BZOJ2115:[WC2011]Xor——题解
https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=2115
https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P4151
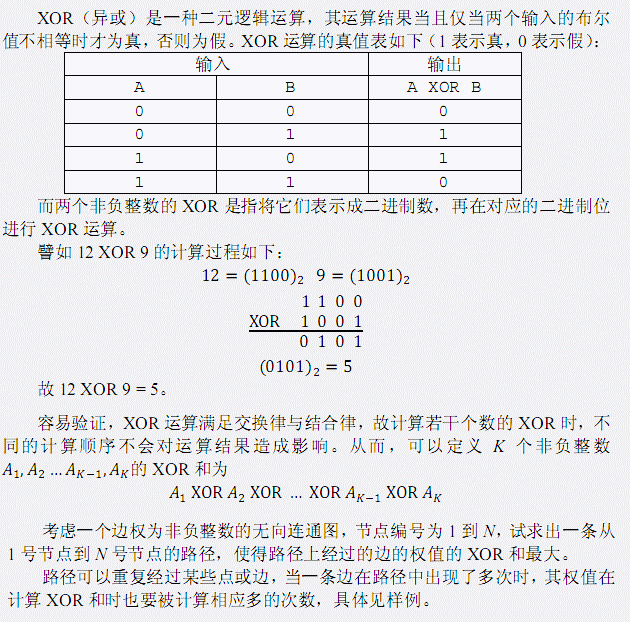
这道题当年还是新题,现在都成线性基套路题了。
参考:https://blog.sengxian.com/algorithms/linear-basis
一个1~n路径值可以拆成一条1~n的路径值^几个环(因为去到环和回来的路的值被异或回去了)。
于是就变成了处理出所有环的异或值和所有1~n的无环路的异或值,然后把环的异或值扔到线性基里面,剩下的就是套路了。
#include<cstdio> #include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<cmath> #include<cctype> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int N=50010; const int M=200010; const int BASE=60; inline ll read(){ ll X=0,w=0;char ch=0; while(!isdigit(ch)){w|=ch=='-';ch=getchar();} while(isdigit(ch))X=(X<<3)+(X<<1)+(ch^48),ch=getchar(); return w?-X:X; } struct node{ int to,nxt; ll w; }e[M]; int cnt,n,m,head[N],tot,num; ll a[M],b[BASE+4],s[M],t[M]; bool vis[N]; inline void add(int u,int v,ll w){ e[++cnt].to=v;e[cnt].w=w;e[cnt].nxt=head[u];head[u]=cnt; } void dfs(int u,ll sum){ vis[u]=1;t[u]=sum; for(int i=head[u];i;i=e[i].nxt){ int v=e[i].to;ll w=e[i].w; ll ans=sum^w^t[v]; if(vis[v]){ if(ans)a[++tot]=ans; continue; } dfs(v,sum^w); } if(u==n)s[++num]=sum; return; } int main(){ n=read(),m=read(); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ int u=read(),v=read();ll w=read(); add(u,v,w);add(v,u,w); } dfs(1,0); for(int i=1;i<=tot;i++){ for(int j=BASE;j>=0;j--){ if(a[i]>>j&1){ if(b[j])a[i]^=b[j]; else{ b[j]=a[i]; break; } } } } ll ans=0; for(int i=1;i<=num;i++){ ll tmp=s[i]; for(int j=BASE;j>=0;j--){ tmp=max(tmp,tmp^b[j]); } ans=max(ans,tmp); } printf("%lld\n",ans); return 0; }
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
+本文作者:luyouqi233。 +
+欢迎访问我的博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/luyouqi233/+
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号