OpenCV实现多目标追踪(2)
本文使用dlib库以及Caffe训练好的SSD模块对短视频流中的人进行目标追踪,并使用多线程进行优化。
步骤:
- 首先需要加载SSD分类标签并读取网络模型,其次,对视频流进行预处理操作,然后,基于第一帧检测人并绘制相对位置的框,接着,使用dlib来进行目标追踪,最后,后面的每一帧根据第一帧检测到的人物框进行更新。
1.预处理操作
(1)给出深度学习分类的标签
# SSD标签(caffe的一个model)
CLASSES = ["background", "aeroplane", "bicycle", "bird", "boat",
"bottle", "bus", "car", "cat", "chair", "cow", "diningtable",
"dog", "horse", "motorbike", "person", "pottedplant", "sheep",
"sofa", "train", "tvmonitor"]
(2)读取网络模型
print("[INFO] loading model...")
net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(args["prototxt"], args["model"])
(3)预处理视频流
# 初始化视频流
print("[INFO] starting video stream...")
vs = cv2.VideoCapture(args["video"])
writer = None
# 一会要追踪多个目标
trackers = []
labels = []
# 计算FPS
fps = FPS().start()
while True:
# 读取一帧
(grabbed, frame) = vs.read()
# 是否是最后了
if frame is None:
break
# 预处理操作
(h, w) = frame.shape[:2]
width=600
r = width / float(w)
dim = (width, int(h * r))
frame = cv2.resize(frame, dim, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
rgb = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)#BGR2RGB
# 如果要将结果保存的话
if args["output"] is not None and writer is None:
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"MJPG")
writer = cv2.VideoWriter(args["output"], fourcc, 30,
(frame.shape[1], frame.shape[0]), True)
2.基于第一帧检测目标
- 用深度学习模型检测图像,得到检测结果(含有多个被检测到的物体信息)。遍历被检测到的物体,如果检测结果表明此物体为人,则得到人在图中的位置。使用dlib来进行目标追踪。保存结果,将所有追踪器放到一个列表中(追踪器的数量表明图中人的数量)。绘图,即将人用方框圈起来。
# 先检测 再追踪
if len(trackers) == 0:
# 获取blob数据
(h, w) = frame.shape[:2]
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, 0.007843, (w, h), 127.5)#127.5均值;0.007843=1/127.5归一化
# 得到检测结果
net.setInput(blob)
detections = net.forward()#多个
# 遍历得到的检测结果
for i in np.arange(0, detections.shape[2]):
# 能检测到多个结果,只保留概率高的
confidence = detections[0, 0, i, 2]
# 过滤
if confidence > args["confidence"]:
# extract the index of the class label from the
# detections list
idx = int(detections[0, 0, i, 1])
label = CLASSES[idx]
# 只保留人的
if CLASSES[idx] != "person":
continue
# 得到BBOX
#print (detections[0, 0, i, 3:7])#得到的结果为相对整张图片的大小占比,不是实际位置
box = detections[0, 0, i, 3:7] * np.array([w, h, w, h])
(startX, startY, endX, endY) = box.astype("int")
# 使用dlib来进行目标追踪
#http://dlib.net/python/index.html#dlib.correlation_tracker
t = dlib.correlation_tracker()
rect = dlib.rectangle(int(startX), int(startY), int(endX), int(endY))#做一个框
t.start_track(rgb, rect)#开始追踪,从第一帧数据开始
# 保存结果
labels.append(label)
trackers.append(t)#每检测到人都会形成一个框,添加追踪
# 绘图
cv2.rectangle(frame, (startX, startY), (endX, endY),
(0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(frame, label, (startX, startY - 15),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.45, (0, 255, 0), 2)
3.追踪目标
- 读取第二帧。同样,进行预处理。更新追踪器。得到人的新的位置。绘图。重复操作,读取第三帧、第四帧……直到视频结束。
# 如果已经有了框,就可以直接追踪了
else:#只有第一帧需要检测人,后面帧根据检测到的人直接进行追踪
# 每一个追踪器都要进行更新
for (t, l) in zip(trackers, labels):
t.update(rgb)
pos = t.get_position()#新的追踪到的位置
# 得到位置
startX = int(pos.left())
startY = int(pos.top())
endX = int(pos.right())
endY = int(pos.bottom())
# 画出来
cv2.rectangle(frame, (startX, startY), (endX, endY),
(0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(frame, l, (startX, startY - 15),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.45, (0, 255, 0), 2)
# 也可以把结果保存下来
if writer is not None:
writer.write(frame)
# 显示
cv2.imshow("Frame", frame)
key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF
# 退出
if key == 27:
break
# 计算FPS
fps.update()
fps.stop()
print("[INFO] elapsed time: {:.2f}".format(fps.elapsed()))
print("[INFO] approx. FPS: {:.2f}".format(fps.fps()))
if writer is not None:
writer.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
vs.release()
4.效果展示
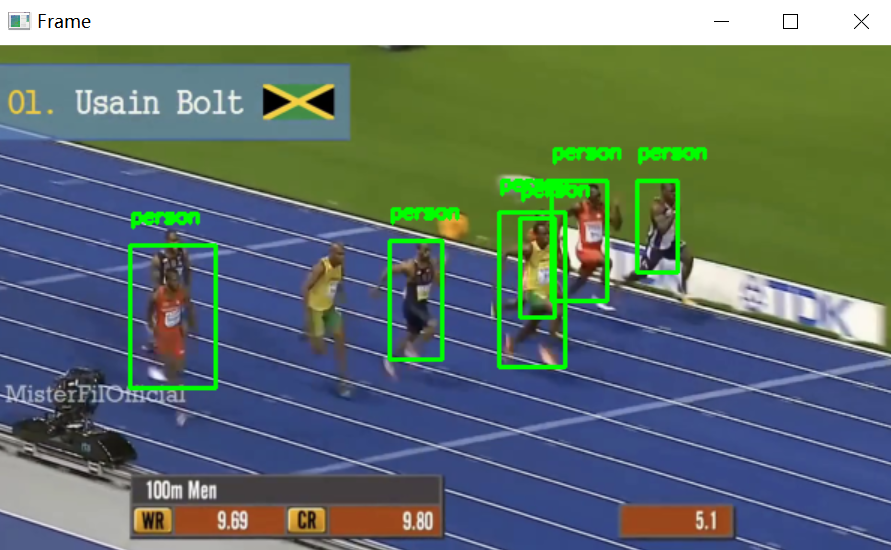
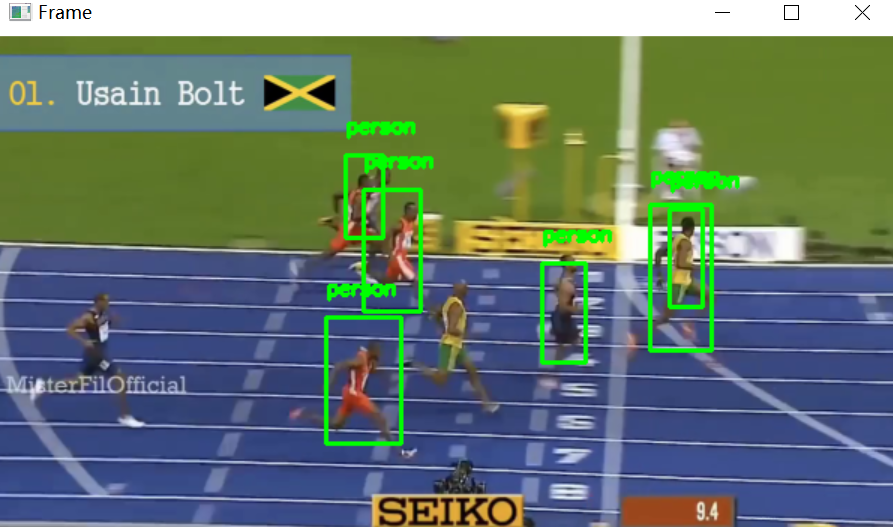
5.多进程优化追踪器
结果(第二张图为多进程结果)
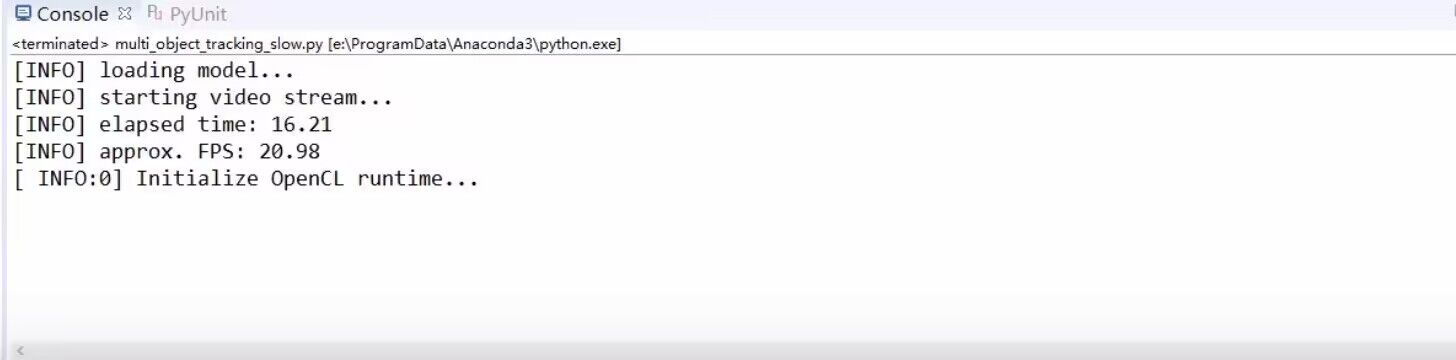
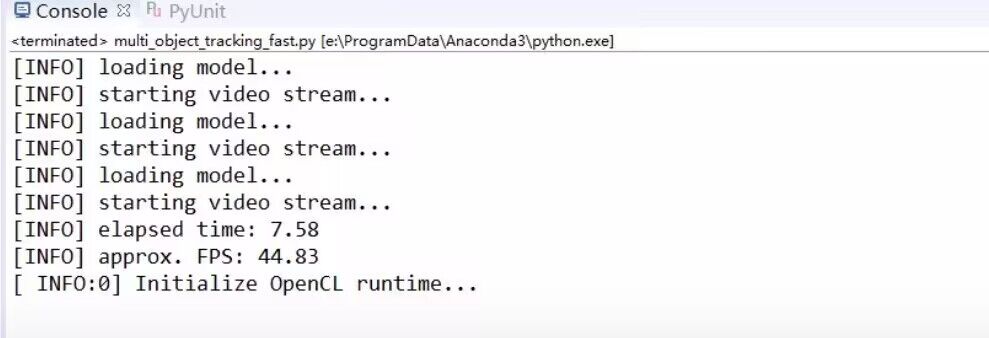
CPU性能(第二张图为多进程结果)
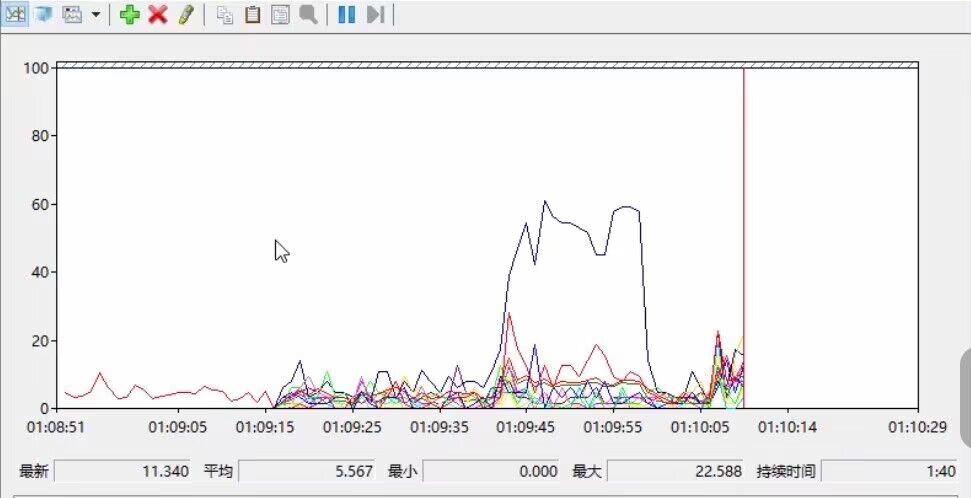
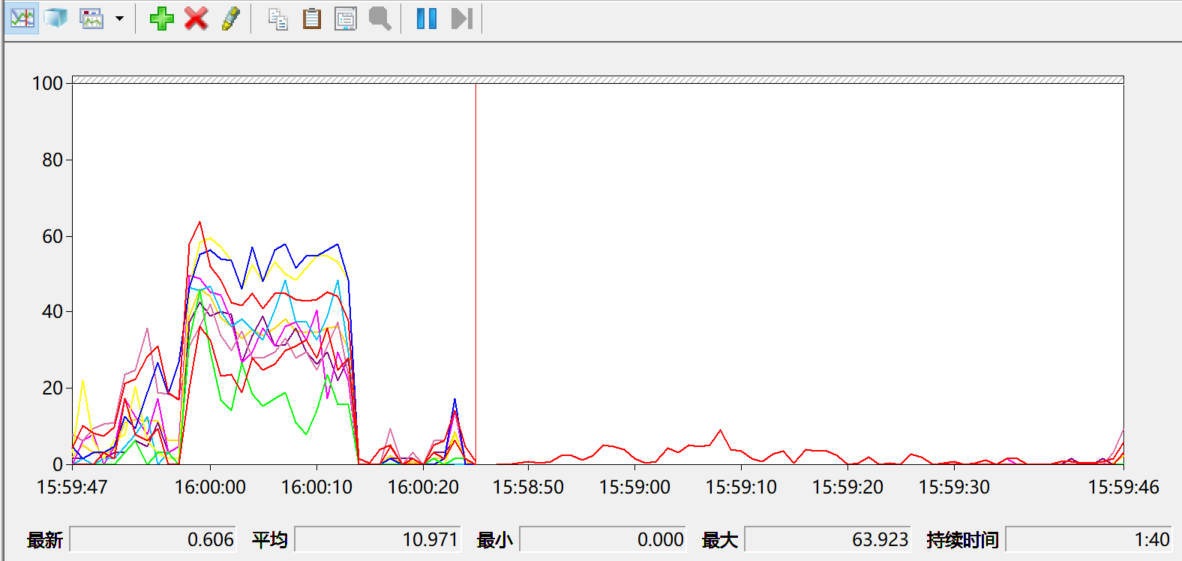
多进程优化完整代码
from utils import FPS
import multiprocessing
import numpy as np
import argparse
import dlib
import cv2
#perfmon
#每个进程都要执行相同的操作,封装成函数
def start_tracker(box, label, rgb, inputQueue, outputQueue):
t = dlib.correlation_tracker()#创建追踪器
rect = dlib.rectangle(int(box[0]), int(box[1]), int(box[2]), int(box[3]))#给定框
t.start_track(rgb, rect)#根据框开始追踪
while True:
# 获取下一帧
rgb = inputQueue.get()
# 非空就开始处理
if rgb is not None:
# 更新追踪器
t.update(rgb)
pos = t.get_position()#得到位置
startX = int(pos.left())
startY = int(pos.top())
endX = int(pos.right())
endY = int(pos.bottom())
# 把结果放到输出q
outputQueue.put((label, (startX, startY, endX, endY)))
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-p", "--prototxt", required=True,
help="path to Caffe 'deploy' prototxt file")
ap.add_argument("-m", "--model", required=True,
help="path to Caffe pre-trained model")
ap.add_argument("-v", "--video", required=True,
help="path to input video file")
ap.add_argument("-o", "--output", type=str,
help="path to optional output video file")
ap.add_argument("-c", "--confidence", type=float, default=0.2,
help="minimum probability to filter weak detections")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
# 一会要放多个追踪器
inputQueues = []
outputQueues = []
CLASSES = ["background", "aeroplane", "bicycle", "bird", "boat",
"bottle", "bus", "car", "cat", "chair", "cow", "diningtable",
"dog", "horse", "motorbike", "person", "pottedplant", "sheep",
"sofa", "train", "tvmonitor"]
print("[INFO] loading model...")
net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(args["prototxt"], args["model"])
print("[INFO] starting video stream...")
vs = cv2.VideoCapture(args["video"])
writer = None
fps = FPS().start()
if __name__ == '__main__':
while True:
(grabbed, frame) = vs.read()
if frame is None:
break
(h, w) = frame.shape[:2]
width=600
r = width / float(w)
dim = (width, int(h * r))
frame = cv2.resize(frame, dim, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
rgb = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
if args["output"] is not None and writer is None:
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"MJPG")
writer = cv2.VideoWriter(args["output"], fourcc, 30,
(frame.shape[1], frame.shape[0]), True)
#首先检测位置
if len(inputQueues) == 0:
(h, w) = frame.shape[:2]
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, 0.007843, (w, h), 127.5)
net.setInput(blob)
detections = net.forward()
for i in np.arange(0, detections.shape[2]):
confidence = detections[0, 0, i, 2]
if confidence > args["confidence"]:
idx = int(detections[0, 0, i, 1])
label = CLASSES[idx]
if CLASSES[idx] != "person":
continue
box = detections[0, 0, i, 3:7] * np.array([w, h, w, h])
(startX, startY, endX, endY) = box.astype("int")
bb = (startX, startY, endX, endY)
# 创建输入q和输出q
iq = multiprocessing.Queue()
oq = multiprocessing.Queue()
inputQueues.append(iq)
outputQueues.append(oq)
# 多核
p = multiprocessing.Process(
target=start_tracker,#调用函数
args=(bb, label, rgb, iq, oq))#传入参数
p.daemon = True
p.start()#开始执行
#绘制结果
cv2.rectangle(frame, (startX, startY), (endX, endY),
(0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(frame, label, (startX, startY - 15),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.45, (0, 255, 0), 2)
else:
# 多个追踪器处理的都是相同输入
for iq in inputQueues:
iq.put(rgb)
for oq in outputQueues:
# 得到更新结果
(label, (startX, startY, endX, endY)) = oq.get()
# 绘图
cv2.rectangle(frame, (startX, startY), (endX, endY),
(0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(frame, label, (startX, startY - 15),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.45, (0, 255, 0), 2)
if writer is not None:
writer.write(frame)
cv2.imshow("Frame", frame)
key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF
if key == 27:
break
fps.update()
fps.stop()
print("[INFO] elapsed time: {:.2f}".format(fps.elapsed()))
print("[INFO] approx. FPS: {:.2f}".format(fps.fps()))
if writer is not None:
writer.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
vs.release()




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧