算法刷题:链表题(8.4,持续更)
刷题记录,持续更新,欢迎交流
0 排序单链表:
- 力扣链接:排序链表
冒泡排、归并排、快排、计数排
指针迭代技巧:
- 力扣链接:两数相加
1 合并有序链表:
- 力扣链接:合并 2 个有序链表
- 力扣链接:合并 K 个有序链表
2 分隔链表:
- 力扣链接:分隔链表
3 链表中点:
4 链表成环 / 环起点:
5 反转链表(下标序、穿针引线):
7 链表相交 / 相交点:
- 力扣链接:相交链表
解题思维
先核心逻辑,再细节
先理清一次迭代的核心逻辑怎么实现,先实现关键代码,再去想细节:
那么有哪些细节?
- 迭代过程:
- 第一次迭代:
- 遍历(循环迭代、递归迭代)的退出条件、while 循环体最后,别忘了 p = p.next
- 迭代的区间(非遍历,只访问中间的一部分):
- 最后一次迭代:
- 定义和初始化时
- 链表太短时(空指针异常):head ?= null / head.next ?= null
- 分段:
- 逻辑分段:一段函数体的代码实现的功能,可能是 几段逻辑按顺序排列,每段逻辑都可以单独作为起点,不要把逻辑弄混
- 定义和初始化按段定义:详情见 反转链表 II 的 优化代码部分
- 具体题型:
- 比如跟随指针,一次迭代代码段(for/while循环),先前进、先跟随还是先关键代码,可能会影响迭代退出条件、简化一些边界情况
- 如果需要操作.next或者.next.next,必须先操作.next.next
- 哨兵节点 / 虚拟头节点:
哨兵节点 dummyHeadNode,可以接收一列新链表或者存储原链表起点,简化一些边界情况的处理 - 并不知道 一个链表的长度多少、也不知道 多个链表的长度是否相等
下标排序和反转链表
下标排序:反序 -> 反转链表,正序
链表相交、成环
链表相交 -> 长短链 对齐处理
成环处理 -> 相对速度 绕环追赶
处理之后可能链表产生相交点 或者 环
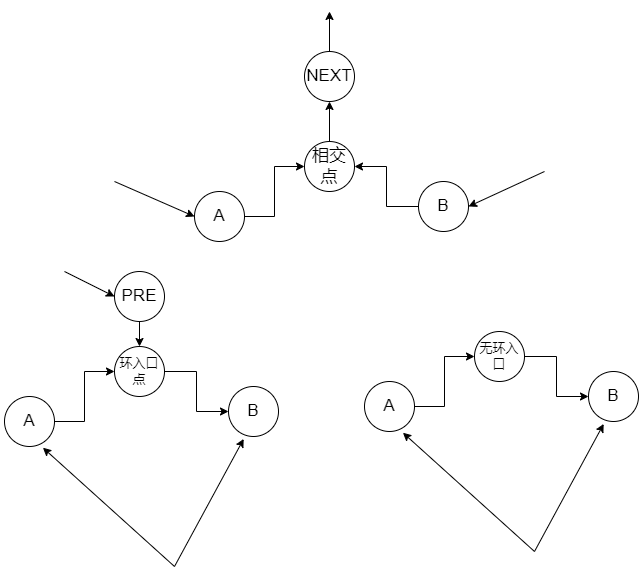
画图分析
穿针引线图
按一定规则排序下标的时候,可能需要画穿针引线图:
如果状态转换的结果是下标按规则重排序,那么就需要画穿针引线图
奇偶节点数链表 - 边界处理
奇数和偶数的节点数的链表,可能需要边界处理
1 多指针迭代
同时需要操作多个链表时,可以使用多个指针,分别记录各个链表的迭代位置,可以避免一些回溯
两数相加
未优化的代码(2ms)
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(), p = dummy;
ListNode p1 = l1, p2 = l2;
int val = 0;
// 以 p、p1、p2 为起点迭代
while(p1 != null && p2 != null){
p.next = new ListNode();
p = p.next;
val += p1.val + p2.val;
if(val > 9){
p.val = val % 10;
val = 1;
} else {
p.val = val;
val = 0;
}
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
ListNode p0 = p1 != null? p1 : p2;
p.next = p0;
if(val == 0 || p0 == null){
if(val == 1) p.next = new ListNode(1);
return dummy.next;
} // val == 1, 开始以 p0 为起点迭代
while(p0.next != null){
if(p0.val != 9){
p0.val ++;
return dummy.next;
}
p0.val = 0; // 进 1 位
p0 = p0.next; // 下一位
}
// 最后一位-单独处理(最后一位的进位需要new一个节点)
if(p0.val == 9){
if(val == 1){
p0.val = 0; // 进 1 位
p0.next = new ListNode(1);
}
} else {
if(val == 1) p0.val++;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
优化后代码(1ms击败100%)
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(), p = dummy;
ListNode p1 = l1, p2 = l2;
int val = 0;
// 以 p、p1、p2 为起点迭代
while(p1 != null || p2 != null){
// 前置迭代
p.next = new ListNode();
p = p.next;
// 取出 值(待处理内容)再 前置迭代
int p1v = (p1 != null)? p1.val: 0;
int p2v = (p2 != null)? p2.val: 0;
if(p1 != null)p1 = p1.next;
if(p2 != null)p2 = p2.next;
// 处理点
val += p1v + p2v;
if(val > 9){
p.val = val % 10;
val = 1;
} else {
p.val = val;
val = 0;
}
}
// 最后一位-单独处理(最后一位的进位需要new一个节点)
if(val == 1) p.next = new ListNode(1);
return dummy.next;
}
}
合并 2 个有序链表
多指针迭代解法(\(O(N)\))
目标链表虚拟头节点dummy + 同时迭代 2 个源链表和 1 个目标链表
- 操作模型:
for -> cur = min(list1 OR list2)
- 关键代码:
// 定义:虚拟头节点 dummy + 目标链表迭代器 p
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = dummy;
// 核心逻辑:合并到目标链表
p.next = list;
list = list.next;
p = p.next;
// 返回值
return dummy.next;
- 实现代码:
- 细节优化前:
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = dummy;
while(list1 != null || list2 != null){
if(list1 == null){
p.next = list2;
break;
} else if(list2 == null) {
p.next = list1;
break;
}
if(list1.val < list2.val){
p.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
p.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
p = p.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
- 细节优化后:
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null) return list2;
if(list2 == null) return list1;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = dummy;
ListNode p1 = list1;
ListNode p2 = list2;
while(p1 != null && p2 != null) {
if(p1.val < p2.val){
cur.next = p1;
p1 = p1.next;
} else {
cur.next = p2;
p2 = p2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = p1 != null ? p1 : p2;
return dummy.next;
}
}
合并 k 个有序链表
K个中minNode解法 (\(O(K * N)\))
每次迭代,比较 K 个链表头,求最小值 minNode,加入返回链表
直到迭代完所有链表
时间复杂度 \(O(K * N)\)
运行时间:210ms
操作模型:
for -> (cur = min(lists.forEach -> node))
优化细节前代码:
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if(lists == null) return null;
if(lists.length == 0) return null;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = dummy;
ListNode min;
int minPos;
boolean keep = true;
while(keep){
keep = false;
minPos = 0;
min = lists[0];
for(int p = 0; p < lists.length; p++) {
if(lists[p] == null) continue;
if(keep != true) keep = true;
if(min == null || (lists[p]).val < min.val) {
min = lists[p];
minPos = p;
}
}
if(keep != true) break;
cur.next = min;
lists[minPos] = min.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
优化细节后:
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = dummy;
ListNode minNd;
int minPos;
while(true){
minPos = -1;
minNd = null;
for(int i = 0; i < lists.length; i++) {
if(lists[i] == null) continue;
if(minNd == null || lists[i].val < minNd.val) {
minNd = lists[i];
minPos = i;
}
}
if(minPos == -1) break;
cur.next = minNd;
lists[minPos] = lists[minPos].next;
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
排序队列取minNode队头
手动实现的排序队列解法 (\(O(K * N)\))
运行时间:216ms
class Solution {
static class SortedQueue {
private static final LinkedList<ListNode> list =
new LinkedList<>();
ListNode popHead() {
return list.removeFirst();
}
void sortedPut(ListNode insert){
if (insert == null) return;
int index = 0;
for (ListNode node : list) {
if (node.val >= insert.val){
list.add(index, insert);
return;
}
index++;
}
if (index != 0){
list.addLast(insert);
} else {
list.addFirst(insert);
}
return;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
for (ListNode node : list){
builder.append(node.val).append(" ");
}
return builder.toString();
}
}
}
未加嵌套的单次逻辑:
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = dummy;
SortedQueue queue = new SortedQueue();
p.next = queue.popHead();
if(p.next.next != null){
queue.sortedPut(p.next.next);
}
p = p.next;
}
加入嵌套、嵌套退出的条件:
while(queue.list.size() != 0){ ...... }
完整代码:
class Solution {
static class SortedQueue {
static final LinkedList<ListNode> list = new LinkedList<>();
ListNode popHead() {
return list.removeFirst();
}
void sortedPut(ListNode insert){
if (insert == null) return;
int index = 0;
for (ListNode node : list) {
if (node.val >= insert.val){
list.add(index, insert);
return;
}
index++;
}
if (index != 0){
list.addLast(insert);
} else {
list.addFirst(insert);
}
return;
}
}
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = dummy;
SortedQueue queue = new SortedQueue();
for(ListNode node : lists){
queue.sortedPut(node);
}
while(queue.list.size() != 0){
p.next = queue.popHead();
if(p.next.next != null){
queue.sortedPut(p.next.next);
}
p = p.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
优先级队列解法 ( \(O(N log(K))\))
本质是小根堆,小根堆的根节点就是最小值,相比于我实现的队列,它的插入效率更高
运行时间:4ms
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists == null || lists.length == 0) return null;
PriorityQueue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(lists.length, new Comparator<ListNode>() {
@Override
public int compare(ListNode o1, ListNode o2) {
if (o1.val < o2.val) return -1;
else if (o1.val == o2.val) return 0;
else return 1;
}
});
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = dummy;
for (ListNode node : lists) {
if (node != null) queue.add(node);
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
p.next = queue.poll();
p = p.next;
if (p.next != null) queue.add(p.next);
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
分治解法:两个一组逐渐合并 (\(O(N log(K))\))
特点是每次合并完就会少一半的(\(O(log K)\))
运行时间:1ms
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if(lists == null || lists.length == 0){
return null;
}
return spilt(lists , 0 , lists.length - 1);
}
public ListNode spilt(ListNode[] lists , int i , int j){
if(i == j){
return lists[i];
}
int m = (i + j) >>> 1;
ListNode left = spilt(lists , i , m);
ListNode right = spilt(lists , m+1 , j);
return mergeTwoLists(left, right);
}
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode p1, ListNode p2) {
ListNode s = new ListNode(-1, null);
ListNode p = s;
while (p1 != null && p2 != null) {
if (p1.val < p2.val) {
p.next = p1;
p1 = p1.next;
} else {
p.next = p2;
p2 = p2.next;
}
p = p.next;
}
p.next = p1 != null ? p1 : p2;
return s.next;
}
}
分隔链表
多指针迭代解法(\(O(N)\))
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
ListNode p = head;
ListNode lowDummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode highDummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode low = lowDummy;
ListNode high = highDummy;
while(p != null){
if(p.val < x){
low.next = p;
low = low.next;
} else {
high.next = p;
high = high.next;
}
ListNode q = p.next;
p.next = null;
p = q;
}
low.next = highDummy.next;
return lowDummy.next;
}
}
2 快慢指针
理论解析:快慢指针的切入点
快慢指针可以以不同的速度迭代:
- 速度的倍数关系:速度 2 是 速度 1 的 2 倍速
- 相对速度:速度 2 和速度 1 的 相对速度是 1
- 指针变量定义:slow、fast
- 跟随问题:快指针先向前,但是慢指针随后就能跟上
- 指针变量定义:master、follow 或 pre、cur、nxt
- 长短链迭代完成速度问题:
速度倍数题:
链表的中间节点 ( \(O(N)\) )
思路:
- 如何找到中间节点:求长度、2 倍速的快慢指针
关键代码:
// 定义快慢指针
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
// 核心:快慢迭代
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// 返回值
return slow;
迭代退出条件:while fast && fast.next
完整代码:
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return null;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
删除链表的中间节点 ( \(O(N)\) )
思路:
- 找到中间节点
- 如何找到中间节点:求长度、2 倍速的快慢指针
- 删除中间节点
- 需要中间节点的前一个节点
- 如何让慢指针慢一步?
slow = head;
fast = head.next;
分析结束,开始梳理
关键代码:
// 定义快慢指针
ListNode fast = head.next;
ListNode slow = head;
// 核心:快慢迭代
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// 核心:删除中点(快指针遍历结束)
ListNode temp = slow.next;
slow.next = temp.next;
temp.next = null;
迭代退出条件:while fast.next && fast.next.next
完整代码:
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteMiddle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while(fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
ListNode temp = slow.next;
slow.next = slow.next.next;
temp.next = null; // 帮助垃圾回收
return head;
}
}
相对速度题:
环形链表 ( \(O(N)\) )
思路:
- 什么是链表成环?
- 首尾相接
- 尾接到中间的某个节点
- 是否成环:
- 如果成环:两指针进入环后,快慢指针相对速度1,意味着快慢指针会不断缩短距离,直到它们相遇
- 如果不成环:快指针迭代到 null
关键代码:
// 定义快慢指针
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
// 核心:快慢迭代
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// 核心:处理成环情况
if(slow == fast) return true;
// 核心:处理不成环情况
if(fast.next == null || fast.next.next == null){
return false;
}
// 迭代退出条件
while(slow != fast){
// --- 迭代逻辑 ---
}
完整代码:
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null){
return false;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
do {
if(fast == null
|| fast.next == null){
return false;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
} while(slow != fast);
return true;
}
}
环形链表的环形入口(\(O(N)\))
数学建模分析
切入点:
各部分长度和迭代次数的关系
首先进入环之前,是有长度的:
- 环前长度:\(a\)
- 环长度:\(m\)
环长度还可以分解:
- 环形入口 到 相遇点 的长度:\(b\)
- 相遇点 到 环形入口 的长度:\(c\)
时间线:
-
在慢指针刚进入环入口时,也就是说,慢指针走了环前长度的距离:
- 快慢指针迭代次数:\(a\)
- 慢指针长度:\(a\)
- 快指针长度:\(2a\)
- 此时快指针离环入口:\((b + c) % a\) 的距离
- \(b = (b + c) % a\)
- 额外圈数:\(k = (b + c) / a\)
-
从慢指针 迭代到环入口 到其 迭代到快慢指针相遇
- 快慢指针迭代次数:\(a + b\)
- 慢指针路程长度:\(a + b\)
- 快指针路程长度:\(2a + 2b = a + b + k * (b + c)\)
公式化简:
\(2a + 2b = a + b + b + c + (k - 1) * (b + c)\)
\(a - c = (k - 1) * (b + c)\)
\(a = c + (k - 1) * (b + c)\)
分析公式:
- (a - c) 是环长的倍数
- 那么 (a - c) 是什么?
- c 是 环长 - 相遇点,环长不知道,c 是未知量
- 那么 a - c 可不可以当成整体来看?
- 从什么时间点看?
- a 是环前长度,此时我构造一个辅助节点开始从 头节点 跟 slow 同时迭代,slow 走了c 长度这个未知量之后,slow 回到环形入口点,而此时辅助节点的 剩余距离 是环形长度的整数倍,也就是说:
若在快慢指针相遇时,辅助节点从头节点迭代、slow继续迭代,那么 slow 和辅助节点最终可以在入口处相遇
代码实现
关键代码:
// 定义快慢指针 \ 数学公式需要的指针
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode help = head;
// 核心:快慢指针相遇
do {
if(fast == null
|| fast.next == null){
/* 不成环 */
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
} while(slow != fast);
/* 成环,并且快慢指针相遇 */
// 核心:辅助指针开始移动、slow继续移动,最终相遇
while(slow != help){
slow = slow.next;
help = help.next;
}
// 返回值
return head;
完整代码:
ublic class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
// ListNode help = head;
// 辅助指针 help 的作用,可以由 fast 替代
do {
if(fast == null
|| fast.next == null){
return null;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
} while(slow != fast);
fast = head;
while(slow != fast){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
跟随(pcn) + 穿针引线
反转链表(\(O(N)\))
这个可以用跟随模型来解决:
快慢指针解法-画图分析、代码实现
这里用图来分析(反转一个4节点链表):
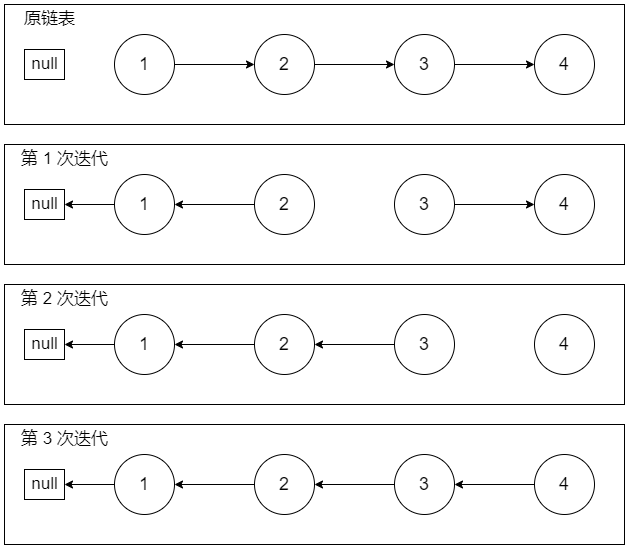
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 边界:链表小于两个节点
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
// 定义多指针
ListNode follow2 = head;
ListNode follow1 = head.next;
ListNode master = head.next.next;
// 开始迭代
// 边界:第一次迭代
follow1.next = follow2;
follow2.next = null;
// 非边界迭代
while(master != null) {
// 迭代
follow2 = follow1; // follow2 跟上 follow1
follow1 = master; // follow1 跟上 master
master = master.next; // master 向前走一步
// 操作
follow1.next = follow2;
}
follow1.next = follow2;
return follow1;
}
}
递归解法(\(O(N)\))
递归解法在链表比较长时,可能会栈溢出(StackOverflow):
(额外空间复杂度 :O(n),因为调用了N层栈空间)
- 首先写一个递归遍历链表的函数:
public ListNode traverse(ListNode cur){
// 递归退出条件
if(cur == null) return null;
// 递归获得下一个
ListNode nxt = traverse(cur.next);
/*
* 遍历时额外的操作 / 反转链表的核心操作单元
*/
// 向上一个返回当前节点
// 当前节点相对于上一个,就是下一个
return cur;
}
- 定义遍历时的递归链表中每一节点的操作
// 核心逻辑:一次反转相邻节点操作
if(nxt != null){
nxt.next = cur;
cur.next = null;
}
- 递归遍历的承载函数:
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return null;
// 提前获取头节点
ListNode tail = head;
while(tail.next != null){
tail = tail.next;
}
// 遍历 + 反转
traverse(head);
return tail;
}
完整代码:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return null;
ListNode tail = head;
while(tail.next != null){
tail = tail.next;
}
traverse(head);
return tail;
}
public ListNode traverse(ListNode cur){
if(cur == null) return null;
ListNode nxt = traverse(cur.next);
if(nxt != null){
nxt.next = cur;
cur.next = null;
}
return cur;
}
}
新建链表解法(其实类似跟随指针)
额外空间复杂度:\(O(N)\)
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode follow = null;
ListNode master = null;
for(ListNode p = head; p != null; p = p.next){
master = new ListNode(p.val);
master.next = follow;
follow = master; // 跟上 master
}
return master;
}
}
反转链表的中间某段 / 反转链表 II
快慢指针解法(\(O(N)\))
思路:
- 首先先找到第 \(left\) 位置的节点
- 之后迭代 \((right - left)\) 次,进行反转
- 之后将 反转的中间部分 和 链表的其余部分 进行对接
关键代码:
// 定义 跟随指针
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode cur = null;
ListNode nxt = null;
// 核心逻辑:找到 left 位置的节点
for(int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++){
pre = pre.next;
}
ListNode start = pre; // 记录端点
pre = pre.next;
cur = pre.next;
nxt = cur.next;
// 核心逻辑:进行中间段的链表反转
int len = right - left;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
// 开始反转
cur.next = pre;
pre.next = null;
// 开始跟随
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
nxt = nxt.next;
}
// 核心逻辑:反转后 和 链表中间段端点进行对接
start.next.next = nxt;
start.next = cur;
return head;
加入细节后的完整代码:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right){
if(left == right) return head; // 优化
if(head == null) return null; // 边界
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode cur = null;
ListNode nxt = null;
ListNode start = null;
for(int i = 0; i < left - 2; i++){
pre = pre.next;
}
if(pre == null){
return head;
}
start = pre;
if(left > 1) { // 边界
pre = pre != null ? pre.next : null;
}
cur = pre != null ? pre.next : null;
nxt = pre != null && pre.next != null ? pre.next.next : null;
if(cur == null) {
return head;
}
int len = right - left;
pre.next = null;
for(int i = 0; i < len && cur != null; i++){
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
if(nxt != null) {
nxt = nxt.next;
continue;
} break;
}
if(left != 1){ // 边界,防止成环
// 1 2 3 4 5, l: 2,r: 4
start.next.next = cur; // 2的后继是5
start.next = pre; // 4的前驱是1
// ~!!注意,必须先修改.next.next之后,才能修改.next
} else { // 换头节点
head = pre;
start.next = cur;
}
return head;
}
}
优化代码
优化思路:
- 逻辑分段
- 定义与初始化变量,按逻辑分段
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
if(left == right) return head; // 优化
/* 第 1 段逻辑:迭代到 left 边界
**/ // 定义和初始化变量
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode p = dummy; // p就是start
for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++){
p = p.next;
}
/* 第 2 段逻辑:反转
**/ // 定义和初始化变量
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = p.next;
ListNode nxt = null;
for (int i = 0; i < right - left + 1; i++) {
nxt = cur.next; // 前进
cur.next = pre; // 反转
pre = cur; // 跟随前进
cur = nxt;
}
p.next.next = cur;
p.next = pre;
return dummy.next;
}
}
K 个一组反转链表
求长度分别反转解法(\(O(K * N)\))
直接0ms,超过100%
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
// 求长度
int len = 0;
for(ListNode p = head ; p != null; ++len, p = p.next);
// 开始反转
int n = len / k;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode p = dummy;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = p.next; // 这里
ListNode nxt = cur;
for(int j = 0; j < k; j++){
nxt = cur.next; // 前进
cur.next = pre; // 反转
pre = cur; // 跟随
cur = nxt;
}
p.next.next = nxt;
// 这里需要修改 p.next,还需要修改之前的 p.next
// 于是引入了临时变量 temp 存储修改前的 p.next
ListNode temp = p.next;
p.next = pre;
p = temp;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
重排链表
题目描述的分析:
原链表:
\(L0 → L1 → … → Ln - 1 → Ln\)
目标链表:
\(L0 → Ln → L1 → Ln - 1 → L2 → Ln - 2 → …\)
思路:
题目描述了一种状态转换,但是什么地方状态转换?
- 链表的下标进行了反序,这不就是反转单链表?
本质是链表下标序反序,马上联想到 '反转链表'
代码:
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = slow;
ListNode nxt = cur;
while(cur != null){
nxt = nxt.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
fast = head;
// while(pre != null && pre.next != null){
while(pre.next != null){
nxt = fast.next;
cur = pre.next;
fast.next = pre;
pre.next = nxt;
pre = cur;
fast = nxt;
}
}
}
回文链表
思路:链表中间节点+反转链表(相交链表)
其实图解之后,和回文链表的图解是一样的
反转后半部分解法(\(O(N)\))
本质就是:fs速度倍数 + pcn跟随
运行时间:2ms,击败 100%
代码:
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// 此时相当于在 slow 节点上有 2 个相交链表
// 1,2,3
if(fast != null){
slow = slow.next;
}
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = slow;
ListNode nxt = cur;
while(cur != null){
nxt = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
ListNode phead = head;
while(pre != null){
if(pre.val != phead.val){
return false;
}
pre = pre.next;
phead = phead.next;
}
return true;
}
}
反转前半部分解法(\(O(N)\),更优)
运行时间:3ms,击败 97%
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next !=null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = slow;
}
if(fast != null){
slow = slow.next;
}
while(pre != null){
if(pre.val != slow.val){
return false;
}
slow = slow.next;
pre = pre.next;
}
return true;
}
}
长短链迭代完成速度题
相交链表
对齐长度解法
其实找到交点很简单,因为公共部分是对齐的,所以问题就是:两链表长度可能不对齐,要想办法去除长度差值进行对齐
求长度·对齐解法(\(O(N)\))
思路:
- 可以求长度
- 之后再根据长度的差值进行对齐
问题:
- 求长度意味着除了迭代还要给长度计数器赋值,多了计数器赋值计数的时间
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode pA = headA;
ListNode pB = headB;
// 计算长度
int lenA = 0;
int lenB = 0;
for(lenA = 0; pA != null; pA = pA.next, ++lenA);
for(lenB = 0; pB != null; pB = pB.next, ++lenB);
pA = headA;
pB = headB;
// 长链表的移动长度差值距差
if(lenA < lenB){
for(int i = 0; i < lenB - lenA; i++){
pB = pB.next;
}
} else {
for(int i = 0; i < lenA - lenB; i++){
pA = pA.next;
}
}
// 开始比较是否重复
while(pA != pB){
pA = pA.next;
pB = pB.next;
}
return pA;
}
}
迭代完成快慢对齐解法(\(O(N)\))
拼接对齐法不需要计算长度,而是根据:
- 长短链表迭代过程中长度差异导致的结果:
- 短的链表必定先迭代完,之后对长链表的剩余节点迭代就能表示出长短链表的长度差值
启示:
- 短链和长链同时迭代,短链迭代完成速度快,长链迭代完成速度慢
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode pA1 = headA;
ListNode pB1 = headB;
while(pA1 != null && pB1 != null){
pA1 = pA1.next;
pB1 = pB1.next;
}
ListNode pA2 = headA;
ListNode pB2 = headB;
while(pA1 != null){
pA1 = pA1.next;
pA2 = pA2.next;
}
while(pB1 != null){
pB1 = pB1.next;
pB2 = pB2.next;
}
while(pA2 != pB2){
pA2 = pA2.next;
pB2 = pB2.next;
}
return pA2;
}
}
拼接成环型链表解法(\(O(N)\))
构造成环形链表,之后按照环形链表的入口点思路、快慢指针(相对速度)+数学公式推导进行解决:(这里相交点就是入口点)
图解:
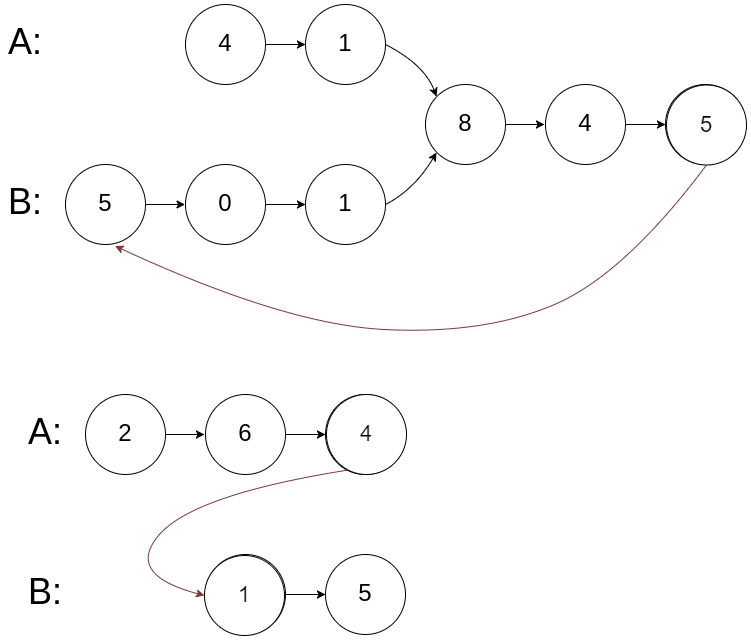
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
// 成环
ListNode pA = headA;
while(pA.next != null){
pA = pA.next;
}
ListNode endA = pA;
pA.next = headB;
// 按照成环的入口点思路进行解决
ListNode head = headA;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if(slow == fast){
fast = head;
while(slow != fast){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
// 断开之前的环接点
endA.next = null;
return slow;
}
}
// 断开之前的环接点
endA.next = null;
return null;
}
}
3 排序
基础排序(\(O(N^2)\),超时)
冒泡排序
单次迭代(单次冒泡)的代码:
- 如果当前节点cur比下一节点nxt大,那么交换彼此的位置
交换需要穿针引线,根据穿针引线图
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
// ListNode end = null;
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode cur = pre.next;
ListNode nxt = cur.next;
// 如果当前节点cur比下一节点nxt大,那么交换彼此的位置
// 交换需要穿针引线,根据穿针引线图
// 写出下面的代码
while(nxt != null){ // nxt != end
if(cur.val > nxt.val){
pre.next = nxt;
cur.next = nxt.next;
nxt.next = cur;
}
pre = pre.next;
cur = pre.next;
nxt = cur.next;
}
System.out.println(cur.val); // 链表最大值,用于测试是否冒泡成功
return dummy.next;
嵌套/迭代/排序的最后一步操作:end 指向 第一个节点(dummy.next)
while(end != dummy.next){
………
while(nxt != end){
………
加入嵌套的完整代码:
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
// bubbleSort
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode end = null;
while(end != dummy.next){
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode cur = pre.next;
ListNode nxt = cur.next;
while(nxt != end){
if(cur.val > nxt.val){
pre.next = nxt;
cur.next = nxt.next;
nxt.next = cur;
}
pre = pre.next;
cur = pre.next;
nxt = cur.next;
}
end = cur;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
选择排序
略
插入排序
略
归并排序(\(O(NlogN)\))
运行时间:10~15ms,不如计数排序
通过递,将整个链表分解成 1~2 个节点一组;
通过归,将分解的链表排序的结果返回
自顶向下归并
直接写出来
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
// int count = 0;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
fast = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
ListNode p1 = head;
if(head.next.next == null){
if(head.val > head.next.val){
head.next.next = head;
p1 = head.next;
head.next = null;
}
} else {
p1 = sortList(head);
}
ListNode p2 = sortList(fast);
// 归并两个有序链表
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(), p = dummy;
while(p1 != null && p2 != null){
// System.out.println(p1.val + " " + p2.val);
if(p1.val < p2.val){
p.next = p1;
p1 = p1.next;
} else {
p.next = p2;
p2 = p2.next;
}
p = p.next;
}
if(p1 != null){
p.next = p1;
} else p.next = p2;
return dummy.next;
}
}
优化代码:
- 处理中点分隔的边界点
ListNode prev = null; ////
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
prev = slow; ////
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
pre.next = null; ///
// fast = slow.next;
// slow.next = null;
// ListNode p1 = head;
// if(head.next.next == null){
// if(head.val > head.next.val){
// head.next.next = head;
// p1 = head.next;
// head.next = null;
// }
//} else {
// p1 = sortList(head);
//}
ListNode p1 = sortList(head);
ListNode p2 = sortList(slow);
- 抽离 merge 方法:
- merge 方法就是:合并两个有序链表 的代码
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
prev = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
prev.next = null;
return merge(sortList(head), sortList(slow));
}
static public ListNode merge(ListNode head1, ListNode head2){
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(), p = dummy;
ListNode p1 = head1, p2 = head2;
while(p1 != null && p2 != null){
if(p1.val < p2.val){
p.next = p1;
p1 = p1.next; // while迭代的最后一步,p = p.next
} else {
p.next = p2;
p2 = p2.next; // ---
}
p = p.next; // while迭代的最后一步,p = p.next
}
if(p1 != null){
p.next = p1;
} else p.next = p2;
return dummy.next;
}
}
自底向上归并
归并排序的本质是:对局部的整体排序,再 合并两个有序链表-插入归并 成整体
画图分析和流程分析
图示:
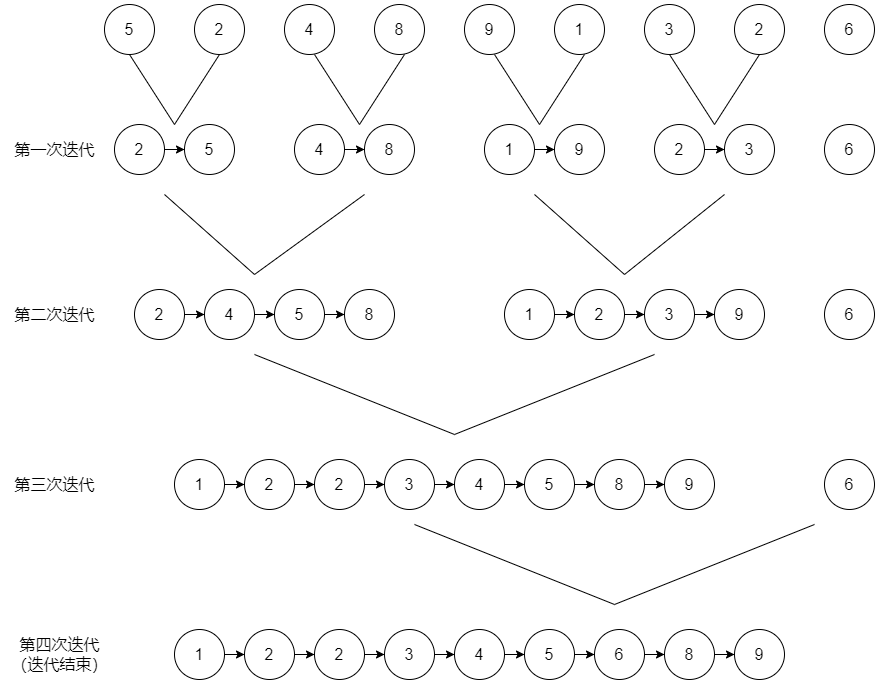
流程分析
- 一次迭代:
1.合并出 若干个组 -> 迭代每个组
2.每个组 有 两个组内部分,内部是有序的
3.合并之后的 每个新组,都将作为 下一次迭代的 组内部分
代码实现
- 关键代码
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
int length = 0;
ListNode node = head;
while (node != null) {
length++;
node = node.next;
}
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
for (int subLength = 1; subLength < length; subLength <<= 1) {
ListNode prev = dummyHead, curr = dummyHead.next;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode head1 = curr;
for (int i = 1; i < subLength && curr.next != null; i++) {
curr = curr.next;
}
ListNode head2 = curr.next;
curr.next = null;
curr = head2;
for (int i = 1; i < subLength && curr != null && curr.next != null; i++) {
curr = curr.next;
}
ListNode next = null;
if (curr != null) {
next = curr.next;
curr.next = null;
}
ListNode merged = merge(head1, head2);
prev.next = merged;
while (prev.next != null) {
prev = prev.next;
}
curr = next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
static public ListNode merge(ListNode head1, ListNode head2){
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(), p = dummy;
ListNode p1 = head1, p2 = head2;
while(p1 != null && p2 != null){
if(p1.val < p2.val){
p.next = p1;
p1 = p1.next; // while迭代的最后一步,p = p.next
} else {
p.next = p2;
p2 = p2.next; // ---
}
p = p.next; // while迭代的最后一步,p = p.next
}
if(p1 != null){
p.next = p1;
} else p.next = p2;
return dummy.next;
}
}
快速排序(\(O(NlogN)\))
超时,因为倒序转升序导致快速排序退化为(\(O(N^2)\))
快速排序的本质就是:对整体的局部排序,再 左右拼接 成整体
- 分隔链表(大区间、小区间)
- 开始分隔时 / 状态起点:
- 节点:对哪个节点分大小区间
- 迭代 / 单次状态转移过程:
- 是否需要新链表?
- 插入原链表,还是大小区间两个链表
- 是否需要 dummy、如何穿针引线
- 迭代终止条件:
- 分隔结束时 / 状态转移结果:
- 区间怎么用:递归
- 开始分隔时 / 状态起点:
- 递归快排:
- 递什么操作:左右区间 分别去排序
- 归什么结果:已排序的左右区间 的 头节点
代码实现:
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
// 传入的链表 为空 或 单节点
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode p = head.next;
int x = head.val;
ListNode left = new ListNode(), pl = left;
ListNode right = new ListNode(), pr = right;
// 分隔成左右区间
while(p != null){
if(p.val > x){
pr.next = p;
pr = pr.next;
} else {
pl.next = p;
pl = pl.next;
}
p = p.next;
}
pl.next = null; // 很关键,否则成环
pr.next = null; // 很关键
// 递:左右区间 分别去排序
// 归:已排序的左右区间 的 头节点
ListNode sortedLeft = sortList(left.next);
ListNode sortedRight = sortList(right.next);
// 将 左区间 和 中间值节点 和 右区间 串联
pl = sortedLeft;
if(sortedLeft != null){
while(pl.next != null){
pl = pl.next;
}
pl.next = head;
} else sortedLeft = head;
head.next = sortedRight;
// 返回排序链表(已排序 的 整体局部)
return sortedLeft;
}
}
计数排序(\(O(N)\))
运行时间:2ms, 击败 100%
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
int max = head.val;
int min = head.val;
ListNode node = head.next;
while (node != null) {
int val = node.val;
if (val > max) {
max = val;
}
if (val < min) {
min = val;
}
node = node.next;
}
int[] count = new int[max - min + 1];
node = head;
while (node != null) {
count[node.val - min]++;
node = node.next;
}
node = head;
max -= min;
for (int i = 0; i <= max; i++) {
int val = min + i;
while (count[i]-- > 0) {
node.val = val;
node = node.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号