JSON-C语言开发指南
一、前言
本文档是基于json-c库对数据交换进行开发所编写的开发指南,及详细解释json-c库中常用api。 适用于开发人员使用c语言对json的编程
(注:此文档json-c库版本为0.8——json-c-0.8)
二、JSON简介
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。易于人阅读和编写。
同时也易于机器解析和生成。它基于JavaScript Programming Language, Standard ECMA-262 3rd Edition - December 1999的一个子集。JSON采用完全独立于语言的文本格式,但是也使用了类似于C语言家族的习惯(包括C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript, Perl, Python等)。这些特性使JSON成为理想的数据交换语言。
跟XML相比,JSON的优势在于格式简洁短小,特别是在处理大量复杂数据的时候,这个优势便显得非常突出。从各浏览器的支持来看,JSON解决了因不同浏览器对XML DOM解析方式不同而引起的问题。
2.1 JSON两种结构:
“名称/值”对的集合(A collection of name/value pairs):
----不同的语言中,它被理解为对象(object),纪录(record),结构(struct),字典(dictionary),
----哈希表(hash table),有键列表(keyed list),或者关联数组 (associative array)。
值的有序列表(An ordered list of values):
----在大部分语言中,它被理解为数组(array)。
这些都是常见的数据结构。事实上大部分现代计算机语言都以某种形式支持它们。这使得一种数据格式在同样基于这些结构的编程语言之间交换成为可能。
2.2 JSON具有以下这些形式:
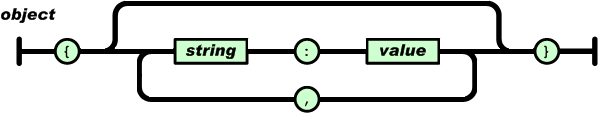
对象是一个无序的“‘名称/值’对”集合;
一个对象以“{”(左括号)开始,“}”(右括号)结束;
每个“名称”后跟一个“:”(冒号);
“‘名称/值’ 对”之间使用“,”(逗号)分隔。
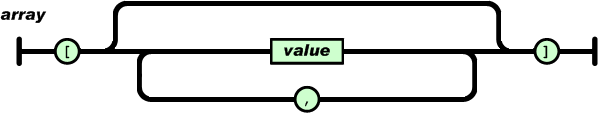
数组是值(value)的有序集合。
一个数组以“[”(左中括号)开始,“]”(右中括号)结束;
值之间使用“,”(逗号)分隔。
值(value)可以是双引号括起来的字符串(string)、数值(number)、true、false、 null、对象(object)或者数组(array)。
这些结构可以嵌套。

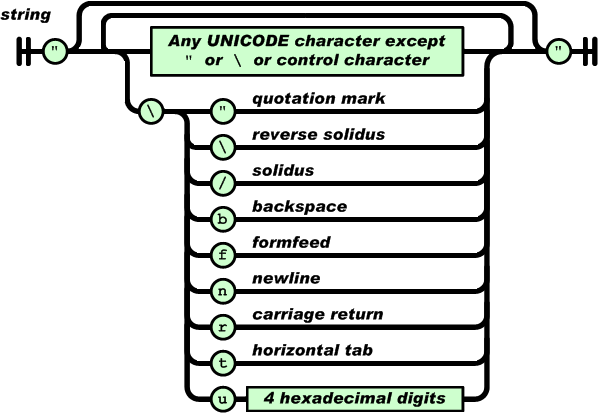
字符串(string)是由双引号包围的任意数量Unicode字符的集合,使用反斜线转义。
一个字符(character)即一个单独的字符串(character string)。
字符串(string)与C或者Java的字符串非常相似。
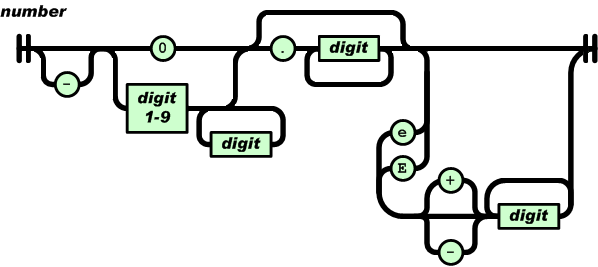
数值(number)也与C或者Java的数值非常相似。
除去未曾使用的八进制与十六进制格式。除去一些编码细节。
三、JSON库函数说明
3.1 JSON对象的生成
Json对象的类型: json_type_object, “名称/值”对的集合 /* Json对象的值类型 */ json_type_boolean, json_type_double, json_type_int, json_type_array, “值”的集合 json_type_string /* 创建个空的json_type_object类型JSON对象 */ struct json_object * json_object_new_object(); /* 创建个json_type_boolean值类型json对象 */ struct json_object* json_object_new_boolean(boolean b); /* 从json对象中boolean值类型得到boolean值 */ boolean json_object_get_boolean(struct json_object *obj); 同样: struct json_object* json_object_new_int(int i) int json_object_get_int(struct json_object *this) struct json_object* json_object_new_double(double d) double json_object_get_double(struct json_object *this) struct json_object* json_object_new_string(char *s) char* json_object_get_string(struct json_object *this) /* 创建个空的json_type_array类型JSON数组值对象。 */ struct json_object * json_object_new_array(); /* 由str里的JSON字符串生成JSON对象,str是son_object_to_json_string() 生成的。 * 参数: * str – json字符串 */ struct json_object * json_tokener_parse(char *str); // /* 从json中按名字取一个对象。 * 参数: * json – json对象 * name - json域名字 */ struct json_object * json_object_object_get(struct json_object * json,char *name);
3.2 JSON对象的释放
/* 增加对象引用计数。使用c库最关心的是内存谁来分配, 谁来释放. * jsonc的内存管理方式, 是基于引用计数的内存树(链), * 如果把一个struct json_object 对象a, add到另一个对象b上, * 就不用显式的释放(json_object_put) a了, 相当于把a挂到了b的对象树上, * 释放b的时候, 就会释放a. 当a即add到b上, 又add到对象c上时会导致a被释放两次(double free), * 这时可以增加a的引用计数(调用函数json_object_get(a)), * 这时如果先释放b, 后释放c, 当释放b时, 并不会真正的释放a, 而是减少a的引用计数为1, 然后释放c时, 才真正释放a. * 参数: * this – json对象 */ struct json_object * * json_object_get(struct json_object * this) /* 减少对象引用次数一次,当减少到0就释放(free)资源 * this – json对象 */ void json_object_put(struct json_object * this) /* 样例片段:*/ my_string = json_object_new_string("\t"); /*输出 my_string= */ \t(table键) printf("my_string=%s\n", json_object_get_string(my_string)); /*转换json格式字符串 输出my_string.to_string()="\t"*/ printf("my_string.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(my_string)); /*释放资源*/ json_object_put(my_string);
3.3 JSON对象的操作
/* 检查json_object是json的某个类型 * 参数: * this: json_object 实例 * type: json_type_boolean,json_type_double, json_type_int, json_type_object, json_type_array, json_type_string */ int json_object_is_type(struct json_object * this, enum json_type type) /* 得到json_object的类型。 * 参数: * this – json对象 */ enum json_type json_object_get_type(struct json_object * this ) /* 将json_object内容转换json格式字符串,其中可能含有转义符。 * 参数: * this – json对象 * 返回值: * json格式字符串 */ char * json_object_to_json_string(struct json_object * this) /* 添加个对象域到json对象中 * 参数: * obj – json对象 * key – 域名字 * val – json值对象 */ void json_object_object_add(struct json_object* obj, char *key, struct json_object *val); /* 删除key值json对象 * 参数: * obj – json对象 * key – 域名字 */ void json_object_object_del(struct json_object* obj, char *key); /* 得到json对象数组的长度。 * 参数: * obj – json数组值对象 */ int json_object_array_length(struct json_object *obj); /* 添加一元素在json对象数组末端 * 参数: * obj – json数组值对象 * val – json值对象 */ extern int json_object_array_add(struct json_object *obj, struct json_object *val); /* 在指定的json对象数组下标插入或替换一个json对象元素。 * 参数: * obj – json数组值对象 * val – json值对象 * idx – 数组下标 */ int json_object_array_put_idx(struct json_object *obj, int idx, struct json_object *val); /* 从数组中,按下标取JSON值对象。 * 参数: * json_array – json 数组类型对象 * i – 数组下标位置 */ struct json_object * json_object_array_get_idx(struct json_object * json_array,int i); /* 定义宏。遍历json对象的key和值 (key, val默认参数不变)*/ json_object_object_foreach(obj,key,val)
============================================
样例片段:
/*创建个空json对象值数组类型*/ my_array = json_object_new_array(); /*添加json值类型到数组中*/ json_object_array_add(my_array, json_object_new_int(1)); json_object_array_add(my_array, json_object_new_int(2)); json_object_array_add(my_array, json_object_new_int(3)); json_object_array_put_idx(my_array, 4, json_object_new_int(5)); printf("my_array=\n"); for(i=0; i < json_object_array_length(my_array); i++) { struct json_object *obj = json_object_array_get_idx(my_array, i); printf("\t[%d]=%s\n", i, json_object_to_json_string(obj)); } printf("my_array.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(my_array)); my_object = json_object_new_object(); /*添加json名称和值到json对象集合中*/ json_object_object_add(my_object, "abc", json_object_new_int(12)); json_object_object_add(my_object, "foo", json_object_new_string("bar")); json_object_object_add(my_object, "bool0", json_object_new_boolean(0)); json_object_object_add(my_object, "bool1", json_object_new_boolean(1)); json_object_object_add(my_object, "baz", json_object_new_string("bang")); /*同样的key 添加会替换掉*/ json_object_object_add(my_object, "baz", json_object_new_string("fark")); json_object_object_del(my_object, "baz"); /*添加数组集合到json对象中*/ json_object_object_add(my_object, "arr", my_array); printf("my_object=\n"); /*遍历json对象集合*/ json_object_object_foreach(my_object, key, val) { printf("\t%s: %s\n", key, json_object_to_json_string(val)); } json_object_put(my_object);
四、 JSON实例开发
样例
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stddef.h> #include <string.h> #include "json.h" int main(int argc, char **argv) { struct json_tokener *tok; struct json_object *my_string, *my_int, *my_object, *my_array; struct json_object *new_obj; int i; my_string = json_object_new_string("\t"); /*输出 my_string= */ printf("my_string=%s\n", json_object_get_string(my_string)); /*转换json格式字符串 输出my_string.to_string()="\t"*/ printf("my_string.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(my_string)); /*释放资源*/ json_object_put(my_string); my_string = json_object_new_string("\\"); printf("my_string=%s\n", json_object_get_string(my_string)); printf("my_string.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(my_string)); json_object_put(my_string); my_string = json_object_new_string("foo"); printf("my_string=%s\n", json_object_get_string(my_string)); printf("my_string.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(my_string)); my_int = json_object_new_int(9); printf("my_int=%d\n", json_object_get_int(my_int)); printf("my_int.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(my_int)); /*创建个空json对象值数组类型*/ my_array = json_object_new_array(); /*添加json值类型到数组中*/ json_object_array_add(my_array, json_object_new_int(1)); json_object_array_add(my_array, json_object_new_int(2)); json_object_array_add(my_array, json_object_new_int(3)); json_object_array_put_idx(my_array, 4, json_object_new_int(5)); printf("my_array=\n"); for(i=0; i < json_object_array_length(my_array); i++) { struct json_object *obj = json_object_array_get_idx(my_array, i); printf("\t[%d]=%s\n", i, json_object_to_json_string(obj)); } printf("my_array.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(my_array)); my_object = json_object_new_object(); /*添加json名称和值到json对象集合中*/ json_object_object_add(my_object, "abc", json_object_new_int(12)); json_object_object_add(my_object, "foo", json_object_new_string("bar")); json_object_object_add(my_object, "bool0", json_object_new_boolean(0)); json_object_object_add(my_object, "bool1", json_object_new_boolean(1)); json_object_object_add(my_object, "baz", json_object_new_string("bang")); /*同样的key 添加会替换掉*/ json_object_object_add(my_object, "baz", json_object_new_string("fark")); json_object_object_del(my_object, "baz"); printf("my_object=\n"); /*遍历json对象集合*/ json_object_object_foreach(my_object, key, val) { printf("\t%s: %s\n", key, json_object_to_json_string(val)); } printf("my_object.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(my_object)); /*对些不规则的串做了些解析测试*/ new_obj = json_tokener_parse("\"\003\""); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("/* hello */\"foo\""); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("// hello\n\"foo\""); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("\"\\u0041\\u0042\\u0043\""); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("null"); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("True"); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("12"); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); /*得到json double类型 new_obj = json_tokener_parse("12.3"); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("[\"\\n\"]"); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("[\"\\nabc\\n\"]"); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("[null]"); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("[]"); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("[false]"); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("[\"abc\",null,\"def\",12]"); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("{}"); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("{ \"foo\": \"bar\" }"); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("{ \"foo\": \"bar\", \"baz\": null, \"bool0\": true }"); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("{ \"foo\": [null, \"foo\"] }"); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("{ \"abc\": 12, \"foo\": \"bar\", \"bool0\": false, \"bool1\": true, \"arr\": [ 1, 2, 3, null, 5 ] }"); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("{ foo }"); if(is_error(new_obj)) printf("got error as expected\n"); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("foo"); if(is_error(new_obj)) printf("got error as expected\n"); new_obj = json_tokener_parse("{ \"foo"); if(is_error(new_obj)) printf("got error as expected\n"); /* test incremental parsing */ tok = json_tokener_new(); new_obj = json_tokener_parse_ex(tok, "{ \"foo", 6); if(is_error(new_obj)) printf("got error as expected\n"); new_obj = json_tokener_parse_ex(tok, "\": {\"bar", 8); if(is_error(new_obj)) printf("got error as expected\n"); new_obj = json_tokener_parse_ex(tok, "\":13}}", 6); printf("new_obj.to_string()=%s\n", json_object_to_json_string(new_obj)); json_object_put(new_obj); json_tokener_free(tok); json_object_put(my_string); json_object_put(my_int); json_object_put(my_object); json_object_put(my_array); /*如果前面没有添加到对象中, 必须显示释放, *如果添加到对象中,已经释放对象,则无需调用, *在这务必小心,否则很容易内存泄漏*/ return 0; }
输出结果:
my_string= my_string.to_string()="\t" my_string=\ my_string.to_string()="\\" my_string=foo my_string.to_string()="foo" my_int=9 my_int.to_string()=9 my_array= [0]=1 [1]=2 [2]=3 [3]=null [4]=5 my_array.to_string()=[ 1, 2, 3, null, 5 ] my_object= abc: 12 foo: "bar" bool0: false bool1: true my_object.to_string()={ "abc": 12, "foo": "bar", "bool0": false, "bool1": true } new_obj.to_string()="\u0003" new_obj.to_string()="foo" new_obj.to_string()="foo" new_obj.to_string()="ABC" new_obj.to_string()=null new_obj.to_string()=true new_obj.to_string()=12 new_obj.to_string()=12.300000 new_obj.to_string()=[ "\n" ] new_obj.to_string()=[ "\nabc\n" ] new_obj.to_string()=[ null ] new_obj.to_string()=[ ] new_obj.to_string()=[ false ] new_obj.to_string()=[ "abc", null, "def", 12 ] new_obj.to_string()={ } new_obj.to_string()={ "foo": "bar" } new_obj.to_string()={ "foo": "bar", "baz": null, "bool0": true } new_obj.to_string()={ "foo": [ null, "foo" ] } new_obj.to_string()={ "abc": 12, "foo": "bar", "bool0": false, "bool1": true, "arr": [ 1, 2, 3, null, 5 ] } got error as expected got error as expected got error as expected new_obj.to_string()={ "foo": { "bar": 13 } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号