Springboot(十五)——集成Swagger
Swagger简介
Swagger 是一个规范且完整的框架,用于生成、描述、调用和可视化 RESTful 风格的 Web 服务。
Swagger 的目标是对 REST API 定义一个标准且和语言无关的接口,可以让人和计算机拥有无须访问源码、文档或网络流量监测就可以发现和理解服务的能力。当通过 Swagger 进行正确定义,用户可以理解远程服务并使用最少实现逻辑与远程服务进行交互。与为底层编程所实现的接口类似,Swagger 消除了调用服务时可能会有的猜测。
Swagger 的优势
- 支持 API 自动生成同步的在线文档:使用 Swagger 后可以直接通过代码生成文档,不再需要自己手动编写接口文档了,对程序员来说非常方便,可以节约写文档的时间去学习新技术。
- 提供 Web 页面在线测试 API:光有文档还不够,Swagger 生成的文档还支持在线测试。参数和格式都定好了,直接在界面上输入参数对应的值即可在线测试接口。
springboot集成Swagger
1、新建一个springboot项目,添加web框架
2、添加相关依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger-ui -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger2 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
3、编写controller层
package com.study.swagger.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
}
编写Swagger的配置类4、编写Swagger的配置类
package com.study.swagger.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2 //开启Swagger
public class SwaggerConfig {
}
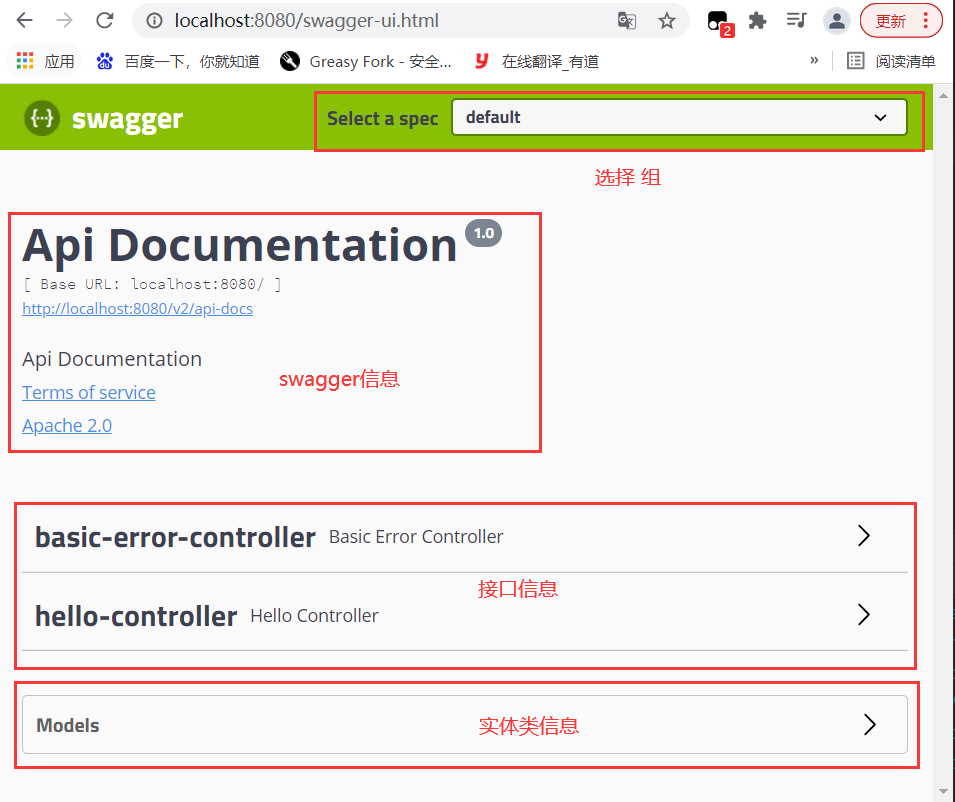
5、测试运行,输入:http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html 进入到页面
配置Swagger信息
Swagger 是通过注解的方式来生成对应的 API,在接口上我们需要加上各种注解来描述这个接口
1、编写Swagger配置类
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean
public Docket docket(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo());
}
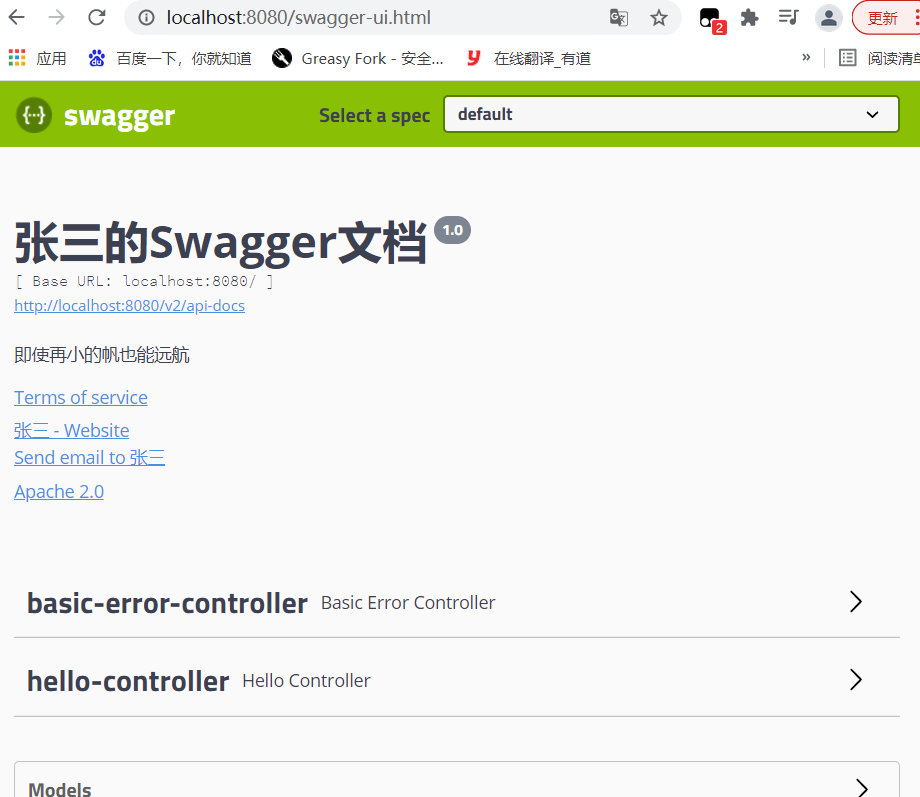
private ApiInfo apiInfo(){
//作者信息
Contact contact = new Contact("张三", "http://localhost:8080", "963330213@qq.com");
return new ApiInfo(
"张三的Swagger文档", //名字
"即使再小的帆也能远航", //座右铭
"1.0", //版本号
"http://localhost:8080",//作者连接
contact,
"Apache 2.0",
"http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0",
new ArrayList()
);
}
}
2、启动测试
配置Swagger扫描接口
1、配置扫描的接口
//配置了Swagger的Docket的bean实例
@Bean
public Docket docket(Environment environment){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
//RequestHandlerSelectors:配置要扫描的api方式
//basePackage:指定包扫描(常用)
//any():扫描全部
//none():不扫描
//withClassAnnotation:扫描类上的注解
//withMethodAnnotation:扫描方法上的注解
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.study.swagger.controller"))
.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/study/**"))//过滤路径,只扫描带有study请求的接口
.build();
}
运行测试:因为配置了只扫描 study请求下的接口,所以显示没有被定义的注解
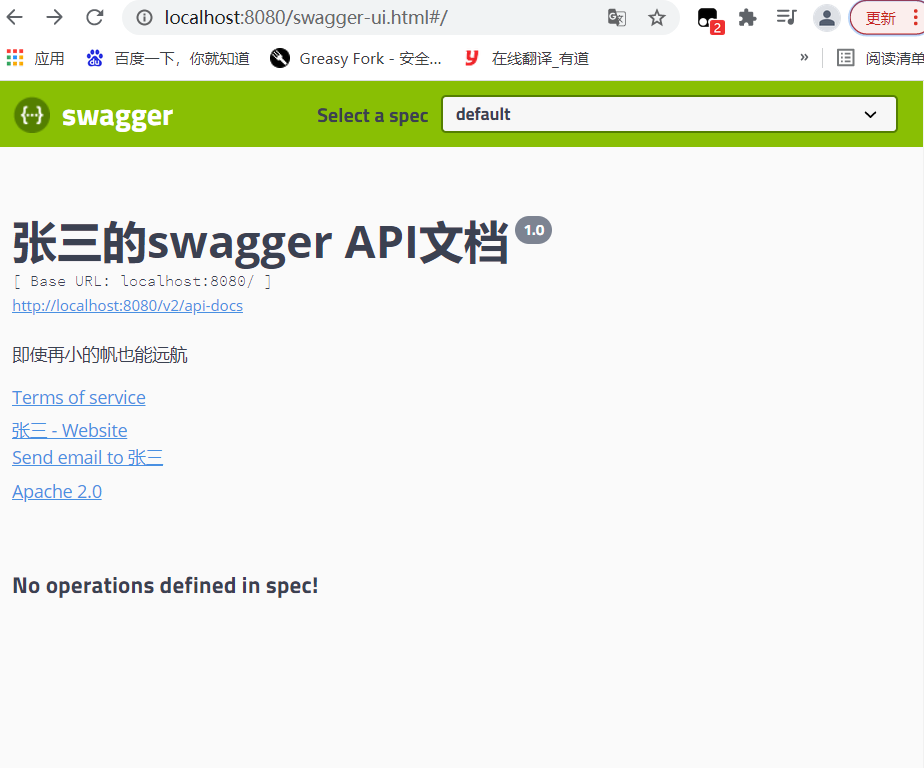
2、配置是否启动Swagger
//配置了Swagger的Docket的bean实例
@Bean
public Docket docket(Environment environment){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.enable(false) //是否启动Swagger,如果为false,则Swagger不能在浏览器中访问
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.study.swagger.controller"))
//.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/study/**"))//过滤路径,只扫描带有study请求的接口
.build();
}
Swagger配置多环境
1、新建application-dev.properties
# 应用名称
spring.application.name=swagger-demo
# 应用服务 WEB 访问端口
server.port=8081
新建application-dev.properties
# 应用名称
spring.application.name=swagger-demo
# 应用服务 WEB 访问端口
server.port=8082
2、编写application.properties
# 应用名称
spring.application.name=swagger-demo
# 应用服务 WEB 访问端口
server.port=8080
spring.profiles.active=dev #选择dev环境
3、编写Swagger配置类
4、运行测试
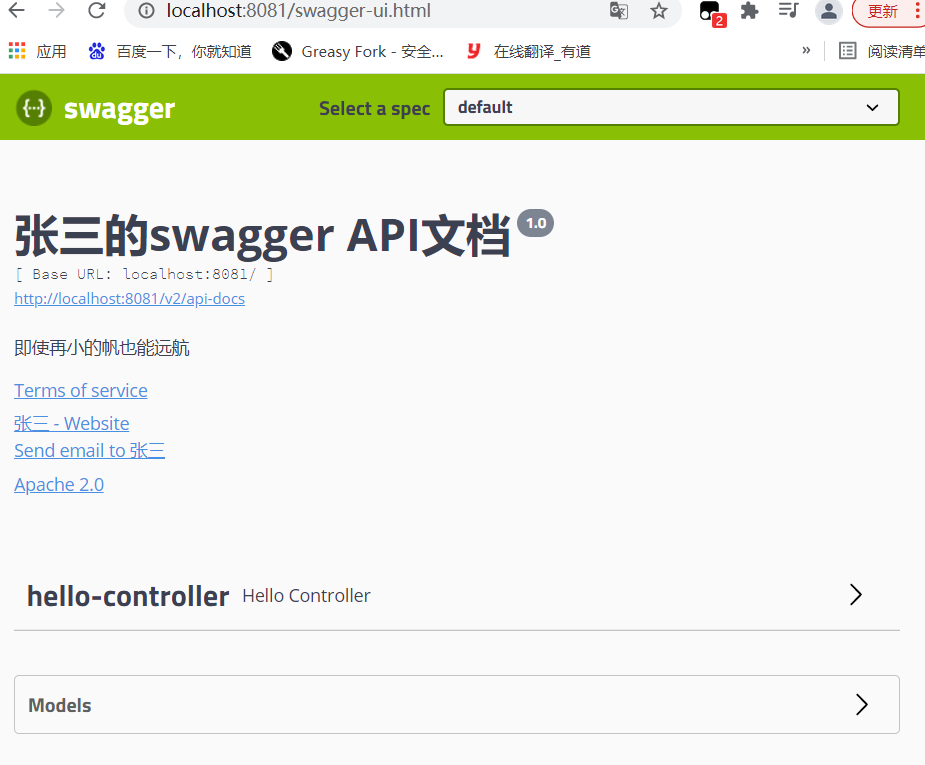
Swagger配置api文档分组
配置多个分组,多个Docket实例
1、编写Swagger配置类,添加多个Docket分组
@Bean
public Docket docket1(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("A组");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket2(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("B组");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket3(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("C组");
}
2、运行测试
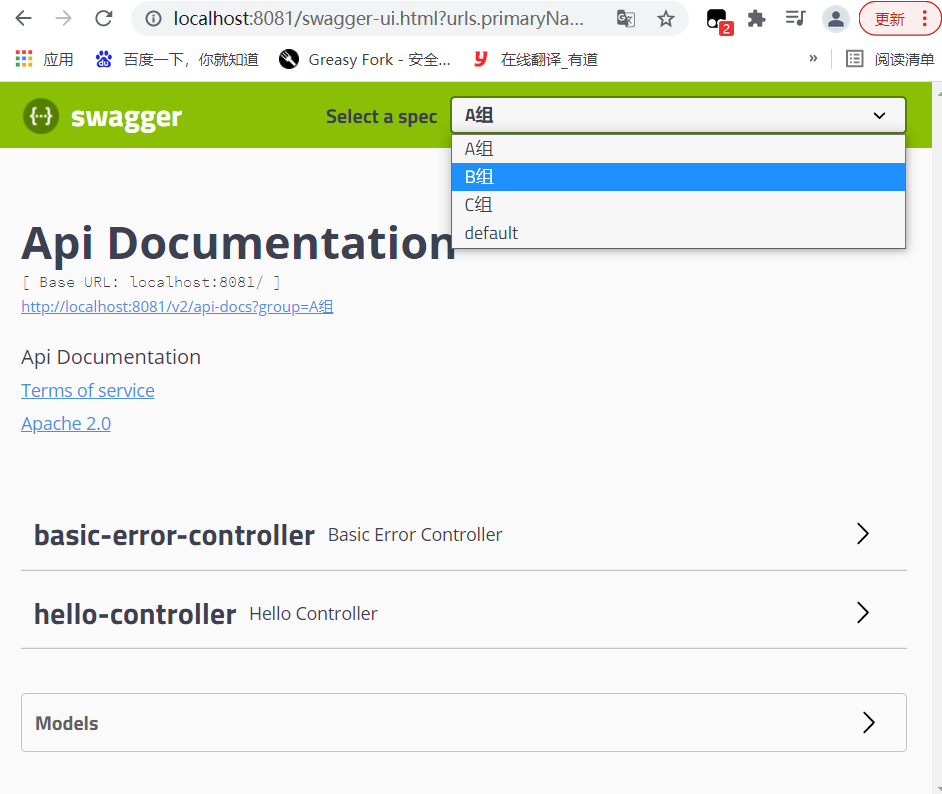
实体类配置
1、添加实体类
package com.study.swagger.pojo;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
@ApiModel("用户实体类")
public class User {
@ApiModelProperty("用户名")
public String username;
@ApiModelProperty("密码")
public String password;
}
2、编写controller
package com.study.swagger.controller;
import com.study.swagger.pojo.User;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
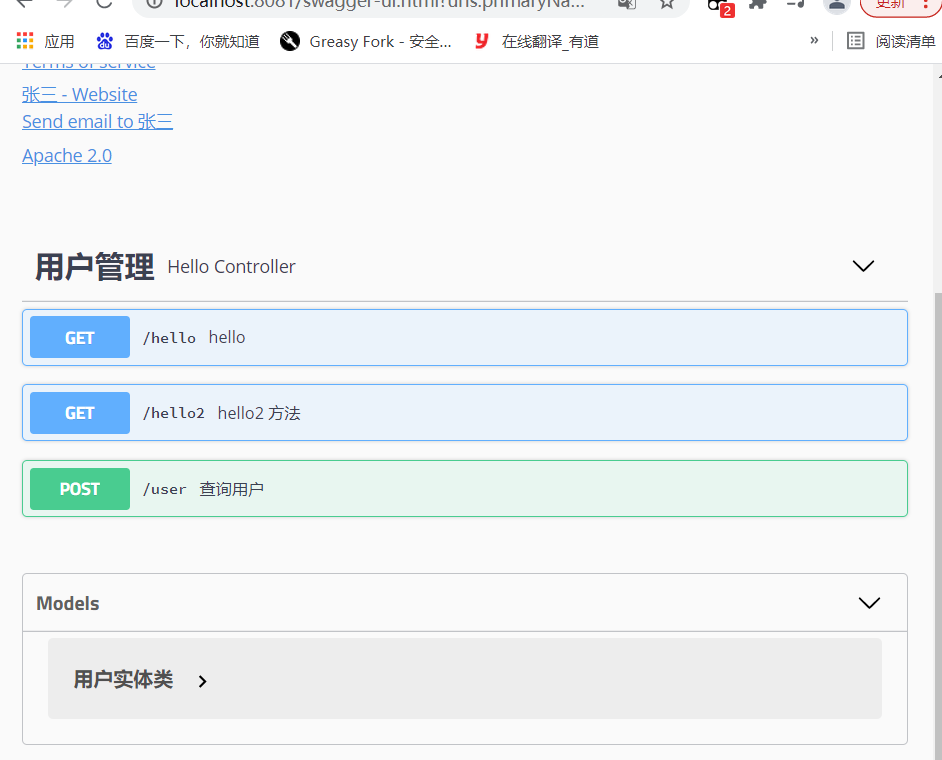
@Api(tags = "用户管理") //模块名称
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
@PostMapping("/user")
@ApiOperation("查询用户")//给接口添加注释
//@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id",value = "用户编号",required = true) 假设有参数可以设置 参数,参数名称,是否必传参数
public User user(){
return new User();
}
@GetMapping("/hello2")
@ApiOperation("hello2 方法")//给接口添加注释
public String hello(@ApiParam("用户名") String username){
return "hello"+username;
}
}
3、测试