Java中的自定义注解Annotation
与注释不同,注解可以被其他程序读取。比如通过反射(Class)读取注解。
内置注解:
1、@Override - 检查该方法是否是重写方法。如果发现其父类,或者是引用的接口中并没有该方法时,会报编译错误。
2、@Deprecated - 标记过时方法。如果使用该方法,会报编译警告。
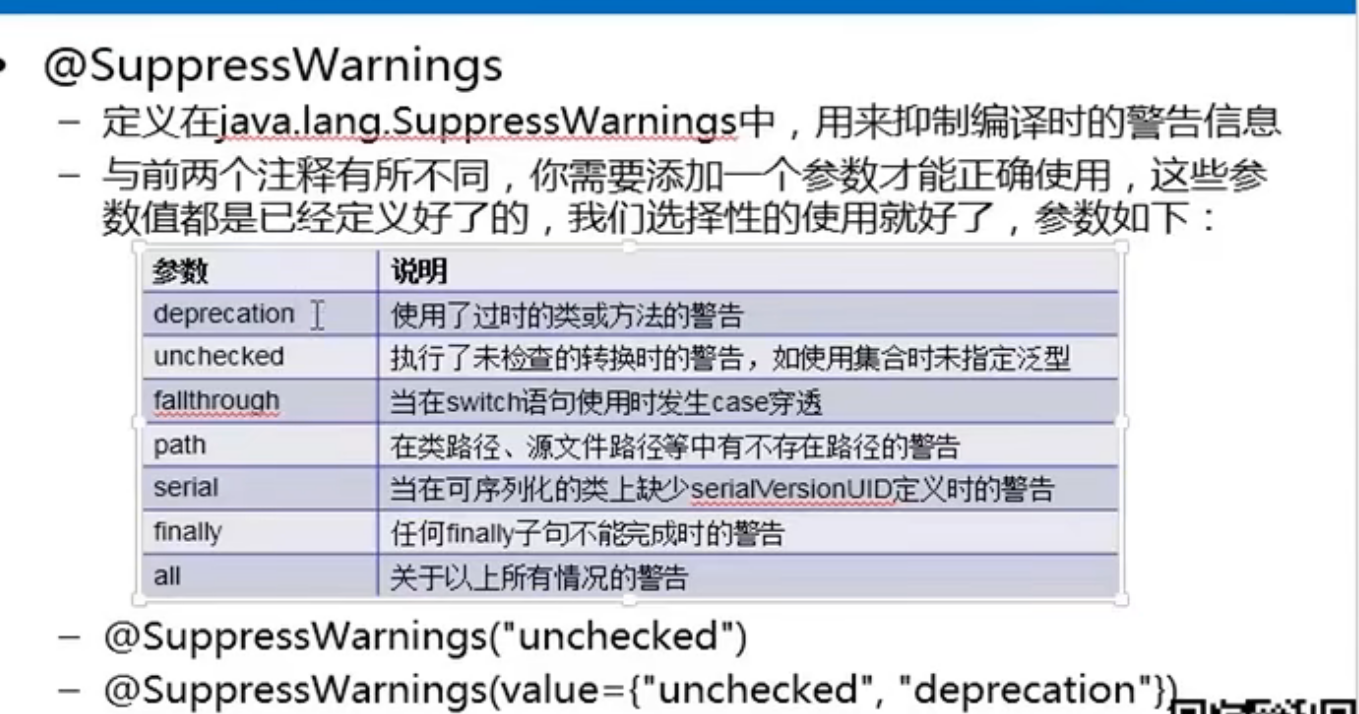
3、@SuppressWarnings - 指示编译器去忽略注解中声明的警告。
@SuppressWarnings参数:
元注解 :
用来注解其它注解的注解。
1、@Target:使用的位置。包括:
- TYPE 意味着,它能标注"类、接口(包括注释类型)或枚举声明"。
- FIELD 意味着,它能标注"属性"。
- METHOD 意味着,它能标注"方法"。
- PARAMETER 意味着,它能标注"参数"。
- CONSTRUCTOR 意味着,它能标注"构造方法"。
- LOCAL_VARIABLE 意味着,它能标注"局部变量"。
2、@Retention:生命周期。包括:
source:注解只保留在源文件,当Java文件编译成class文件的时候,注解被遗弃;被编译器忽略。
class:注解被保留到class文件,但jvm加载class文件时候被遗弃,这是默认的生命周期。
runtime:注解不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在。
这3个生命周期分别对应于:Java源文件(.java文件) ---> .class文件 ---> 内存中的字节码。
3、@Documented:标记这些注解是否包含在用户文档中。
4、@Inherited:标记这个注解是继承于哪个注解类(默认注解并没有继承于任何子类)。
自定义注解及用反射解析注解
创建:
package lrj.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; /** * 被此注释标注的属性需要给定 * 字段名columnName,类型type,长度length * */ @Target(ElementType.FIELD ) //用来注释属性 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //生命周期 public @interface Datas { String cilumnName(); String type(); int length(); }
package lrj.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; /** * 使用此声明的类,必须注释此类表示的对象是谁 */ @Target(ElementType.TYPE) //用来注释类 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//生命周期 public @interface IsUser { String value(); }
使用:
package lrj.annotation; @IsUser("学生") public class Student { @Datas(cilumnName = "id",type = "int",length = 10) private int id; @Datas(cilumnName = "name",type = "String",length = 20) private String name; @Datas(cilumnName = "age",type = "int",length = 3) private int age; }
解析:
package lrj.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation; import java.lang.reflect.Field; /** * 通过反射获取注释内容 */ public class TestClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1、获取Student的class对象 Class clsStudent =Class.forName("lrj.annotation.Student"); //2、获取类的指定注释 IsUser clsAno= (IsUser) clsStudent.getAnnotation(IsUser.class); System.out.println(clsAno); //3、获取注释的内容 System.out.println(clsAno.value()); //2、获取类的全部注释 Annotation[] allAno = clsStudent.getAnnotations(); //1、获取私有属性 Field fieldId = clsStudent.getDeclaredField("id"); fieldId.setAccessible(true); //2、获取属性的指定注释 Datas fieAno = fieldId.getAnnotation(Datas.class); //3、获取注释的内容 System.out.println(fieAno.cilumnName()); System.out.println(fieAno.length()); System.out.println(fieAno.type()); //2、获取属性的所有注释 Annotation[] s = fieldId.getDeclaredAnnotations(); } }
运行结果:
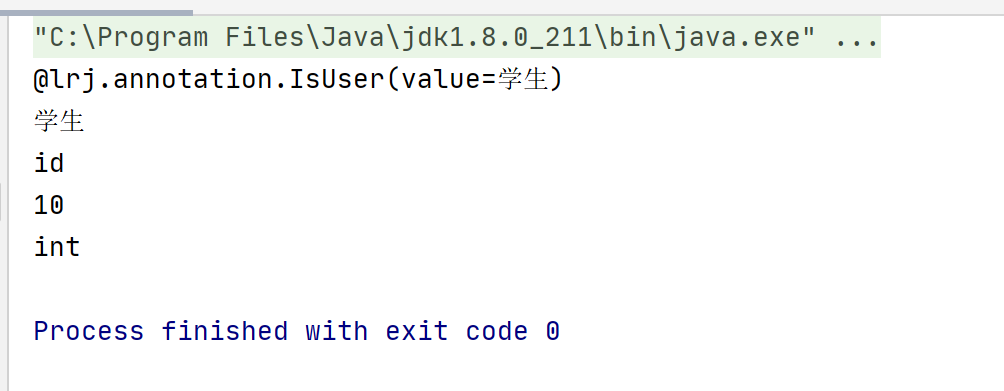
在使用注解时
如果:注释中需要设置的值只有一个(可能其他值有默认值,或者没有其他值),且名字为value。
那么:在设置值时,“ value= ”可省。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步