Java注解和反射04:Class对象的使用
1.Java入门——介绍及安装2.Java基础01:注释、标识符、数据类型3.Java基础02:类型转换、变量、常量4.Java基础03:基本运算符5.Java基础04:包机制、JavaDoc生成文档6.Java流程控制01:Scanner对象7.Java流程控制02:顺序结构和选择结构8.Java流程控制03:循环结构9.Java方法10.Java数组01:数组的定义、声明、创建、初始化和内存分析11.Java数组02:数组使用、多维数组、冒泡排序和稀疏数组12.Java面向对象01:类与对象的关系、创建和初始化对象13.Java面向对象02:封装和继承14.Java面向对象03:抽象类、接口和内部类15.Java异常16.SpringBoot和微服务架构17.SpringBoot基础01:创建项目和编写HTTP接口18.SpringBoot基础02:自动装配原理、yaml语法和JSR-303数据校验19.SpringBoot基础03:静态资源和首页定制20.Java多线程01:什么是线程和线程的创建21.Java多线程02:静态代理模式和Lambda表达式22.Java多线程03:线程的五大状态23.Java多线程04:线程优先级、守护线程和线程同步24.Java多线程05:死锁、LOCK和线程协作25.网络编程基础01:网络编程概述、IP和端口26.网络编程基础02:TCP实现聊天和文件上传27.Java注解和反射01:注解28.Java注解和反射02:反射基本概述和获得Class类的几种方式29.Java注解和反射03:类加载
30.Java注解和反射04:Class对象的使用
Java注解和反射04:Class对象的使用
有了Class对象,能做什么
- 创建类的对象:调用Class对象的newInstance()方法
- 类必须有一个无参的构造器
- 类的构造器的 访问权限需要足够
- 步骤如下:
- 通过Class类的getDeclaredConstructor(Class ... parameterTypes)取得本类的指定形参类型的构造器
- 向构造器的形参中传递一个对象数组进去,里面包含了构造器中所有的各个参数
- 通过Constructor实例化对象
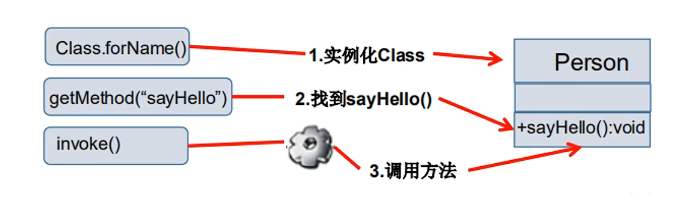
调用指定的方法
通过反射,调用类中的方法,通过Method类完成
- 通过Class类的getMethod(String name,Class...parameterTypes)方法取得一个Method对象,并设置此方法操作时所需要的参数类型
- 之后使用Object invoke(Object obj,Object[] args)进行调用,并向方法中传递要设置的obj对象的参数信息
package com.lurenj.reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
//动态的创建对象,通过反射
public class Test09 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException {
//获得Class对象
Class c1 = Class.forName("com.lurenj.reflection.User");
//构造一个对象
User user = (User) c1.newInstance();//本质是调用了类的无参构造器
System.out.println(user);//User{name='null', id=0, age=0}
//通过构造器创建对象
Constructor constructor = c1.getConstructor(String.class, int.class, int.class);
User user2 = (User) constructor.newInstance("lurenj", 001, 18);
System.out.println(user2);//User{name='lurenj', id=1, age=18}
//通过反射调用普通方法
User user3 = (User) c1.newInstance();
//通过反射获取一个方法
Method setName = c1.getDeclaredMethod("setName", String.class);
//invoke:激活的意思
//(对象,”方法的值“)
setName.invoke(user3,"lurenj");
System.out.println(user3.getName());//lurenj
//通过反射操作属性
System.out.println("==========================");
User user4 = (User) c1.newInstance();
Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
//不能直接操作私有属性,我们需要关闭程序的安全检测,属性或者方法的setAccessible(true)
name.setAccessible(true);//取消安全检测
name.set(user4,"lurenj");
System.out.println(user4.getName());//lurenj
}
}
setAccessible
- Method和Field、Constructor对象都有setAccessible()方法
- setAccessible作用是启动和禁用访问安全检查的开关
- 参数值为true则指示反射的对象在使用时应该取消Java语言访问检查
- 提高反射的效率。如果代码中必须用反射,而该句代码需要频繁的被调用,那么请设置为true
- 使得原本无法访问的私有成员也可以访问
- 参数值为false则指示反射的对象应该实施Java语言的访问检查
package com.lurenj.reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
//分析性能问题
public class Test10 {
//普通方式调用
public static void test01() {
User user = new User();
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
user.getName();
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("普通方式执行10E次:" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
//反射方式调用
public static void test02() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
User user = new User();
Class c1 = user.getClass();
Method getName = c1.getDeclaredMethod("getName", null);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
getName.invoke(user, null);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("反射方式执行10E次:" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
//反射方式调用 关闭检测
public static void test03() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
User user = new User();
Class c1 = user.getClass();
Method getName = c1.getDeclaredMethod("getName", null);
getName.setAccessible(true);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
getName.invoke(user, null);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("反射方式关闭检测执行10E次:" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
test01();//普通方式执行10E次:4ms
test02();//反射方式执行10E次:1507ms
test03();//反射方式关闭检测执行10E次:978ms
}
}
反射操作泛型
- Java采用泛型擦除的机制来引入泛型,Java中的泛型仅仅是给编译器javac使用的,确保数据的安全性和免去强制类型转换问题,但是,一旦编译完成,所有和泛型有关的类型全部擦除
- 为了通过反射操作这些类型,Java新增了ParameterizedType,GenericArrayType,TypeVariable和WildcardType几种类型来代表不能被归一到Class类型但是又和原始类型齐名的类型
- ParameterizedType:表示一种参数化类型,比如Collection
- GenericArrayType:表示一种元素类型是参数化类型或者类型变量的数组类型
- TypeVariable:是各种类型变量的公共父接口
- WildcardType:代表一种通配符类型表达式
package com.lurenj.reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
//通过反射获取泛型
public class Test11 {
public void test01(Map<String,User> map, List<User> list){
}
public Map<String,User> test02(){
System.out.println("test02");
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException {
Method method = Test11.class.getMethod("test01", Map.class, List.class);
Type[] genericParameterTypes = method.getGenericParameterTypes();
for (Type genericParameterType : genericParameterTypes) {
System.out.println("#" + genericParameterType);
if (genericParameterType instanceof ParameterizedType){
Type[] actualTypeArguments = ((ParameterizedType) genericParameterType).getActualTypeArguments();
for (Type actualTypeArgument : actualTypeArguments) {
System.out.println(actualTypeArgument);
}
}
}
method = Test11.class.getMethod("test02",null);
Type genericReturnType = method.getGenericReturnType();
if (genericReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType){
Type[] actualTypeArguments = ((ParameterizedType) genericReturnType).getActualTypeArguments();
for (Type actualTypeArgument : actualTypeArguments) {
System.out.println(actualTypeArgument);
}
}
}
}
反射操作注解
- getAnnotations
- getAnnotation
package com.lurenj.reflection;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
//练习反射操作注解
public class Test12 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class c1 = Class.forName("com.lurenj.reflection.Student2");
//通过反射获得注解
Annotation[] annotations = c1.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
//获取注解的value值
Tablelurenj tablelurenj = (Tablelurenj) c1.getAnnotation(Tablelurenj.class);
String value = tablelurenj.value();
System.out.println(value);
//获得类指定的注解
Field f = c1.getDeclaredField("id");
Filedlurenj annotation = f.getAnnotation(Filedlurenj.class);
System.out.println(annotation.columnName());
System.out.println(annotation.type());
System.out.println(annotation.length());
}
}
@Tablelurenj("db_student")
class Student2{
@Filedlurenj(columnName = "db_id",type = "int",length = 10)
private int id;
@Filedlurenj(columnName = "db_age",type = "int",length = 10)
private int age;
@Filedlurenj(columnName = "db_name",type = "varchar",length = 10)
private String name;
public Student2() {
}
public Student2(int id, int age, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student2{" +
"id=" + id +
", age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
//类名的注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Tablelurenj{
String value();
}
//属性的注解
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Filedlurenj{
String columnName();
String type();
int length();
}





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通