[] getConstructors() 返回一个包含 Constructor对象的数组, Constructor对象反映了此 类对象所表示的类的所有公共构造函数。
Constructor<?>[] constructors = c4.getConstructors();
for (Constructor c:constructors){
System.out.println(c);//public fanshe.Student()//public fanshe.Student(java.lang.String,int,java.lang.String)
}
// Constructor<?>[] getDeclaredConstructors() 返回 Constructor对象的数组, Constructor对象反映由此 类对象表示的类声明的所有构造函数。
Constructor<?>[] constructors1 = c4.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor c:constructors1){
System.out.println(c);
/***
* private fanshe.Student(java.lang.String)
* fanshe.Student(java.lang.String,int)
* public fanshe.Student()
* public fanshe.Student(java.lang.String,int,java.lang.String)
*/
}
// Constructor<T> getConstructor(类<?>... parameterTypes) 返回一个 Constructor对象,该对象反映此 类对象所表示的类的指定公共构造函数。
// Constructor<T> getDeclaredConstructor(类<?>... parameterTypes) 返回一个 Constructor对象,该对象反映此 类对象所表示的类或接口的指定构造函数。
// 上面两个构造方法所需要的参数是:你要获取的构造方法的参数的数据类型对应的字节码文件对象(例如:String.class)
// Constructor 提供有关类的单个构造函数的信息和访问权限。
// T newInstance(Object... initargs) 使用由此 Constructor对象表示的构造函数,使用指定的初始化参数来创建和初始化构造函数的声明类的新实例。
Constructor<?> constructor = c4.getConstructor();
Object o = constructor.newInstance();
System.out.println(o);//fanshe.Student@1540e19d
2.4反射获取构造方法并使用练习

Class<?> c = Class.forName("fanshe.Student");
Constructor<?> constructor = c.getConstructor(String.class, int.class, String.class);
Object o = constructor.newInstance("李沁", 17, "河南");
System.out.println(o);


Class<?> c = Class.forName("fanshe.Student");
/**
* private Student(String name) {
* this.name = name;
* }
*/
//私有构造方法创建对象需要使用"暴力反射":public void setAccessible(boolean flag)将此反射对象的accessible标志设置为指示的布尔值。 值为true表示反射对象应该在使用Java语言访问控制时抑制检查。
Constructor<?> declaredConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o1 = declaredConstructor.newInstance("李沁");
System.out.println(o1);

2.5反射获取成员变量并使用

public class Chengyuanbianliang { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException { Class<?> c = Class.forName("fanshe.Student"); // Field[] getFields() 返回一个包含 Field对象的数组, Field对象反映由该 Class对象表示的类或接口的所有可访问的公共字段。 // Field getField(String name) 返回一个 Field对象,该对象反映由该 Class对象表示的类或接口的指定公共成员字段。 // Field[] getDeclaredFields() 返回一个 Field对象的数组,反映了由该 Class对象表示的类或接口声明的所有字段。 // Field getDeclaredField(String name) 返回一个 Field对象,该对象反映由该 Class对象表示的类或接口的指定声明字段。 /** * private String name; * int age; * public String addr; */ Field[] fields = c.getFields(); for (Field field : fields) { System.out.println(field);//public java.lang.String fanshe.Student.addr } Field[] fields2 = c.getDeclaredFields(); for (Field field : fields2) { System.out.println(field); /** * private java.lang.String fanshe.Student.name * int fanshe.Student.age * public java.lang.String fanshe.Student.addr */ } Field name = c.getDeclaredField("name"); System.out.println(name);//private java.lang.String fanshe.Student.name Field addrField = c.getField("addr"); System.out.println(addrField);//public java.lang.String fanshe.Student.addr // 如何使用获取的字段属性呢? // 1.根据反射获取无参构造方法,并创建对象 Constructor<?> constructor = c.getConstructor(); Object obj = constructor.newInstance(); // Field提供有关类或接口的单个字段的信息和动态访问。 // void set(Object obj, Object value) 将指定的对象参数中由此 Field对象表示的字段设置为指定的新值。 addrField.set(obj, "北京"); System.out.println(obj); } }
2.6反射获取成员变量并使用练习

public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException { Class<?> c = Class.forName("fanshe.Student"); Constructor<?> constructor = c.getConstructor(); // Constructor<?> constructor = c.getConstructor(String.class, int.class, String.class); Object o = constructor.newInstance(); Field name = c.getDeclaredField("name"); Field age = c.getDeclaredField("age"); Field addr = c.getField("addr"); /** * private String name; * int age; * public String addr; */ name.setAccessible(true); age.setAccessible(true); name.set(o,"李沁"); age.set(o,17); addr.set(o,"北京"); System.out.println(o); }
2.7反射获取成员方法

public class GetMethoedDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException { Class<?> c = Class.forName("fanshe.Student"); // Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes) 返回一个 方法对象,该对象反映由该 Class对象表示的类或接口的指定公共成员方法。 // Method[] getMethods() 返回一个包含 方法对象的数组, 方法对象反映由该 Class对象表示的类或接口的所有公共方法,包括由类或接口声明的对象以及从超类和超级接口继承的类。 // Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes) 返回一个 方法对象,它反映此表示的类或接口的指定声明的方法 Class对象。 // Method[] getDeclaredMethods() 返回一个包含 方法对象的数组, 方法对象反映由 Class对象表示的类或接口的所有声明方法,包括public,protected,default(package)访问和私有方法,但不包括继承方法。 Method[] methods = c.getMethods(); for (Method method : methods) { System.out.println(method); } /** * public void publicMethod1(){ * System.out.println("我是Student的公共成员方法"); * } */ Method publicMethod1 = c.getMethod("publicMethod1"); // 创建对象使用方法 Constructor<?> constructor = c.getConstructor(); Object obj = constructor.newInstance(); // Method 在类或接口上提供有关单一方法的信息和访问权限。 // Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args) 在具有指定参数的指定对象上调用此方法对象表示的基础方法 // Object :返回值类型 // obj:调用方法的对象 // args:方法所需要的参数 publicMethod1.invoke(obj);//我是Student的公共成员方法 } }
2.8反射获取成员方法练习

public class GetMethodPractice { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException { /** * public void publicMethod1(){ * System.out.println("我是Student的公共成员方法"); * } * private void privateMethod(String s){ * System.out.println(s); * } * public String publicMethod1(String s,int age){ * return s+","+age; * } * private String privateMethod1(String s){ * return s; * } */ Class<?> c = Class.forName("fanshe.Student"); Constructor<?> constructor = c.getConstructor(); Object obj = constructor.newInstance(); // 1.公共无参方法调用 Method publicMethod1 = c.getMethod("publicMethod1"); publicMethod1.invoke(obj); // 2.私有带参无返回值方法调用 Method privateMethod = c.getDeclaredMethod("privateMethod", String.class); privateMethod.setAccessible(true);//抑制检查 privateMethod.invoke(obj, "帯参无返回值方法的参数字符串"); // 3.公共帯参带返回值方法调用 Method publicMethod11 = c.getMethod("publicMethod1", String.class, int.class); Object o = publicMethod11.invoke(obj, "帯参有返回值方法的参数字符串", 88); System.out.println(o); } }
2.9反射练习 之 越过泛型检查

public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException { ArrayList<Integer> integers = new ArrayList<>(); integers.add(66); integers.add(88); // integers.add("李沁");//不可以直接添加 Class<? extends ArrayList> c = integers.getClass(); Method add = c.getMethod("add", Object.class); add.invoke(integers, "hello"); add.invoke(integers, "java"); System.out.println(integers);//[66, 88, hello, java] }
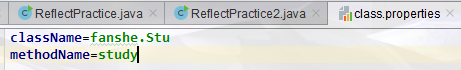
2.9反射练习 之 运行配置文件指定内容

public class Teacher { public void teach(){ System.out.println("李沁老师,用爱成就学员!!!"); } } public class Stu { public void study(){ System.out.println("good good study,day day up!!!"); } } public class ReflectPractice2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException { /** * class.properties * className=*** * methodName=*** */ Properties properties = new Properties(); FileReader filereader = new FileReader("file\\class.properties"); properties.load(filereader); filereader.close(); String className = properties.getProperty("className"); String methodName = properties.getProperty("methodName"); Class<?> c = Class.forName(className); Method method = c.getMethod(methodName); Constructor<?> constructor = c.getConstructor(); Object o = constructor.newInstance(); method.invoke(o); } }