N维整型向量类
一、问题描述。
线性代数里面我们学习过n维向量,请用类vector_N来封装n维整型向量,成员如下;
私有数据成员:
² 向量维数n, int型
² 指针 p,int型
公有函数成员:
- 无参默认构造函数,在该函数中,将n置0,将p置null;
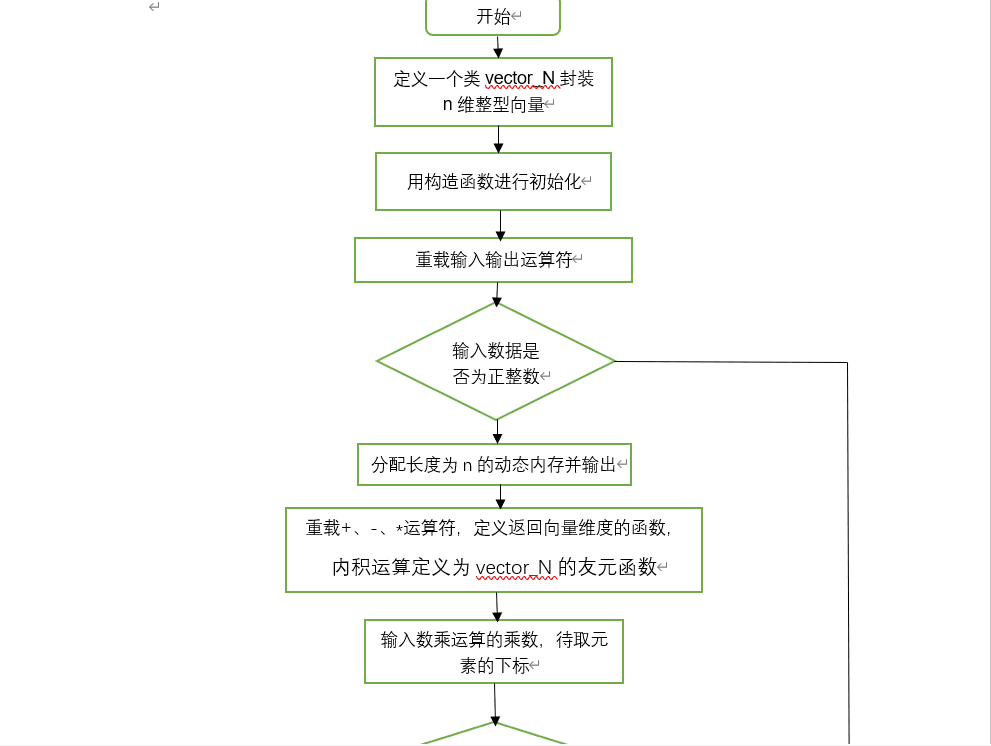
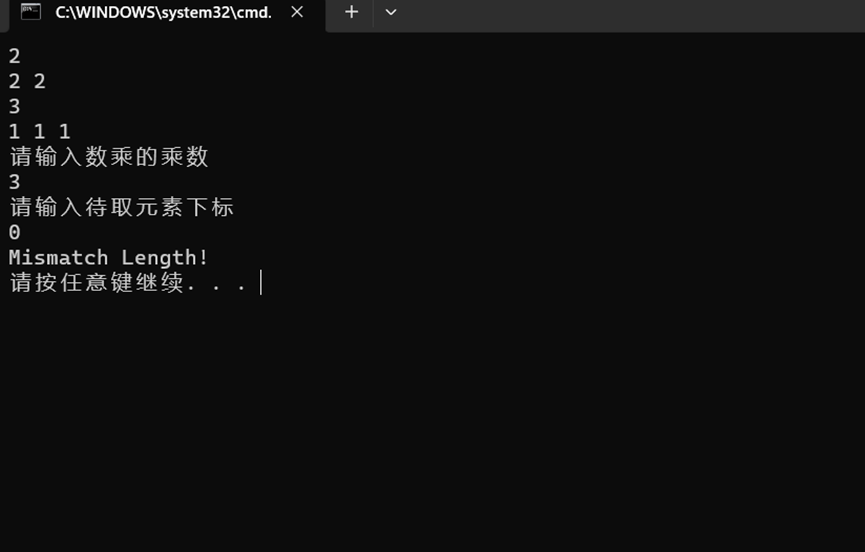
- 重载输入输出运算符,输入运算符,先指定向量维数,若输入为非正整数,则提示错误信息,“Error Length!”然后退出程序,若维数输入正确则分配长度为n的动态内存,并用指针p指向该内存,输出运算符依次输出向量各元素即可;
- 重载向量的加法+、减法-、数乘*(乘数在前,乘数为int型)这三运算符;
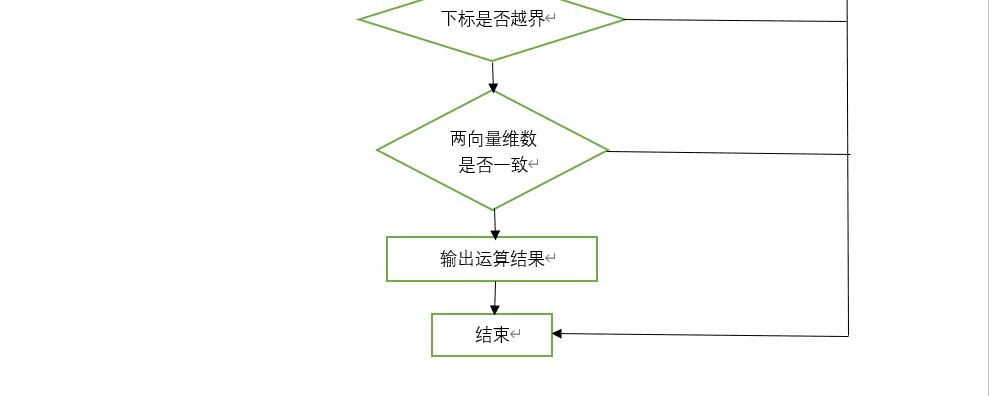
- 重载[]运算,例如,向量a=(1,2,3,4),a[0]的值为1,若下标越界,则输出“Error Index”,然后退出程序;
- 返回向量维数的函数;
- 将两个向量的内积运算定义为vector_N的友元函数;
在主函数中定义两个vector_N类对象v1,v2,均不带参数,之后对两个对象进行输入赋值,输入数乘运算的乘数,输入待取元素的下标,对两个向量进行加、减、数乘和内积运算,并将结果输出,输出v1中对应下标对应的元素。加法、减法和内积运算先判断两向量维数是否一致,若一致则输出运算结果,否则输出错误提示信息“Mismatch Length!”
二、设计思路。
1.此类需要用到动态内存的分配,所以在析构函数中应释放空间,并将指针置null,将维数n置0
2.需要显式定义复制构造函数vector_N(vector_N &)
3.需要重载复制运算符 vector_N operator= (vector_N &)
4.退出程序用函数 _exit(0)
5.返回值类型需要为引用的形式,另一方面,在使用时就要考虑不能返回临时变量的引用
三、程序流程图。
四、代码实现。
#include<iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class vector_N{
private:
int n;
int *p;
public:
vector_N(int nn = 0, int *pp = NULL);
vector_N(vector_N& p);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& input, vector_N& N);
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& output, vector_N& N);
vector_N operator+(vector_N B);
vector_N operator-(vector_N B);
float operator*(vector_N B);
vector_N operator*(int B);
float operator[](int b);
bool check(vector_N B);
};
vector_N:: vector_N(int nn, int *pp ) : n(nn), p(pp){}
vector_N::vector_N(vector_N& pp)
{
n = pp.n;
p = pp.p;
}
bool vector_N:: check(vector_N B)
{
if (n != B.n){
cout << "Mismatch Length!" << endl;
return false;
}
else{
return true;
}
}
vector_N vector_N:: operator+(vector_N A)
{
vector_N sum(A);
if (check(A))
{
for (int i = 0; i < A.n; i++)
{
sum.p[i] = p[i] + A.p[i];
}
return sum;
}
else
{
exit(0);
}
}
vector_N vector_N:: operator-(vector_N B)
{
vector_N sum(B);
if (check(B))
{
for (int i = 0; i < B.n; i++)
{
sum.p[i] = this->p[i] - B.p[i];
}
return sum;
}
else
{
exit(0);
}
}
float vector_N:: operator*(vector_N B)
{
vector_N sum(B);
float sum1 = 0;
if (check(B))
{
for (int i = 0; i < B.n; i++)
{
sum.p[i] = p[i] * B.p[i];
sum1 += sum.p[i];
}
return sum1;
}
else
{
exit(0);
}
}
vector_N vector_N:: operator*(int B)
{
vector_N re(n,p);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
re.p[i] = p[i] * n;
}
return re;
}
float vector_N:: operator[](int b)
{
return p[b];
}
istream& operator>>(istream& input, vector_N& N)
{
input >> N.n;
if (N.n <= 0){
cout << "Error Lenth!" << endl;
exit(0);
}
else{
N.p = new int[N.n];
for (int i = 0; i < N.n; i++)
{
input >> N.p[i];
}
}
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& output, vector_N& N)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N.n; i++)
{
if (i == 0) output << "(";
output << N.p[i];
if (i != N.n - 1)
output << ",";
if (i == N.n-1) output << ")"<<endl;
}
return output;
}
int main()
{
vector_N a, b, c; int w,e;
cin >> a;
cin.sync();
cin >> b;
cout << "请输入数乘的乘数" << endl;
cin >> w;
cin.sync();
cout << "请输入待取元素下标" << endl;
cin >> e;
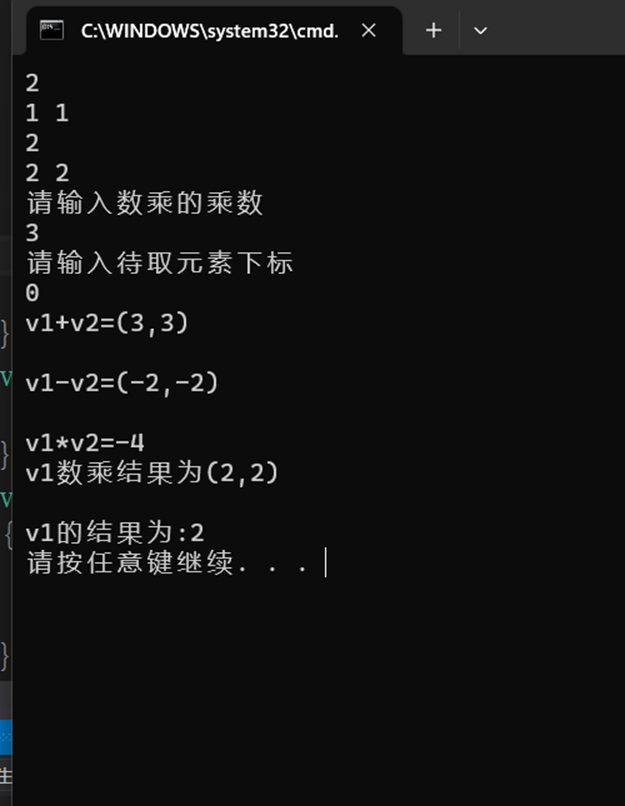
cout << "v1+v2=" << a + b << endl;
cout << "v1-v2=" << a - b << endl;
cout << "v1*v2=" << a*b << endl;
cout << "v1数乘结果为" << a*w << endl;
cout << "v1的结果为:" << a[e] << endl;
}





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通