Flink中的双流join和维表join
一、双流join#
在数据库中的静态表上做OLAP分析时,两表join是非常常见的操作。同理,在流式处理作业中,有时也需要在两条流上做join以获得更丰富的信息。
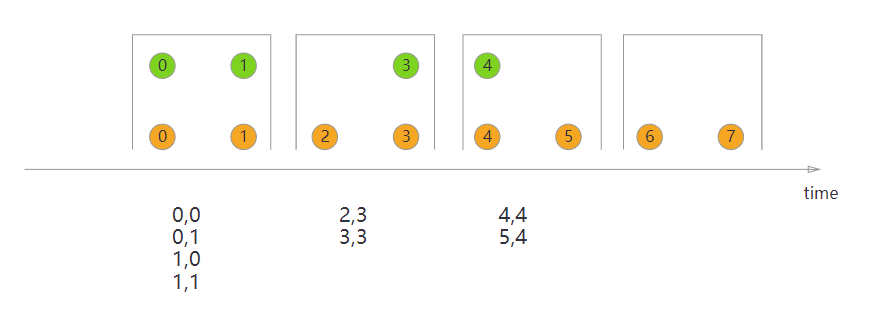
1、Tumbling Window Join #
代码示例:
DataStream<Integer> orangeStream = ... DataStream<Integer> greenStream = ... orangeStream.join(greenStream) .where(<KeySelector>) .equalTo(<KeySelector>) .window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.milliseconds(2))) .apply(new JoinFunction<Integer, Integer, String> (){ @Override public String join(Integer first, Integer second) { return first + "," + second; } });
2、Sliding Window Join#
示例代码:
DataStream<Integer> orangeStream = ... DataStream<Integer> greenStream = ... orangeStream.join(greenStream) .where(<KeySelector>) .equalTo(<KeySelector>) .window(SlidingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.milliseconds(2) /* size */, Time.milliseconds(1) /* slide */)) .apply(new JoinFunction<Integer, Integer, String> (){ @Override public String join(Integer first, Integer second) { return first + "," + second; } });
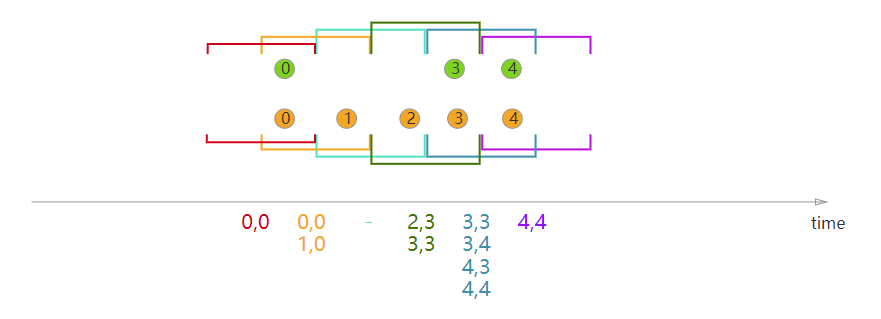
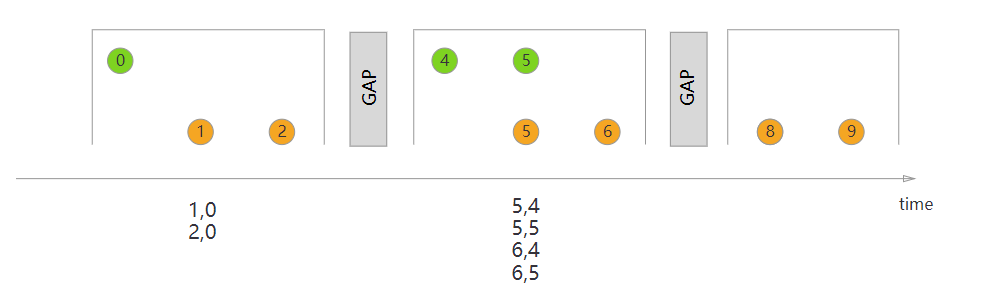
3、Session Window Join#
示例代码:
DataStream<Integer> orangeStream = ... DataStream<Integer> greenStream = ... orangeStream.join(greenStream) .where(<KeySelector>) .equalTo(<KeySelector>) .window(EventTimeSessionWindows.withGap(Time.milliseconds(1))) .apply(new JoinFunction<Integer, Integer, String> (){ @Override public String join(Integer first, Integer second) { return first + "," + second; } });
以上3种都是“inner join”,只是窗口类型不一样。
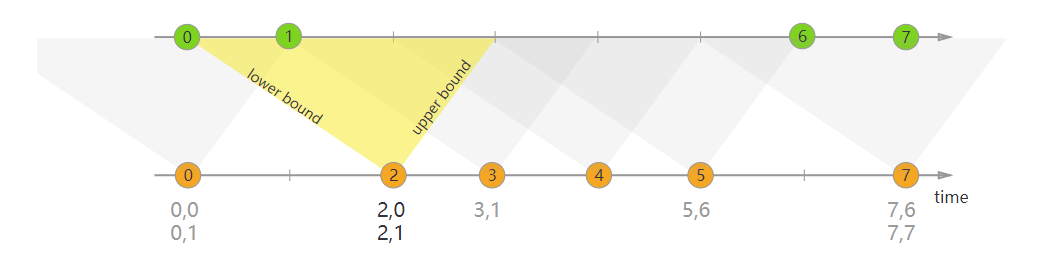
4、Interval Join#
右流相对左流偏移的时间区间进行关联,即:
right.timestamp ∈ [left.timestamp + lowerBound; left.timestamp + upperBound]
In the example above, we join two streams ‘orange’ and ‘green’ with a lower bound of -2 milliseconds and an upper bound of +1 millisecond. Be default, these boundaries are inclusive, but .lowerBoundExclusive() and .upperBoundExclusive can be applied to change the behaviour.
Using the more formal notation again this will translate to
orangeElem.ts + lowerBound <= greenElem.ts <= orangeElem.ts + upperBound
注意:目前 interval join 只支持 Event time
示例代码:
DataStream<Integer> orangeStream = ... DataStream<Integer> greenStream = ... orangeStream .keyBy(<KeySelector>) .intervalJoin(greenStream.keyBy(<KeySelector>)) .between(Time.milliseconds(-2), Time.milliseconds(1)) .process(new ProcessJoinFunction<Integer, Integer, String(){ @Override public void processElement(Integer left, Integer right, Context ctx, Collector<String> out) { out.collect(first + "," + second); } });
5、coGroup#
只有inner join肯定还不够,如何实现left/right outer join呢?答案就是利用coGroup()算子。它的调用方式类似于join()算子,也需要开窗,但是CoGroupFunction比JoinFunction更加灵活,可以按照用户指定的逻辑匹配左流和/或右流的数据并输出。
以下的例子就实现了点击流left join订单流的功能,是很朴素的nested loop join思想(二重循环)。
clickRecordStream .coGroup(orderRecordStream) .where(record -> record.getMerchandiseId()) .equalTo(record -> record.getMerchandiseId()) .window(TumblingProcessingTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(10))) .apply(new CoGroupFunction<AnalyticsAccessLogRecord, OrderDoneLogRecord, Tuple2<String, Long>>() { @Override public void coGroup(Iterable<AnalyticsAccessLogRecord> accessRecords, Iterable<OrderDoneLogRecord> orderRecords,
Collector<Tuple2<String, Long>> collector) throws Exception { for (AnalyticsAccessLogRecord accessRecord : accessRecords) { boolean isMatched = false; for (OrderDoneLogRecord orderRecord : orderRecords) { // 右流中有对应的记录 collector.collect(new Tuple2<>(accessRecord.getMerchandiseName(), orderRecord.getPrice())); isMatched = true; } if (!isMatched) { // 右流中没有对应的记录 collector.collect(new Tuple2<>(accessRecord.getMerchandiseName(), null)); } } } }) .print().setParallelism(1);
二、维表join#
1、 预加载维表#
通过定义一个类实现RichMapFunction,在open()中读取维表数据加载到内存中,在probe流map()方法中与维表数据进行关联。
RichMapFunction中open方法里加载维表数据到内存的方式特点如下:
- 优点:实现简单
- 缺点:因为数据存于内存,所以只适合小数据量并且维表数据更新频率不高的情况下。虽然可以在open中定义一个定时器定时更新维表,但是还是存在维表更新不及时的情况。
class MapJoinDemo1 extends RichMapFunction<Tuple2<String, Integer>, Tuple3<String, Integer, String>> { //定义一个变量,用于保存维表数据在内存 Map<Integer, String> dim; @Override public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception { //在open方法中读取维表数据,可以从数据中读取、文件中读取、接口中读取等等。 dim = new HashMap<>(); dim.put(1001, "beijing"); dim.put(1002, "shanghai"); dim.put(1003, "wuhan"); dim.put(1004, "changsha"); } @Override public Tuple3<String, Integer, String> map(Tuple2<String, Integer> value) throws Exception { //在map方法中进行主流和维表的关联 String cityName = ""; if (dim.containsKey(value.f1)) { cityName = dim.get(value.f1); } return new Tuple3<>(value.f0, value.f1, cityName); } } }
2、 热存储维表#
这种方式是将维表数据存储在Redis、HBase、MySQL等外部存储中,实时流在关联维表数据的时候实时去外部存储中查询,这种方式特点如下:
- 优点:维度数据量不受内存限制,可以存储很大的数据量。
- 缺点:因为维表数据在外部存储中,读取速度受制于外部存储的读取速度;另外维表的同步也有延迟。
(1) 使用cache来减轻访问压力#
可以使用缓存来存储一部分常访问的维表数据,以减少访问外部系统的次数,比如使用guava Cache。
class MapJoinDemo1 extends RichMapFunction<Tuple2<String, Integer>, Tuple3<String, Integer, String>> { LoadingCache<Integer, String> dim; @Override public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception { //使用google LoadingCache来进行缓存 dim = CacheBuilder.newBuilder() //最多缓存个数,超过了就根据最近最少使用算法来移除缓存 .maximumSize(1000) //在更新后的指定时间后就回收 .expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES) //指定移除通知 .removalListener(new RemovalListener<Integer, String>() { @Override public void onRemoval(RemovalNotification<Integer, String> removalNotification) { System.out.println(removalNotification.getKey() + "被移除了,值为:" + removalNotification.getValue()); } }) .build( //指定加载缓存的逻辑 new CacheLoader<Integer, String>() { @Override public String load(Integer cityId) throws Exception { String cityName = readFromHbase(cityId); return cityName; } } ); } private String readFromHbase(Integer cityId) { //读取hbase,模拟从hbase读取数据 Map<Integer, String> temp = new HashMap<>(); temp.put(1001, "beijing"); temp.put(1002, "shanghai"); temp.put(1003, "wuhan"); temp.put(1004, "changsha"); String cityName = ""; if (temp.containsKey(cityId)) { cityName = temp.get(cityId); } return cityName; } @Override public Tuple3<String, Integer, String> map(Tuple2<String, Integer> value) throws Exception { //在map方法中进行主流和维表的关联 String cityName = ""; if (dim.get(value.f1) != null) { cityName = dim.get(value.f1); } return new Tuple3<>(value.f0, value.f1, cityName); } } }
(2) 使用异步IO来提高访问吞吐量#
Flink与外部存储系统进行读写操作的时候可以使用同步方式,也就是发送一个请求后等待外部系统响应,然后再发送第二个读写请求,这样的方式吞吐量比较低,可以用提高并行度的方式来提高吞吐量,但是并行度多了也就导致了进程数量多了,占用了大量的资源。
Flink中可以使用异步IO来读写外部系统,这要求外部系统客户端支持异步IO,不过目前很多系统都支持异步IO客户端。但是如果使用异步就要涉及到三个问题:
- 超时:如果查询超时那么就认为是读写失败,需要按失败处理;
- 并发数量:如果并发数量太多,就要触发Flink的反压机制来抑制上游的写入。
- 返回顺序错乱:顺序错乱了要根据实际情况来处理,Flink支持两种方式:允许乱序、保证顺序。
public class JoinDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); DataStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>> textStream = env.socketTextStream("localhost", 9000, "\n") .map(p -> { //输入格式为:user,1000,分别是用户名称和城市编号 String[] list = p.split(","); return new Tuple2<String, Integer>(list[0], Integer.valueOf(list[1])); }) .returns(new TypeHint<Tuple2<String, Integer>>() { }); DataStream<Tuple3<String,Integer, String>> orderedResult = AsyncDataStream //保证顺序:异步返回的结果保证顺序,超时时间1秒,最大容量2,超出容量触发反压 .orderedWait(textStream, new JoinDemo3AyncFunction(), 1000L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 2) .setParallelism(1); DataStream<Tuple3<String,Integer, String>> unorderedResult = AsyncDataStream //允许乱序:异步返回的结果允许乱序,超时时间1秒,最大容量2,超出容量触发反压 .unorderedWait(textStream, new JoinDemo3AyncFunction(), 1000L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 2) .setParallelism(1); orderedResult.print(); unorderedResult.print(); env.execute("joinDemo"); } //定义个类,继承RichAsyncFunction,实现异步查询存储在mysql里的维表 //输入用户名、城市ID,返回 Tuple3<用户名、城市ID,城市名称> static class JoinDemo3AyncFunction extends RichAsyncFunction<Tuple2<String, Integer>, Tuple3<String, Integer, String>> { // 链接 private static String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:mysql://192.168.145.1:3306?useSSL=false"; private static String username = "root"; private static String password = "123"; private static String driverName = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; java.sql.Connection conn; PreparedStatement ps; @Override public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception { super.open(parameters); Class.forName(driverName); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, username, password); ps = conn.prepareStatement("select city_name from tmp.city_info where id = ?"); } @Override public void close() throws Exception { super.close(); conn.close(); } //异步查询方法 @Override public void asyncInvoke(Tuple2<String, Integer> input, ResultFuture<Tuple3<String,Integer, String>> resultFuture) throws Exception { // 使用 city id 查询 ps.setInt(1, input.f1); ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery(); String cityName = null; if (rs.next()) { cityName = rs.getString(1); } List list = new ArrayList<Tuple2<Integer, String>>(); list.add(new Tuple3<>(input.f0,input.f1, cityName)); resultFuture.complete(list); } //超时处理 @Override public void timeout(Tuple2<String, Integer> input, ResultFuture<Tuple3<String,Integer, String>> resultFuture) throws Exception { List list = new ArrayList<Tuple2<Integer, String>>(); list.add(new Tuple3<>(input.f0,input.f1, "")); resultFuture.complete(list); } } }
3、 广播维表#
利用Flink的Broadcast State将维度数据流广播到下游做join操作。特点如下:
- 优点:维度数据变更后可以即时更新到结果中。
- 缺点:数据保存在内存中,支持的维度数据量比较小。
//定义城市流 DataStream<Tuple2<Integer, String>> cityStream = env.socketTextStream("localhost", 9001, "\n") .map(p -> { //输入格式为:城市ID,城市名称 String[] list = p.split(","); return new Tuple2<Integer, String>(Integer.valueOf(list[0]), list[1]); }) .returns(new TypeHint<Tuple2<Integer, String>>() { }); //将城市流定义为广播流 final MapStateDescriptor<Integer, String> broadcastDesc = new MapStateDescriptor("broad1", Integer.class, String.class); BroadcastStream<Tuple2<Integer, String>> broadcastStream = cityStream.broadcast(broadcastDesc); DataStream result = textStream.connect(broadcastStream) .process(new BroadcastProcessFunction<Tuple2<String, Integer>, Tuple2<Integer, String>, Tuple3<String, Integer, String>>() { //处理非广播流,关联维度 @Override public void processElement(Tuple2<String, Integer> value, ReadOnlyContext ctx, Collector<Tuple3<String, Integer, String>> out) throws Exception { ReadOnlyBroadcastState<Integer, String> state = ctx.getBroadcastState(broadcastDesc); String cityName = ""; if (state.contains(value.f1)) { cityName = state.get(value.f1); } out.collect(new Tuple3<>(value.f0, value.f1, cityName)); } @Override public void processBroadcastElement(Tuple2<Integer, String> value, Context ctx, Collector<Tuple3<String, Integer, String>> out) throws Exception { System.out.println("收到广播数据:" + value); ctx.getBroadcastState(broadcastDesc).put(value.f0, value.f1); } });
4、 Temporal table function join#
Temporal table是持续变化表上某一时刻的视图,Temporal table function是一个表函数,传递一个时间参数,返回Temporal table这一指定时刻的视图。
可以将维度数据流映射为Temporal table,主流与这个Temporal table进行关联,可以关联到某一个版本(历史上某一个时刻)的维度数据。
Temporal table function join的特点如下:
- 优点:维度数据量可以很大,维度数据更新及时,不依赖外部存储,可以关联不同版本的维度数据。
- 缺点:只支持在Flink SQL API中使用。
public class JoinDemo5 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); EnvironmentSettings bsSettings = EnvironmentSettings.newInstance().useBlinkPlanner().inStreamingMode().build(); StreamTableEnvironment tableEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env, bsSettings); //定义主流 DataStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>> textStream = env.socketTextStream("localhost", 9000, "\n") .map(p -> { //输入格式为:user,1000,分别是用户名称和城市编号 String[] list = p.split(","); return new Tuple2<String, Integer>(list[0], Integer.valueOf(list[1])); }) .returns(new TypeHint<Tuple2<String, Integer>>() { }); //定义城市流 DataStream<Tuple2<Integer, String>> cityStream = env.socketTextStream("localhost", 9001, "\n") .map(p -> { //输入格式为:城市ID,城市名称 String[] list = p.split(","); return new Tuple2<Integer, String>(Integer.valueOf(list[0]), list[1]); }) .returns(new TypeHint<Tuple2<Integer, String>>() { }); //转变为Table Table userTable = tableEnv.fromDataStream(textStream, "user_name,city_id,ps.proctime"); Table cityTable = tableEnv.fromDataStream(cityStream, "city_id,city_name,ps.proctime"); //定义一个TemporalTableFunction TemporalTableFunction dimCity = cityTable.createTemporalTableFunction("ps", "city_id"); //注册表函数 tableEnv.registerFunction("dimCity", dimCity); //关联查询 Table result = tableEnv .sqlQuery("select u.user_name,u.city_id,d.city_name from " + userTable + " as u " + ", Lateral table (dimCity(u.ps)) d " + "where u.city_id=d.city_id"); //打印输出 DataStream resultDs = tableEnv.toAppendStream(result, Row.class); resultDs.print(); env.execute("joinDemo"); } }
5、四种维表关联方式比较#
参考:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/45ec888332df
https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-release-1.12/dev/stream/operators/joining.html
https://blog.csdn.net/chybin500/article/details/106482620
作者:阿凡卢
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/luxiaoxun/p/14245609.html
版权:本作品采用「署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际」许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 如何调用 DeepSeek 的自然语言处理 API 接口并集成到在线客服系统
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 2025年我用 Compose 写了一个 Todo App