Linux-进程控制
进程控制
进程控制理论基础
定义:进程是一个具有一定独立功能的程序的一次运行活动。
特点:1.动态性 2.并发性 3.独立性 4.异步性
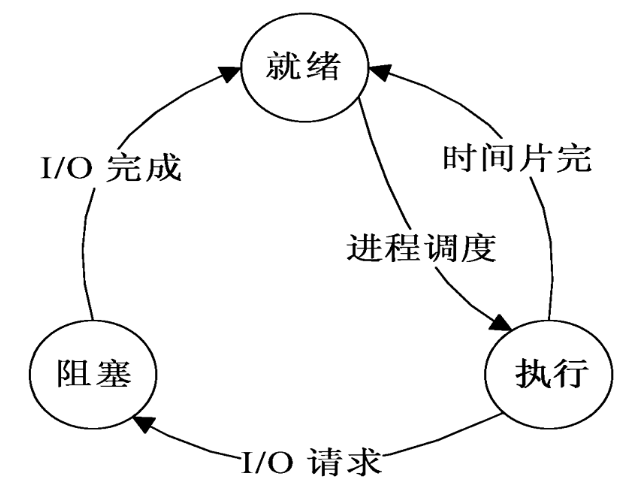
状态:执行、阻塞、就绪
进程ID(PID):标识进程的唯一数字
父进程的ID(PPID)
启动进程的用户ID(UID)
进程互斥是指当有若干进程都要使用某一共享资源时,任何时刻最多允许一个进程使用,其他要使用该资源的进程必须等待,直到占用该资源者释放了该资源为止。
临界资源:操作系统中将一次只允许一个进程访问的资源称为临界资源。
临界区:进程中访问临界资源的那段程序代码称为临界区。为实现对临界资源的互斥访问,应保证诸进程互斥地进入各自的临界区。
进程同步:一组并发进程按一定的顺序执行的过程称为进程间的同步。具有同步关系的一组并发进程称为合作进程,合作进程间互相发送的信号称为消息或事件。
进程调度:
-
概念:按一定算法,从一组待运行的进程中选出一个来占有CPU运行
-
调度方式:
-
抢占式
-
非抢占式
-
调度算法:
-
先来先服务调度算法
-
短进程优先调度算法
-
高优先级优先调度算法
-
时间片轮转法
死锁:多个进程因竞争资源而形成一种僵局,若无外力作用,这些进程将永不能再向前推进。
进程控制编程
获取ID
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
pid_t getpid(void)
//获取本进程ID
pid_t getppid(void)
//获取父进程ID
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
printf("PID = %d\n", getpid());
printf("PPID = %d\n", getppid());
return 0;
}
进程创建-fork
#include <unistd.h>
pid_t fork(void)
功能:创建子进程
fork的奇妙之处在与它被调用一次,却返回两次,它可能有三种不同的返回值:
-
在父进程中,fork返回新创建的子进程的PID;
-
在子进程中,fork返回0
-
如果出现错误,fork返回一个负值
子进程的数据空间、堆栈空间都会从父进程得到一个拷贝,而不是共享。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(void)
{
pid_t pid;
int count = 0;
pid = fork();
count++;
if(pid == 0)
printf("I am the child process, ID is %d\n", getpid());
else
printf("I am the parent process, ID is %d\n", getpid());
printf("count = %d\n", count);
return 0;
}
进程创建vfork
#include <sys/types>
#include <unistd.h>
pid_t vfork(void)
功能:创建子进程
区别:
-
fork:子进程拷贝父进程的数据段
vfork:子进程与父进程共享数据段
-
fork:父、子进程的执行次序不确定
vfork:子进程先运行,父进程后运行
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(void)
{
pid_t pid;
int count = 0;
pid = vfork();
count++;
printf("count = %d\n", count);
return 0;
}
exec函数族
exec用被执行的程序替换调用它的程序。
区别:
-
fork创建一个新的进程,产生一个新的PID
-
exec启动一个新程序,替换原有的进程,因此进程的PID不会改变。
#include <unistd.h>
int execl(const char *path, const char *arg1, ...)
参数:
path:被执行程序名(含完整路径)
arg1-argn:被执行程序所需的命令行参数,含程序名。以空指针(NULL)结束
#include <unistd.h>
int main(void)
{
execl("/bin/ls", "ls", "-al", "/etc/passwd", (char *)0);
}
int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg1, ...)
参数:
path:被执行的程序名(不含路径,将从path环境变量中查找该程序)
arg1-argn:被执行程序所需的命令行参数,含程序名。以空指针(NULL)结束
#include <unistd.h>
int main(void)
{
execlp("ls", "ls", "-al", "/etc/passwd", (char *)0);
}
int execv(const char *path, char * const argv[])
参数:
path:被执行的程序名(含完整路径)
argv[]:被执行程序所需的命令行参数数组
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(void)
{
char *argv[] = {"ls", "-al", "/etc/passwd", (char*)0};
execv("/bin/ls", argv);
}
#include <stdlib.h>
int system(const char *string)
功能:
调用fork产生子进程,由子进程来调用 /bin/sh -c string 来执行参数string所代表的命令
#include <stdlib.h>
void main(void)
{
system("ls -al /etc/passwd");
}
进程等待
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
pid_t wait(int *status)
功能:阻塞该进程,直到其某个子进程退出
wait.c
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void main(void)
{
pid_t pc, pr;
pc = fork();
if(pc == 0)
{
printf("This is child process with pid of %d\n", getpid());
sleep(10);
}
else if( pc > 0)
{
pr = wait(NULL);
printf("I catched a child process with pid of %d\n", pr);
}
exit(0);
}



