YoloX实战
目录
YOLOX是在YOLOV3基础上做的改进,数据处理部分同Yolov5的Mosaic数据增强(利用了四张图片进行拼接实现数据中增强);backbone部分使用了Yolov5的Focus网络结构,并且把SPP结构用到了backbone部分(Yolov5用到FPN结构); Head部分,以前版本的Yolo所用的解耦头是分类和回归在一个1X1卷积里实现,在YoloX中,Yolo Head被分为了两部分,分别实现,最后预测的时候才整合在一起。另外,引入了Anchor free,降低了计算量,不涉及IoU计算,另外产生的预测框数量也更少。其次,使用SimOTA 为不同大小的目标动态匹配正样本。
1.数据处理
(1)Mosaic数据增强
- 将4张照片组合成一张。首先,在中间的一个范围里选取图片拼接的中心点,另对传入的1张图像随机找3张图片做拼友;其次,计算每一个小图取哪一部分放到大图中;然后,将映射关系对应到图片的标签上;最后,处理超过边界的检测框坐标。
展开backbone代码
def get_random_data_with_Mosaic(self, annotation_line, input_shape, jitter=0.3, hue=.1, sat=0.7, val=0.4):
h, w = input_shape
min_offset_x = self.rand(0.3, 0.7)
min_offset_y = self.rand(0.3, 0.7)
image_datas = []
box_datas = []
index = 0
for line in annotation_line:
#---------------------------------#
# 每一行进行分割
#---------------------------------#
line_content = line.split()
#---------------------------------#
# 打开图片
#---------------------------------#
image = Image.open(line_content[0])
image = cvtColor(image)
#---------------------------------#
# 图片的大小
#---------------------------------#
iw, ih = image.size
#---------------------------------#
# 保存框的位置
#---------------------------------#
box = np.array([np.array(list(map(int,box.split(',')))) for box in line_content[1:]])
#---------------------------------#
# 是否翻转图片
#---------------------------------#
flip = self.rand()<.5
if flip and len(box)>0:
image = image.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
box[:, [0,2]] = iw - box[:, [2,0]]
#------------------------------------------#
# 对图像进行缩放并且进行长和宽的扭曲
#------------------------------------------#
new_ar = iw/ih * self.rand(1-jitter,1+jitter) / self.rand(1-jitter,1+jitter)
scale = self.rand(.4, 1)
if new_ar < 1:
nh = int(scale*h)
nw = int(nh*new_ar)
else:
nw = int(scale*w)
nh = int(nw/new_ar)
image = image.resize((nw, nh), Image.BICUBIC)
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 将图片进行放置,分别对应四张分割图片的位置
#-----------------------------------------------#
if index == 0:
dx = int(w*min_offset_x) - nw
dy = int(h*min_offset_y) - nh
elif index == 1:
dx = int(w*min_offset_x) - nw
dy = int(h*min_offset_y)
elif index == 2:
dx = int(w*min_offset_x)
dy = int(h*min_offset_y)
elif index == 3:
dx = int(w*min_offset_x)
dy = int(h*min_offset_y) - nh
new_image = Image.new('RGB', (w,h), (128,128,128))
new_image.paste(image, (dx, dy))
image_data = np.array(new_image)
index = index + 1
box_data = []
#---------------------------------#
# 对box进行重新处理
#---------------------------------#
if len(box)>0:
np.random.shuffle(box)
box[:, [0,2]] = box[:, [0,2]]*nw/iw + dx
box[:, [1,3]] = box[:, [1,3]]*nh/ih + dy
box[:, 0:2][box[:, 0:2]<0] = 0
box[:, 2][box[:, 2]>w] = w
box[:, 3][box[:, 3]>h] = h
box_w = box[:, 2] - box[:, 0]
box_h = box[:, 3] - box[:, 1]
box = box[np.logical_and(box_w>1, box_h>1)]
box_data = np.zeros((len(box),5))
box_data[:len(box)] = box
image_datas.append(image_data)
box_datas.append(box_data)
#---------------------------------#
# 将图片分割,放在一起
#---------------------------------#
cutx = int(w * min_offset_x)
cuty = int(h * min_offset_y)
new_image = np.zeros([h, w, 3])
new_image[:cuty, :cutx, :] = image_datas[0][:cuty, :cutx, :]
new_image[cuty:, :cutx, :] = image_datas[1][cuty:, :cutx, :]
new_image[cuty:, cutx:, :] = image_datas[2][cuty:, cutx:, :]
new_image[:cuty, cutx:, :] = image_datas[3][:cuty, cutx:, :]
new_image = np.array(new_image, np.uint8)
#---------------------------------#
# 对图像进行色域变换
# 计算色域变换的参数
#---------------------------------#
r = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, 3) * [hue, sat, val] + 1
#---------------------------------#
# 将图像转到HSV上
#---------------------------------#
hue, sat, val = cv2.split(cv2.cvtColor(new_image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV))
dtype = new_image.dtype
#---------------------------------#
# 应用变换
#---------------------------------#
x = np.arange(0, 256, dtype=r.dtype)
lut_hue = ((x * r[0]) % 180).astype(dtype)
lut_sat = np.clip(x * r[1], 0, 255).astype(dtype)
lut_val = np.clip(x * r[2], 0, 255).astype(dtype)
new_image = cv2.merge((cv2.LUT(hue, lut_hue), cv2.LUT(sat, lut_sat), cv2.LUT(val, lut_val)))
new_image = cv2.cvtColor(new_image, cv2.COLOR_HSV2RGB)
#---------------------------------#
# 对框进行进一步的处理
#---------------------------------#
new_boxes = self.merge_bboxes(box_datas, cutx, cuty)
return new_image, new_boxes
def get_random_data_with_MixUp(self, image_1, box_1, image_2, box_2):
new_image = np.array(image_1, np.float32) * 0.5 + np.array(image_2, np.float32) * 0.5
if len(box_1) == 0:
new_boxes = box_2
elif len(box_2) == 0:
new_boxes = box_1
else:
new_boxes = np.concatenate([box_1, box_2], axis=0)
return new_image, new_boxes
2.主干网络backbone提取特征
- 整体网络结构
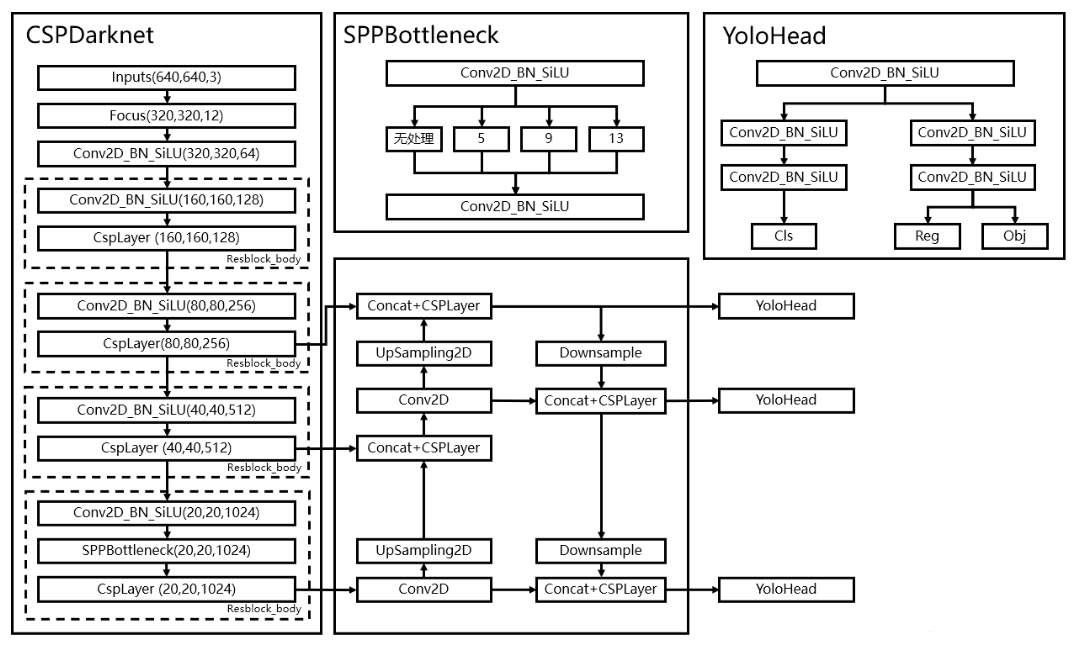
- backbone部分
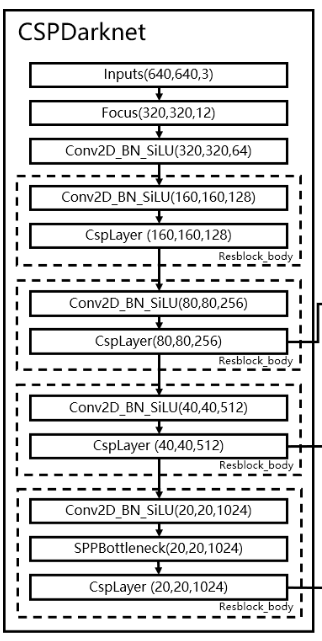
- backbone代码
展开backbone代码
class CSPDarknet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dep_mul, wid_mul, out_features=("dark3", "dark4", "dark5"), depthwise=False, act="silu",):
super().__init__()
assert out_features, "please provide output features of Darknet"
self.out_features = out_features
Conv = DWConv if depthwise else BaseConv
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 输入图片是640, 640, 3
# 初始的基本通道是64
#-----------------------------------------------#
base_channels = int(wid_mul * 64) # 64
base_depth = max(round(dep_mul * 3), 1) # 3
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 利用focus网络结构进行特征提取
# 640, 640, 3 -> 320, 320, 12 -> 320, 320, 64
#-----------------------------------------------#
self.stem = Focus(3, base_channels, ksize=3, act=act)
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 完成卷积之后,320, 320, 64 -> 160, 160, 128
# 完成CSPlayer之后,160, 160, 128 -> 160, 160, 128
#-----------------------------------------------#
self.dark2 = nn.Sequential(
Conv(base_channels, base_channels * 2, 3, 2, act=act),
CSPLayer(base_channels * 2, base_channels * 2, n=base_depth, depthwise=depthwise, act=act),
)
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 完成卷积之后,160, 160, 128 -> 80, 80, 256
# 完成CSPlayer之后,80, 80, 256 -> 80, 80, 256
#-----------------------------------------------#
self.dark3 = nn.Sequential(
Conv(base_channels * 2, base_channels * 4, 3, 2, act=act),
CSPLayer(base_channels * 4, base_channels * 4, n=base_depth * 3, depthwise=depthwise, act=act),
)
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 完成卷积之后,80, 80, 256 -> 40, 40, 512
# 完成CSPlayer之后,40, 40, 512 -> 40, 40, 512
#-----------------------------------------------#
self.dark4 = nn.Sequential(
Conv(base_channels * 4, base_channels * 8, 3, 2, act=act),
CSPLayer(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 8, n=base_depth * 3, depthwise=depthwise, act=act),
)
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 完成卷积之后,40, 40, 512 -> 20, 20, 1024
# 完成SPP之后,20, 20, 1024 -> 20, 20, 1024
# 完成CSPlayer之后,20, 20, 1024 -> 20, 20, 1024
#-----------------------------------------------#
self.dark5 = nn.Sequential(
Conv(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 16, 3, 2, act=act),
SPPBottleneck(base_channels * 16, base_channels * 16, activation=act),
CSPLayer(base_channels * 16, base_channels * 16, n=base_depth, shortcut=False, depthwise=depthwise, act=act),
)
def forward(self, x):
outputs = {}
x = self.stem(x)
outputs["stem"] = x
x = self.dark2(x)
outputs["dark2"] = x
#-----------------------------------------------#
# dark3的输出为80, 80, 256,是一个有效特征层
#-----------------------------------------------#
x = self.dark3(x)
outputs["dark3"] = x
#-----------------------------------------------#
# dark4的输出为40, 40, 512,是一个有效特征层
#-----------------------------------------------#
x = self.dark4(x)
outputs["dark4"] = x
#-----------------------------------------------#
# dark5的输出为20, 20, 1024,是一个有效特征层
#-----------------------------------------------#
x = self.dark5(x)
outputs["dark5"] = x
return {k: v for k, v in outputs.items() if k in self.out_features}
(1)Focus网络结构
- 一张图片中每隔一个像素拿到一个值,这个时候获得了四个独立的特征层,然后将四个独立的特征层进行堆叠,此时宽高信息就集中到了通道信息,输入通道扩充了四倍。拼接起来的特征层相对于原先的三通道变成了十二个通道。
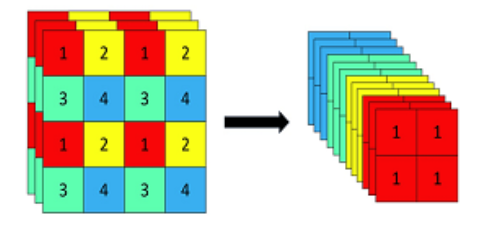
class Focus(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, ksize=1, stride=1, act="silu"):
super().__init__()
self.conv = BaseConv(in_channels * 4, out_channels, ksize, stride, act=act)
def forward(self, x):
patch_top_left = x[..., ::2, ::2]
patch_bot_left = x[..., 1::2, ::2]
patch_top_right = x[..., ::2, 1::2]
patch_bot_right = x[..., 1::2, 1::2]
x = torch.cat((patch_top_left, patch_bot_left, patch_top_right, patch_bot_right,), dim=1,)
return self.conv(x)
(2)CSPLayer
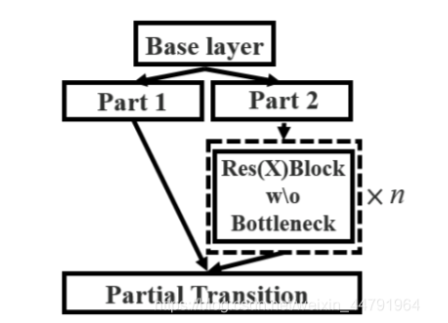
- 将原来的残差块的堆叠进行了一个拆分,拆成左右两部分:主干部分继续进行原来的残差块的堆叠;另一部分则像一个残差边一样,经过少量处理直接连接到最后。
class CSPLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, n=1, shortcut=True, expansion=0.5, depthwise=False, act="silu",):
# ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
hidden_channels = int(out_channels * expansion)
#--------------------------------------------------#
# 主干部分的初次卷积
#--------------------------------------------------#
self.conv1 = BaseConv(in_channels, hidden_channels, 1, stride=1, act=act)
#--------------------------------------------------#
# 大的残差边部分的初次卷积
#--------------------------------------------------#
self.conv2 = BaseConv(in_channels, hidden_channels, 1, stride=1, act=act)
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 对堆叠的结果进行卷积的处理
#-----------------------------------------------#
self.conv3 = BaseConv(2 * hidden_channels, out_channels, 1, stride=1, act=act)
#--------------------------------------------------#
# 根据循环的次数构建上述Bottleneck残差结构
#--------------------------------------------------#
module_list = [Bottleneck(hidden_channels, hidden_channels, shortcut, 1.0, depthwise, act=act) for _ in range(n)]
self.m = nn.Sequential(*module_list)
def forward(self, x):
#-------------------------------#
# x_1是主干部分
#-------------------------------#
x_1 = self.conv1(x)
#-------------------------------#
# x_2是大的残差边部分
#-------------------------------#
x_2 = self.conv2(x)
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 主干部分利用残差结构堆叠继续进行特征提取
#-----------------------------------------------#
x_1 = self.m(x_1)
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 主干部分和大的残差边部分进行堆叠
#-----------------------------------------------#
x = torch.cat((x_1, x_2), dim=1)
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 对堆叠的结果进行卷积的处理
#-----------------------------------------------#
return self.conv3(x)
(3)SiLU激活函数
- SiLU是Sigmoid和ReLU的改进版。SiLU具备无上界有下界、平滑、非单调的特性。SiLU在深层模型上的效果优于 ReLU。可以看做是平滑的ReLU激活函数。
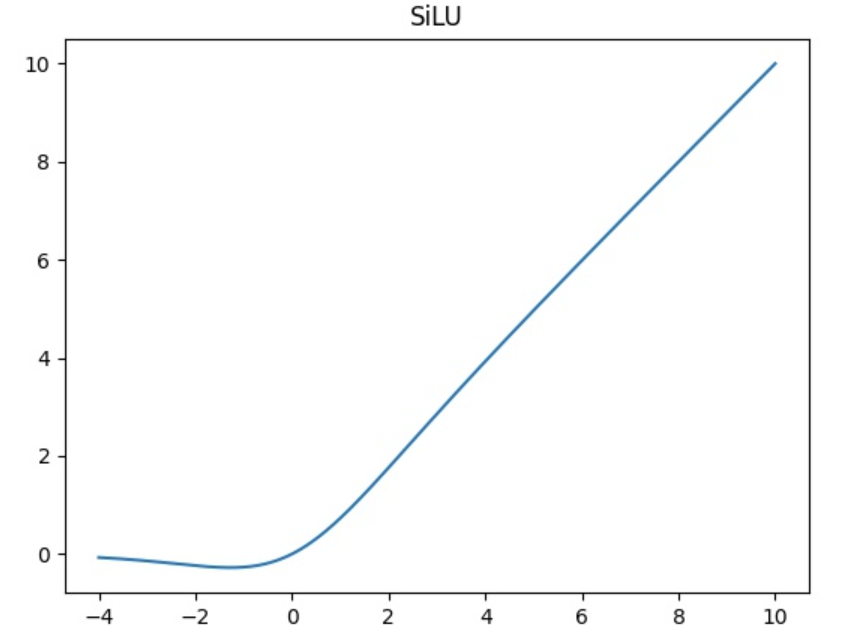
class SiLU(nn.Module):
@staticmethod
def forward(x):
return x * torch.sigmoid(x)
def get_activation(name="silu", inplace=True):
if name == "silu":
module = SiLU()
elif name == "relu":
module = nn.ReLU(inplace=inplace)
elif name == "lrelu":
module = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=inplace)
else:
raise AttributeError("Unsupported act type: {}".format(name))
return module
(4)SPP结构
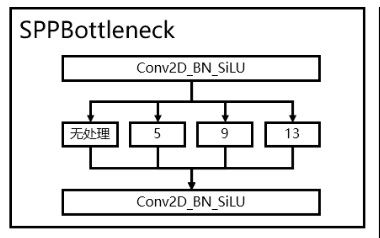
- 通过不同池化核大小的最大池化进行特征提取,提高网络的感受野。在YoloV5中,SPP是用在FPN里面的,在YoloX中,SPP模块被用在了主干特征提取网络中。
class SPPBottleneck(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_sizes=(5, 9, 13), activation="silu"):
super().__init__()
hidden_channels = in_channels // 2
self.conv1 = BaseConv(in_channels, hidden_channels, 1, stride=1, act=activation)
self.m = nn.ModuleList([nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=ks, stride=1, padding=ks // 2) for ks in kernel_sizes])
conv2_channels = hidden_channels * (len(kernel_sizes) + 1)
self.conv2 = BaseConv(conv2_channels, out_channels, 1, stride=1, act=activation)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = torch.cat([x] + [m(x) for m in self.m], dim=1)
x = self.conv2(x)
return x
3.构建FPN特征金字塔进行加强特征提取
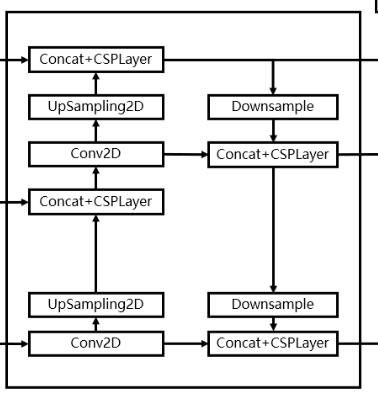
- Yolox采用PAFPN的结构进行融合。如下图所示,将高层的特征信息,先通过上采样的方式进行传递融合,再通过下采样融合方式得到预测的特征图,最终输出3个特征层组成的元组结果,分别为:(256,80,80)、(512,40,40)、(1024,20,20)
展开PAFPN代码
class YOLOPAFPN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, depth = 1.0, width = 1.0, in_features = ("dark3", "dark4", "dark5"), in_channels = [256, 512, 1024], depthwise = False, act = "silu"):
super().__init__()
Conv = DWConv if depthwise else BaseConv
self.backbone = CSPDarknet(depth, width, depthwise = depthwise, act = act)
self.in_features = in_features
self.upsample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode="nearest")
#-------------------------------------------#
# 20, 20, 1024 -> 20, 20, 512
#-------------------------------------------#
self.lateral_conv0 = BaseConv(int(in_channels[2] * width), int(in_channels[1] * width), 1, 1, act=act)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 40, 40, 1024 -> 40, 40, 512
#-------------------------------------------#
self.C3_p4 = CSPLayer(
int(2 * in_channels[1] * width),
int(in_channels[1] * width),
round(3 * depth),
False,
depthwise = depthwise,
act = act,
)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 40, 40, 512 -> 40, 40, 256
#-------------------------------------------#
self.reduce_conv1 = BaseConv(int(in_channels[1] * width), int(in_channels[0] * width), 1, 1, act=act)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 80, 80, 512 -> 80, 80, 256
#-------------------------------------------#
self.C3_p3 = CSPLayer(
int(2 * in_channels[0] * width),
int(in_channels[0] * width),
round(3 * depth),
False,
depthwise = depthwise,
act = act,
)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 80, 80, 256 -> 40, 40, 256
#-------------------------------------------#
self.bu_conv2 = Conv(int(in_channels[0] * width), int(in_channels[0] * width), 3, 2, act=act)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 40, 40, 256 -> 40, 40, 512
#-------------------------------------------#
self.C3_n3 = CSPLayer(
int(2 * in_channels[0] * width),
int(in_channels[1] * width),
round(3 * depth),
False,
depthwise = depthwise,
act = act,
)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 40, 40, 512 -> 20, 20, 512
#-------------------------------------------#
self.bu_conv1 = Conv(int(in_channels[1] * width), int(in_channels[1] * width), 3, 2, act=act)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 20, 20, 1024 -> 20, 20, 1024
#-------------------------------------------#
self.C3_n4 = CSPLayer(
int(2 * in_channels[1] * width),
int(in_channels[2] * width),
round(3 * depth),
False,
depthwise = depthwise,
act = act,
)
def forward(self, input):
out_features = self.backbone.forward(input)
[feat1, feat2, feat3] = [out_features[f] for f in self.in_features]
#-------------------------------------------#
# 20, 20, 1024 -> 20, 20, 512
#-------------------------------------------#
P5 = self.lateral_conv0(feat3)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 20, 20, 512 -> 40, 40, 512
#-------------------------------------------#
P5_upsample = self.upsample(P5)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 40, 40, 512 + 40, 40, 512 -> 40, 40, 1024
#-------------------------------------------#
P5_upsample = torch.cat([P5_upsample, feat2], 1)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 40, 40, 1024 -> 40, 40, 512
#-------------------------------------------#
P5_upsample = self.C3_p4(P5_upsample)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 40, 40, 512 -> 40, 40, 256
#-------------------------------------------#
P4 = self.reduce_conv1(P5_upsample)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 40, 40, 256 -> 80, 80, 256
#-------------------------------------------#
P4_upsample = self.upsample(P4)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 80, 80, 256 + 80, 80, 256 -> 80, 80, 512
#-------------------------------------------#
P4_upsample = torch.cat([P4_upsample, feat1], 1)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 80, 80, 512 -> 80, 80, 256
#-------------------------------------------#
P3_out = self.C3_p3(P4_upsample)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 80, 80, 256 -> 40, 40, 256
#-------------------------------------------#
P3_downsample = self.bu_conv2(P3_out)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 40, 40, 256 + 40, 40, 256 -> 40, 40, 512
#-------------------------------------------#
P3_downsample = torch.cat([P3_downsample, P4], 1)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 40, 40, 256 -> 40, 40, 512
#-------------------------------------------#
P4_out = self.C3_n3(P3_downsample)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 40, 40, 512 -> 20, 20, 512
#-------------------------------------------#
P4_downsample = self.bu_conv1(P4_out)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 20, 20, 512 + 20, 20, 512 -> 20, 20, 1024
#-------------------------------------------#
P4_downsample = torch.cat([P4_downsample, P5], 1)
#-------------------------------------------#
# 20, 20, 1024 -> 20, 20, 1024
#-------------------------------------------#
P5_out = self.C3_n4(P4_downsample)
return (P3_out, P4_out, P5_out)
4.利用Yolo Head获得预测结果
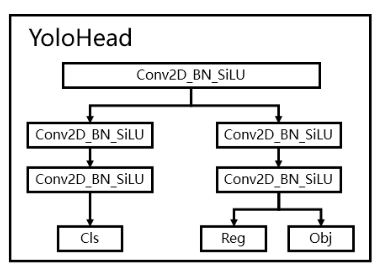
(1)Decoupled Head
- YoloX中的YoloHead与之前版本的YoloHead不同。以前版本的Yolo所用的解耦头是一起的,也就是分类和回归在一个1X1卷积里实现,YoloX认为这给网络的识别带来了不利影响。在YoloX中,Yolo Head被分为了两部分,分别实现,最后预测的时候才整合在一起。
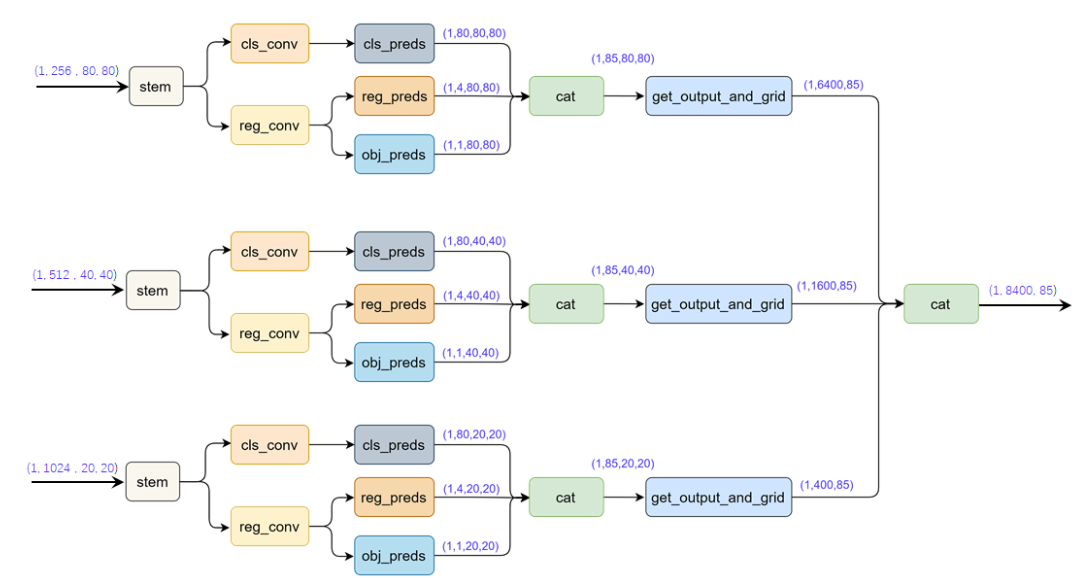
class YOLOXHead(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes, width = 1.0, in_channels = [256, 512, 1024], act = "silu", depthwise = False,):
super().__init__()
Conv = DWConv if depthwise else BaseConv
self.cls_convs = nn.ModuleList()
self.reg_convs = nn.ModuleList()
self.cls_preds = nn.ModuleList()
self.reg_preds = nn.ModuleList()
self.obj_preds = nn.ModuleList()
self.stems = nn.ModuleList()
for i in range(len(in_channels)):
self.stems.append(BaseConv(in_channels = int(in_channels[i] * width), out_channels = int(256 * width), ksize = 1, stride = 1, act = act))
self.cls_convs.append(nn.Sequential(*[
Conv(in_channels = int(256 * width), out_channels = int(256 * width), ksize = 3, stride = 1, act = act),
Conv(in_channels = int(256 * width), out_channels = int(256 * width), ksize = 3, stride = 1, act = act),
]))
self.cls_preds.append(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels = int(256 * width), out_channels = num_classes, kernel_size = 1, stride = 1, padding = 0)
)
self.reg_convs.append(nn.Sequential(*[
Conv(in_channels = int(256 * width), out_channels = int(256 * width), ksize = 3, stride = 1, act = act),
Conv(in_channels = int(256 * width), out_channels = int(256 * width), ksize = 3, stride = 1, act = act)
]))
self.reg_preds.append(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels = int(256 * width), out_channels = 4, kernel_size = 1, stride = 1, padding = 0)
)
self.obj_preds.append(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels = int(256 * width), out_channels = 1, kernel_size = 1, stride = 1, padding = 0)
)
def forward(self, inputs):
#---------------------------------------------------#
# inputs输入
# P3_out 80, 80, 256
# P4_out 40, 40, 512
# P5_out 20, 20, 1024
#---------------------------------------------------#
outputs = []
for k, x in enumerate(inputs):
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 利用1x1卷积进行通道整合
#---------------------------------------------------#
x = self.stems[k](x)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 利用两个卷积标准化激活函数来进行特征提取
#---------------------------------------------------#
cls_feat = self.cls_convs[k](x)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 判断特征点所属的种类
# 80, 80, num_classes
# 40, 40, num_classes
# 20, 20, num_classes
#---------------------------------------------------#
cls_output = self.cls_preds[k](cls_feat)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 利用两个卷积标准化激活函数来进行特征提取
#---------------------------------------------------#
reg_feat = self.reg_convs[k](x)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 特征点的回归系数
# reg_pred 80, 80, 4
# reg_pred 40, 40, 4
# reg_pred 20, 20, 4
#---------------------------------------------------#
reg_output = self.reg_preds[k](reg_feat)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 判断特征点是否有对应的物体
# obj_pred 80, 80, 1
# obj_pred 40, 40, 1
# obj_pred 20, 20, 1
#---------------------------------------------------#
obj_output = self.obj_preds[k](reg_feat)
output = torch.cat([reg_output, obj_output, cls_output], 1)
outputs.append(output)
return outputs
(2)Anchor-free
-
使用Anchor-free可以:降低了计算量,不涉及IoU计算,另外产生的预测框数量也更少;缓解正负样本不平衡问题;避免了anchor的调参。
-
将目标中心3x3的区域内的像素点都作为 target
def get_in_boxes_info(self, gt_bboxes_per_image, expanded_strides, x_shifts, y_shifts, total_num_anchors, num_gt, center_radius = 2.5):
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# expanded_strides_per_image [n_anchors_all]
# x_centers_per_image [num_gt, n_anchors_all]
# x_centers_per_image [num_gt, n_anchors_all]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
expanded_strides_per_image = expanded_strides[0]
x_centers_per_image = ((x_shifts[0] + 0.5) * expanded_strides_per_image).unsqueeze(0).repeat(num_gt, 1)
y_centers_per_image = ((y_shifts[0] + 0.5) * expanded_strides_per_image).unsqueeze(0).repeat(num_gt, 1)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# gt_bboxes_per_image_x [num_gt, n_anchors_all]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
gt_bboxes_per_image_l = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 0] - 0.5 * gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 2]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, total_num_anchors)
gt_bboxes_per_image_r = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 0] + 0.5 * gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 2]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, total_num_anchors)
gt_bboxes_per_image_t = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 1] - 0.5 * gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 3]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, total_num_anchors)
gt_bboxes_per_image_b = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 1] + 0.5 * gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 3]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, total_num_anchors)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# bbox_deltas [num_gt, n_anchors_all, 4]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
b_l = x_centers_per_image - gt_bboxes_per_image_l
b_r = gt_bboxes_per_image_r - x_centers_per_image
b_t = y_centers_per_image - gt_bboxes_per_image_t
b_b = gt_bboxes_per_image_b - y_centers_per_image
bbox_deltas = torch.stack([b_l, b_t, b_r, b_b], 2)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# is_in_boxes [num_gt, n_anchors_all]
# is_in_boxes_all [n_anchors_all]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
is_in_boxes = bbox_deltas.min(dim=-1).values > 0.0
is_in_boxes_all = is_in_boxes.sum(dim=0) > 0
gt_bboxes_per_image_l = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 0]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, total_num_anchors) - center_radius * expanded_strides_per_image.unsqueeze(0)
gt_bboxes_per_image_r = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 0]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, total_num_anchors) + center_radius * expanded_strides_per_image.unsqueeze(0)
gt_bboxes_per_image_t = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 1]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, total_num_anchors) - center_radius * expanded_strides_per_image.unsqueeze(0)
gt_bboxes_per_image_b = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 1]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, total_num_anchors) + center_radius * expanded_strides_per_image.unsqueeze(0)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# center_deltas [num_gt, n_anchors_all, 4]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
c_l = x_centers_per_image - gt_bboxes_per_image_l
c_r = gt_bboxes_per_image_r - x_centers_per_image
c_t = y_centers_per_image - gt_bboxes_per_image_t
c_b = gt_bboxes_per_image_b - y_centers_per_image
center_deltas = torch.stack([c_l, c_t, c_r, c_b], 2)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# is_in_centers [num_gt, n_anchors_all]
# is_in_centers_all [n_anchors_all]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
is_in_centers = center_deltas.min(dim=-1).values > 0.0
is_in_centers_all = is_in_centers.sum(dim=0) > 0
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# is_in_boxes_anchor [n_anchors_all]
# is_in_boxes_and_center [num_gt, is_in_boxes_anchor]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
is_in_boxes_anchor = is_in_boxes_all | is_in_centers_all
is_in_boxes_and_center = is_in_boxes[:, is_in_boxes_anchor] & is_in_centers[:, is_in_boxes_anchor]
return is_in_boxes_anchor, is_in_boxes_and_center
5.标签分配
(1)SimOTA动态匹配正样本
1、计算每个真实框和当前特征点预测框的重合程度。
2、计算将重合度最高的十个预测框与真实框的IOU加起来求得每个真实框的k,也就代表每个真实框有k个特征点与之对应。
3、计算每个真实框和当前特征点预测框的种类预测准确度。
4、判断真实框的中心是否落在了特征点的一定半径内。
5、计算Cost代价矩阵。
6、将Cost最低的k个点作为该真实框的正样本。
展开标签分配代码
@torch.no_grad()
def get_assignments(self, num_gt, total_num_anchors, gt_bboxes_per_image, gt_classes, bboxes_preds_per_image, cls_preds_per_image, obj_preds_per_image, expanded_strides, x_shifts, y_shifts):
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# fg_mask [n_anchors_all]
# is_in_boxes_and_center [num_gt, len(fg_mask)]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
fg_mask, is_in_boxes_and_center = self.get_in_boxes_info(gt_bboxes_per_image, expanded_strides, x_shifts, y_shifts, total_num_anchors, num_gt)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# fg_mask [n_anchors_all]
# bboxes_preds_per_image [fg_mask, 4]
# cls_preds_ [fg_mask, num_classes]
# obj_preds_ [fg_mask, 1]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
bboxes_preds_per_image = bboxes_preds_per_image[fg_mask]
cls_preds_ = cls_preds_per_image[fg_mask]
obj_preds_ = obj_preds_per_image[fg_mask]
num_in_boxes_anchor = bboxes_preds_per_image.shape[0]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# pair_wise_ious [num_gt, fg_mask]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
pair_wise_ious = self.bboxes_iou(gt_bboxes_per_image, bboxes_preds_per_image, False)
pair_wise_ious_loss = -torch.log(pair_wise_ious + 1e-8)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# cls_preds_ [num_gt, fg_mask, num_classes]
# gt_cls_per_image [num_gt, fg_mask, num_classes]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
if self.fp16:
with torch.cuda.amp.autocast(enabled=False):
cls_preds_ = cls_preds_.float().unsqueeze(0).repeat(num_gt, 1, 1).sigmoid_() * obj_preds_.unsqueeze(0).repeat(num_gt, 1, 1).sigmoid_()
gt_cls_per_image = F.one_hot(gt_classes.to(torch.int64), self.num_classes).float().unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, num_in_boxes_anchor, 1)
pair_wise_cls_loss = F.binary_cross_entropy(cls_preds_.sqrt_(), gt_cls_per_image, reduction="none").sum(-1)
else:
cls_preds_ = cls_preds_.float().unsqueeze(0).repeat(num_gt, 1, 1).sigmoid_() * obj_preds_.unsqueeze(0).repeat(num_gt, 1, 1).sigmoid_()
gt_cls_per_image = F.one_hot(gt_classes.to(torch.int64), self.num_classes).float().unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, num_in_boxes_anchor, 1)
pair_wise_cls_loss = F.binary_cross_entropy(cls_preds_.sqrt_(), gt_cls_per_image, reduction="none").sum(-1)
del cls_preds_
cost = pair_wise_cls_loss + 3.0 * pair_wise_ious_loss + 100000.0 * (~is_in_boxes_and_center).float()
num_fg, gt_matched_classes, pred_ious_this_matching, matched_gt_inds = self.dynamic_k_matching(cost, pair_wise_ious, gt_classes, num_gt, fg_mask)
del pair_wise_cls_loss, cost, pair_wise_ious, pair_wise_ious_loss
return gt_matched_classes, fg_mask, pred_ious_this_matching, matched_gt_inds, num_fg
def bboxes_iou(self, bboxes_a, bboxes_b, xyxy=True):
if bboxes_a.shape[1] != 4 or bboxes_b.shape[1] != 4:
raise IndexError
if xyxy:
tl = torch.max(bboxes_a[:, None, :2], bboxes_b[:, :2])
br = torch.min(bboxes_a[:, None, 2:], bboxes_b[:, 2:])
area_a = torch.prod(bboxes_a[:, 2:] - bboxes_a[:, :2], 1)
area_b = torch.prod(bboxes_b[:, 2:] - bboxes_b[:, :2], 1)
else:
tl = torch.max(
(bboxes_a[:, None, :2] - bboxes_a[:, None, 2:] / 2),
(bboxes_b[:, :2] - bboxes_b[:, 2:] / 2),
)
br = torch.min(
(bboxes_a[:, None, :2] + bboxes_a[:, None, 2:] / 2),
(bboxes_b[:, :2] + bboxes_b[:, 2:] / 2),
)
area_a = torch.prod(bboxes_a[:, 2:], 1)
area_b = torch.prod(bboxes_b[:, 2:], 1)
en = (tl < br).type(tl.type()).prod(dim=2)
area_i = torch.prod(br - tl, 2) * en
return area_i / (area_a[:, None] + area_b - area_i)
def get_in_boxes_info(self, gt_bboxes_per_image, expanded_strides, x_shifts, y_shifts, total_num_anchors, num_gt, center_radius = 2.5):
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# expanded_strides_per_image [n_anchors_all]
# x_centers_per_image [num_gt, n_anchors_all]
# x_centers_per_image [num_gt, n_anchors_all]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
expanded_strides_per_image = expanded_strides[0]
x_centers_per_image = ((x_shifts[0] + 0.5) * expanded_strides_per_image).unsqueeze(0).repeat(num_gt, 1)
y_centers_per_image = ((y_shifts[0] + 0.5) * expanded_strides_per_image).unsqueeze(0).repeat(num_gt, 1)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# gt_bboxes_per_image_x [num_gt, n_anchors_all]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
gt_bboxes_per_image_l = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 0] - 0.5 * gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 2]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, total_num_anchors)
gt_bboxes_per_image_r = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 0] + 0.5 * gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 2]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, total_num_anchors)
gt_bboxes_per_image_t = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 1] - 0.5 * gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 3]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, total_num_anchors)
gt_bboxes_per_image_b = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 1] + 0.5 * gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 3]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, total_num_anchors)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# bbox_deltas [num_gt, n_anchors_all, 4]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
b_l = x_centers_per_image - gt_bboxes_per_image_l
b_r = gt_bboxes_per_image_r - x_centers_per_image
b_t = y_centers_per_image - gt_bboxes_per_image_t
b_b = gt_bboxes_per_image_b - y_centers_per_image
bbox_deltas = torch.stack([b_l, b_t, b_r, b_b], 2)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# is_in_boxes [num_gt, n_anchors_all]
# is_in_boxes_all [n_anchors_all]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
is_in_boxes = bbox_deltas.min(dim=-1).values > 0.0
is_in_boxes_all = is_in_boxes.sum(dim=0) > 0
gt_bboxes_per_image_l = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 0]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, total_num_anchors) - center_radius * expanded_strides_per_image.unsqueeze(0)
gt_bboxes_per_image_r = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 0]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, total_num_anchors) + center_radius * expanded_strides_per_image.unsqueeze(0)
gt_bboxes_per_image_t = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 1]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, total_num_anchors) - center_radius * expanded_strides_per_image.unsqueeze(0)
gt_bboxes_per_image_b = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 1]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, total_num_anchors) + center_radius * expanded_strides_per_image.unsqueeze(0)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# center_deltas [num_gt, n_anchors_all, 4]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
c_l = x_centers_per_image - gt_bboxes_per_image_l
c_r = gt_bboxes_per_image_r - x_centers_per_image
c_t = y_centers_per_image - gt_bboxes_per_image_t
c_b = gt_bboxes_per_image_b - y_centers_per_image
center_deltas = torch.stack([c_l, c_t, c_r, c_b], 2)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# is_in_centers [num_gt, n_anchors_all]
# is_in_centers_all [n_anchors_all]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
is_in_centers = center_deltas.min(dim=-1).values > 0.0
is_in_centers_all = is_in_centers.sum(dim=0) > 0
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# is_in_boxes_anchor [n_anchors_all]
# is_in_boxes_and_center [num_gt, is_in_boxes_anchor]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
is_in_boxes_anchor = is_in_boxes_all | is_in_centers_all
is_in_boxes_and_center = is_in_boxes[:, is_in_boxes_anchor] & is_in_centers[:, is_in_boxes_anchor]
return is_in_boxes_anchor, is_in_boxes_and_center
def dynamic_k_matching(self, cost, pair_wise_ious, gt_classes, num_gt, fg_mask):
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# cost [num_gt, fg_mask]
# pair_wise_ious [num_gt, fg_mask]
# gt_classes [num_gt]
# fg_mask [n_anchors_all]
# matching_matrix [num_gt, fg_mask]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
matching_matrix = torch.zeros_like(cost)
#------------------------------------------------------------#
# 选取iou最大的n_candidate_k个点
# 然后求和,判断应该有多少点用于该框预测
# topk_ious [num_gt, n_candidate_k]
# dynamic_ks [num_gt]
# matching_matrix [num_gt, fg_mask]
#------------------------------------------------------------#
n_candidate_k = min(10, pair_wise_ious.size(1))
topk_ious, _ = torch.topk(pair_wise_ious, n_candidate_k, dim=1)
dynamic_ks = torch.clamp(topk_ious.sum(1).int(), min=1)
for gt_idx in range(num_gt):
#------------------------------------------------------------#
# 给每个真实框选取最小的动态k个点
#------------------------------------------------------------#
_, pos_idx = torch.topk(cost[gt_idx], k=dynamic_ks[gt_idx].item(), largest=False)
matching_matrix[gt_idx][pos_idx] = 1.0
del topk_ious, dynamic_ks, pos_idx
#------------------------------------------------------------#
# anchor_matching_gt [fg_mask]
#------------------------------------------------------------#
anchor_matching_gt = matching_matrix.sum(0)
if (anchor_matching_gt > 1).sum() > 0:
#------------------------------------------------------------#
# 当某一个特征点指向多个真实框的时候
# 选取cost最小的真实框。
#------------------------------------------------------------#
_, cost_argmin = torch.min(cost[:, anchor_matching_gt > 1], dim=0)
matching_matrix[:, anchor_matching_gt > 1] *= 0.0
matching_matrix[cost_argmin, anchor_matching_gt > 1] = 1.0
#------------------------------------------------------------#
# fg_mask_inboxes [fg_mask]
# num_fg为正样本的特征点个数
#------------------------------------------------------------#
fg_mask_inboxes = matching_matrix.sum(0) > 0.0
num_fg = fg_mask_inboxes.sum().item()
#------------------------------------------------------------#
# 对fg_mask进行更新
#------------------------------------------------------------#
fg_mask[fg_mask.clone()] = fg_mask_inboxes
#------------------------------------------------------------#
# 获得特征点对应的物品种类
#------------------------------------------------------------#
matched_gt_inds = matching_matrix[:, fg_mask_inboxes].argmax(0)
gt_matched_classes = gt_classes[matched_gt_inds]
pred_ious_this_matching = (matching_matrix * pair_wise_ious).sum(0)[fg_mask_inboxes]
return num_fg, gt_matched_classes, pred_ious_this_matching, matched_gt_inds
6.计算损失
- 损失=真实框和预测框计算IOU损失+正负样本和特征点的是否包含物体的预测结果计算交叉熵损失+真实框的种类和特征点的种类预测结果计算交叉熵损失
展开计算损失代码
class IOUloss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, reduction="none", loss_type="iou"):
super(IOUloss, self).__init__()
self.reduction = reduction
self.loss_type = loss_type
def forward(self, pred, target):
assert pred.shape[0] == target.shape[0]
pred = pred.view(-1, 4)
target = target.view(-1, 4)
tl = torch.max(
(pred[:, :2] - pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] - target[:, 2:] / 2)
)
br = torch.min(
(pred[:, :2] + pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] + target[:, 2:] / 2)
)
area_p = torch.prod(pred[:, 2:], 1)
area_g = torch.prod(target[:, 2:], 1)
en = (tl < br).type(tl.type()).prod(dim=1)
area_i = torch.prod(br - tl, 1) * en
area_u = area_p + area_g - area_i
iou = (area_i) / (area_u + 1e-16)
if self.loss_type == "iou":
loss = 1 - iou ** 2
elif self.loss_type == "giou":
c_tl = torch.min(
(pred[:, :2] - pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] - target[:, 2:] / 2)
)
c_br = torch.max(
(pred[:, :2] + pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] + target[:, 2:] / 2)
)
area_c = torch.prod(c_br - c_tl, 1)
giou = iou - (area_c - area_u) / area_c.clamp(1e-16)
loss = 1 - giou.clamp(min=-1.0, max=1.0)
if self.reduction == "mean":
loss = loss.mean()
elif self.reduction == "sum":
loss = loss.sum()
return loss
class YOLOLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes, fp16, strides=[8, 16, 32]):
super().__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.strides = strides
self.bcewithlog_loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(reduction="none")
self.iou_loss = IOUloss(reduction="none")
self.grids = [torch.zeros(1)] * len(strides)
self.fp16 = fp16
def forward(self, inputs, labels=None):
outputs = []
x_shifts = []
y_shifts = []
expanded_strides = []
#-----------------------------------------------#
# inputs [[batch_size, num_classes + 5, 20, 20]
# [batch_size, num_classes + 5, 40, 40]
# [batch_size, num_classes + 5, 80, 80]]
# outputs [[batch_size, 400, num_classes + 5]
# [batch_size, 1600, num_classes + 5]
# [batch_size, 6400, num_classes + 5]]
# x_shifts [[batch_size, 400]
# [batch_size, 1600]
# [batch_size, 6400]]
#-----------------------------------------------#
for k, (stride, output) in enumerate(zip(self.strides, inputs)):
output, grid = self.get_output_and_grid(output, k, stride)
x_shifts.append(grid[:, :, 0])
y_shifts.append(grid[:, :, 1])
expanded_strides.append(torch.ones_like(grid[:, :, 0]) * stride)
outputs.append(output)
return self.get_losses(x_shifts, y_shifts, expanded_strides, labels, torch.cat(outputs, 1))
def get_output_and_grid(self, output, k, stride):
grid = self.grids[k]
hsize, wsize = output.shape[-2:]
if grid.shape[2:4] != output.shape[2:4]:
yv, xv = torch.meshgrid([torch.arange(hsize), torch.arange(wsize)])
grid = torch.stack((xv, yv), 2).view(1, hsize, wsize, 2).type(output.type())
self.grids[k] = grid
grid = grid.view(1, -1, 2)
output = output.flatten(start_dim=2).permute(0, 2, 1)
output[..., :2] = (output[..., :2] + grid.type_as(output)) * stride
output[..., 2:4] = torch.exp(output[..., 2:4]) * stride
return output, grid
def get_losses(self, x_shifts, y_shifts, expanded_strides, labels, outputs):
#-----------------------------------------------#
# [batch, n_anchors_all, 4]
#-----------------------------------------------#
bbox_preds = outputs[:, :, :4]
#-----------------------------------------------#
# [batch, n_anchors_all, 1]
#-----------------------------------------------#
obj_preds = outputs[:, :, 4:5]
#-----------------------------------------------#
# [batch, n_anchors_all, n_cls]
#-----------------------------------------------#
cls_preds = outputs[:, :, 5:]
total_num_anchors = outputs.shape[1]
#-----------------------------------------------#
# x_shifts [1, n_anchors_all]
# y_shifts [1, n_anchors_all]
# expanded_strides [1, n_anchors_all]
#-----------------------------------------------#
x_shifts = torch.cat(x_shifts, 1).type_as(outputs)
y_shifts = torch.cat(y_shifts, 1).type_as(outputs)
expanded_strides = torch.cat(expanded_strides, 1).type_as(outputs)
cls_targets = []
reg_targets = []
obj_targets = []
fg_masks = []
num_fg = 0.0
for batch_idx in range(outputs.shape[0]):
num_gt = len(labels[batch_idx])
if num_gt == 0:
cls_target = outputs.new_zeros((0, self.num_classes))
reg_target = outputs.new_zeros((0, 4))
obj_target = outputs.new_zeros((total_num_anchors, 1))
fg_mask = outputs.new_zeros(total_num_anchors).bool()
else:
#-----------------------------------------------#
# gt_bboxes_per_image [num_gt, num_classes]
# gt_classes [num_gt]
# bboxes_preds_per_image [n_anchors_all, 4]
# cls_preds_per_image [n_anchors_all, num_classes]
# obj_preds_per_image [n_anchors_all, 1]
#-----------------------------------------------#
gt_bboxes_per_image = labels[batch_idx][..., :4].type_as(outputs)
gt_classes = labels[batch_idx][..., 4].type_as(outputs)
bboxes_preds_per_image = bbox_preds[batch_idx]
cls_preds_per_image = cls_preds[batch_idx]
obj_preds_per_image = obj_preds[batch_idx]
gt_matched_classes, fg_mask, pred_ious_this_matching, matched_gt_inds, num_fg_img = self.get_assignments(
num_gt, total_num_anchors, gt_bboxes_per_image, gt_classes, bboxes_preds_per_image, cls_preds_per_image, obj_preds_per_image,
expanded_strides, x_shifts, y_shifts,
)
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
num_fg += num_fg_img
cls_target = F.one_hot(gt_matched_classes.to(torch.int64), self.num_classes).float() * pred_ious_this_matching.unsqueeze(-1)
obj_target = fg_mask.unsqueeze(-1)
reg_target = gt_bboxes_per_image[matched_gt_inds]
cls_targets.append(cls_target)
reg_targets.append(reg_target)
obj_targets.append(obj_target.type(cls_target.type()))
fg_masks.append(fg_mask)
cls_targets = torch.cat(cls_targets, 0)
reg_targets = torch.cat(reg_targets, 0)
obj_targets = torch.cat(obj_targets, 0)
fg_masks = torch.cat(fg_masks, 0)
num_fg = max(num_fg, 1)
loss_iou = (self.iou_loss(bbox_preds.view(-1, 4)[fg_masks], reg_targets)).sum()
loss_obj = (self.bcewithlog_loss(obj_preds.view(-1, 1), obj_targets)).sum()
loss_cls = (self.bcewithlog_loss(cls_preds.view(-1, self.num_classes)[fg_masks], cls_targets)).sum()
reg_weight = 5.0
loss = reg_weight * loss_iou + loss_obj + loss_cls
return loss / num_fg
7.预测结果
展开预测代码
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# predict.py将单张图片预测、摄像头检测、FPS测试和目录遍历检测等功能
# 整合到了一个py文件中,通过指定mode进行模式的修改。
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------#
import time
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from yolo import YOLO
if __name__ == "__main__":
yolo = YOLO()
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# mode用于指定测试的模式:
# 'predict' 表示单张图片预测,如果想对预测过程进行修改,如保存图片,截取对象等,可以先看下方详细的注释
# 'video' 表示视频检测,可调用摄像头或者视频进行检测,详情查看下方注释。
# 'fps' 表示测试fps,使用的图片是img里面的street.jpg,详情查看下方注释。
# 'dir_predict' 表示遍历文件夹进行检测并保存。默认遍历img文件夹,保存img_out文件夹,详情查看下方注释。
# 'heatmap' 表示进行预测结果的热力图可视化,详情查看下方注释。
# 'export_onnx' 表示将模型导出为onnx,需要pytorch1.7.1以上。
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
mode = "predict"
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# crop 指定了是否在单张图片预测后对目标进行截取
# count 指定了是否进行目标的计数
# crop、count仅在mode='predict'时有效
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
crop = False
count = False
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# video_path 用于指定视频的路径,当video_path=0时表示检测摄像头
# 想要检测视频,则设置如video_path = "xxx.mp4"即可,代表读取出根目录下的xxx.mp4文件。
# video_save_path 表示视频保存的路径,当video_save_path=""时表示不保存
# 想要保存视频,则设置如video_save_path = "yyy.mp4"即可,代表保存为根目录下的yyy.mp4文件。
# video_fps 用于保存的视频的fps
#
# video_path、video_save_path和video_fps仅在mode='video'时有效
# 保存视频时需要ctrl+c退出或者运行到最后一帧才会完成完整的保存步骤。
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
video_path = 0
video_save_path = ""
video_fps = 25.0
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# test_interval 用于指定测量fps的时候,图片检测的次数。理论上test_interval越大,fps越准确。
# fps_image_path 用于指定测试的fps图片
#
# test_interval和fps_image_path仅在mode='fps'有效
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
test_interval = 100
fps_image_path = "img/street.jpg"
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# dir_origin_path 指定了用于检测的图片的文件夹路径
# dir_save_path 指定了检测完图片的保存路径
#
# dir_origin_path和dir_save_path仅在mode='dir_predict'时有效
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
dir_origin_path = "img/"
dir_save_path = "img_out/"
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# heatmap_save_path 热力图的保存路径,默认保存在model_data下
#
# heatmap_save_path仅在mode='heatmap'有效
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
heatmap_save_path = "model_data/heatmap_vision.png"
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# simplify 使用Simplify onnx
# onnx_save_path 指定了onnx的保存路径
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
simplify = True
onnx_save_path = "model_data/models.onnx"
if mode == "predict":
'''
1、如果想要进行检测完的图片的保存,利用r_image.save("img.jpg")即可保存,直接在predict.py里进行修改即可。
2、如果想要获得预测框的坐标,可以进入yolo.detect_image函数,在绘图部分读取top,left,bottom,right这四个值。
3、如果想要利用预测框截取下目标,可以进入yolo.detect_image函数,在绘图部分利用获取到的top,left,bottom,right这四个值
在原图上利用矩阵的方式进行截取。
4、如果想要在预测图上写额外的字,比如检测到的特定目标的数量,可以进入yolo.detect_image函数,在绘图部分对predicted_class进行判断,
比如判断if predicted_class == 'car': 即可判断当前目标是否为车,然后记录数量即可。利用draw.text即可写字。
'''
while True:
img = input('Input image filename:')
try:
image = Image.open(img)
except:
print('Open Error! Try again!')
continue
else:
r_image = yolo.detect_image(image, crop = crop, count=count)
r_image.show()
elif mode == "video":
capture = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
if video_save_path!="":
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'XVID')
size = (int(capture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)), int(capture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)))
out = cv2.VideoWriter(video_save_path, fourcc, video_fps, size)
ref, frame = capture.read()
if not ref:
raise ValueError("未能正确读取摄像头(视频),请注意是否正确安装摄像头(是否正确填写视频路径)。")
fps = 0.0
while(True):
t1 = time.time()
# 读取某一帧
ref, frame = capture.read()
if not ref:
break
# 格式转变,BGRtoRGB
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 转变成Image
frame = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(frame))
# 进行检测
frame = np.array(yolo.detect_image(frame))
# RGBtoBGR满足opencv显示格式
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame,cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
fps = ( fps + (1./(time.time()-t1)) ) / 2
print("fps= %.2f"%(fps))
frame = cv2.putText(frame, "fps= %.2f"%(fps), (0, 40), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow("video",frame)
c= cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xff
if video_save_path!="":
out.write(frame)
if c==27:
capture.release()
break
print("Video Detection Done!")
capture.release()
if video_save_path!="":
print("Save processed video to the path :" + video_save_path)
out.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
elif mode == "fps":
img = Image.open(fps_image_path)
tact_time = yolo.get_FPS(img, test_interval)
print(str(tact_time) + ' seconds, ' + str(1/tact_time) + 'FPS, @batch_size 1')
elif mode == "dir_predict":
import os
from tqdm import tqdm
img_names = os.listdir(dir_origin_path)
for img_name in tqdm(img_names):
if img_name.lower().endswith(('.bmp', '.dib', '.png', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.pbm', '.pgm', '.ppm', '.tif', '.tiff')):
image_path = os.path.join(dir_origin_path, img_name)
image = Image.open(image_path)
r_image = yolo.detect_image(image)
if not os.path.exists(dir_save_path):
os.makedirs(dir_save_path)
r_image.save(os.path.join(dir_save_path, img_name.replace(".jpg", ".png")), quality=95, subsampling=0)
elif mode == "heatmap":
while True:
img = input('Input image filename:')
try:
image = Image.open(img)
except:
print('Open Error! Try again!')
continue
else:
yolo.detect_heatmap(image, heatmap_save_path)
elif mode == "export_onnx":
yolo.convert_to_onnx(simplify, onnx_save_path)
else:
raise AssertionError("Please specify the correct mode: 'predict', 'video', 'fps', 'heatmap', 'export_onnx', 'dir_predict'.")




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人