下面是一个简单的实现 操作自定义window performance counter的实例。在运行程序的过程中我们通过操作系统的performance面板查看或者写log文件,对我们应用程序的性能进行监视,分析。将有助于我们分析解决系统的性能等问题。
代码功能:
1,实现添加一个counter 类别
2,添加一个或者多个counter对象
3,获取counter对象,并赋值。
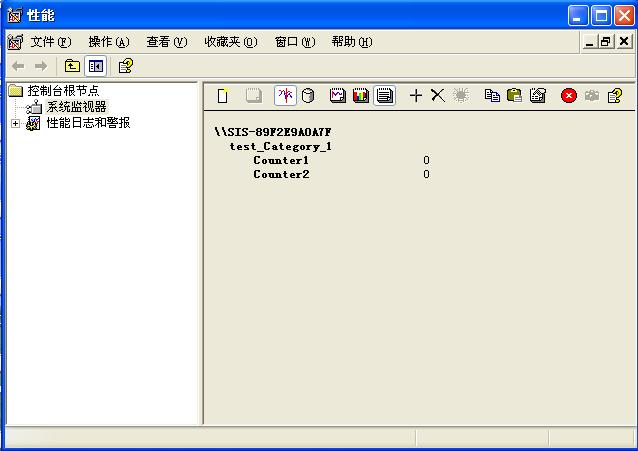
在系统的performance 面板中查看。效果如下图:
代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace WritePerformanceLog
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
if (!PerformanceCounterCategory.Exists("test_Category_1"))
{
// Create a collection of type CounterCreationDataCollection.
System.Diagnostics.CounterCreationDataCollection CounterDatas =
new System.Diagnostics.CounterCreationDataCollection();
// Create the counters and set their properties.
System.Diagnostics.CounterCreationData cdCounter1 =
new System.Diagnostics.CounterCreationData();
System.Diagnostics.CounterCreationData cdCounter2 =
new System.Diagnostics.CounterCreationData();
cdCounter1.CounterName = "Counter1";
cdCounter1.CounterHelp = "help string1";
cdCounter1.CounterType = System.Diagnostics.PerformanceCounterType.NumberOfItems64;
cdCounter2.CounterName = "Counter2";
cdCounter2.CounterHelp = "help string 2";
cdCounter2.CounterType = System.Diagnostics.PerformanceCounterType.NumberOfItems64;
// Add both counters to the collection.
CounterDatas.Add(cdCounter1);
CounterDatas.Add(cdCounter2);
// Create the category and pass the collection to it.
System.Diagnostics.PerformanceCounterCategory.Create(
"test_Category_1", "Category help", CounterDatas);
}
else
{
PerformanceCounter cdCounter1 = new PerformanceCounter("test_Category_1", "Counter1", false);
PerformanceCounter cdCounter2 = new PerformanceCounter("test_Category_1", "Counter2", false);
cdCounter1.ReadOnly = false;
for( int i=0;i<10000;i++ )
{
cdCounter1.RawValue = i;
//cdCounter1.Increment();
cdCounter2.RawValue = i+1;
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
Console.WriteLine(cdCounter1.NextValue());
Console.WriteLine(cdCounter2.RawValue);
Console.WriteLine(cdCounter1.NextSample());
Console.Read();
}
}
}
}
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace WritePerformanceLog
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
if (!PerformanceCounterCategory.Exists("test_Category_1"))
{
// Create a collection of type CounterCreationDataCollection.
System.Diagnostics.CounterCreationDataCollection CounterDatas =
new System.Diagnostics.CounterCreationDataCollection();
// Create the counters and set their properties.
System.Diagnostics.CounterCreationData cdCounter1 =
new System.Diagnostics.CounterCreationData();
System.Diagnostics.CounterCreationData cdCounter2 =
new System.Diagnostics.CounterCreationData();
cdCounter1.CounterName = "Counter1";
cdCounter1.CounterHelp = "help string1";
cdCounter1.CounterType = System.Diagnostics.PerformanceCounterType.NumberOfItems64;
cdCounter2.CounterName = "Counter2";
cdCounter2.CounterHelp = "help string 2";
cdCounter2.CounterType = System.Diagnostics.PerformanceCounterType.NumberOfItems64;
// Add both counters to the collection.
CounterDatas.Add(cdCounter1);
CounterDatas.Add(cdCounter2);
// Create the category and pass the collection to it.
System.Diagnostics.PerformanceCounterCategory.Create(
"test_Category_1", "Category help", CounterDatas);
}
else
{
PerformanceCounter cdCounter1 = new PerformanceCounter("test_Category_1", "Counter1", false);
PerformanceCounter cdCounter2 = new PerformanceCounter("test_Category_1", "Counter2", false);
cdCounter1.ReadOnly = false;
for( int i=0;i<10000;i++ )
{
cdCounter1.RawValue = i;
//cdCounter1.Increment();
cdCounter2.RawValue = i+1;
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
Console.WriteLine(cdCounter1.NextValue());
Console.WriteLine(cdCounter2.RawValue);
Console.WriteLine(cdCounter1.NextSample());
Console.Read();
}
}
}
}





