properties类以及.properties文件的使用
1.关于Properties类
概述


1.Properties作为Map使用
// 创建对象不可使用泛型 Properties properties = new Properties(); // 存储元素 properties.put("张飞","18"); properties.put("关羽","19"); properties.put("刘备","20"); Set<Object> objects = properties.keySet(); // 遍历元素 for (Object o:objects){ System.out.println(o+":"+properties.get(o)); }
2.Properties作为Map使用的特有方法
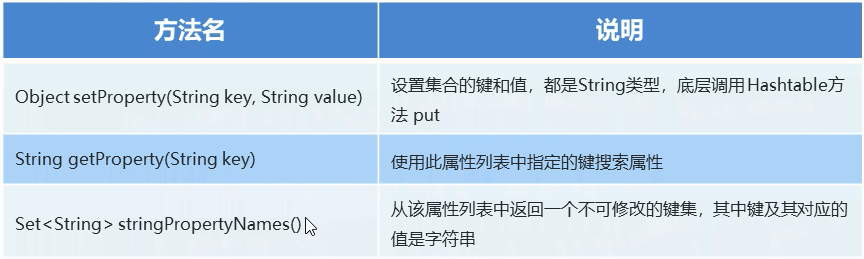
// setProperty(String key, String value) 设置集合的键和值,都是String类型,调用 Hashtable方法 put 。 Properties prop = new Properties(); prop.setProperty("001","张飞"); /** * public synchronized Object setProperty(String key, String value) {//注意学习这种设计方法 * return put(key, value); * } * public synchronized Object put(Object,Object){ * return map.put(Object,Object); * } */ prop.setProperty("002","关羽"); prop.setProperty("003","刘备"); // String getProperty(String key) 使用此属性列表中指定的键搜索属性。 System.out.println(prop.getProperty("001"));//张飞 // Set<String> stringPropertyNames() 从该属性列表中返回一个不可修改的键集,其中键及其对应的值是字符串 Set<String> strings = prop.stringPropertyNames(); for (String s:strings){ System.out.println(s+":"+prop.getProperty(s)); }
.properties文件读取方法汇总
方法1:Properties和IO相结合
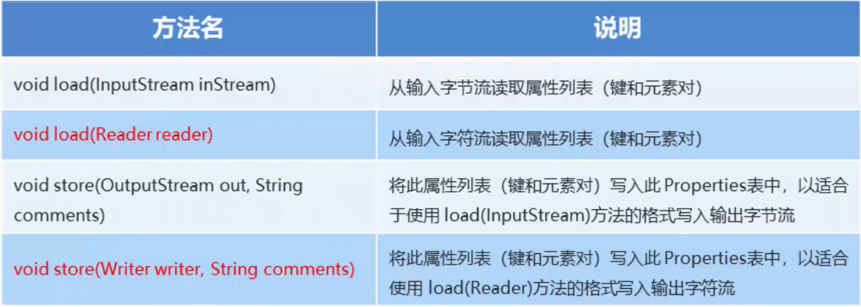
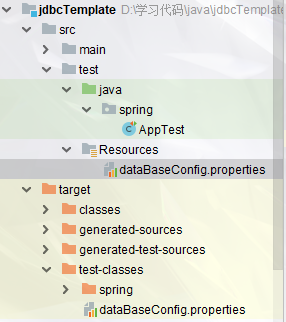

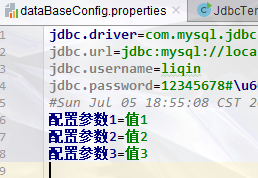
@Test public void testProperties() throws IOException { //读取文件里面的内容 Properties properties = new Properties(); //下面的路径我使用的是 Relative path(相对路径) //src/test/Resources/dataBaseConfig.properties FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("src\\test\\Resources\\dataBaseConfig.properties"); properties.load(fileReader); Set<String> strings = properties.stringPropertyNames(); System.out.println(strings);//[jdbc.password, jdbc.username, jdbc.url, jdbc.driver] System.out.println(properties.getProperty("jdbc.driver"));//com.mysql.jdbc.Driver; //将内容写到文件 Properties properties2 = new Properties(); FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("src\\test\\Resources\\dataBaseConfig.properties",true);//第二个参数为true,追加写入,不会覆盖之前内容 properties2.setProperty("配置参数1","值1"); properties2.setProperty("配置参数2","值2"); properties2.setProperty("配置参数3","值3"); properties2.store(fileWriter,"注释内容"); }
方法2:ResourceBundle

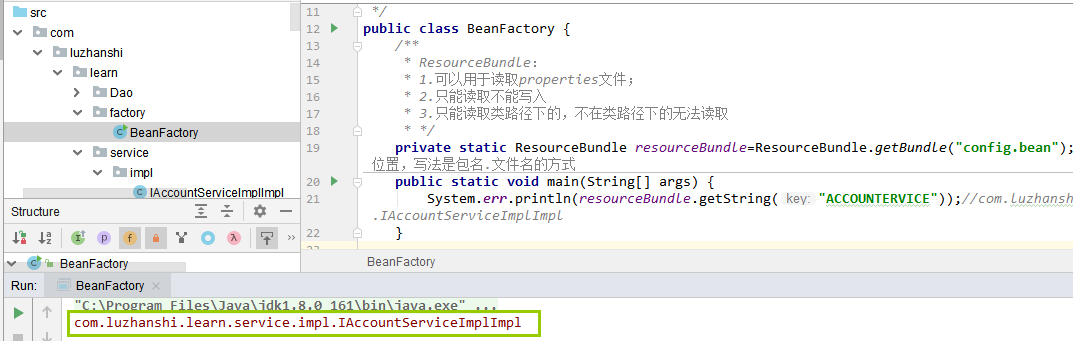
/** * ResourceBundle: * 1.可以用于读取properties文件; * 2.只能读取不能写入 * 3.只能读取类路径下的,不在类路径下的无法读取 * */ private static ResourceBundle resourceBundle=ResourceBundle.getBundle("config.bean");//参数指的是properties文件的位置,写法是包名.文件名的方式 public static void main(String[] args) { System.err.println(resourceBundle.getString("ACCOUNTERVICE"));//com.luzhanshi.learn.service.impl.IAccountServiceImplImpl }
方法3:配合Spring注解:@Value获取值
前提:
1.我们要提前创建了相应的配置文件:

2.我们在spring的xml配置文件里面添加如下注解:
<!-- 告知Spring,properties配置文件的位置-->
<context:property-placeholder location="dataBaseConfig.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
3.使用如下方式获取:
@Repository(value = "IAccountService_annotation") public class IAccountService_annotationImpl implements IAccountService_annotation { @Value("https://www.hao123.com/") public String url; @Value("${jdbc.driver}") private String driver; @Override public void saveAccount() { System.out.println(url);//https://www.hao123.com/ System.out.println(driver);//com.mysql.jdbc.Driver; iAccountDao_annotation.save(); } }
********************************************************************************************************************************************
spring纯注解的情况下使用@value:
@Configuration//将该类声明为spring配置类 @ComponentScan("spring")//配置扫描包 @PropertySource("dataBaseConfig.properties")//配置properties的路径 public class AppTest { ... }
声明一个类,使用配置文件内容装配变量值:
@Component("jdbc")
public class Jdbc {
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
public String url;
}
获取bean对象,打印值:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppTest.class); Jdbc jdbc = (Jdbc) context.getBean("jdbc"); System.out.println(jdbc.url);//com.mysql.jdbc.Driver; } }
方法4:读取出来的内容直接转为map
在很多项目中我们都会使用到.properties文件对我们的项目进行配置,今天就介绍一下.properties文件在项目中的使用:
如下图,我们项目中有一个名为project.properties的properties文件

从图中可以看出,该文件配置了许多参数的默认值,那么我们在项目中如何引用它呢?:
首先我们书写一个工具类ProjectUtils:
/** * 传入配置文件路径,将其中属性映射到Map中 * * @param filepath * @return map */ public Map<String, String> getPropertiesValueMap(String filepath) { InputStreamReader isr = null; logger.info("接收到配置文件路径是 filepath + " +filepath); Map<String, String> properties = new HashMap<>(); if ("".equals(filepath)) { logger.info("传入配置文件路径不能为空!!"); return properties; } try { Properties pro = new Properties(); isr = new InputStreamReader(getClass().getClassLoader() .getResourceAsStream(filepath),"UTF-8"); pro.load(isr); @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") Enumeration enu = pro.propertyNames(); while (enu.hasMoreElements()) { String obj =(String) enu.nextElement(); String objv = pro.getProperty(obj); properties.put(obj, objv); } } catch (Exception e) { properties.put("retCode","01"); properties.put("retMsg","读取配置文件失败,请检查配置文件"); logger.info("解析配置文件失败,请检查配置文件是否正确!!,原因是:"+e.getMessage()); return properties; } return properties; }
然后在需要获取配置信息的地方调用上面我们封装的方法(传入配置文件的路径):
ProjectUtils pro = new ProjectUtils(); Map<String ,String> map = pro.getPropertiesValueMap("project.properties"); //System.out.println(map.get("440600")); int port =Integer.valueOf(map.get("port")); System.out.println(map.get("port"));


