012_linuxC++之_类的继承定义
(一)访问控制和继承
- 公有继承(public):当一个类派生自公有基类时,基类的公有成员也是派生类的公有成员,基类的保护成员也是派生类的保护成员,基类的私有成员不能直接被派生类访问,但是可以通过调用基类的公有和保护成员来访问。
- 保护继承(protected): 当一个类派生自保护基类时,基类的公有和保护成员将成为派生类的保护成员。
- 私有继承(private):当一个类派生自私有基类时,基类的公有和保护成员将成为派生类的私有成员。
访问权限总结出不同的访问类型,如下所示:
| 访问 | public | protected | private |
|---|---|---|---|
| 同一个类 | yes | yes | yes |
| 派生类 | yes | yes | no |
| 外部的类 | yes | no | no |
(二)使用示例
1. 在同一个类中都可以使用

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class test{ 4 public: 5 int test1; 6 private: 7 int test2; 8 protected: 9 int test3; 10 11 void A(void) 12 { 13 test1 = 0; 14 test2 = 0; /*error*/ 15 test3 = 0; 16 } 17 }; 18 19 20 int main(int argc, char **argv) 21 22 { 23 24 }
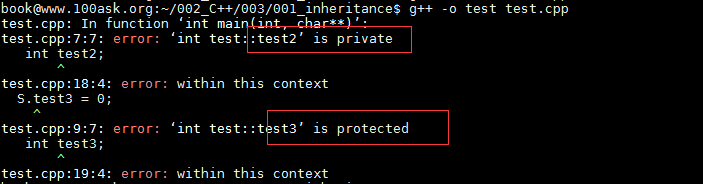
2. 在派生类中不能访问private中的

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class test{ 4 public: 5 int test1; 6 private: 7 int test2; 8 protected: 9 int test3; 10 11 }; 12 13 class Rectangle:public test{ 14 public: 15 void A(void) 16 { 17 test1 = 0; 18 // test2 = 0; /*error*/ 19 test3 = 0; 20 } 21 22 }; 23 int main(int argc, char **argv) 24 25 { 26 27 }
运行结果,注销掉就能编译成功了
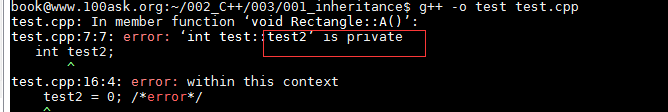
3. 外部的类使用

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class test{ 4 public: 5 int test1; 6 private: 7 int test2; 8 protected: 9 int test3; 10 }; 11 12 13 int main(int argc, char **argv) 14 15 { 16 test S; 17 S.test1 = 0; 18 //S.test2 = 0; /*error*/ 19 //S.test3 = 0; /*error*/ 20 }
运行结果,外部类无法使用protected和private,注销掉就成功了