Codeforces Round 250(Div. 2)
A.The Child and Homework (签到题)
题意
给出四个字符串A,B,C,D,让你按照其中如下规则输出答案
1:如果有一个字符串的长度小于其他字符串的长度至少两倍 输出他的序号
2.如果有一个字符串的长度大于其他字符串的长度至少两倍 输出他的序号
3.如果都不符合输出C
思路
一开始直接做了,发现果断wa 发现如下坑
1.是必须要一直有一个字符串满足如上属性,如果有两个字符串满足 比如长度分别为( 1 ,2 , 4 , 8 )这里有多个符合条件 所有需要输出C;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll mod=998244353;
const int maxn=1e6+50;
const ll inf=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
int num[1500];
int cnt[1500];
int tnc[1500];
int main()
{
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(0);
std::cout.tie(0);
string a;
bool doul=false;
for(int i=1;i<=4;i++){
cin>>a;
num[i]=a.length()-2;
cnt[num[i]]++;
tnc[num[i]]++;
}
for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++){
cnt[i]+=cnt[i-1];
}
for(int i=1000;i>=1;i--){
tnc[i]+=tnc[i+1];
}
int id=0,nu=0;
for(int i=1;i<=4;i++){
if(tnc[num[i]*2]>=3||cnt[num[i]/2]>=3){
id=i;nu++;
}
}
if(nu!=1)
cout<<"C"<<endl;
else{
cout<<char(id-1+'A')<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
B.The Child and Set (二进制的性质)
题意
让你在1-limit中选一个集合,使得集合元素的值等于sum
元素的值为编号的lowbit值
思路
lowbit值很好处理(废话)
然后lowbit的性质是绝对是2的次方,所以集合里面的元素值肯定都是相差多倍或者是相等的情况 所以我们就可以直接对1-limit中的lowbit值从大到小排序 每次取最大的小于等于sum的lowbit值,就行。
具体证明是 如果有一个值为x 那么如果你不去他,你就只能取x/2,和x/4 和x/8,会发现这些值就算都取你也得不到原来的x
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll mod=998244353;
const int maxn=1e6+50;
const ll inf=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
struct node{
int num;
int lowbit;
}my[maxn];
int main()
{
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(0);
std::cout.tie(0);
int sum,limit;
cin>>sum>>limit;
for(int i=1;i<=limit;i++){
my[i].num=i;
my[i].lowbit=i&(-i);
}
sort(my+1,my+1+limit,[](node a,node b)
{
return a.lowbit>b.lowbit;
});
vector<int>ve;
for(int i=1;i<=limit;i++){
if(my[i].lowbit<=sum){
ve.push_back(my[i].num);
sum-=my[i].lowbit;
}
}
if(sum)cout<<-1<<endl;
else {
cout<<ve.size()<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<ve.size();i++)cout<<ve[i]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
C.The Child and Toy (贪心)
题意
给出n个点m条边让你把所有点删除 删除的花费是所有和该点连接的点的值的总和。
问你吧所有点删除的最小值是多少
思路
首先把删点转换成删边,根据题意 在删点的过程中也相当于删边。
根据题意对于每条边删去的花费是其中一个点的费用,所以就每次贪心取每条边的费用最小的那个点。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll mod=998244353;
const int maxn=1e6+50;
const ll inf=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
int a[maxn];
int main()
{
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(0);
std::cout.tie(0);
int n,m,sum=0;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>a[i];
while(m--){
int u,v;
cin>>v>>u;
sum+=min(a[v],a[u]);
}
cout<<sum;
return 0;
}
D.The Child and Zoo (最大生成树)
题意
给出一个图,对于任意两个点之间的路径中的最小值的和,让你把这个值最大化 输出他的平均值。
思路
首先想到最大生成树,可以保证每两个点之间的路径都是最大费用,然后对于两个子树合并,他们的答案就是子树结点数的乘积(方案数)再乘上这条关键边的费用。
因为我们只求了单向的一次值,所以需要把值乘2 才算是答案
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll mod=998244353;
const int maxn=1e6+50;
const ll inf=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
struct Edge{
int u,v;
ll value;
bool operator <( const Edge &a)const {
return value>a.value;
}
};
vector<Edge>G;
ll a[maxn];
int fa[maxn];
int sz[maxn];
int Find(int u){
return u==fa[u]?u:fa[u]=Find(fa[u]);
}
int main()
{
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(0);
std::cout.tie(0);
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>a[i];
while(m--){
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
G.push_back(Edge{u,v,min(a[v],a[u])});
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)sz[i]=1,fa[i]=i;
ll ans=0;
sort(G.begin(),G.end());
for(int i=0;i<G.size();i++){
int aa=Find(G[i].u),bb=Find(G[i].v);
if(aa^bb){
ans+=1LL*(2LL*sz[aa]*sz[bb])*1LL*G[i].value;
fa[aa]=bb;
sz[bb]+=sz[aa];
}
}
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(6);
cout<<1.0*ans/n/(n-1);
return 0;
}
E.The Child and Polygon (基础几何+区间DP)
题意
给出一个简单多边形,其中的点根据顺时针或者逆时针排列
让你把这个多边形分成许多三角形满足以下情况
1.三角形的每个端点都在简单多边形的端点上
2.简单多边形的每一条边都要属于一个三角形
3.三角形之间不能重叠和有间隙
4.每个三角形都必须严格在多边形中
5.三角形的每一条边都要连接多边形的两个端点
思路
一开始毫无思路....
首先 利用分治的想法把一整个多边形变成两个小多边形 那么大多边形的答案就是小多边形各自的答案相乘(比如小A的答案是4种,小B的答案是5种,那么他们各自的组合就是4*5=20种),然后把就是怎么分多边形了,假设我们现在的多边形是(0-(n-1))这几个大点构成的,那么小多边形之间的分割点 肯定就是在这些(0~n-1)点之间的某个点 也就是 1,2,3,->n-2 ,那么什么时候结束呢,如果两个点之间没有间隔了就结束。也就是i+1=j了的时候
这时候发现有些分割点并不能取,能取的分割点 和边界也必须要符合构成一个三角形
如下图
\E1.png)
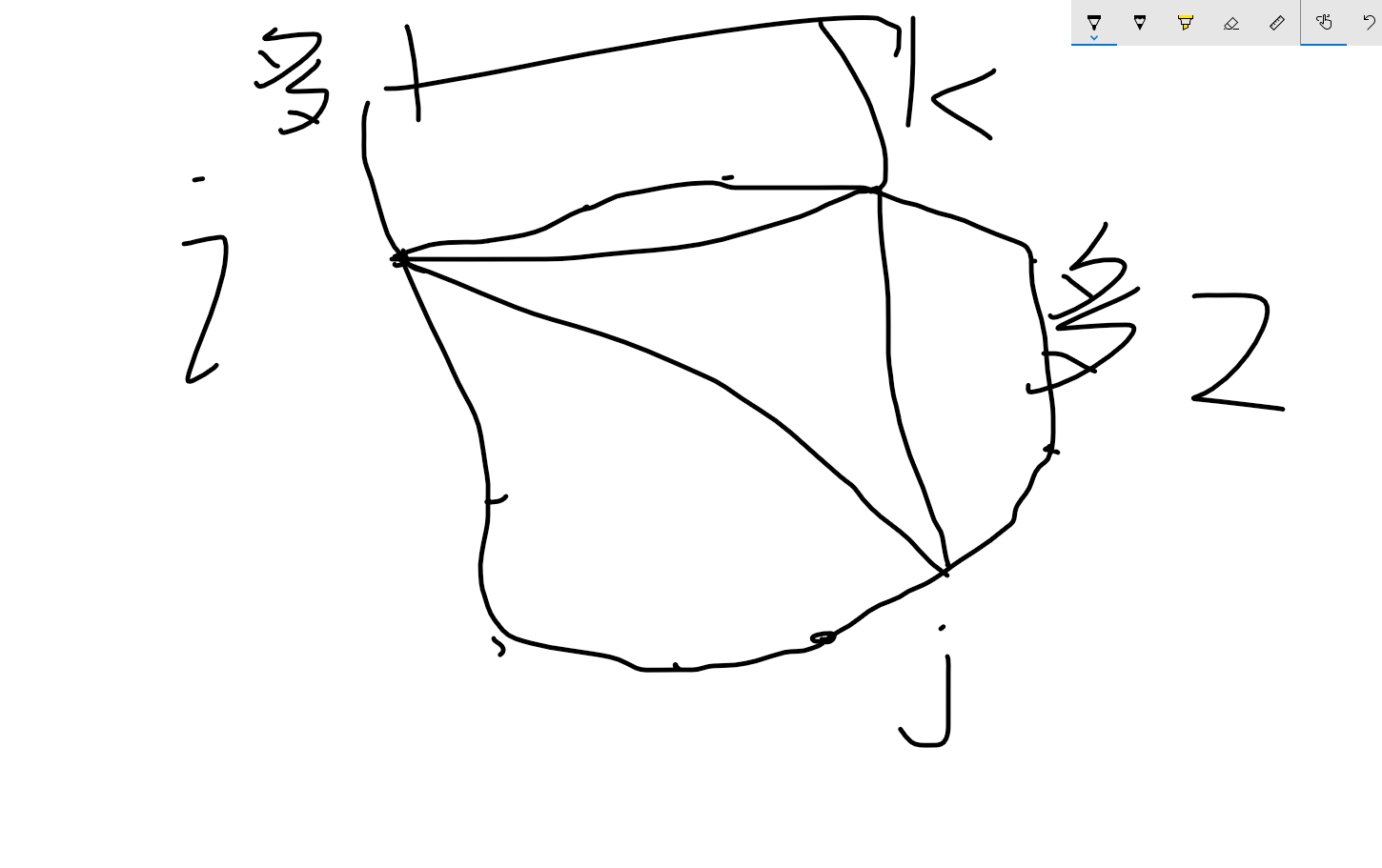
另一种情况不能选择这个K点为分割点
\E2.png)
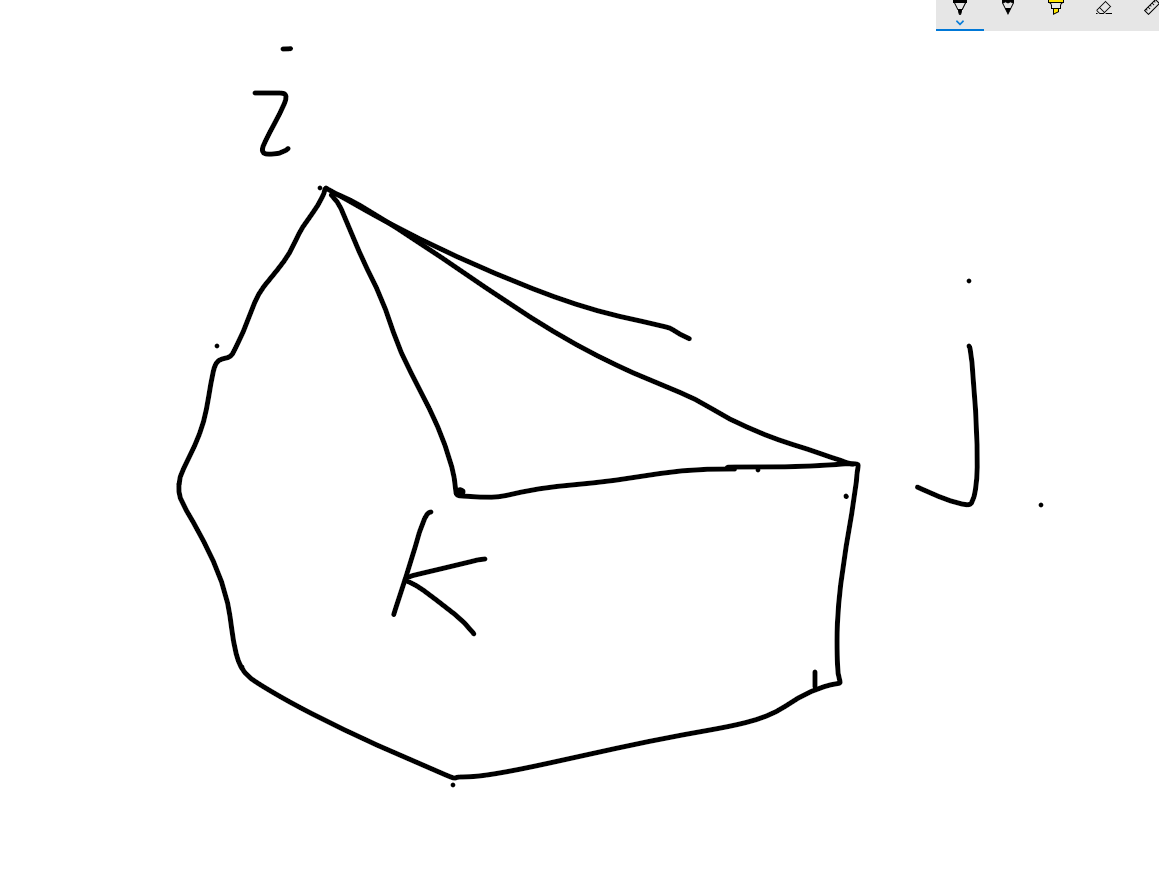
这种情况是K在i-j这条线之内的情况
然后那么怎么判断这个点在不在呢,就直接判断线段i -k 和线段k -j是不是在同一个方向的就行.
为了统一我们可以在输入数据的时候就统一指定为顺时针
ps:给出一个序列的点,判断它是顺时针还是逆时针:计算连续两个点的叉积,包括第一个和最后一个,求他们的和,大于0为顺时针,小于0为逆时针。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll mod=1e9+7;
const int maxn=1e6+50;
const ll inf=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
struct node{
ll x,y;
node operator -(const node &a)const{
return node{x-a.x,y-a.y};
}
ll operator *(const node &a)const{
return x*a.y-y*a.x;
}
}my[550];
ll dp[250][250];
ll dfs(int l,int r){
if(l+1==r)return 1;
if(~dp[l][r])return dp[l][r];
ll ans=0;
for(int i=l+1;i<r;i++){
if((my[l]-my[i])*(my[i]-my[r])<=0)continue;
ans+=dfs(l,i)*dfs(i,r)%mod;
ans%=mod;
}
return dp[l][r]=ans;
}
int main()
{
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(0);
std::cout.tie(0);
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)cin>>my[i].x>>my[i].y;
ll ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
ans+=my[i]*my[(i+1)%n];
}
if(ans<0){
reverse(my,my+n);
}
memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));
cout<<dfs(0,n-1)<<endl;
return 0;
}




